Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Badi in Collection Management
Hochgeladen von
rajankunalOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Badi in Collection Management
Hochgeladen von
rajankunalCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
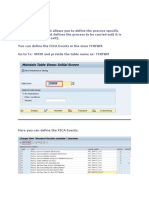
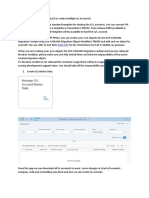
List of BADIS Used in Collection management:
Difference Between BADI and User Exits
Business Add-Ins are a new SAP enhancement technique based on ABAP Objects. They can be inserted into the SAP
System to accommodate user requirements too specific to be included in the standard delivery. Since specific industries
often require special functions, SAP allows you to predefine these points in your software.
As with customer exits two different views are available:
In the definition view, an application programmer predefines exit points in a source that allow specific industry sectors,
partners, and customers to attach additional software to standard SAP source code without having to modify the
original object.
In the implementation view, the users of Business Add-Ins can customize the logic they need or use a standard logic if
one is available.
In contrast to customer exits, Business Add-Ins no longer assume a two-level infrastructure (SAP and customer
solutions), but instead allow for a multi-level system landscape (SAP, partner, and customer solutions, as well as
country versions, industry solutions, and the like). Definitions and implementations of Business Add-Ins can be created
at each level within such a system infrastructure.
SAP guarantees the upward compatibility of all Business Add-In interfaces. Release upgrades do not affect
enhancement calls from within the standard software nor do they affect the validity of call interfaces. You do not have
to register Business Add-Ins in SSCR.
The Business Add-In enhancement technique differentiates between enhancements that can only be implemented once
and enhancements that can be used actively by any number of customers at the same time. In addition, Business AddIns can be defined according to filter values. This allows you to control add-in implementation and make it dependent
on specific criteria (on a specific Country value, for example).
All ABAP sources, screens, GUIs, and table interfaces created using this enhancement technique are defined in a
manner that allows customers to include their own enhancements in the standard. A single Business Add-In contains all
of the interfaces necessary to implement a specific task.
The actual program code is enhanced using ABAP Objects. In order to better understand the programming techniques
behind the Business Add-In enhancement concept, SAP recommends reading the section on ABAP Objects.
What is difference between badi and user-exists?
What is difference between enhancements and user-exists? and what is the full form of BADI?What is the
system landscape?
1) Difference between BADI and USER-EXIT.
i) BADI's can be used any number of times, where as USER-EXITS can be used only one time.
Ex:- if your assigning a USER-EXIT to a project in (CMOD), then you can not assign the same to other project.
ii) BADI's are oops based.
2) About 'BDCMSGCOLL' it is a structure. Used for finding error records.
3) Full form of BADI 'Business addins'.
3) System land scape will be depends on your project
Ex:- 'Development server'-->'Quality server'---> 'Production server'.
List BADIS in BP collection management
1.CVI_BBPCUSTOM_MAPPER
Mapping for SRM-Specific Enhancements
2.CVI_MAP_BUSINESS_ADDRESS
Implementation: BADI: Data Assignment BP-Customer/Vendor/Contact Person
(You can use this BAdI to change and extend field assignments for Customer/Vendor Integration. You can adjust the
assignments between business partner/customer/vendor and contact person data, and the assignments between
business partner relationship data and contact person data.)
3.IF_EX_CVI_MAP_BANKDETAILS.
( You can use this BAdI to change and extend field assignments for bank data in Customer/Vendor Integration. You can
adjust the assignments between bank details for the business partner and bank details for the customer/vendor).
4.IF_EX_CVI_MAP_CREDIT_CARDS
(You can use this BAdI to change and extend field assignments for customer integration. You can adjust the assignments
between payment cards for the business partner and payment cards for the customer master record)
5.CVI_MAP_TITLE_DIRECT .
( You can use this BAdI to change and extend field assignments for Customer/Vendor Integration. You can adjust the
assignments between the form of address for the business partner and the form of address for the customer/vendor. This
is possible only for the direction customer/vendor to business partner)
6.CVI_MAP_BP_CATEGORY
(Determine Business Partner Category Based on Form of Address)
7.CVI_DEFAULT_VALUES_CLASSIC
(With this BAdI you can set default fields for Customer/Vendor Integration that are relevant for synchronization, such as
general data and company code data for the customer, when creating data in the direction business partner to
customer/vendor.)
8.MAP_PARTNER_2_CUSTOMER:
Mapping of business partner number (Partner-ID) to customer number (KUNNR)
9.MAP_CUSTOMER_2_PARTNER:
Mapping of customer number (KUNNR) to business partner number (Partner-ID)
10.MAP_CONTACTPARTNER_2_CONTACT:
Mapping of business partner number (Partner-ID) to contact person number (PARNR)
11.MAP_CONTACT_2_CONTACTPARTNER:
Mapping of contact person number (PARNR) to business partner number (Partner-ID)
Work list Add in BADI
1.UDM_S_WORKLIST_ITEM_ATTR_C
Example 1: You calculate additional key figures for the business partner and display these in the worklist. You distribute
additional indicators from Accounts Receivable Accounting to Collections Management and display these in the worklist.
2. UDM_COLL_AMT_C
You use it to define the amount to be collected
3. UDM_WL_ITEM_DISP_C
With this BAdI, you can fill customer-specific fields when displaying worklist items
4. UDM_EXT_RATING_C
You use it to determine which external rating of the business partner is to be displayed in the worklist
Data Distribution BADI
1. FDM_COLL_SEND_ITEMS
You use it to provided additional data for the distribution of data in Collections Management</. This data can be prepared
for the collection specialists worklist and displayed there. It can also be used to prioritize the business partners to be
contacted
2. FDM_COLL_DETERMINE_BRANCH
The method DETERMINE_BRANCH is used to determine the relevant customer from an invoice item for Collections
Management, differently from the behavior of the SAP standard system.
3. IF_FDM_COLL_DETERMINE_PAYER
With this Business Add-In (BAdI) you can determine an alternative payer from an invoice item for Collections Management
4. FDM_COLL_DISPLAY_DUNN_HISTORY
You can use this BAdI to implement the display of customer contacts having a contact type other thancall or visit. It is
called if the user in receivables processing wants to display details for a customer contact on the Customer Contacts tab.
The contact type is used a filter value for the BadI implementation.
5. FDM_P2P_JUDGE
With this BAdI you have two options for how you valuate promises to pay:
You can valuate a promise to pay without installment plan and specify whether is was kept, partially kept or
broken.
You specify Tolerance Days for the valuation, and so override the entries that you have made in Customizing.
This is possible for both promises to pay with or without installment plan.
6. FDM_COLL_INSTALLMENT_PLAN
You can use this Business Add-In (BAdI) to propose either an installment plan type or a standard installment plan when
you create an installment plan. You can use the method GET_DEFAULT for this. This method is called in receivables
processing if the user navigates to the user interface that allows the creation or change of an installment plan. However, it
is only called if no installment plan has yet been created for the promise to pay.
7. FDM_INST_DISTRIB_RELATIVELY
You can use this Business Add-In (BAdI) to distribute the installments of an installment plan to the invoices for which
promises to pay have been created
8. UDM_BR00000001 to UDM_ BR00000024
The implementation of all basic rules delivered by SAP is active in the standard system. You should not modify or
deactivate these basic rules. In the definition of rules, you decide which of the rules delivered by SAP and which
additionally implemented rules are to be used in strategies and therefore in SAP Collections Management.
Add ins for B.P
1. UDM_BP_PROFILE_C
By implementing this Business Add-In, you can determine, for each business partner, which collection profile is entered in
the respective master record.
2. UDM_CHNG_SGMT_DATA_C
By implementing this BAdI, you can determine, for each segment of a business partner, which collection group and
collection specialist are entered in the respective master record
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- SAP MDG Customer A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandSAP MDG Customer A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- Fin FSCM CCD 3Dokument4 SeitenFin FSCM CCD 3car_pierreNoch keine Bewertungen
- BAdIs For The Process Integration - SAP Dispute Management Configuration Guide For FI-AR - SAP LibraryDokument3 SeitenBAdIs For The Process Integration - SAP Dispute Management Configuration Guide For FI-AR - SAP LibraryRajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Note 859998 - Installing SAP Credit Management 6.0: SymptomDokument4 SeitenNote 859998 - Installing SAP Credit Management 6.0: SymptomNidhi Rathi MantriNoch keine Bewertungen
- FSCM User Manual: Disputes & Collections ManagementDokument30 SeitenFSCM User Manual: Disputes & Collections ManagementkamranahmedaslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Addon Integration ModuleDokument19 SeitenAddon Integration ModuleRajib Bose100% (1)
- Trading Partner Company SetupDokument2 SeitenTrading Partner Company SetupamaravatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contents-SAP FSCM Configuration and User GuideDokument3 SeitenContents-SAP FSCM Configuration and User Guidesapfico2k8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Questions FicoDokument11 SeitenQuestions FicoSathya Ganesan100% (1)
- Copa Interview QuestionDokument13 SeitenCopa Interview QuestionK KUMAR JENANoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP DunningDokument13 SeitenSAP DunningFarhad012Noch keine Bewertungen
- POD - Series 1 POD - Series 2: RefurbishmentDokument3 SeitenPOD - Series 1 POD - Series 2: RefurbishmentshekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sapbrainsonline Com Help FSCM Module Tutorials HTMLDokument8 SeitenSapbrainsonline Com Help FSCM Module Tutorials HTMLCarlos CasañoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revenue Accounting and Reporting (RAR) - Concept and ConfigurationDokument33 SeitenRevenue Accounting and Reporting (RAR) - Concept and ConfigurationAnand prakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deepa Karuppiah SAP FICODokument4 SeitenDeepa Karuppiah SAP FICO437ko7Noch keine Bewertungen
- FKKBILLBIX - MA and EventDokument24 SeitenFKKBILLBIX - MA and EventSanjeev SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valuation Class enDokument4 SeitenValuation Class ensudhir_wdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rar CoceptsDokument18 SeitenRar CoceptsMoorthy EsakkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP Fiori KPI ConfigurationDokument19 SeitenSAP Fiori KPI ConfigurationmoulayNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP FSCM Sample Resume 2Dokument4 SeitenSAP FSCM Sample Resume 2ASHOKA GOWDANoch keine Bewertungen
- Cash Manaagement ConceptDokument4 SeitenCash Manaagement ConceptRoberto De FlumeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dunning, Dunning Procedure in SAPDokument3 SeitenDunning, Dunning Procedure in SAPmr_relyNoch keine Bewertungen
- S4 HANA FI-GL User ManualDokument27 SeitenS4 HANA FI-GL User Manualcv babuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fixed Term Deposit in Sap S4hana TRM 1704610757Dokument41 SeitenFixed Term Deposit in Sap S4hana TRM 1704610757vamsi100% (1)
- Configuration Documentation For Group ReportingDokument22 SeitenConfiguration Documentation For Group ReportingAlonso PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Guidelines For SAP CertificationDokument30 SeitenQuestion Guidelines For SAP CertificationRakesh KathuriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FSCM Credit CollectionsDokument6 SeitenFSCM Credit CollectionsAparna PelleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Payment Program Use in General, Installment and Multiple Partial Payment - SAP BlogsDokument59 SeitenAutomatic Payment Program Use in General, Installment and Multiple Partial Payment - SAP BlogsAnanthakumar ANoch keine Bewertungen
- F 54Dokument10 SeitenF 54madyeid31Noch keine Bewertungen
- FSCM - Credit Management (Light Implementation Solution) Manage and Collect CreditsDokument55 SeitenFSCM - Credit Management (Light Implementation Solution) Manage and Collect CreditsRajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP Biller Direct Step by Step ConfiguraDokument16 SeitenSAP Biller Direct Step by Step ConfiguraSurani shaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vdocument - in Sap Fica Configuration Step by StepDokument32 SeitenVdocument - in Sap Fica Configuration Step by StepmayuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Head Office and Branch Concept Demostrated For Both Vendors CustomersDokument13 SeitenHead Office and Branch Concept Demostrated For Both Vendors CustomersAvinash Malladhi0% (1)
- Streamlining The Financial Close With The SAP Financial Closing CockpitDokument4 SeitenStreamlining The Financial Close With The SAP Financial Closing Cockpitpravnb4u634Noch keine Bewertungen
- C TFIN52 67 Sample Questions10082016bDokument5 SeitenC TFIN52 67 Sample Questions10082016bnamank005Noch keine Bewertungen
- SAP MM Material Ledger Activation in S - 4HANADokument11 SeitenSAP MM Material Ledger Activation in S - 4HANACassio RegalloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Configuration and Design Document Funds: Management Page 1 of 146Dokument146 SeitenConfiguration and Design Document Funds: Management Page 1 of 146Reddaveni Nagaraju100% (1)
- Dunning: SAP Dunning Process FlowDokument3 SeitenDunning: SAP Dunning Process FlowT SAIKIRANNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP Credit Management Configuration PDFDokument8 SeitenSAP Credit Management Configuration PDFMadhuparan senNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP Partners With Banks and Customers To Speed Delivery of Corporate-To-Bank Connectivity Support (Tool)Dokument25 SeitenSAP Partners With Banks and Customers To Speed Delivery of Corporate-To-Bank Connectivity Support (Tool)Cat-o Obillos100% (1)
- Exploring Special Procurement Types-Phantom AssembliesDokument6 SeitenExploring Special Procurement Types-Phantom AssembliesRjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Filter Rules For Central FinanceDokument3 SeitenFilter Rules For Central FinanceRishab GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Better Bank Monitor PDFDokument33 SeitenBetter Bank Monitor PDFdavid cooperfeldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retention: PurposeDokument7 SeitenRetention: PurposeSagnik ChakravartyNoch keine Bewertungen
- FICA Documents 2Dokument4 SeitenFICA Documents 2SaChibvuri JeremiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP BW ConsolidationsDokument19 SeitenSAP BW ConsolidationsNitin Sai Avirneni0% (1)
- SAP FSCM Credit Management Config StepsDokument3 SeitenSAP FSCM Credit Management Config StepsDamodar Naidu PaladuguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interview Questions - SAP RAR (60 Questions)Dokument18 SeitenInterview Questions - SAP RAR (60 Questions)pammi veeranji ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dispute Case Creation SapDokument10 SeitenDispute Case Creation SapmayuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- BPC Consolidation User Manual - Planning ContributorDokument50 SeitenBPC Consolidation User Manual - Planning ContributorRam PNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP FSCM Course ContentDokument6 SeitenSAP FSCM Course ContentSubhas GuhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP FSCM BasicsDokument5 SeitenSAP FSCM BasicspaiashokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adding Customer Fields in Vendor MasterDokument14 SeitenAdding Customer Fields in Vendor MasterGautam MalhotraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sap Kirloskar Blue Print343411327053679Dokument85 SeitenSap Kirloskar Blue Print343411327053679Rohan AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cookbook Deprecation of Commodity ID PDFDokument35 SeitenCookbook Deprecation of Commodity ID PDFBülent Değirmencioğlu100% (1)
- J1IG ISDN Process v1Dokument7 SeitenJ1IG ISDN Process v1KAMALJEET SINGH100% (1)
- SAP Foreign Currency Revaluation: FAS 52 and GAAP RequirementsVon EverandSAP Foreign Currency Revaluation: FAS 52 and GAAP RequirementsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Millikan Oil Drop ExperimentDokument6 SeitenMillikan Oil Drop ExperimentruleevanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taipei 102Dokument2 SeitenTaipei 102militansinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flexible Ac Transmission SystemDokument18 SeitenFlexible Ac Transmission SystemVinod Kumar VeeramreddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hela Bojuna - Comparative StatementDokument27 SeitenHela Bojuna - Comparative StatementNadeeshani MunasingheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opus UserguideDokument313 SeitenOpus UserguideMoez EssafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DP Chipset 15045 DriversDokument592 SeitenDP Chipset 15045 DriversRajesh1146Noch keine Bewertungen
- September 2015Dokument2 SeitenSeptember 2015Patriziah Marie SeldaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ARSTRUCTS Chapter1Dokument15 SeitenARSTRUCTS Chapter1Aila MaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Karcher K - 791 - MDokument12 SeitenKarcher K - 791 - MJoão Paulo FernandesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Add A Thermometer To Your Digital Multimeter - Embedded LabDokument13 SeitenAdd A Thermometer To Your Digital Multimeter - Embedded LabGourmand OishiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Family Handyman - October 2020 PDFDokument86 SeitenThe Family Handyman - October 2020 PDFFabian MaunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Pressure Gauge XP2i PSI Data Sheet USDokument5 SeitenDigital Pressure Gauge XP2i PSI Data Sheet USAbdurrachman JalaludinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heavy Duty 2.5 Ton Long Frame Floor Jack Product ManualDokument3 SeitenHeavy Duty 2.5 Ton Long Frame Floor Jack Product ManualChris Epler100% (2)
- 02 - Student Lesson 2 Pile Driving SystemDokument91 Seiten02 - Student Lesson 2 Pile Driving SystemdannyzuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cable TrenchDokument57 SeitenCable TrenchHari Krishna AaryanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Management Quick Reference GuideDokument5 SeitenProject Management Quick Reference GuidejcpolicarpiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Dynamics in The 21st CenturyDokument270 SeitenBusiness Dynamics in The 21st CenturyskilmagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Citrix Xenserver ® 6.0.2 Emergency Network Reset: Published Wednesday, 29 February 2012 1.0 EditionDokument6 SeitenCitrix Xenserver ® 6.0.2 Emergency Network Reset: Published Wednesday, 29 February 2012 1.0 EditionJuan CarlosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single Col - Tank-2013Dokument35 SeitenSingle Col - Tank-2013Hgagselim SelimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bloor Research On Data MigrationDokument13 SeitenBloor Research On Data MigrationivahdamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scarifier 9 Piecies Tooth TypeDokument2 SeitenScarifier 9 Piecies Tooth Typeangga setyawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piping Handbook Hydrocarbon Processing 1968 PDFDokument140 SeitenPiping Handbook Hydrocarbon Processing 1968 PDFbogdan_chivulescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Result Summary: Beam To Girder Shear Tab Shear Connection Code AISC 360-10 LRFDDokument14 SeitenResult Summary: Beam To Girder Shear Tab Shear Connection Code AISC 360-10 LRFDLexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Figure 7.4 - Roughly One Third of The Projects Studied WereDokument9 SeitenFigure 7.4 - Roughly One Third of The Projects Studied WerelenanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Customizing The ADFS Sign-In PagesDokument4 SeitenCustomizing The ADFS Sign-In Pagesmicu0% (1)
- RDSL 993K Z4D - Z4ZDokument11 SeitenRDSL 993K Z4D - Z4ZDAnielNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAX Brochure - Web ReadyDokument4 SeitenSAX Brochure - Web ReadyEng-Ahmad Abo-AledousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saurabh ShrivastavaDokument37 SeitenSaurabh ShrivastavaMahendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Review 1 ScheduleDokument1 SeiteProject Review 1 ScheduleH R VALANoch keine Bewertungen
- WS500 Operator WorkstationDokument2 SeitenWS500 Operator WorkstationNayants GuzmánNoch keine Bewertungen