Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Homework 1
Hochgeladen von
yana33Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Homework 1
Hochgeladen von
yana33Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
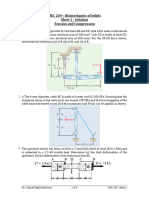
Strength of Materials
Homework 1
HOMEWORK 1
Solve any five of the following problems.
Please remember to write the number of problems you solved.
Homework assignments are to be submitted in class due 17 March, 2010.
You may discuss the problems with your classmates, but you are responsible for your own
works.
Dr. Mehmet evik
e-mail: mehmet.cevik@deu.edu.tr
website: http://kisi.deu.edu.tr/mehmet.cevik/
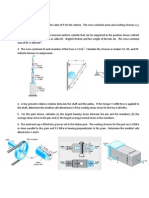
1. Link BD consists of a single bar 30 mm wide and
12 mm thick. Knowing that each pin has a 10-mm
diameter, determine the maximum value of the
average normal stress in link BD if (a) = 0, (b) =
90.
2. Each of the four vertical links has an 8 x 36- mm
uniform rectangular cross section and each of the four
pins has a 16- mm diameter. Determine the maximum
value of the average normal stress in the links
connecting (a) points B and D, (b) points C and E.
3. A couple of M of magnitude 1500 Nm is applied to the crank
of an engine. For the position shown, determine (a) the force P
required to hold the engine system in equilibrium, (b) the average
normal stress in the connecting rod BC, which has a 450-mm2
uniform cross section.
Strength of Materials
Homework 1
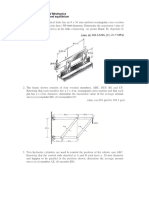
4. Each of the four vertical links has an 8 x 36- mm
uniform rectangular cross section and each of the four
pins has a 16- mm diameter.
For the assembly and loading of Prob. 2, determine (a)
the average shearing stress in the pin at B, (b) the
average bearing stress at B in link BD, (c) the average
bearing stress at B in member ABC, knowing that this
member has a 10 x 50-mm uniform rectangular cross
section.
5. Link BC is 6 mm thick, has a width of w = 25 mm, and is
made of a steel with a 480-MPa ultimate strength in tension.
What was the safety factor used if the structure shown was
designed to support a 16-kN load P ?
6. Link BC is 6 mm thick and is made of a steel with a 450MPa ultimate strength in tension. What should be its width w if
the structure shown is being designed to support a 20-kN load
P with a safety factor of 3 ?
Strength of Materials
Homework 1
7. Member ABC, which is supported by a pin and
bracket at C and a cable BD, was designed to support
the 15-kN load P as shown. Knowing that the ultimate
load for cable BD is 100 kN, determine the factor of
safety with respect to cable failure.
8. Knowing that the ultimate load for cable BD is
100 kN and that a factor of safety of 3.2 with
respect to cable failure is required, determine the
magnitude of the largest force P which can be
safely applied as shown to member ABC.
9. Members AB and AC of the truss shown consists of bars of
square cross section made of the same alloy. It is known that a 20mm square bar of the same alloy was tested to failure and that an
ultimate load of 120kN was recorded. If bar AB has a 15-mm
square cross section, determine (a) the factor of safety for bar AB,
(b) the dimensions of the cross section of bar AC if it is to have the
same factor of safety as bar AB.
10. The two wooden members shown, which support a
20-kN load, are joined by plywood splices fully glued on
the surfaces in contact. The ultimate shearing stress in the
glue is 2.8 MPa and the clearance between the members is
8 mm. Determine the factor of safety, knowing that the
length of each splice is L = 200 mm.
Strength of Materials
Homework 1
11. The two portions of member AB are glued together along
a plane forming an angle with the horizontal. Knowing that
the ultimate stress for the glued joint is 17 MPa in tension and
9 MPa in shear, determine the range of values of for which
the factor of safety of the member is at least 3.0.
12. The wooden members A and B are to be joined by plywood
splice plates which will be fully glued on the surfaces in contact.
As part of the design of the joint and knowing that the clearance
between the ends of the members is to be 8 mm, determine the
smallest allowable length L if the average shearing stress in the
glue is not to exceed 800 kPa.
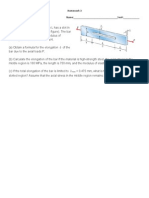
13. The 6- kN load P is supported by two wooden members of 75
x 125- mm uniform rectangular cross-section which are joined by
the simple glued scarf splice shown. Determine the normal and
shearing stresses in the glued splice.
14. The two wooden members of 75 x 125- mm uniform
rectangular cross-section are joined by the simple glued scarf
splice shown. Knowing that the maximum allowable tensile stress
in the glued splice is 500 kPa, determine (a) the largest load P
which can be safely supported, (b) the corresponding shearing
stress in the splice.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- How Two Boys Made Their Own Electrical Apparatus Containing Complete Directions for Making All Kinds of Simple Apparatus for the Study of Elementary ElectricityVon EverandHow Two Boys Made Their Own Electrical Apparatus Containing Complete Directions for Making All Kinds of Simple Apparatus for the Study of Elementary ElectricityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stresses, Loads, and Factors of Safety in Structural ElementsDokument6 SeitenStresses, Loads, and Factors of Safety in Structural ElementsMark Louies Mago VillarosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 34 Assignment 7Dokument2 Seiten34 Assignment 7venuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Composite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsVon EverandComposite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concepts of Stress1 PDFDokument18 SeitenConcepts of Stress1 PDFCarl Malone Lotivio LorillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionVon EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical stress problemsDokument7 SeitenMechanical stress problemsDhenil ManubatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ans. σ = 70 psi; τ = 40.4 psi: ExercisesDokument2 SeitenAns. σ = 70 psi; τ = 40.4 psi: ExercisesJasleneDimarananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Stress Problem SetDokument3 SeitenSimple Stress Problem SetJeff BayedNoch keine Bewertungen
- STRESS AND STRAIN CALCULATIONSDokument3 SeitenSTRESS AND STRAIN CALCULATIONSSaketh BoggavarapuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ES 13 ProbSet 1Dokument2 SeitenES 13 ProbSet 1Sammy Marquez50% (2)
- Strength of Materials PDFDokument35 SeitenStrength of Materials PDFromeo08100% (1)
- Tugas 1 (Allowable Stress)Dokument5 SeitenTugas 1 (Allowable Stress)WAHYU DWI LESTARINoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 1Munish NaickerNoch keine Bewertungen
- BAUTISTA, DARLENE JOY C. - 2CE-C - Activity 1-Prelim TermDokument24 SeitenBAUTISTA, DARLENE JOY C. - 2CE-C - Activity 1-Prelim TermDARLENE JOY C. BAUTISTA67% (3)
- Tutorial 1 Concept of StressDokument3 SeitenTutorial 1 Concept of Stresswilliamgacc11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 1Dokument7 SeitenProblem Set 1Percival ArcherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Review ProblemsDokument7 SeitenMechanics of Deformable Bodies Review ProblemsadrianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Es 13 THR: Problem Set Part I. Stresses and Strains (Submission Is On February 5, 2018 Before 5 PM)Dokument3 SeitenEs 13 THR: Problem Set Part I. Stresses and Strains (Submission Is On February 5, 2018 Before 5 PM)akosikapitansinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Hydrology VT Chow 1988Dokument3 SeitenApplied Hydrology VT Chow 1988kaicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENSC 13 Problem Set 1 (2sem AY 2019-2020)Dokument5 SeitenENSC 13 Problem Set 1 (2sem AY 2019-2020)Sean CrispoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials Homework 3Dokument9 SeitenStrength of Materials Homework 3felipe GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of Materials: Tutorial 3Dokument6 SeitenMechanics of Materials: Tutorial 3S.A. BeskalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bolted Connection ModuleDokument5 SeitenBolted Connection ModuleMakolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design strength of steel connectionsDokument9 SeitenDesign strength of steel connectionsCrisnico PeligrinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment No. 1_Simple StressDokument5 SeitenAssignment No. 1_Simple StressSakura BlossomsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE22S CE BSC 232b Activity 1 StressDokument2 SeitenCE22S CE BSC 232b Activity 1 StressJoshua John JulioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stress Practice ProblemsDokument6 SeitenStress Practice ProblemsSayantan ChakmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- prac prob PSADDokument10 Seitenprac prob PSADjeannechoiashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet 1Dokument3 SeitenSheet 1محمد معوضNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept of Stress PDFDokument8 SeitenConcept of Stress PDFMahad MahmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.2 Taller #5 Esfuerzo Permisible. Diseño de Conexiones SimplesDokument6 Seiten5.2 Taller #5 Esfuerzo Permisible. Diseño de Conexiones SimplesCamilo HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problemario 2Dokument5 SeitenProblemario 2Aguilar007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of Materials 1 PDFDokument2 SeitenMechanics of Materials 1 PDFEj ApeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 5 PDFDokument4 SeitenExercise 5 PDFchetanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 5 PDFDokument4 SeitenExercise 5 PDFAvinash IyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem SetDokument3 SeitenProblem SetChristian RigonNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGG 410 Problem Set 3 - Shear - Torsional StressDokument4 SeitenENGG 410 Problem Set 3 - Shear - Torsional StressJoana Rosette TordecillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plate1 Es205Dokument1 SeitePlate1 Es205RicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet 1Dokument3 SeitenSheet 1Olavo DélcioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prelim Emt313nDokument9 SeitenPrelim Emt313npaulineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Tube Stress and Diameter CalculationDokument18 SeitenSteel Tube Stress and Diameter CalculationRuth Abegail de VeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- StrengthDokument101 SeitenStrengthSigue Ramel Hinayas0% (1)
- Solid Tutorial 7Dokument9 SeitenSolid Tutorial 7Mohammad Afandi Azmi RaifNoch keine Bewertungen
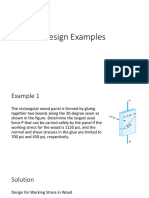
- Design Examples for Structural Joints and Wood PanelsDokument24 SeitenDesign Examples for Structural Joints and Wood PanelsAlan Peter100% (2)
- Mechanics Prob 2Dokument3 SeitenMechanics Prob 2Paul Angelou CiriacoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determining Minimum Diameters and Factors of Safety for Structural Components Under LoadDokument4 SeitenDetermining Minimum Diameters and Factors of Safety for Structural Components Under LoadJustin ShingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of MaterialsDokument61 SeitenStrength of MaterialsEkajara JoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- STRESS AND STRAIN CONCEPTS FOR OPTIMAL DESIGNDokument3 SeitenSTRESS AND STRAIN CONCEPTS FOR OPTIMAL DESIGNYasser ZubaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Problems - STRESS Sem 2 2023-2024Dokument8 SeitenPractice Problems - STRESS Sem 2 2023-2024Xavier LervineNoch keine Bewertungen
- HandoutsDokument3 SeitenHandoutssheena Marjorie Cabidog100% (1)
- Determine structural member dimensions and stressesDokument3 SeitenDetermine structural member dimensions and stressesMayoune GalvezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Stress ProblemsDokument5 SeitenChapter 1 Stress ProblemsKarthik Kalash100% (1)
- 2021 Theme 1 - Homework ProblemsDokument6 Seiten2021 Theme 1 - Homework ProblemsMartin MugoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument5 SeitenChapter 1Fizz MartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Mechanical Engineering ME-311, Fundamentals of Machine Design Assignment Sheet No.1 1Dokument6 SeitenDepartment of Mechanical Engineering ME-311, Fundamentals of Machine Design Assignment Sheet No.1 1VishnuNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEC211 Stress and Strain Tutorial QuestionsDokument7 SeitenMEC211 Stress and Strain Tutorial Questionsha haNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet - 1 (MEng 2110)Dokument2 SeitenWorksheet - 1 (MEng 2110)eyobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Probset 1.1Dokument1 SeiteProbset 1.1John Louie CarmenNoch keine Bewertungen
- UKCAT OfficialGuide 2015Dokument84 SeitenUKCAT OfficialGuide 2015kate2494Noch keine Bewertungen
- Worked ExamplesDokument8 SeitenWorked Examplesyana33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Army Reserve Information BookletDokument32 SeitenArmy Reserve Information Bookletyana33Noch keine Bewertungen
- QuantumDokument388 SeitenQuantumyana33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Analysis - Beams, Trusses EtcDokument79 SeitenStructural Analysis - Beams, Trusses EtcСергей Кравченко100% (1)
- A Mathematics Primer For Physics Graduate StudentsDokument78 SeitenA Mathematics Primer For Physics Graduate StudentsChung Chee Yuen100% (2)
- Steps in Stress Analysis Using AnsysDokument57 SeitenSteps in Stress Analysis Using AnsysChandrasekar MuthukumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Driving Test DSA DTESDokument381 SeitenDriving Test DSA DTESAnkit Yadav100% (6)
- Ansyslinxr 15 LinuxDokument70 SeitenAnsyslinxr 15 LinuxCipar ClauNoch keine Bewertungen
- MeshingGuide Ansys PDFDokument280 SeitenMeshingGuide Ansys PDFJulio David SaquingaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Airplane Orientation: Euler AnglesDokument10 SeitenAirplane Orientation: Euler AnglesJihan FarzanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Mathematics Primer For Physics Graduate StudentsDokument78 SeitenA Mathematics Primer For Physics Graduate StudentsChung Chee Yuen100% (2)
- A Mathematics Primer For Physics Graduate StudentsDokument78 SeitenA Mathematics Primer For Physics Graduate StudentsChung Chee Yuen100% (2)
- UKSEDS Nations Rocketry CompetitionDokument5 SeitenUKSEDS Nations Rocketry Competitionyana33Noch keine Bewertungen
- OPQ Test Guide - 2Dokument3 SeitenOPQ Test Guide - 2yana33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Aircraft Performance and Static Stability: 16.885J/ESD.35J Aircraft Systems EngineeringDokument36 SeitenIntroduction To Aircraft Performance and Static Stability: 16.885J/ESD.35J Aircraft Systems Engineeringginno18019048Noch keine Bewertungen
- Airplane Orientation: Euler AnglesDokument10 SeitenAirplane Orientation: Euler AnglesJihan FarzanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration Analysis of The Space Shuttle External Tank Cable Tray Flight Data With and Without PAL RampDokument24 SeitenVibration Analysis of The Space Shuttle External Tank Cable Tray Flight Data With and Without PAL Rampyana33Noch keine Bewertungen
- OPQ Test Guide - 2Dokument3 SeitenOPQ Test Guide - 2yana33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Airplane Orientation: Euler AnglesDokument10 SeitenAirplane Orientation: Euler AnglesJihan FarzanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Airplane Orientation: Euler AnglesDokument10 SeitenAirplane Orientation: Euler AnglesJihan FarzanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- X and y Are Related by The Equation: Linear Law Paper 1Dokument5 SeitenX and y Are Related by The Equation: Linear Law Paper 1Loh Chee WeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Large-Scale Systems Methodology Interpretive Structural ModelingDokument9 SeitenLarge-Scale Systems Methodology Interpretive Structural ModelingAleBribiescaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer From Heating Coil PDFDokument28 SeitenHeat Transfer From Heating Coil PDFMuhammad Naveed100% (1)
- SkinDokument8 SeitenSkinYamal E Askoul TNoch keine Bewertungen
- NMRDokument17 SeitenNMRSourabhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Field Test of An Old RC Bridge Before and After NSM StrengtheningDokument9 SeitenField Test of An Old RC Bridge Before and After NSM StrengtheningArun KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument60 SeitenChapter 1Izlaikha AzizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curso EMSO 2engDokument48 SeitenCurso EMSO 2enghelenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide For The Selection and Application of Energy-Efficient Motors PDFDokument10 SeitenGuide For The Selection and Application of Energy-Efficient Motors PDFEliseu RibeiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantum PhysicsDokument3 SeitenQuantum PhysicsAthena HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Дигитайзеры CR 85-X (5148100), CR 75.0 (5146105) (AGFA) СИ PDFDokument605 SeitenДигитайзеры CR 85-X (5148100), CR 75.0 (5146105) (AGFA) СИ PDFuser proNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions On Logarithmic Functions and IndicesDokument5 SeitenQuestions On Logarithmic Functions and IndicesCgzam Zam100% (1)
- Evaporation Pond SizingDokument3 SeitenEvaporation Pond SizingSaeid Rahimi Mofrad100% (1)
- Rotor Flux Oriented Induction Machine As A DC Power GeneratorDokument8 SeitenRotor Flux Oriented Induction Machine As A DC Power Generatorapi-27014626Noch keine Bewertungen
- Optimization of Chemical SynthesisDokument3 SeitenOptimization of Chemical SynthesisFahrudin MarbulakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution To Problem 403 - Shear and Moment Diagrams - Strength of Materials ReviewDokument2 SeitenSolution To Problem 403 - Shear and Moment Diagrams - Strength of Materials ReviewimrancenakkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tek 14-19aDokument6 SeitenTek 14-19akip2001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Well Deliverability TestDokument105 SeitenGas Well Deliverability TestAlIbtidaSultanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insta Base Export Data IntegrityDokument5 SeitenInsta Base Export Data IntegrityRyan SegalNoch keine Bewertungen
- VLSI Design Interview Questions With AnswersDokument27 SeitenVLSI Design Interview Questions With AnswersNitya SiddagangappaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatigue and Bond Properties For High Performance ConcreteDokument23 SeitenFatigue and Bond Properties For High Performance ConcretesakolkongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finite Element Analysis of Large Diameter Concrete Spherical Shell Domes - Hani Aziz AmeenDokument16 SeitenFinite Element Analysis of Large Diameter Concrete Spherical Shell Domes - Hani Aziz AmeenHani Aziz AmeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCP: New Performance Equations For Optimal DesignDokument5 SeitenPCP: New Performance Equations For Optimal DesignIndra Bayu100% (1)
- Differential CalculusDokument4 SeitenDifferential CalculusIsiahTanEdquibanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zadaca ImfDokument3 SeitenZadaca ImfAzra HumićNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCH CP12 E7Dokument1 SeiteCCH CP12 E7colinyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEET 2019: Analysis ofDokument4 SeitenNEET 2019: Analysis ofPankaj JakharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shape of Relativistically Moving ObjectsDokument9 SeitenShape of Relativistically Moving ObjectsDalimil MazáčNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aersys Knowledge Unit: Typical Uses of MPCDokument14 SeitenAersys Knowledge Unit: Typical Uses of MPCantonellodelreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis and Modeling of Coplanar Waveguide: Chapter - 5Dokument58 SeitenAnalysis and Modeling of Coplanar Waveguide: Chapter - 5Muhammad AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artificial Intelligence: From Medieval Robots to Neural NetworksVon EverandArtificial Intelligence: From Medieval Robots to Neural NetworksBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- Artificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureVon EverandArtificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindVon EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Collection of Raspberry Pi ProjectsVon EverandCollection of Raspberry Pi ProjectsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Comprehensive Guide to Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessVon EverandComprehensive Guide to Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessNoch keine Bewertungen
- PLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsVon EverandPLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.Von EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5)
- Artificial You: AI and the Future of Your MindVon EverandArtificial You: AI and the Future of Your MindBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- Arduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!Von EverandArduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- Mastering Drones - A Beginner's Guide To Start Making Money With DronesVon EverandMastering Drones - A Beginner's Guide To Start Making Money With DronesBewertung: 2.5 von 5 Sternen2.5/5 (3)
- What to Expect When You're Expecting Robots: The Future of Human-Robot CollaborationVon EverandWhat to Expect When You're Expecting Robots: The Future of Human-Robot CollaborationBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Dark Aeon: Transhumanism and the War Against HumanityVon EverandDark Aeon: Transhumanism and the War Against HumanityBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Atlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial IntelligenceVon EverandAtlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial IntelligenceBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (9)
- ChatGPT: The Future of Intelligent ConversationVon EverandChatGPT: The Future of Intelligent ConversationBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (8)
- Robotics: Designing the Mechanisms for Automated MachineryVon EverandRobotics: Designing the Mechanisms for Automated MachineryBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (8)
- How to Survive a Robot Uprising: Tips on Defending Yourself Against the Coming RebellionVon EverandHow to Survive a Robot Uprising: Tips on Defending Yourself Against the Coming RebellionBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (129)
- Projects With Microcontrollers And PICCVon EverandProjects With Microcontrollers And PICCBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- In the Age of AI: How AI and Emerging Technologies Are Disrupting Industries, Lives, and the Future of WorkVon EverandIn the Age of AI: How AI and Emerging Technologies Are Disrupting Industries, Lives, and the Future of WorkBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Modeling, Dynamics, and Control of Electrified VehiclesVon EverandModeling, Dynamics, and Control of Electrified VehiclesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Arduino: The ultimate Arduino guide for beginners, including Arduino programming, Arduino cookbook, tips, tricks, and more!Von EverandArduino: The ultimate Arduino guide for beginners, including Arduino programming, Arduino cookbook, tips, tricks, and more!Bewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)