Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Intermolecular Forces Handout
Hochgeladen von
anurag yadav0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
146 Ansichten1 SeiteIntermolecular forces determine whether mixtures will mix or not. There are four main types of intermolecular forces - ionic bonds, dipole-dipole interactions, hydrogen bonding, and London dispersion forces. Hydrogen bonding is particularly strong due to the small size and high partial charge of hydrogen. While ionic bonds and dipole interactions cause polar substances to mix, non-polar substances rely on weaker London dispersion forces to mix or form liquids and solids. The strength of intermolecular forces and the speed of molecules determines whether more solid will dissolve in warmer water or a gas will be less soluble at higher temperatures.
Originalbeschreibung:
forces
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenIntermolecular forces determine whether mixtures will mix or not. There are four main types of intermolecular forces - ionic bonds, dipole-dipole interactions, hydrogen bonding, and London dispersion forces. Hydrogen bonding is particularly strong due to the small size and high partial charge of hydrogen. While ionic bonds and dipole interactions cause polar substances to mix, non-polar substances rely on weaker London dispersion forces to mix or form liquids and solids. The strength of intermolecular forces and the speed of molecules determines whether more solid will dissolve in warmer water or a gas will be less soluble at higher temperatures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
146 Ansichten1 SeiteIntermolecular Forces Handout
Hochgeladen von
anurag yadavIntermolecular forces determine whether mixtures will mix or not. There are four main types of intermolecular forces - ionic bonds, dipole-dipole interactions, hydrogen bonding, and London dispersion forces. Hydrogen bonding is particularly strong due to the small size and high partial charge of hydrogen. While ionic bonds and dipole interactions cause polar substances to mix, non-polar substances rely on weaker London dispersion forces to mix or form liquids and solids. The strength of intermolecular forces and the speed of molecules determines whether more solid will dissolve in warmer water or a gas will be less soluble at higher temperatures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
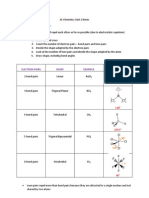
Intermolecular forces
and solubility
Why mixtures mix
Consider a glass of wine. Why do
alcohol, water, & pigment mix together?
There must be attractive forces.
Intramolecular forces
Intermolecular forces
occur between atoms occur between molecules
The factors that determine solubility are the
strength of IMFs and speed of molecules.
4 types of intermolecular forces: ionic, dipoledipole, hydrogen bonding, and London forces.
Hydrogen bonding
Electronegativity & IMFs
EN essentially defines the type of IMF.
Ionic bonds form if the EN is 1.7 or greater.
Dipole-dipole (polar covalent) is around 0.5-1.7.
Hydrogen bonding is a type of dipole-dipole.
London forces exist in all molecules, but are
especially important in non-polar covalent
molecules (where EN is less than 0.5). +
Recall that ionic are strongest.
+
Dipole-dipole are not as strong.
Hydrogen bonds are about five +
+
times stronger than a regular
+
dipole-dipole bonds.
+
London forces are weakest.
London forces
Why oil and water dont mix
+
+
The high EN of NH, OH, and HF bonds
cause these to be strong forces.
Also, because of the small size of hydrogen,
its positive charge can get very close to the
negative dipole of another molecule.
It is so strongly positive that it will H O H O
sometimes exert a pull on a lone
H
H
pair in a non-polar compound
London forces
Non-polar molecules do not have dipoles like
polar molecules. How, then, can non-polar
compounds form solids or liquids?
London forces result from a type of tiny dipole.
These forces exist between all molecules.
They are masked by stronger forces (e.g.
dipole-dipole) so are sometimes insignificant,
but they are important in non-polar molecules.
Because electrons are moving around in
atoms there will be instants when the charge
around an atom is not symmetrical.
The resulting tiny dipoles result in attractions
between atoms and/or molecules.
H-bonding is a special type of dipole-dipole
attraction that is very strong.
It occurs when N, O, or F are bonded to H.
Q- Calculate the EN for HCl and H2O
Instantaneous dipole:
Induced dipole:
Eventually electrons A dipole forms in one atom
are situated so that or molecule, inducing a
dipole in the other
tiny dipoles form
Temperature and Solubility
+ +
+ +
+ +
The non-polar substance is
pushed away. If it were
moving faster it might break
+ +
through the attractive forces.
+ +
Solubility is a balance be
tween speed and attraction.
Also, the more similar the strength of their dipoles
the more likely two compounds are to mix.
+
Solubility is influenced by temperature.
In warmer water, more solid will dissolve.
This is because a high temperature means
H2O molecules are moving faster (keeping
more solid molecules suspended).
Conversely a gas will be less soluble
at a higher temperature.
This is because when gas molecules
are moving faster they are able to
escape from the liquid surface.
Think of cold soda vs. warm soda.
Warm soda goes flat faster.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Die Correction Manual PDFDokument10 SeitenDie Correction Manual PDFLUAI BARAKAT100% (3)
- SACE Stage 1 Chemistry - Materials and Their AtomsDokument1 SeiteSACE Stage 1 Chemistry - Materials and Their AtomsMarcusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter11 1212 Liquids SolidsDokument90 SeitenChapter11 1212 Liquids SolidsVirgilio AbellanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conceptual Physical Science: 5 EditionDokument72 SeitenConceptual Physical Science: 5 EditionoperationmanagerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Powerpoint Lesson PlanDokument17 SeitenPowerpoint Lesson PlanMuhamad Haziq HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Packet Unit 1Dokument36 SeitenPacket Unit 1Amelia Simmons0% (1)
- Iit Jee Screening Chemistry 2005 SolutionDokument5 SeitenIit Jee Screening Chemistry 2005 Solutionsaurav guptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm E280Dokument3 SeitenAstm E280hlagos123100% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical Bonding with AnswersVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical Bonding with AnswersBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Chemistry of Cell Review: Quick Review Notes Chapter 2Von EverandChemistry of Cell Review: Quick Review Notes Chapter 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- IB Chemistry Syllabus - Core OnlyDokument89 SeitenIB Chemistry Syllabus - Core OnlyHavila SaafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12 - Liquids and SolidsDokument35 SeitenChapter 12 - Liquids and SolidsGörkem DamdereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Middle School ChemistryDokument691 SeitenMiddle School ChemistryChristian Homeschool-HubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5 ChemicChemical Kinetics and Equilibriumal Kinetics and Equilibrium Notes (Answers)Dokument22 SeitenUnit 5 ChemicChemical Kinetics and Equilibriumal Kinetics and Equilibrium Notes (Answers)Muhammad IrfanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inter Molecular ForcesDokument47 SeitenInter Molecular ForcesMaan PlatonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9halogens Group PresentationDokument31 Seiten9halogens Group PresentationQueen GeminiNoch keine Bewertungen
- As Chemistry Unit 2 NotesDokument21 SeitenAs Chemistry Unit 2 NotescluendoNoch keine Bewertungen
- HalogenoalkanesDokument21 SeitenHalogenoalkanesallaura1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Separation HW BOOK PDFDokument9 SeitenSeparation HW BOOK PDFAngela KocevskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry MYP 3 Section 3Dokument15 SeitenChemistry MYP 3 Section 3Hadeel IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Properties of Liquids and Intermolecular ForcesDokument5 SeitenProperties of Liquids and Intermolecular ForcesJohnnard BelenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 1.1 Intermolecular Forces: Liquids, Solids, and Phase ChangesDokument2 SeitenWorksheet 1.1 Intermolecular Forces: Liquids, Solids, and Phase ChangesRisciella 18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Distillation of Binary LiquidsDokument29 SeitenDistillation of Binary LiquidsJan Lloyd ProbitsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- F321 Group 7Dokument5 SeitenF321 Group 7Doc_CrocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Principle S: Chapter 17 Properties of SolutionsDokument56 SeitenChemical Principle S: Chapter 17 Properties of SolutionsjovitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronegativity WorksheetDokument3 SeitenElectronegativity WorksheetShermer100% (1)
- Lesson 3 Exo and EndoDokument7 SeitenLesson 3 Exo and Endoapi-385539760Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ib PPT 4 HL PDFDokument55 SeitenIb PPT 4 HL PDFzarna nirmal rawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ismail Yusuf: Arts, Science and Commerce College, MumbaiDokument43 SeitenIsmail Yusuf: Arts, Science and Commerce College, MumbaiBapu ThoratNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naming Covalent CompoundsDokument6 SeitenNaming Covalent Compoundsapi-296446442Noch keine Bewertungen
- POGIL Avg Atomic Mass KEYDokument4 SeitenPOGIL Avg Atomic Mass KEYbobNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.2 - The Mole ConceptDokument14 Seiten1.2 - The Mole ConceptKruti PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- PeriodicityDokument6 SeitenPeriodicityHadi AlnaherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solubility and Polarity C11!4!5Dokument8 SeitenSolubility and Polarity C11!4!5doctorguy770% (1)
- Inter Molecular ForcesDokument59 SeitenInter Molecular ForcesKc McCulloughNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 - Impacts of Chemical Industries - Tasksheet 1Dokument7 SeitenUnit 1 - Impacts of Chemical Industries - Tasksheet 1Llama jennerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Worksheet of Chemical BondingDokument2 SeitenPractice Worksheet of Chemical Bondingch khakanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polar Covalent BondsDokument10 SeitenPolar Covalent BondsParas ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Chemical Reactions Close Reading PDFDokument4 SeitenTypes of Chemical Reactions Close Reading PDFStefanie CorcoranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes - Chemistry FoldableDokument21 SeitenNotes - Chemistry Foldableapi-271661638Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3 - Gravimetric Analysis of Calcium and Hard Water - S PDFDokument6 Seiten3 - Gravimetric Analysis of Calcium and Hard Water - S PDFJon CranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energi Kisi Dan Born HaberDokument31 SeitenEnergi Kisi Dan Born HaberNovi CherlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.05 POGIL Molfgarity KeyDokument8 Seiten7.05 POGIL Molfgarity KeyXazerco LaxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atoms and Atomic Theory: Essential Questions: How Can We Describe TH e Molecular Motion of TH e States of Matter?Dokument29 SeitenAtoms and Atomic Theory: Essential Questions: How Can We Describe TH e Molecular Motion of TH e States of Matter?Anonymous eMOb79RNt5Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 11 Liquids, Solids and Intermolecular Forces StudentDokument113 SeitenCH 11 Liquids, Solids and Intermolecular Forces StudentAneeqa YounasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shapes of Molecules and Ions PDFDokument9 SeitenShapes of Molecules and Ions PDFMagenta SparklegemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Chemical Reactions Powerpoint PresentationDokument6 SeitenTypes of Chemical Reactions Powerpoint Presentationapi-1991761550% (6)
- 1.1 Introduction To The Particulate Nature of Matter and Chemical ChangeDokument19 Seiten1.1 Introduction To The Particulate Nature of Matter and Chemical ChangeJuan Fernando Velasco ForeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 1 Paper2 - Grade 10-11 IGCSE - 2020 - MoodleDokument13 SeitenTest 1 Paper2 - Grade 10-11 IGCSE - 2020 - MoodleJadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pure Substances and MixturesDokument21 SeitenPure Substances and MixturesJane Michelle EmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 3 EnergeticsDokument47 SeitenSection 3 Energeticsapi-3734333Noch keine Bewertungen
- AP Chem Bonding NotesDokument3 SeitenAP Chem Bonding NotesKristela RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonding Test ReviewDokument5 SeitenChemical Bonding Test ReviewAlakh Jagtap100% (1)
- Modified Review WS KEYDokument4 SeitenModified Review WS KEYKatsuragi ShintaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonding: Presented By: Mohammad Fayiz Akhtar SP05-AA-0017 Presented To: Afsheen Khalil Presented On: 04-OCT-2006Dokument12 SeitenChemical Bonding: Presented By: Mohammad Fayiz Akhtar SP05-AA-0017 Presented To: Afsheen Khalil Presented On: 04-OCT-2006helperforeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes Intermolecular ForcesDokument2 SeitenNotes Intermolecular Forceslaliberte68100% (3)
- Chemical Bonding WS Packet Margie Core 2013Dokument4 SeitenChemical Bonding WS Packet Margie Core 2013Lama DebanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5 Chemical KineticsDokument37 SeitenUnit 5 Chemical KineticsSanjay SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DP Chem Unit 7 EquilibriumDokument5 SeitenDP Chem Unit 7 EquilibriumPatrick AbidraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonding - FINALDokument9 SeitenChemical Bonding - FINALSabsNoch keine Bewertungen
- C18 PolymersDokument31 SeitenC18 PolymersKris DookharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Fajan's RuleDokument13 Seiten3 Fajan's RuleNazmi LatifNoch keine Bewertungen
- AreasDokument16 SeitenAreasShaik BajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics Type 1Dokument24 SeitenThermodynamics Type 1Balagovind BaluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gmail Inbox 2Dokument2 SeitenGmail Inbox 2anurag yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review PaperDokument7 SeitenReview Paperanurag yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yadav Matrimony, Matrimony, Indian MatrimonyDokument3 SeitenYadav Matrimony, Matrimony, Indian Matrimonyanurag yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job DescriptionparttimefreelancersmDokument1 SeiteJob Descriptionparttimefreelancersmanurag yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anu Front12Dokument15 SeitenAnu Front12anurag yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- FINAl 3Dokument41 SeitenFINAl 3anurag yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job DescriptionparttimefreelancersmDokument1 SeiteJob Descriptionparttimefreelancersmanurag yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anu Front PDFDokument15 SeitenAnu Front PDFanurag yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 Syllabus 12 Computer ScienceDokument8 Seiten2014 Syllabus 12 Computer Sciencesabhari_ramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report On Drug Designing Using Insilico MethodDokument74 SeitenProject Report On Drug Designing Using Insilico Methodanurag yadav0% (1)
- Pen Drive Containing Video Lecture With JEE Complete Syllabus ChemistryDokument1 SeitePen Drive Containing Video Lecture With JEE Complete Syllabus Chemistryanurag yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inorganic Chemistry - Predicting Bond-Strength of Metal Carbonyls - Chemistry Stack ExchangeDokument1 SeiteInorganic Chemistry - Predicting Bond-Strength of Metal Carbonyls - Chemistry Stack Exchangeanurag yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of CBSE Schools in Satna, Madhya PradeshDokument2 SeitenList of CBSE Schools in Satna, Madhya Pradeshanurag yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welcome To University of Allahabad123Dokument1 SeiteWelcome To University of Allahabad123anurag yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lanthanides, Properties of Lanthanides, Characteristics of Lanthanides - Chemistry@TutorVistaDokument4 SeitenLanthanides, Properties of Lanthanides, Characteristics of Lanthanides - Chemistry@TutorVistaanurag yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yadav Matrimony, Matrimony, Indian Matrimony2Dokument3 SeitenYadav Matrimony, Matrimony, Indian Matrimony2anurag yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yadav Matrimony, Matrimony, Indian Matrimony4Dokument3 SeitenYadav Matrimony, Matrimony, Indian Matrimony4anurag yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class11 Chemistry1 Appendix NCERT TextBook EnglishEditionDokument14 SeitenClass11 Chemistry1 Appendix NCERT TextBook EnglishEditionRobin AhujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Form SU FacultyDokument10 SeitenApplication Form SU Facultyanurag yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yadav Matrimony, Matrimony, Indian MatrimonyDokument3 SeitenYadav Matrimony, Matrimony, Indian Matrimonyanurag yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- XI Chem Ch2 StructureOfAtom ConceptsDokument14 SeitenXI Chem Ch2 StructureOfAtom Conceptsanurag yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yadav Matrimony, Matrimony, Indian Matrimony4Dokument3 SeitenYadav Matrimony, Matrimony, Indian Matrimony4anurag yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework - Volume of Gas Needed To Heat Air in Room - Chemistry Stack ExchangeDokument2 SeitenHomework - Volume of Gas Needed To Heat Air in Room - Chemistry Stack Exchangeanurag yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between Alkali and BaseDokument3 SeitenDifference Between Alkali and Baseanurag yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isothermal Vs AdiabaticDokument2 SeitenIsothermal Vs Adiabaticanurag yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Admission Notice Jee Mains 2015Dokument6 SeitenAdmission Notice Jee Mains 2015w3w2Noch keine Bewertungen
- CTVPRC 007 enDokument56 SeitenCTVPRC 007 enrommel duranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Slab DesignDokument18 SeitenChapter 6 Slab DesignZAX100% (1)
- SP 1211Dokument87 SeitenSP 1211Anoop gokhaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Public Review Draft 2404Dokument115 SeitenPublic Review Draft 2404Said100% (1)
- 8.3 Factors Affecting RXN RateDokument36 Seiten8.3 Factors Affecting RXN RateNur AleyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Completecoat™ Corrosion Protection: Corrosion-Resistant, Flexible Coating Uniformly Bonded To All Condenser Coil SurfacesDokument2 SeitenCompletecoat™ Corrosion Protection: Corrosion-Resistant, Flexible Coating Uniformly Bonded To All Condenser Coil SurfacesdjoletetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper No. 609Dokument15 SeitenPaper No. 609ravi kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACI 301 Section 2 and 3 - MilwaukeeDokument16 SeitenACI 301 Section 2 and 3 - MilwaukeeerosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section Capacity AnalysisDokument4 SeitenSection Capacity AnalysisAhmed IsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- QP Am Ii SemDokument6 SeitenQP Am Ii SemnishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ti Alloy HandbookDokument122 SeitenTi Alloy HandbookBahubali KabnureNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Distance Measurement (EDM)Dokument29 SeitenElectronic Distance Measurement (EDM)Kavi MaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Plunger With Stopper DynamicsDokument28 SeitenElectromagnetic Plunger With Stopper DynamicsCatanescu Alexandru-LaurentiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Eccentric Footing With StrapDokument11 SeitenDesign of Eccentric Footing With StrapKrijan MaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12H, 140H and 160H Electrical System Motor Graders (NA Version)Dokument2 Seiten12H, 140H and 160H Electrical System Motor Graders (NA Version)jorge william ramirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzyme Lab ReportDokument9 SeitenEnzyme Lab ReportSafaa TatouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Static IndeterminacyDokument36 SeitenStatic IndeterminacyKarthik KrishNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCERT Class 12 Physics Book (Part I)Dokument236 SeitenNCERT Class 12 Physics Book (Part I)Deepesh TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Temperature MeasurementDokument18 SeitenFundamentals of Temperature MeasurementHeather KramerNoch keine Bewertungen
- NH-Armaflex SpecificationDokument2 SeitenNH-Armaflex SpecificationPanya PurahongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blowing AgentDokument12 SeitenBlowing AgentHimanshu PainulyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 March 2024 Term 1 Physical Sciences TestDokument11 SeitenGrade 10 March 2024 Term 1 Physical Sciences TestTererai Lalelani Masikati HoveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virtual Work MethodDokument7 SeitenVirtual Work Methodviveksp99Noch keine Bewertungen
- #Derivation of Mechanical Properties For SandDokument8 Seiten#Derivation of Mechanical Properties For SandkingmajorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methods of Artificial Lift: Presented To: Prof DR: El Ayouty - ElsaidDokument11 SeitenMethods of Artificial Lift: Presented To: Prof DR: El Ayouty - Elsaidcmrig74Noch keine Bewertungen
- Taller 2Dokument3 SeitenTaller 2Quispe Inga Americo GiuseppeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duet Dhaka University of Engineering & Technology Civil, CSE, Industrial, ArchitectureDokument6 SeitenDuet Dhaka University of Engineering & Technology Civil, CSE, Industrial, ArchitectureMd Sohrab Hossain SohelNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITT American Electric Horizontal Luminaire Series 13 & 14 Spec Sheet 2-81Dokument8 SeitenITT American Electric Horizontal Luminaire Series 13 & 14 Spec Sheet 2-81Alan MastersNoch keine Bewertungen