Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
3.2 Theophylline
Hochgeladen von
sarahabdullahOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
3.2 Theophylline
Hochgeladen von
sarahabdullahCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
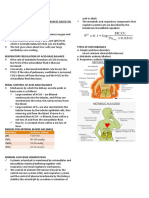
THEOPHYLLINE
USES
CIRCUMSTAN
CES OF
POISONING
1.Accidental
Treatmen -can be
t of
ingested by
bronchia curious
l asthma toddlers due
and other to its general
syndrome availability.
s of
airway
2.Suicidal
obstructi
-by
on
adolescents
including or adults.
COPD in
adults
3.Unintenti
and
onal acute
bronchioli intoxication
tis in
on top of long
children.
term therapy
in asthmatic
patients due
to narrow
therapeutic
index of
TOXICOKINETICS
1.Absorption
-absorbed rapidly and
completely after oral
therapeutic
doses,reaching peak
serum concentration
within 2 hours .
-Sustained release
preparations reach
peak concentration
within 4-12 hours
after ingestion
2.Metabolism and
Excretion
-in plasma
,theophylline 60%
protein bound.
-in liver,it is
metabolized primarily
by hepatic p450
cytochrome oxidase
system.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
1.Competitive
antagonism of
endogenous
adenosine >
bronchoconstrictor,
anticonvulsant and
regulator of cardiac
rhythm.
2.Release of
endogenous
catecholamines
CLINICAL PICTURE OF ACUTE
POISONING
Serum theophylline concentration up to
20g/mL > toxicity
1.GIT - nausea,repeated
vomiting,diarrhea, abdominal pain,upper
GI bleeding.
2.CNS stimulation irritability,agitation,tremors,lethargy,seizu
res
Status epilepticus and coma
(prolonged seizures > rhabdomyolysis)
elevation of plasma
3.CVS
epinephrine and
- tachyarrhythmias(supraventricular
norepinephrine with
tachycardia)
resulting -adrenergic -hypotension > increased 2 adrenergic
receptor stimulation.
receptor stimulation with resultant
relaxation of arteriolar tone.
Theophylline induced
-cardiac arrest.
tachycardia,hypokalemi 4.Metabolic
a(intracellular shift)
-increased respiration > respiratory
,lactic
alkalosis > metabolic
theophylline.
-90% is metabolized
and 10% excreted
unchanged in urine.
acidosis,hyperglycemia. acidosis(compensation).
-increase level of endogenous
3.Direct stimulation catecholamines.
of respiratory centre
hypokalemia,hyperglycemia and
Increased rate and
hypercalcemia.
depth of breathing
THEOPHYLLINE
1-INVESTIGATION
A.Toxicological
-Serum level of theophylline (according to concentration , toxicity classified into mild ,moderate
and severe.
B.Non toxicological
-ECG, chest X ray ,measurement of arterial blood gases and acid bases status,
-serum electrolytes and blood glucose,myoglobin in urine,
-brain computed tomography ( for those who develop convulsions as seizures maye related to
cerebrovascular stroke )
MANAGEMENT
2-TREATMENT (ABCDES)
A.General supportive treatment (ABC)
B.Decontamination
-Gastric lavage
-Multiple dose activated charcoal is an effective method of enhancing the clearance of
theophylline especially in sustained release theophylline tablets.( 50g every 4 hour for 2 days )
< gut dialysis
-Concomitant use of charcoal with cathartic has been shown to be more effective in reducing
serum theophylline.
-syrup of ipecac is best avoided > can cause protracted vomiting.
C.Elimination
-Hemoperfusion. (haemodialysis considered when haemoperfusion not available)
D.Symptomatic treatment.
-convulsions > diazepam (5-10 mg IV).
-tachyarrhytmias >
beta blocker( propranolol)-may produce bronchoconstriction in susceptible individual.
Esmolol-short acting 1 specific adrenoreceptor antagonist > used succesfully for
reversal of tachycardia
-metabolic acidosis > IV NaHCO3.
-hypokalemia > potassium supplement.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Icm 2 Week 6Dokument34 SeitenIcm 2 Week 6Syaimee Annisa AzzahraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Penatalaksanaan Keracunan ObatDokument23 SeitenPenatalaksanaan Keracunan ObatbimayuswantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical ToxicologyDokument79 SeitenClinical ToxicologySaddam HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Treatment of PoisoningDokument4 SeitenGeneral Treatment of PoisoningmahnoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug OrnDokument25 SeitenDrug OrnOrnwadee Jit-owatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Task #3: AnswerDokument5 SeitenCourse Task #3: AnswerAria100% (3)
- Arterial Blood Gas (Abg)Dokument10 SeitenArterial Blood Gas (Abg)Kita kitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PoisoningDokument36 SeitenPoisoningsalah almozahemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poisoning & BitesDokument12 SeitenPoisoning & BitesJudy HandlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toxicology: Question - 1Dokument8 SeitenToxicology: Question - 1VasanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ct8 Electrolyte and Acid-Base ImbalancesDokument4 SeitenCt8 Electrolyte and Acid-Base ImbalancesAlondra VelascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Local Anesthesia and Concious SedationDokument43 SeitenLocal Anesthesia and Concious Sedationpawi18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Theophylline and Caffeine Toxicity: DR - Qayssar Joudah Fadheel Ph.D.Pharmacology and TherapeuticsDokument24 SeitenTheophylline and Caffeine Toxicity: DR - Qayssar Joudah Fadheel Ph.D.Pharmacology and TherapeuticsMustafa Salah MahdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Discussion 4Dokument6 SeitenCase Discussion 4Siraj INoch keine Bewertungen
- Paracetamol PoisoningDokument42 SeitenParacetamol PoisoningsnigdhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acetaminophen (Paracetamol) : Clinical ToxicologyDokument34 SeitenAcetaminophen (Paracetamol) : Clinical Toxicologymalak amerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Care CasesDokument7 SeitenCritical Care CasesJude Micko Bunyi AlipitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antidotes in Clinical Practice SeminarDokument77 SeitenAntidotes in Clinical Practice Seminarkhaled eissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- KGD 2 IvanDokument92 SeitenKGD 2 IvanrikarikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatrics MS WordDokument13 SeitenPediatrics MS WordSamhitha SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- C1-Pediatrics 5th-Lec 1Dokument10 SeitenC1-Pediatrics 5th-Lec 1عمر احمد شاكرNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intoxication or Acute PoisoningDokument37 SeitenIntoxication or Acute Poisoningcitra dewiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Untitled PresentationDokument16 SeitenUntitled PresentationRutuja UmateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Toxicology-Poisoned Patient Cases W Answers/ExplanationsDokument7 SeitenClinical Toxicology-Poisoned Patient Cases W Answers/ExplanationsMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.100% (3)
- Poisoning: PWM Olly Indrajani 2014Dokument45 SeitenPoisoning: PWM Olly Indrajani 2014arieska daraNoch keine Bewertungen
- JULAUG 2014 - Selected PagesDokument5 SeitenJULAUG 2014 - Selected PagesStephen PopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- methotrexate-Anti-Asthmatic Drugs Toxicity-1Dokument9 Seitenmethotrexate-Anti-Asthmatic Drugs Toxicity-1joonabil29Noch keine Bewertungen
- Toxicology Lecture 7 (Chapter 4 Analgesic and Antipyretic)Dokument23 SeitenToxicology Lecture 7 (Chapter 4 Analgesic and Antipyretic)MowlidAbdirahman Ali madaaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- PharmacologyDokument116 SeitenPharmacologyvargheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 8Dokument5 SeitenWeek 8MARIKA BALONDONoch keine Bewertungen
- Poisoning 2Dokument5 SeitenPoisoning 2Lily AddamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toxicology Final YearDokument131 SeitenToxicology Final YearAbdur RasheedNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEC A Pharma Drugs PDFDokument11 SeitenSEC A Pharma Drugs PDFzzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric PoisoningDokument47 SeitenPediatric PoisoningDr-Jagadeesh Mangamoori75% (4)
- Kent R. Olson, MDDokument13 SeitenKent R. Olson, MDIya GerzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Management Guidline in Organophosphors Poisoning: DR - Surendra Khosya Guided by Dr. S.R Meena Dr. Meenaxi ShardaDokument28 SeitenCurrent Management Guidline in Organophosphors Poisoning: DR - Surendra Khosya Guided by Dr. S.R Meena Dr. Meenaxi ShardasurendrakhosyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Biochemical Pathway of Paraquat ToxicityDokument16 SeitenThe Biochemical Pathway of Paraquat ToxicitysuderiNoch keine Bewertungen
- سموم عملي٣Dokument16 Seitenسموم عملي٣مصطفى ابراهيم سعيد100% (1)
- Organophospha Te (Op) Poisining: Presented byDokument44 SeitenOrganophospha Te (Op) Poisining: Presented byShantanu Kr VatsyayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tylenol OverdoseDokument9 SeitenTylenol OverdoseTyler HempelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acetaminophen ToxicityDokument16 SeitenAcetaminophen ToxicityMohil PratapNoch keine Bewertungen
- CC Junsay Nicole Xyza T. Learning Interaction FormDokument10 SeitenCC Junsay Nicole Xyza T. Learning Interaction FormNicole Xyza JunsayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kreozan PoisoningDokument9 SeitenKreozan Poisoningdr Alex stanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apnea 2019Dokument10 SeitenApnea 2019aiswarya sreekumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Emergencies ?-1Dokument96 SeitenPediatric Emergencies ?-1zahraaNoch keine Bewertungen
- E - Cart DrugsDokument18 SeitenE - Cart Drugs'SheenMarkReal'100% (2)
- Hippo EM Board Review - Toxicology (New 2017) Written SummaryDokument15 SeitenHippo EM Board Review - Toxicology (New 2017) Written Summarykaylawilliam01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Organophosphate Poisoning 2Dokument12 SeitenOrganophosphate Poisoning 2Diana MurguiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- All DrugsDokument482 SeitenAll DrugsJessica IbañezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contora, Isah TblrenalDokument7 SeitenContora, Isah TblrenalisahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dept - Farmakologi & Terapeutik Fak - Kedokteran U S U Medan: Prof - Dr.H.Aznan Lelo PHD - SPFK DR - Datten Bangun MSC, SPFKDokument62 SeitenDept - Farmakologi & Terapeutik Fak - Kedokteran U S U Medan: Prof - Dr.H.Aznan Lelo PHD - SPFK DR - Datten Bangun MSC, SPFKAnonymous zZrGTONhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paediatric Clinical GuidelinesDokument7 SeitenPaediatric Clinical GuidelinesAndriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hepatotoxic Substances Davao 092019Dokument66 SeitenHepatotoxic Substances Davao 092019nonoybenedictNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation and Management of Delayed Awakening or Emergence From AnaesthesiaDokument19 SeitenEvaluation and Management of Delayed Awakening or Emergence From AnaesthesiaMuhammad UmairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 2Dokument20 SeitenPresentation 2Muhammad UmairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology Nursing ReviewDokument19 SeitenPharmacology Nursing Reviewp_dawg50% (2)
- Pharma ChartsDokument33 SeitenPharma ChartsNooreen Hussain100% (1)
- Alert Medical Series: Internal Medicine Alert I, II, IIIVon EverandAlert Medical Series: Internal Medicine Alert I, II, IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- Signal Molecule TrackerDokument4 SeitenSignal Molecule Trackerarman_azad_2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology (Receptors)Dokument17 SeitenPhysiology (Receptors)Omar NuhicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ma Huang (Ephedrae Herba) : Setting The Record StraightDokument14 SeitenMa Huang (Ephedrae Herba) : Setting The Record StraightInfohoggNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 473 Cardiac Activity Lab ReportDokument4 SeitenBio 473 Cardiac Activity Lab Reportapi-253602935Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial On ANS PharmacologyDokument23 SeitenTutorial On ANS PharmacologyRomaine-Ricardo FrancisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Pre.. Cushing SyndromeDokument11 SeitenCase Pre.. Cushing Syndromedee_day_8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Health Challenges ANSWER KeyDokument97 SeitenChronic Health Challenges ANSWER KeyDol PhinNoch keine Bewertungen
- MeditationDokument114 SeitenMeditationNAITIKNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Endocrine Pancreas: Regulation of Carbohydrate MetabolismDokument61 SeitenThe Endocrine Pancreas: Regulation of Carbohydrate MetabolismFatima OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- El - Pharmacology ReportDokument46 SeitenEl - Pharmacology ReportShiela P CayabanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Featuring Christian Thibaudeau, Lonnie Lowery, PHD, David Barr, and Dr. John BerardiDokument17 SeitenFeaturing Christian Thibaudeau, Lonnie Lowery, PHD, David Barr, and Dr. John Berardiogre600100% (1)
- CMG Pharmacology Adrenaline Jan10Dokument2 SeitenCMG Pharmacology Adrenaline Jan10honeytrap99Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7.effects of Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Stimulation On SpecificDokument16 Seiten7.effects of Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Stimulation On SpecificSanthoshi Sadhanaa SankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- EAP (4) Reading Grammar (Answered)Dokument5 SeitenEAP (4) Reading Grammar (Answered)Nova ZaenalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pheochromocytoma: Dr. Suvyl Rodricks Dr. Meera KharbandaDokument74 SeitenPheochromocytoma: Dr. Suvyl Rodricks Dr. Meera KharbandaRichgirl DayawonNoch keine Bewertungen
- SWT Pharmacology DamsDokument84 SeitenSWT Pharmacology DamsvamshidhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcohol in Health and DiseaseDokument648 SeitenAlcohol in Health and DiseaseYuli KiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Tagging Methode For Sea CucumberDokument6 SeitenNew Tagging Methode For Sea CucumberMuhammad IdrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Secondary ThrombocytosisDokument7 SeitenSecondary ThrombocytosisAya Avellana100% (1)
- Pycnogenol For Sports NutritionDokument5 SeitenPycnogenol For Sports NutritionLubimOffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stress Definitions Mechanisms and EffectsDokument9 SeitenStress Definitions Mechanisms and EffectsDaisyNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Bio Ch. 11 Cell CommunicationDokument78 SeitenAP Bio Ch. 11 Cell CommunicationRavider JadejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.2 TheophyllineDokument3 Seiten3.2 TheophyllinesarahabdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- The BodyDokument4 SeitenThe BodySheila G. DolipasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transkrip StressDokument26 SeitenTranskrip StressPrasetyo Hendy KurniawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SnaDokument11 SeitenSnaFisiologiaUFCGNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effects of Stress On Short-Term and Long-Term MemoryDokument12 SeitenThe Effects of Stress On Short-Term and Long-Term MemoryCarmen MihalachiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rapid Interpretation of EcgsDokument41 SeitenRapid Interpretation of EcgsAdela abboudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of Drugs On The Frogs HeartDokument16 SeitenEffects of Drugs On The Frogs HeartGreetingwedausezzt50% (2)
- Theories and Concepts of Aging: Reynaldo S. Alipio, RN, MD, Mha, ManDokument82 SeitenTheories and Concepts of Aging: Reynaldo S. Alipio, RN, MD, Mha, ManTuTitNoch keine Bewertungen