Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
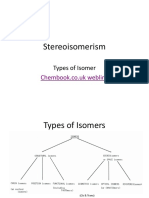
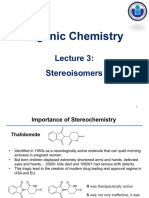
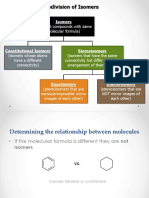
Importance of Stereochemistry
Hochgeladen von
Siddarth PalletiOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Importance of Stereochemistry
Hochgeladen von
Siddarth PalletiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1
Importance of stereochemistry
Enantiomers have identical chemical and physical properties
Differ - rotating polarised light
R
R
Me
Me2N
....... ..- interaction with other chiral molecules
Important in biology...
enzyme
only one enantiomer matches
chiral enzyme
Ph O
O
Et
darvon
Darvon is a
painkiller.
Its enantiomer is an
anticough agent.
Polarised light
Ordinary light has EM radiation oscillating in all possible planes (3 shown)
Polarised light is in a single plane
ordinary light
polarised light
Chiral
H NH2
CO2H
measure rotation
derive []D = +14
H2N H
CO2H
measure rotation
derive []D = -14
compounds rotate
polarised
light
.
A pair of enantiomers rotate
the plane of polarised light by
equal amounts in opposite
directions
.
A 1:1 mixture of enantiomers
does not rotate light and is
called a racemate
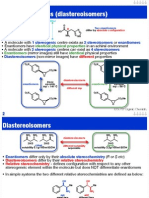
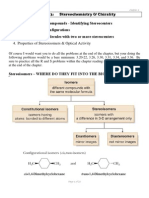
Diastereoisomers I
Cyclic compounds can exist as diastereoisomers
Diastereoisomers differ by the spatial orientation of atoms
Can have very different physical properties
Do NOT have to be chiral (if they have a plane of symmetry)
OH
OH
diastereoisomers
identical
identical
OH
OH
molecule has a
plane of symmetry
OH
Diastereoisomers II
O2N
O2N
CO2Me
CO2Me
O
enantiomers
trans
epoxide
mp = 141C
O2N
diastereoisomers
cis
epoxide
mp = 98C
enantiomers
O2N
CO2Me
O
CO2Me
O
2 stereocentres can result in FOUR compounds (4 diastereoisomers)
No plane of symmetry chiral & 2 pairs of enantiomers (mirror images)
2 enantiomeric pairs - each enantiomer has identical physcial properties
But diastereoisomers have different physical properties
Enantiomers have same relative stereochemistry but different absolute
stereochemistry
Diastereoisomers III
OH
CHO
HO
OH OH
ribose
(2R,3R,4R)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxypentanal
OH
OH
CHO
HO
OH OH
(2R,3R,4R)-ribose
CHO
HO
OH OH
(2R,3R,4S)-arabinose
OH
HO
OH
OH OH
(2S,3S,4S)-ribose
HO
CHO
HO
OH OH
(2R,3S,4R)-xylose
OH
CHO
OH
OH OH
(2R,3S,4S)-lyxose
OH
CHO
OH OH
(2S,3S,4R)-arabinose
HO
CHO
HO
four
diastereomers
OH
CHO
OH OH
(2S,3R,4S)-xylose
HO
CHO
OH OH
(2S,3R,4R)-lyxose
and their 4
enantiomers
If a molecule has 3 stereocentres then it has potentially 8
stereoisomers (4 diastereoisomers & their enantiomers)
If a molecule has n stereocentres then potentially 2n stereoisomers
But if a molecule has a plane of symmetry it wil be less...
Meso compounds I
OH
HO2C
OH
HO2C
CO2H
OH
tartaric acid
OH
HO2C
CO2H
OH
OH
diastereoisomers
enantiomers
identical
OH
HO2C
CO2H
OH
CO2H
OH
HO2C
CO2H
OH
2 stereocentres so 4 stereoisomers?
There are 2 diastereoisomers - one has an enantiomer
...................................na......... - the other does NOT
Meso compounds II
Two compound on previous slide identical as rotation below shows...
OH
HO2C
CO2H
OH
OH
HO2C
CO2H
OH
HO2C
CO2H
HO
CO2H
OH
HO2C
OH
rotate around
central axis
OH
Even though compound has TWO stereocentres it
It is achiral because it has a plane of symmtery...
HO2C
OH
HO
CO2H
rotate LHS
HO
HO2C
OH
HO2C
CO2H
OH
is ACHIRAL
OH
CO2H
mirror
plane
Meso compounds - compounds containing stereocentres but are
still achiral
Meso compounds have a plane of symmetry with (R) configuration
on one side and (S) on the other
Resolution
O
H OH
HO2C
Ph
OMe
O
Ph
Ph
OMe
OMe
2 diastereoisomers
(hopefully
separable)
() or (R) / (S)
racemate
NaOH
H2O
NaOH
H2O
need enantiomerically pure
..compounds
OH
OH
If you can't synthesise it pure
..how do you purify enantiomers?
Separation of enantiomers is
pure (S)
pure (R)
..called resolution
Enantiomers physically the same - diastereoisomers are not!
React 2 chiral compounds to form diastereoisomers
Separate these (if possible)
Regenerate required compound
We
Chirality in nature I
Natural amino acids are enantiomerically pure
These are the building blocks of proteins and enzymes
HO2C
Me
NH2
alanine
HO2C
H
N
HO2C
NH2
phenylalanine
NH2
histidine
Why this enantiomer? Who knows...
But why just one enantiomer is more obvious...
Insulin is made of 2 peptide chains - 1x30 amino acids & 1x21 amino acids
Potentially 2.25 x 1015 diastereoisomers
A relatively small protein is ribonuclease at 124 amino acids or
Potentially 2.13 x 1037 diastereoisomers
10
Chirality in nature II
O
NH2
N
HO
HO O HO O HO O
O
O
HO
O
HO
OH
adenosine triphosphate ATP
NH
N
N
HO
thymine derivative of
deoxyribonucleic acid
(DNA)
HO
O
NH
N
NH2
HO
OH
guanine derivative of
ribonucleic acid (RNA)
Nucleosides are enantiomerically pure
These are the basis of all life via DNA and / or RNA
Also ATP which is the main sourse of energy in our cells
O
H
(R)-carvone
spearmint
(R)-2-methyl-5-(prop-1-en-2yl)cyclohex-2-enone
H
(S)-carvone
caraway
(S)-2-methyl-5-(prop-1-en-2yl)cyclohex-2-enone
H
(S)-limonene
lemons
(S)-1-methyl-4-(prop-1en-2-yl)cyclohex-1-ene
H
(R)-limonene
oranges
(R)-1-methyl-4-(prop-1en-2-yl)cyclohex-1-ene
Enantiomers are identical except their interaction with polarised light and other
chiral molecules (like our bodies)
This can have trivial effects...like smell / taste
11
Chirality in nature III
O
H H H
N
S
HO
O
N
O
penicillin skeleton
N
O
CO2H
N
N
NH
AZT
azidothymidine
N
H
(R)-thalidomide
OMe
dextromethorphan
Drugs frequently need to be optically pure
(R)-Thalidomide is a sedative - (S) isomer cause birth defects
Dextromethorphan is a cough suppresant
Levomethorphan (its enantiomer) is a narcotic
Top two drugs were Lipitor and Zucor and are single enantiomers
They generated $14 billion in 2002
Single enantiomer drugs worth $159 billion in 2002
Big buisiness!
12
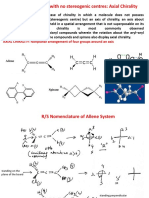
Other forms of chirality
axial
chirality
PPh2
Ph2P
PPh2
Ph2P
full rotation
impossible
(S)-BINAP
(R)-BINAP
2-(diphenylphosphino)-1-((R)-22-(diphenylphosphino)-1-((S)-2(diphenylphosphino)naphthalen-1(diphenylphosphino)naphthalen-1yl)naphthalene
yl)naphthalene
mirror
plane
planar
chirality
NH2
(Rp)-4amino[2.2]paracyclophane
H2N
mirror
plane
(Sp)-4amino[2.2]paracyclophane
It is not necessary for a compound to have a tetrahedral
stereocentre to be a chiral compound!!
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionVon EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- StereoisomerismDokument32 SeitenStereoisomerismbruno de jesus fontesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dia Stereo IsomerDokument13 SeitenDia Stereo IsomerKhairunnisa FadhilahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of Biological Macromolecules: ChiralityDokument27 SeitenStructure of Biological Macromolecules: ChiralityArshaan ShaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 21 Ochem IsomDokument69 SeitenChapter 21 Ochem IsombobNoch keine Bewertungen
- CYI101 Common CHEMISTRY (Organic) : 21 December 2020/sec G & HDokument30 SeitenCYI101 Common CHEMISTRY (Organic) : 21 December 2020/sec G & HdhdfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chirality: DiastereomersDokument6 SeitenChirality: DiastereomersfritzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture11 PDFDokument12 SeitenLecture11 PDFprema koliNoch keine Bewertungen
- IntroductionDokument29 SeitenIntroductionczharee ann cacNoch keine Bewertungen
- lct8 PDFDokument14 Seitenlct8 PDFSeanMarxAdanzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- S.SEETARAM SWAMY, M.Pharm.,: Asst. Professor, Dept. of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Chilkur Balaji College of PharmacyDokument46 SeitenS.SEETARAM SWAMY, M.Pharm.,: Asst. Professor, Dept. of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Chilkur Balaji College of PharmacyAli Akbar JamshaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MonosaccharidesDokument29 SeitenMonosaccharides21-56762Noch keine Bewertungen
- 13 ChiralityDokument33 Seiten13 ChiralityKazel Lyca SarmientoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 StereoisomersimDokument65 Seiten4 StereoisomersimRayonesh RayanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- S.SEETARAM SWAMY, M.Pharm.,: Asst. Professor, Dept. of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Chilkur Balaji College of PharmacyDokument46 SeitenS.SEETARAM SWAMY, M.Pharm.,: Asst. Professor, Dept. of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Chilkur Balaji College of PharmacyAVVARI AMMUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical IsomerismDokument70 SeitenOptical IsomerismJ.XNoch keine Bewertungen
- 163 StereochemisteyDokument37 Seiten163 StereochemisteyJelica ŠutovićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coordination Chemistry II: Isomers and Coordination GeometriesDokument25 SeitenCoordination Chemistry II: Isomers and Coordination GeometriesAb IrizarryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stereochemistry: Prof. Dr. Harno Dwi PranowoDokument45 SeitenStereochemistry: Prof. Dr. Harno Dwi Pranowoyosita ruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stereochemistry & Chiral MoleculesDokument76 SeitenStereochemistry & Chiral MoleculesDr. Tara WorkmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Chirality and Handedness of MoleculesDokument70 SeitenChapter 6 Chirality and Handedness of MoleculesCameron TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chm102a Oc-L4-SdDokument42 SeitenChm102a Oc-L4-SdDanish VasdevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry: StereoisomersDokument34 SeitenOrganic Chemistry: StereoisomersPhú BìnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sujitlal Bhakta: Ph. D. ChemistryDokument137 SeitenSujitlal Bhakta: Ph. D. ChemistryMuskan Sachdeva 0047Noch keine Bewertungen
- MCAT Organic Summary SheetDokument6 SeitenMCAT Organic Summary SheetSpencer Thomas100% (2)
- 13.4 Optical IsomerismDokument31 Seiten13.4 Optical Isomerismlianchen251110Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1Dokument38 SeitenTopic 1KAI YANG LIMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stereo IsomerismDokument23 SeitenStereo Isomerismcassie010890Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument43 SeitenChapter 3George KingNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM 210 Chapter 5 Wrap-UpDokument27 SeitenCHEM 210 Chapter 5 Wrap-UpTuan NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter4 Amino AcidDokument25 SeitenChapter4 Amino Acidkidpu100% (2)
- Stereochemistry Arrangement of Atoms in SpaceDokument59 SeitenStereochemistry Arrangement of Atoms in SpaceNAGARAJUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Warm Up (5/21) : Name The Common Prefixes Starting With MethDokument24 SeitenWarm Up (5/21) : Name The Common Prefixes Starting With MethVaughn MyersNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHM 102 (Stereochemistry)Dokument15 SeitenCHM 102 (Stereochemistry)christdan75Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 IsomerismDokument65 SeitenLesson 1 Isomerismtiahayes2801Noch keine Bewertungen
- Organic - Class 7Dokument27 SeitenOrganic - Class 7Sajan Singh LUCKYNoch keine Bewertungen
- StereochemistryDokument199 SeitenStereochemistryPolash MiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-4 StereochemistryDokument54 SeitenChapter-4 StereochemistrytuanijoshuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asymmetric SynthesisDokument55 SeitenAsymmetric Synthesisevsgoud_goud0% (1)
- Cip RulesDokument13 SeitenCip Rules김철수Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 07 StereochemistryDokument52 SeitenTopic 07 StereochemistryJhunessa Mae JalagatNoch keine Bewertungen
- C341 S2010 CH3 ChiralitystudentDokument21 SeitenC341 S2010 CH3 ChiralitystudentAlbert CorderoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stereoisomerism: AH Chemistry Unit 3 (C)Dokument38 SeitenStereoisomerism: AH Chemistry Unit 3 (C)Gramoz CubreliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stereochem 2011-PharmDokument78 SeitenStereochem 2011-PharmRecter Rien BasinganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6.2 StereochemistryDokument57 SeitenChapter 6.2 StereochemistryNa Ru ToNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stereochemistry 21medDokument70 SeitenStereochemistry 21med蔡秉宏Noch keine Bewertungen
- Isomer in Organic ChemistryDokument111 SeitenIsomer in Organic ChemistryyenquynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stereochemistry: Md. Mahbubol Alam Lecturer, Department of Pharmacy, Bangladesh UniversityDokument45 SeitenStereochemistry: Md. Mahbubol Alam Lecturer, Department of Pharmacy, Bangladesh Universityjustin rodrigoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Optical Isomers 1Dokument42 Seiten2 Optical Isomers 1aya almouselliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nomenclature of Optical IsomersDokument4 SeitenNomenclature of Optical Isomersparmarkeval1610Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pelatihan Olimpiade Kimia: Guru Dan Pelajar Jenjang SMADokument30 SeitenPelatihan Olimpiade Kimia: Guru Dan Pelajar Jenjang SMAWahyu AdjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Short ChemistryDokument121 SeitenShort ChemistryNAVEEN KUMAR SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Nomenclature CML-101Dokument86 SeitenChapter 1 Nomenclature CML-101rashmimeena19832005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry 1 Rekaps: R C O NH R NHDokument13 SeitenOrganic Chemistry 1 Rekaps: R C O NH R NHHi1234_0999Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3 UV IR NMR CD IssariyaDokument57 Seiten3 UV IR NMR CD IssariyaSonaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCAT Prep Organic Equation SheetDokument6 SeitenMCAT Prep Organic Equation SheetChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stereokimia 5Dokument48 SeitenStereokimia 5Nurmaruliha RaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- StereochemistryDokument22 SeitenStereochemistryVenkataramana KondepaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specific Catabolic PathwaysDokument28 SeitenSpecific Catabolic PathwaysSiddarth PalletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument27 SeitenChapter 3Siddarth PalletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medicinal Chemistry (Basic Principles) : 24 November 2010 Andrej Boháč, Milan RemkoDokument49 SeitenMedicinal Chemistry (Basic Principles) : 24 November 2010 Andrej Boháč, Milan RemkoSiddarth PalletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phytochemical Screening and Anti-Emetic Activity of LeonotisDokument4 SeitenPhytochemical Screening and Anti-Emetic Activity of LeonotisSiddarth PalletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S1319610313000744 MainDokument10 Seiten1 s2.0 S1319610313000744 MainSiddarth PalletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NMR-2-chem Shift and CouplingDokument68 SeitenNMR-2-chem Shift and CouplingSiddarth PalletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NMR-1-theory and InstrDokument38 SeitenNMR-1-theory and InstrSiddarth PalletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selective Synthesis, Structural Studies and Antitumor Evaluation of Some Novel Unsymmetrical 1-Hetaryl-4 - (2-Chloroquinolin-3-Yl) AzinesDokument8 SeitenSelective Synthesis, Structural Studies and Antitumor Evaluation of Some Novel Unsymmetrical 1-Hetaryl-4 - (2-Chloroquinolin-3-Yl) AzinesSiddarth PalletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stereoselective and Stereospefic ReactionDokument34 SeitenStereoselective and Stereospefic ReactionSiddarth PalletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Mumbai 400 076, E-Mail: Irishi@iitb - Ac.inDokument16 SeitenDepartment of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Mumbai 400 076, E-Mail: Irishi@iitb - Ac.inSiddarth PalletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extraction of Active Principles From Natural SourcesDokument9 SeitenExtraction of Active Principles From Natural SourcesSiddarth PalletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Y SahithiDokument13 SeitenY SahithiSiddarth PalletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NMR-1-theory and InstrDokument38 SeitenNMR-1-theory and InstrSiddarth PalletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- IR Before ApplicationsDokument64 SeitenIR Before ApplicationsSiddarth PalletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 19.) 12.) 2019 Alkaloids and Glyc KeyDokument4 Seiten19.) 12.) 2019 Alkaloids and Glyc KeySiddarth Palleti100% (2)
- Unit 3 Pharmacognosy PDFDokument37 SeitenUnit 3 Pharmacognosy PDFSiddarth PalletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Pharmacognosy PDFDokument6 SeitenUnit 2 Pharmacognosy PDFSiddarth PalletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polar Protic Vs Polar Aprotic Vs Nonpolar: About Solvents in Organic ChemistryDokument11 SeitenPolar Protic Vs Polar Aprotic Vs Nonpolar: About Solvents in Organic ChemistrySiddarth PalletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- P. Siddartha Kumar: Professional ExperienceDokument6 SeitenP. Siddartha Kumar: Professional ExperienceSiddarth PalletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of Analgesic Activity of Methanolic Extract of Trapa Natans L.var. Bispinosa Roxb. RootsDokument4 SeitenEvaluation of Analgesic Activity of Methanolic Extract of Trapa Natans L.var. Bispinosa Roxb. RootsSiddarth PalletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spring 2013 Lecture 24-25 PDFDokument17 SeitenSpring 2013 Lecture 24-25 PDFSiddarth PalletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Swisstargetprediction: Target Common Name Uniprot Id Chembl Id Target Class Probability Known Actives (3D/2D)Dokument5 SeitenSwisstargetprediction: Target Common Name Uniprot Id Chembl Id Target Class Probability Known Actives (3D/2D)Siddarth PalletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerobic Respiration: The Krebs Cycle: Glycolysis Pyruvate Acetyl CoaDokument3 SeitenAerobic Respiration: The Krebs Cycle: Glycolysis Pyruvate Acetyl CoaSiddarth PalletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report Emulsion PolymerizationDokument7 SeitenLab Report Emulsion PolymerizationNUR AMNI QHAIRUNNAJWA BINTI ARIFFIN STUDENTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supplier+Quality+Manual+V+01 - ChemicalDokument62 SeitenSupplier+Quality+Manual+V+01 - ChemicalTrinhTruongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Farmcares: Organic Pesticide IndustriesDokument12 SeitenFarmcares: Organic Pesticide IndustriesHrìthìk HàrryNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRJ ManuscriptDokument11 SeitenPRJ ManuscriptGebi TukuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weld Metal Selector GuideDokument28 SeitenWeld Metal Selector GuideBassam AbdelazeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quartz Glued 2Dokument5 SeitenQuartz Glued 2jNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength and of Pond Ash ConcreteDokument29 SeitenStrength and of Pond Ash ConcreteNaveed BNoch keine Bewertungen
- API 510 Petrosync Course PDFDokument301 SeitenAPI 510 Petrosync Course PDFAkramKassis100% (1)
- Bacterial Reverse Mutation TestDokument12 SeitenBacterial Reverse Mutation TestOtilia TeixeiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moles and Empirical FormulaDokument11 SeitenMoles and Empirical FormulaZenoxu 7zNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jason Urethane Power Transmission Belts PDFDokument13 SeitenJason Urethane Power Transmission Belts PDFKeviin CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- On The Applicability of Flory-Huggins Theory To Ternary Starch-Water-Solute SystemsDokument10 SeitenOn The Applicability of Flory-Huggins Theory To Ternary Starch-Water-Solute SystemsjuarsrdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Category 2-Bonus PacketDokument9 SeitenCategory 2-Bonus Packetapi-312542882Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Turbine Report RotorDokument10 SeitenGas Turbine Report RotorThanapaet RittirutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specific Heat and Temperature of A Hot BodyDokument5 SeitenSpecific Heat and Temperature of A Hot BodyAna Marie Besa Battung-ZalunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating InstructionsDokument17 SeitenOperating Instructionsmasinac01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analisis Sensori Produk Stik Sukun (Artocarpus Altilis) Dengan Perlakuan Pendahuluan Blanching Dan Perendaman Dalam Larutan Kalsium KloridaDokument6 SeitenAnalisis Sensori Produk Stik Sukun (Artocarpus Altilis) Dengan Perlakuan Pendahuluan Blanching Dan Perendaman Dalam Larutan Kalsium KloridaTommy ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genuine Viton Sheeting Material Data SheetDokument2 SeitenGenuine Viton Sheeting Material Data Sheetnicares718Noch keine Bewertungen
- Montreal ProtocolDokument17 SeitenMontreal ProtocolJan Aldrin AfosNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAFTAR OBAT-WPS OfficeDokument5 SeitenDAFTAR OBAT-WPS OfficeTony RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biodegradation of Sewage Wastewater Using Autochthonous BacteriaDokument9 SeitenBiodegradation of Sewage Wastewater Using Autochthonous BacteriaJonatan Moises Polo SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OIS-91 Basic H S TrainingDokument33 SeitenOIS-91 Basic H S TrainingTej PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- DS 099 Rev01 Zinc Anode 304 MZDokument2 SeitenDS 099 Rev01 Zinc Anode 304 MZvkvc soodNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2017 Sec 3 Science NT 18sDokument552 Seiten2017 Sec 3 Science NT 18sprolearn.bishanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Development of Micro-Channel Using PDMS For Biomedical ApplicationsDokument6 SeitenDesign and Development of Micro-Channel Using PDMS For Biomedical ApplicationsgpaivNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of Innovative Pharmaceutical ResearchDokument9 SeitenInternational Journal of Innovative Pharmaceutical Researchعبدالعزيز بدرNoch keine Bewertungen
- FERT18Dokument253 SeitenFERT18Margarit AnamaryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 6Dokument17 SeitenWorksheet 6Sumair Khan MasoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotor General Characteristics: Flowmeter 4.2. Rototron RRIDokument2 SeitenRotor General Characteristics: Flowmeter 4.2. Rototron RRIAvneet MaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook Sewage HandlingDokument147 SeitenHandbook Sewage HandlingMannar MannanNoch keine Bewertungen