Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
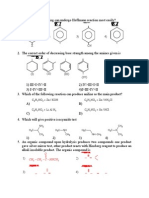
Chap 01
Hochgeladen von
Prasad YarraOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
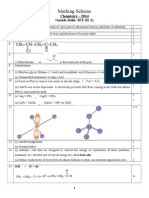
Chap 01
Hochgeladen von
Prasad YarraCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1
Unit2Statesofmatter
Matter: It is something that occupies space possessing certain mass. Hence all the Substances
presentinthisuniversearematters.
Classificationofmatteronthebasisoftheirphysicalstate:
Onthebasisofphysicalstate,mattercanbeclassifiedassolid,liquid,gasandplasma.
Solid: Matter which possesses definite mass , volume and shape are called solids.In this state
particlesareheldveryclosetoeachother.Theseparticleshavenofreedomofmovement.
Ex:Wood,stone,copperetc.
Liquid:Matterwhichpossessesdefinitemassandvolumebutindefiniteshapearecalledliquid.
Inthisstateparticlesareclosetoeachotherandtheycanmovewithintheirvolume.
Ex:water,Benzene,carbontetrachloride,kerosene.
Gas: Matterwhichpossessdefinitemassbutindefinitevolumeandshapearecalledgases.In
gasesparticlesarefarapartascomparedtosolidandliquid.Theparticlescanmovefreelyfrom
onepointtoanother.Ex:Nitrogen,Oxygen,Carbondioxideetc.
Plasma:Itisahighlyionizedgas,madeupofalmostequalnumberofpositiveionsandnegative
electrons. It is formed only at a extremely high temperature of the order of 50000C. It is
describedasthefourthstateofamatter.Plasmaisbelievedtobethemainconstituentofstars
includingsun.
Note:ThefifthstateofmatteriscalledBoseEinsteincondensate(BEC).Thisstateoccuratthe
endofthetemperaturescaleatastepaboveabsolutezeroKelvin.
Classificationofmatteronthebasisofcomposition:
Onthebasisofthechemicalcompositionmattercanbeclassifiedasfallows.
1. Heterogeneousmatter
2. Homogeneousmatter
1)Heterogeneousmatter:Asubstanceisheterogeneousifitexhibitsdifferentpropertiesatits
differentposition.Differenttypesofheterogeneousmatterare
a)suspension b)colloid
c)heteromixture
Matter
Heterogeneousmatter
______________________
Homogeneousmatter
____________________
Suspension colloidHetero.mixture
HomogeneousmixturePuresubstance
Element
______________________
MetalNonmetalmetalloid
_________________
Compound
a)Suspension:Itisaheterogeneousmixtureinwhichthesoluteparticlesdonotdissolvebut
remain suspended throughout the bulk of the medium.These particles can be seen by the
nakedeye.Thesoluteparticlessettledownwhenthesuspensionisleftundisturbed.Thesecan
beseparatedfromthemixturebytheprocessoffiltration.
Ex:dirtparticlesinwater,soarmilk.
b)Colloid:Colloidsaretheheterogeneousmixtureoftwocomponentswiththesizeofthe
particleis1nmto100nm(or10A0to1000A0).Theseparticlesofcolloidareuniformlyspread
throughoutthesolution.Duetorelativelysmallersizeoftheparticlesascomparedtothe
mixtures,Itappearstobehomogeneous,butactuallycolloidsareheterogeneous.Theseare
possessingtwophases.(Dispersedphaseanddispersionmedium)
c)Heteromixture:Itisobtainedbymixingtwoormoresubstanceinanyratio.Theseare
possessing the mixed properties of the combined substance.These can be separated by
physicalmethod.
Ex:Amixtureofsandandcommonsalt.
2)Homogeneousmatter:A substance is a homogeneous matter if the smallest part of it
exhibitsthesamechemicalandphysicalproperties.Ex:Air,Solutionofsugarwithwater,
anintimatemixtureoftwoormorethantwometals(alloys).
Homogeneousmattercanbeclassifiedintotwotypes.
a)Homogeneousmixtures
b)Puresubstances
a)Homogeneousmixture:Amixtureoftwocomponentsthatappearsinasinglephaseis
calledhomogeneousmixtures.Thesearecalledassolutions.
Ahomogeneousmixtureofsoluteandsolventarecalledsolutions.Thesesolutionsare
alsocalledastruesolutionsorcrystalloids
Ex:Ahomogeneousmixtureofsugarandwatergivestruesolutions.
b) Pure substance: These are made of only one type of particles such as atoms or
molecules.Furthertheseareclassifiedaselementsandcompounds.
Element: Simple forms of matter which cannot be decomposed into further simple
substancesarecalledelements.118elementsarediscoveredtilltoday,outofwhich92are
naturallyoccurringelementsandremainingareartificiallypreparedelements.
Ex:Hydrogen,mercury,gold,ironetc.
Elementsarefurtherclassifiedasmetals,nonmetalsandmetalloids
Metal:Theelementswiththeelectropositivenatureoflosingoneormoreelectronsreadily
togivepositivelychargedcationsarecalledmetals.
M M++e
Ex:Copper,Zinc,Iron
Nonmetal: The electronegative elements which have a tendency to gain one or more
electronsarecallednonmetals.Aftergettingtheelectronsnegativeionsformedarecalled
anions.AisanonmetalandAisanion.
A+e A
Ex:Chlorine,Bromine,sulphuretc
.
Figure1Magnesiummetal
Figure2Sodiummetal
Metalloids:Elementspossessingpropertiesofbothmetalsandnonmetalsarecalled
metalloids.
Ex:Antimony,arsenic,Germiniumetc.
Compounds:Thesubstancesmadeoftwoormorethantwoelementscombinedwitheach
otherinadefiniteratiobymassarecalledcompounds.Thesecanbedecomposedintoits
elementsbychemicalorelectrochemicalreactions.
Ex:1.Inwater(H2O)numberofhydrogenandoxygenatomsareintheratio2:1orit
containshydrogenandoxygencombinedwitheachotherintheratioof1:8bytheirmass.
i.e.2gofhydrogencombineswith16gofoxygen.
2.Sulphuricacid(H2SO4):InthiscompoundtheratioofnumberofatomsofH:S:Ocombinedis
2:1:4.TheratiobymassofH:S:Ois1:16:32.Inthiscompound2gofhydrogen32gofsulpher64
gramsofoxygencombinewitheachothertoform98gofH2SO4.
Solution:Ahomogeneousmixturesofsoluteandsolventarecalledsolutions.Inasolution,
asubstancewhichisinalessquantityissoluteandotherwhichisinmorequantityis
solvent.Inaqueoussolutionofsugar,waterissolventandsugarissolute.
Concentrationofsolution.Theamountofasolutepresentinaunitvolumeofthesolution
iscalledconcentrationofthesolution.
Concentrationofthesolutioncanbeexpressedintermssuchaspercentagebymassor
byvolume,molarity,molality,normality,molefraction,ppm.Outofthesetermsthemost
familiartermstoexpresstheconcentrationofthesolutionarepercentagebymassor
volume,molarityandnormality.
Percentagebymass:Itisthemassofthesolutepresentin100gofthesolution.
Percentagebymass=
Percentagebyvolume:Itisthemassofthesolutepresentin100cm3ofthesolution.
Percentagebyvolume=
Problem:50gofglucoseisdissolvedin400gofwater,thencalculate%bymassofthe
solute.
Ans:Totalmassofthesolution=massofglucose+massofwater
=50+400=450g
Percentagebymass=
=
=11.11
Hence%bymassofglucoseinthesolutionis11.11
Problem:300cm3ofsolutioncontains20gofNaCldissolvedwithwater,thencalculate%
byvolumeofthesolution.
Ans:
Percentagebyvolume=
=
=6.67
Hence%byvolumeofNaClinthesolutionis6.67
Molarity:Molaritycanbedefinedasthenumberofgrammolecularmassofsolutedissolvedin
onedm3ofthesolution.ItisdenotedbyM
Molarity=
Molarity=
or
Wherem=massofthesolute
M=Molecularmassofthesolute
V=volumeofthesolution
MolarityofNaOHsolutionis0.5Mmeans0.5mole(or0.5grammolecularmass)ofNaOH
isdissolvedinonedm3ofthesolution.
Problem.:Calculatethemolarityofthesolutionobtainedbydissolving6gofoxalicacidin
200cm3ofsolution.Mol.massofoxalicacidis126.
Solution.Giventhingsm=6gM=126V=200cm3
Molarity=
=0.238M
Normality:Normalitycanbedefinedasthenumberofgramequivalentmassofsolute
dissolvedinonedm3ofthesolution.ItisrepresentedbyN
Normality=
ORNormality=
Wherem=massofthesolute
E=Equivalentmassofthesolute
V=volumeofthesolution
NormalityofH2SO4solutionis0.5N,Itmeansthat0.5gramequivalentmassofH2SO4is
dissolvedinonedm3ofthesolution
Problem:Calculatethenormalityofthesolutioncontaining4gofsodiumhydroxidein500
cm3ofthesolution.(Equ.massofNaOHis40)
Normality=
=0.2N
HencethenormalityofNaOHsolutionis0.2N
Questions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
Definematter
Mentionthedifferenttypesofmatteronthebasisoftheirphysicalstate.
Whatisasolid?Giveanexample.
Whatisaliquid?Giveanexample
Whatisagas?Giveanexample
Writetheclassificationofmatteronthebasisoftheirchemicalcomposition.
Whatisaheterogeneousmatter?
Whatisahomogeneousmatter?
Mentionthedifferenttypesofheterogeneousmatter.
Whatisasuspension?Giveanexample.
Whatisacolloid?Giveanexample.
Mentionthedifferenttypesofhomogeneousmatter.
Definesolution.
Giveanexampleforsolution.Mentionthesoluteandsolventpresentinit.
Whatisanelement?Giveexample.
Whataremetals?Giveanexample.
Whatarenonmetals?Giveanexample.
Whataremetalloids?Giveanexample.
Whatarecompounds?Giveanexample.
MentiontheratiobymassofhydrogenandchlorinepresentinHCl.
Definetheconcentrationofasolution.Mentionthedifferenttermsusedtoexpressthe
concentrationofthesolution.
22 Whatis%bymassofthesoluteinsolution?Expressitintheformofequation.
23 Whatispercentagebyvolumeofthesolution?Expressitintheformofequation.
24 Definemolarityofasolution.Expressitintheformofequation.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Per I CyclicDokument44 SeitenPer I CyclicPrasad YarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surface Chemistry Easy NotesDokument11 SeitenSurface Chemistry Easy NotesPrasad YarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids BasesDokument34 SeitenAcids BasesPrasad YarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Required Viteee NotesDokument9 SeitenRequired Viteee NotesPrasad YarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkene and Alkyne - by Resonance PDFDokument45 SeitenAlkene and Alkyne - by Resonance PDFPrasad Yarra100% (1)
- Exercise - 5: Passage: I Passage: II Passage: III Passage: IV Passage: V Passage: VIDokument1 SeiteExercise - 5: Passage: I Passage: II Passage: III Passage: IV Passage: V Passage: VIPrasad YarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Goc 060412Dokument5 Seiten1 Goc 060412Prasad YarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkyl and Aryl HalidesDokument1 SeiteAlkyl and Aryl HalidesPrasad YarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio MoleculesDokument8 SeitenBio MoleculesPrasad YarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics: Class Puc 2 YrDokument4 SeitenPhysics: Class Puc 2 YrPrasad YarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument2 SeitenChapter 3Prasad YarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 PolymersDokument25 Seiten7 PolymersPrasad YarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry XII 2011 12Dokument167 SeitenChemistry XII 2011 12Prasad YarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Properties of CompoundsDokument15 SeitenProperties of CompoundsPrasad YarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- AminesDokument3 SeitenAminesPrasad YarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 09 Organic ChemistryDokument13 SeitenUnit 09 Organic ChemistryPrasad YarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem PaperDokument4 SeitenChem PaperPrasad YarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outside Delhi - Set 2-15-03-14Dokument8 SeitenOutside Delhi - Set 2-15-03-14Prasad YarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- ParabolaDokument10 SeitenParabolaPrasad YarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Catalysis by Doped OxidesDokument37 SeitenCatalysis by Doped OxidesDr-Bhairi LakshminarayanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Us03cicv21 Unit3Dokument28 SeitenUs03cicv21 Unit3ashokNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEDokument22 SeitenCHEshajib_sust0% (1)
- Chemicals Zetag DATA Powder Zetag 8180 - 0410Dokument2 SeitenChemicals Zetag DATA Powder Zetag 8180 - 0410PromagEnviro.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 - What Is The S3 ScannerDokument4 Seiten01 - What Is The S3 ScannerViet PhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ishihara2019 MPCDokument11 SeitenIshihara2019 MPCKrisna MertaNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper With Solution 08 Jan 2020 Shift 1 Memory BasedDokument34 SeitenJEE Main 2020 Question Paper With Solution 08 Jan 2020 Shift 1 Memory BasedmisostudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Physics IB Physics: Topic 3 & Option CDokument55 SeitenThermal Physics IB Physics: Topic 3 & Option CMoiz Dhanerawala100% (1)
- Worksheet Elements Compounds Mixtures ks3Dokument4 SeitenWorksheet Elements Compounds Mixtures ks3eric sivanesh0% (1)
- Cooling Load Calculation: (Aircon Lab)Dokument24 SeitenCooling Load Calculation: (Aircon Lab)matthew ocampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cyanate Ester Resin5Dokument26 SeitenCyanate Ester Resin5rkkumarcpriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics 2Dokument8 SeitenThermodynamics 2BINITHA MPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1 IMFADokument10 SeitenExperiment 1 IMFALuis BergonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leak QuestionsDokument47 SeitenLeak Questions9672114Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stripping VoltammetryDokument12 SeitenStripping Voltammetry20tamilselvi-ugche100% (1)
- Welding and Welding Technology by Richard L. LittleDokument444 SeitenWelding and Welding Technology by Richard L. LittleSamiksha UrsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combustion of AlkanesDokument12 SeitenCombustion of Alkaneszara_1692Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrolysis-Condensation Processes of The Tetra-Alkoxysilanes TPOS, TEOS and TMOS in Some Alcoholic SolventsDokument13 SeitenHydrolysis-Condensation Processes of The Tetra-Alkoxysilanes TPOS, TEOS and TMOS in Some Alcoholic SolventssorescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual For Financial Statement Analysis 11th Edition by Subramanyam PDFDokument61 SeitenSolution Manual For Financial Statement Analysis 11th Edition by Subramanyam PDFMNHS67% (3)
- Strategies To Design Modified Activated Carbon Fibers For The Decontamination of Water and AirDokument32 SeitenStrategies To Design Modified Activated Carbon Fibers For The Decontamination of Water and AirMadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXPERIMENT 2 Colloids and Their Properties - Odango - BSN1bDokument4 SeitenEXPERIMENT 2 Colloids and Their Properties - Odango - BSN1bclint xavier odangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bisacodyl Suppositories JPXVIIIDokument2 SeitenBisacodyl Suppositories JPXVIIITống Ái Linh NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSC - Basics PrincipleDokument2 SeitenDSC - Basics PrincipleSayantan ChakrabortyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Herrera Alisson Deber3 EjerciciosBraytonEESDokument11 SeitenHerrera Alisson Deber3 EjerciciosBraytonEESAly HerreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absorption ChillersDokument8 SeitenAbsorption ChillerssanastasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 - Heat and TemperatureDokument18 SeitenLesson 1 - Heat and TemperatureElijah AlcorezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summative Test Science 9Dokument2 SeitenSummative Test Science 9jennifer lacambra75% (4)
- Chemsheets GCSE 1069 Allotropes of CarbonDokument1 SeiteChemsheets GCSE 1069 Allotropes of CarbonNoah KellerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construccion de Turbo ExpanderDokument175 SeitenConstruccion de Turbo ExpanderJonatan MamaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of Peracetic Acid by Potentiometric Titration: Sample Preparation and ProceduresDokument6 SeitenDetermination of Peracetic Acid by Potentiometric Titration: Sample Preparation and ProceduresHasan Zeki BayrakNoch keine Bewertungen