Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Design of Steel Structures
Hochgeladen von
prkshdvOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Design of Steel Structures
Hochgeladen von
prkshdvCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
DESIGHN OF STEEL STRUCTURES
UNIT -1
1. What are the factors that willgovern the structural design?
? It should have adequate strength
? It should have adequate stability and rigidity
? It should be durable
? It should not interfere with the functional requirement
? It should be economical
2. what are the structural element of a building?
? Flexural members: beams or girders
? Tension members :ties
? Compression members : column ,stanchions ,struts
? Torsional members
3. What is meant by spandrel beam?
Beam around the outsideperimeter of a floor that support the exterior wallsand o
utside edge of the floor
4. What are the steps involved in structural design?
? Selection of the structure
? Layout of the structure
? Determination of force on the structure in the elements of the structure
? Checking the performance of the structure underservice condition
5. Which type of steel is generally used in construction?
? Mild steel
? Medium carbon steel
? High carbon steel
This three types of steel are known as structural steel
6. What are the various types of structural steel section?
? Rolled steel beam section
? Rolled steel angle section
? Rolled steel bars
? Rolled steel sheets or strip
? Rolled steel channel section
? Rolled steel tee section
? Rolled steel plates
? Mild steel
7. What are the types of connections used for connecting structural members? www
.Rejinpaul.com
? Riveted connections
? Bolded connections
? Pinned connections
? Welded connections
8. What is rivet and riveting? Rivet:
A piece of round steel forged in place to connect two steel members together is
known as a rivet. The body of is termed as shank
Riveting:
Riveting is a method of joining together , structural steel components by insert
ing ductile metal pins called rivets into holes of the components to be connecte
d
9. What are hot driven and cold driven? Hot driven:
If the rivets used in structural steel work are steel work are heated and driven
, these rivets are known as hot driven rivets
Cold driven:
If the rivets are driven at atmospheric temperature , they are known as cold riv
ets
10. What are the types of rivets joints?
When one member is placed above the other and the other two are connected by mea
ns of rivets , the joint is known as lap joints
11. Definerivet value?
Strength of rivet in shearing and bearing are calculated and the lesser value am
ong two is known as rivet value
12. What are the arrangements of rivets?
? Chain riveting
? Diamond riveting
13. What are eccentric riveted connection?
Whenthe centre of gravity of a group of rivets does not lie on the line of actio
n of the load, the connections are known as riveted connection
14. Define bolts?
A bolt is a metal pin with a head at one end and the shank threads at the other
in order
to receive anut
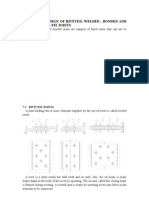
15. What are the types of welded joints?
? Butt weld www.Rejinpaul.com
? Fillet weld
? Slot weld and plug weld
? Spot weld
? Seam weld
? Pipe weld
16. Define butt weld?
Butt weld is also called as groove weld. The faces of two members are placed wit
h each other and connected by filletmetals. Butt weld is used to join structural
members carrying direct compression or tension.
17. Define fillet weld ?
A fillet weld is a weld of approximately triangular cross section joining two su
rface approximately at right angles to each other in lap joint.
18. Write down the equation for calculating the effective throat thickness of a
weld ? Effective throat thickness, t=0.7x size of weld.
19. Define factor of safety ?
It is defined as the factor by which the yield stress of the material is divided
to givethe stress in the material.
20. Write Unwin s formulav ? d=6.04
where,
t= thickness of plate in mm d= diameter of rivet in mm. www.Rejinpaul.com
UNIT-II
TENSION MEMBERS
1. Define tension members ?
Tension member is defined as a structural member subjected toa tensile force in
the direction parallel to its longitudinal axis. A tension member is also called
as tie member or simply a tie. The term tie ia commonly used for tension member
in the roof truss.
2. What are the types of tension members ?
? Wires and cables
? Rods and bars
? Single structural shapes and plates
? Built up members.
3. What is net selection area ?
The net selection area of a tension member is the gross sectional area of the me
mber, less the maximum deduction for holes.
4. Why lug angles are not very common ?
? They provide eccentric connections because of rivets placed along lug angles
? Stress distribution in the rivet of lug is not uniform
? Rivets on the lug angle are not as sufficient as other rivets.
5. What is lug angle ?
A lug angle is a short length of anangle section which is attached to the main t
ension member at the connecting end to provide extra gauge lines for accomodatin
g the recquired number of rivets.
6. Write notes on tension splices ?
When the recquired length of a tension member is less than the available length
or two lengths of tension member have different cross sectional area, tesion spl
ices are provided to join the two length of the member. Tension splices are the
cover plates used on both side of the butt jointed members.
7. Write notes on lug angles ?
When a tension member is connected to a gusset plate and its ends a large number
of rivets are required, especially when the tension member is large, necessitat
ing in the provision of a big size gusset plate. The size of the gusset plate ca
n be decreasd by the use of a lug angle. A lug angle is a short length of an
www.Rejinpaul.com
angle section which is attached to a main tension member at the connecting end t
o provide extra gauge lines for accommodating the recquired number of rivets.
8. How is the net sectional area calculeted in case of i) chain revetting ii)zig
zag rivetting ?
? Chain rivetting Anet =t(b-nd)
? Zig zag rivetting
Anet =t[(b-nd)+ms2/4g] Where,
t= thikness of plate d=diameter of the hole
n= no of rivets in the section considered m =no of zig zag or inclined lines.
9. What is net effictive area ?
The net cross sectional area on a section is reduced to account for this non-uni
form stress distribution resulting from eccentricity. The reduced net sectional
area of such a section is known as net effective area.
10. How is net effective area of a single angle used as tension member calculate
d ? In case of single angle connected through one leg the
Net sectional area =A1+A2k
Where,A1=effective cross sectional area of the connected leg A2=gross cross sect
ional area of the un connected leg K=3A1/(3A1+A2)
11. Write down the formula for permissible stress in axial tension ?
As per IS:800-1984:the permissible stress in axial tension ,
= 0.6
/
2
(Mpa)
2
Where, fy= minimum yield sterss in steel, N/mm
12. Write down thespecification for the design of lug angle ?
? Lug angle connected a channel shaped member shall, as far as possible, be disp
osed symmetrically with respect to the section.
? In no case shall fewer than two bolts or rivets be used for attaching the lug
angle tothe gusset or other supporting member.
13. How is net effective area of a double angle used as tension member calculate
d ?
In case of double angle connected through one leg,
Net sectional area =A1+A2k
Where,A1=effective cross sectional area of the connectedleg
A2=gross cross sectional area of the un connected leg
K=5A1/(5A1+A2) www.Rejinpaul.com
14. What are hangers ?
A tension member is the one which is intended to resist axial tension. Tension m
ember are also called ties or hangers.
15. What is the advantages of rods and bars ?
The major disadvantage of these section is the inadequate stiffness resulting in
noticeable sag under their own weight especially during erection.
16. Notes on single structural shapes and plates ?
The common single structural shapes are angle section, tee section, channel sect
ion. Angle sections are considered more rigid than ropes, rods, bars. So=ingle a
ngle are mainly used for bracing, for light truss tension member.
17. If Fe250 grade steel is used, calculated the alliwable stress in axial tensi
on as per IS=800 ? Allowable stress in axial tension= 0.6 fy
=0.6x250
=150 N/mm2.
18. Explain the member?
Tension member are also called as tie member. A tension member per tie member is
the one which is intended to resist axial tension.
19. Write notes on biult up section ?
When amember is required to take heavy tensile load, built up sections, consisti
ng of two or more plates or shors are used.Such a built up section is used to pr
ovide
? Greater area which cannot be provided by a single rolled shape,
? Greater rigidity by way of greater moment of inertia,
? Suitable dimension to proper connection.
20. What is bearing stress ?
When the load is exerted or transferredby the application of load through one su
rface for the other surface in contact to the sterss is known as bearing stress.
The bearing =stress/ is calculated on net projected area of contact. . www.Reji
npaul.com
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Design of Steel Structures 2marksDokument6 SeitenDesign of Steel Structures 2marksVijay RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.design of Steel StructuresDokument13 Seiten3.design of Steel Structuresarju21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Steel Structures Connections - Riveted, Welded & BoltedDokument23 SeitenDesign of Steel Structures Connections - Riveted, Welded & BoltedNi MeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE1354 - Design of Steel Structures Two Mark Questions AnswersDokument19 SeitenCE1354 - Design of Steel Structures Two Mark Questions AnswersFinney Wilson100% (1)
- UNIT - I - Connections - Riveted, Welded & Bolted: AdvantagesDokument24 SeitenUNIT - I - Connections - Riveted, Welded & Bolted: AdvantagesSuresh RajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Structure Design QuestionsDokument13 SeitenSteel Structure Design QuestionsRaguram pNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - I - Connections - Riveted, Welded & BoltedDokument23 SeitenUnit - I - Connections - Riveted, Welded & BoltedPraveenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Structure DesignDokument14 SeitenSteel Structure DesignNiraj ShindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fdocuments - Us Ce2352 Design of Steel STR Design of Steel Structures 1 Introduction DesignDokument31 SeitenFdocuments - Us Ce2352 Design of Steel STR Design of Steel Structures 1 Introduction DesignEpahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1Dokument30 SeitenUnit 1balachandran143Noch keine Bewertungen
- CE1354 - Design of Steel StructuresDokument17 SeitenCE1354 - Design of Steel Structuresஆனந்த் கிருஷ்ணன்Noch keine Bewertungen
- LESSON 8. Tension MemberDokument8 SeitenLESSON 8. Tension MemberAdarsh bhatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 PDFDokument30 SeitenUnit 1 PDFpankajNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT-III Design of Fasteners and Welded Joints: Session - 1Dokument18 SeitenUNIT-III Design of Fasteners and Welded Joints: Session - 1Narendra ChavdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Two, Tension Members PDFDokument10 SeitenChapter Two, Tension Members PDFZeleke TaimuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Srividya College of Engineering and Technology Question BankDokument7 SeitenSrividya College of Engineering and Technology Question Bankindira subramoniapillaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 3 L-1 Bolt DesignDokument34 SeitenChapter - 3 L-1 Bolt DesignBerihunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bolted and Welded ConnectionsDokument12 SeitenBolted and Welded ConnectionsTemesgenAbiy100% (2)
- Mahalakshmi: Engineering CollegeDokument30 SeitenMahalakshmi: Engineering CollegeSawan HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 4 Bolted JointsDokument25 SeitenChap 4 Bolted JointsMelese AschalewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1 Design of FastenersDokument15 SeitenTopic 1 Design of FastenersSimon DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design For Beams: Prepared By: Engr. Jo Ann C. CeledioDokument28 SeitenDesign For Beams: Prepared By: Engr. Jo Ann C. CeledioMugiwara SparrowNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 MarksDokument56 Seiten2 MarksKarthik PandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cad & Component DrawingDokument36 SeitenCad & Component DrawingkousikkumaarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition For SpringDokument18 SeitenDefinition For SpringamanpurushothNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Tension MembersDokument13 Seiten2 Tension MembersAbel MulugetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welded and Riveted ConnectionsDokument58 SeitenWelded and Riveted ConnectionsDennis Manejero0% (1)
- Steel Structure 1Dokument14 SeitenSteel Structure 1Ranajit MajhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter III-V Types of Joint and Torque Transmitting JointDokument18 SeitenChapter III-V Types of Joint and Torque Transmitting JointfetenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical ComponentsDokument14 SeitenMechanical ComponentspushkarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Riveted JointDokument12 SeitenDesign of Riveted JointYogesh DandekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Failures Modes of Riveted JointsDokument5 SeitenFailures Modes of Riveted JointsGokul Goku SanthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of tension members and splicesDokument7 SeitenDesign of tension members and splicesSourabh SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ex. No Date Name of The Experiment Mark No Staff SignatureDokument35 SeitenEx. No Date Name of The Experiment Mark No Staff SignaturesivagamipalaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOS II PPT 2Dokument40 SeitenDOS II PPT 2revathisasikumar5420Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bolts, Nuts and Keys: Threaded Joints GuideDokument32 SeitenBolts, Nuts and Keys: Threaded Joints GuideAmalkrishna KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE2352 DSS 2 Marks With AnswerDokument33 SeitenCE2352 DSS 2 Marks With Answerkavithamartin28Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment CE163 - RivetsDokument3 SeitenAssignment CE163 - RivetsJems MansuetoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Considerations of CastingsDokument8 SeitenDesign Considerations of Castingshaqjmi100% (2)
- 2.2.design of Member in CompressionDokument12 Seiten2.2.design of Member in CompressionWilfharry billyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tension MemberDokument35 SeitenTension MemberLUGHANO NGAJILONoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Riveted, Welded, Bonded and Interference-Fit JointsDokument9 SeitenDesign of Riveted, Welded, Bonded and Interference-Fit Jointsaryan2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bolted ConnectionDokument36 SeitenBolted ConnectionMeenuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Structure Connection MethodsDokument60 SeitenSteel Structure Connection MethodsMorad AJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank: Department of Civil Engineering Design of Steel StructuresDokument61 SeitenQuestion Bank: Department of Civil Engineering Design of Steel Structuresbrownpepper30Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 JointsDokument70 SeitenChapter 4 JointsnunuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bolted ConnectionsDokument23 SeitenBolted ConnectionsNaresh ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 - Joint Types in Machine DesignDokument28 SeitenModule 3 - Joint Types in Machine DesignMahmud HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Riveted/Bolted Connections TypesDokument9 SeitenRiveted/Bolted Connections TypesAeron Xavier PimentelNoch keine Bewertungen
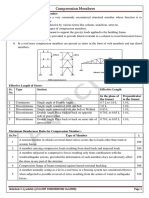
- Compression MembersDokument8 SeitenCompression MembersAbhi ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Fastners - Screwed JointsDokument25 SeitenDesign of Fastners - Screwed JointsKunal AhiwaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Bolted ConnectionsDokument29 SeitenChapter 2 Bolted ConnectionsKishan Purohit100% (1)
- Riveted JointsDokument45 SeitenRiveted JointsHarish kumarreddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Bolted JointsDokument30 SeitenDesign of Bolted JointsKrishna VamsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3Dokument3 SeitenUnit 3shadowsamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Connections-Lacing-Bridge BearingDokument11 SeitenSteel Connections-Lacing-Bridge BearingRaheelAfzaalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Permanent JointsDokument80 SeitenDesign of Permanent JointsRayan IsranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muna 1234Dokument2 SeitenMuna 1234shadowsamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Permanent Joints RivetsDokument37 SeitenDesign of Permanent Joints RivetsAmunyela FelistasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CadDokument1 SeiteCadprkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- CadDokument1 SeiteCadprkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- CadDokument1 SeiteCadprkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bme Assmt23Dokument2 SeitenBme Assmt23prkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Ret WallDokument1 SeiteDesign of Ret WallprkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition of Ret WallDokument1 SeiteDefinition of Ret WallprkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- CadDokument1 SeiteCadprkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bme Assmt25Dokument2 SeitenBme Assmt25prkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bme 2Dokument1 SeiteBme 2prkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNCDokument1 SeiteCNCprkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bme Assmt21Dokument2 SeitenBme Assmt21prkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMT TechDokument1 SeiteSMT TechprkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bme 2Dokument1 SeiteBme 2prkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bme Assmt23Dokument2 SeitenBme Assmt23prkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bme Assmt21Dokument2 SeitenBme Assmt21prkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bme Assmt2Dokument2 SeitenBme Assmt2prkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil MechanicsDokument1 SeiteSoil MechanicsprkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of RC ElementsDokument1 SeiteDesign of RC ElementsprkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prestressing MethodDokument1 SeitePrestressing MethodprkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure Book ListDokument1 SeiteStructure Book ListprkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suspension BridgeDokument1 SeiteSuspension BridgeprkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- About AuthorDokument1 SeiteAbout AuthorprkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Source BookDokument4 SeitenSource BookprkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prestressing UseDokument1 SeitePrestressing UseprkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure AuthorDokument1 SeiteStructure AuthorprkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil MechanicsDokument1 SeiteSoil MechanicsprkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suspension Bridge1Dokument1 SeiteSuspension Bridge1prkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mech201 SyllabusDokument1 SeiteMech201 SyllabusprkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Desighn of Steel 4structuresDokument3 SeitenDesighn of Steel 4structuresprkshdvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report 1galvanic and Concentrated CellDokument12 SeitenReport 1galvanic and Concentrated CellOmar SamirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 Potensial ListrikDokument40 Seiten04 Potensial Listrikphona mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antifouling 2Dokument2 SeitenAntifouling 2gulsumNoch keine Bewertungen
- AHDokument114 SeitenAHReyza PrasetyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patent 1 - WO2017122216A1Dokument61 SeitenPatent 1 - WO2017122216A1sci pusatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomass GasdificationDokument358 SeitenBiomass GasdificationHo Minh Phuong100% (1)
- PTS 15.13.01 - Thermal AmmendmendDokument40 SeitenPTS 15.13.01 - Thermal AmmendmendJustin LowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula Sheet Class 12Dokument5 SeitenFormula Sheet Class 12shikhary167100% (1)
- 8 Metals&NonmetalsDokument12 Seiten8 Metals&NonmetalsKiranmai NamuduriNoch keine Bewertungen
- 104 DR Fixit Dampguard ClassicDokument3 Seiten104 DR Fixit Dampguard Classicag4460Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Exam 1st Tri Multiple Choice 2016-2017 - KeyDokument7 SeitenPractice Exam 1st Tri Multiple Choice 2016-2017 - KeyJohn YuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemistryDokument4 SeitenChemistryTamerlan KudaibergenNoch keine Bewertungen
- SLA Earthworks Guideline Acceptance CriteriaDokument2 SeitenSLA Earthworks Guideline Acceptance CriteriaCheng Yi LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch13 Solution Manual Soil Mechanics and Foundations PDFDokument32 Seitench13 Solution Manual Soil Mechanics and Foundations PDFArnel Suarez100% (1)
- Thermal DegasserDokument2 SeitenThermal DegasserKapwell LimitedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical, Visual Strength Grading and Inspection of Structural TimberDokument3 SeitenMechanical, Visual Strength Grading and Inspection of Structural TimberErick WanduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Studies On Cyclohexanone FormaldehydeDokument5 SeitenStudies On Cyclohexanone FormaldehydeNanasaheb PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designation System of Screws and BoltsDokument3 SeitenDesignation System of Screws and BoltsGiri DharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wall Panelling SystemsDokument70 SeitenWall Panelling SystemsNicole Francis100% (1)
- Nanofabrication Techniques Using Electron Beam LithographyDokument16 SeitenNanofabrication Techniques Using Electron Beam LithographyJulio HernandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultra-Violet Coatings Tricks and TipsDokument1 SeiteUltra-Violet Coatings Tricks and TipsAdriano AraujoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISRO3 WWW Matterhere Com NRRDokument6 SeitenISRO3 WWW Matterhere Com NRRParth PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aviones PDFDokument5 SeitenAviones PDFJimmyFigueroaANoch keine Bewertungen
- Ceralastic: Elastomeric Waterproof CoatingDokument2 SeitenCeralastic: Elastomeric Waterproof Coatingharish GiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- CM 601 Process Equipment Design 1 Jun 2020Dokument1 SeiteCM 601 Process Equipment Design 1 Jun 2020RAHUL MATHURNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decorative and Acoustic Wall Coverings: Product SpecificationsDokument4 SeitenDecorative and Acoustic Wall Coverings: Product SpecificationsrahulnavetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Reactions and Balancing Chemical Equations Web Quest 1Dokument5 SeitenChemical Reactions and Balancing Chemical Equations Web Quest 1api-2625864460% (1)
- Finshing BOQ - RevDokument14 SeitenFinshing BOQ - RevAmmar HattabNoch keine Bewertungen
- CP 201: Material and Energy Balances Chapter 3: Energy and Energy BalancesDokument20 SeitenCP 201: Material and Energy Balances Chapter 3: Energy and Energy BalancesEvelynNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOC Approach for Cooling Water SystemsDokument73 SeitenMOC Approach for Cooling Water SystemsFelipe Miguel Sánchez ClementsNoch keine Bewertungen