Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chapter 02. Sketching
Hochgeladen von
asimbuyukCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 02. Sketching
Hochgeladen von
asimbuyukCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
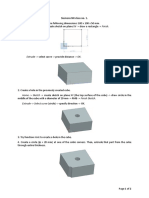
Chapter 2 Sketching
Chapter 2
Sketching
2.1
W16x50 Beam
2.2
Triangular Plate
2.3
More Details
2.4
M20x2.5 Threaded Bolt
2.5
Spur Gears
2.6
Microgripper
2.7
Review
Chapter 2 Sketching
Section 2.1 W16x50 Beam
Section 2.1
W16x50 Beam
7.07 "
Problem Description
.380 "
[1] Wide-ange
I-shape section.
[2] Nominal
depth 16 in.
W16x50
16.25"
.628 "
[3] Weight 50
lb/ft.
R.375"
Chapter 2 Sketching
Techniques/Concepts
Section 2.1 W16x50 Beam
Start up DesignModeler
Sketching/Modeling modes
Draw>Rectangle
Draw>Polyline
Dimensions>General
Dimension>Horizontal
Dimensions>Display
Dimensions>Move
Modify>Copy/Paste
Modify>Trim
Modify>Fillet
Constraints>Symmetry
Auto Constraints
Constraint Status
Extrude
Chapter 2 Sketching
Section 2.1 W16x50 Beam
Basic Mouse Operations in Sketching Mode
[6] Middle-click-drag: rotate.
Shift-middle-click-drag: zoom.
Control-middle-click-drag: pan.
[1] Click: add/remove a sketching
entity to/from the selection set.
(ESC to deselect all.)
[5] Scroll-wheel: zoom
in/out.
[4] Right-click-drag:
box zoom.
[2] Click-sweep:
continuous selection.
[3] Right-click: open
context menu.
Chapter 2 Sketching
Section 2.2 Triangular Plate
Section 2.2
Triangular Plate
40 mm
Problem Description
[2] Radii of
the llets
are 10 mm.
[1] The plate
has three
planes of
symmetry.
30 mm
300 mm
Chapter 2 Sketching
Section 2.2 Triangular Plate
Techniques/Concepts
Draw>Arc by Center
Dimensions> Radius
Modify>Replicate
Modify>Offset
Constraints>Equal Length
Weak/Strong Dimensions
Weak/Strong Constraints
Selection Filter
Single/Box Selection
Chapter 2 Sketching
Section 2.2 Triangular Plate
2D Graphics Controls
[3] Pan.
[5] Zoom.
[2] Zoom to Fit.
[4] Box Zoom.
[8] Undo.
[7] Next View.
[6] Previous View.
[9] Redo.
[1] Look At.
Chapter 2 Sketching
Section 2.3
Pull-down Menus and
Toolbars
Mode Tabs
Tree Outline
Sketching Toolboxes
Graphics area
Details View
Status Bar
Separators
Section 2.3 More Details
More Details
Chapter 2 Sketching
Section 2.3 More Details
Sketching Planes
A sketch must be created on a
[1] Currently
active plane.
[2] To create a new
plane, click New
Plane.
sketching plane; each plane may contain
multiple sketches.
In the beginning of a DesignModeler
session, three planes are automatically
created: XYPlane,YZPlane, and
ZXPlane.
[3] Active sketch can be switched
using the pull-down list, or by clicking
in Tree Outline.
[4] There are many ways
of creating new planes.
Chapter 2 Sketching
Section 2.3 More Details
Sketches
A sketch consists of points and edges; edges may be straight lines or curves.
Multiple sketches may be created on a plane.
[2] Currently
active sketch.
[1] To create a new sketch on
the active sketching plane,
click New Sketch.
[3] Active sketching plane can be
switched using the pull-down list, or by
clicking in Tree Outline.
10
Chapter 2 Sketching
Section 2.3 More Details
Auto Constraints
- The cursor is coincident with a line.
- The cursor is coincident with another point.
- The cursor is a tangent point.
- The cursor is a perpendicular foot.
- The line is horizontal.
- The line is vertical.
//
- The line is parallel to another line.
- The radius is equal to another radius.
You can turn on/off Auto
Constraints.
11
Chapter 2 Sketching
Sketching Toolboxes
Section 2.3 More Details
12
Chapter 2 Sketching
Section 2.4 M20x2.5 Threaded Bolt
Section 2.4
M20x2.5 Threaded Bolt
Problem Description
[1] Metric
system.
[2] Nominal
diameter
d = 20 mm.
M20x2.5
[3] Pitch
p = 2.5 mm.
13
Chapter 2 Sketching
Section 2.4 M20x2.5 Threaded Bolt
H
H
4
d
d1
p
11 p = 27.5
H
8
p
32
External
threads
(bolt)
Internal
threads
(nut)
H = ( 3 2)p = 2.165 mm
d1 = d (5 8)H 2 =17.294 mm
Minor diameter of internal thread d1
Nominal diameter d
14
Chapter 2 Sketching
Techniques/Concepts
Modify>Replicate
Constraints>Fixed
Revolve
Section 2.4 M20x2.5 Threaded Bolt
15
Chapter 2 Sketching
Section 2.5
Spur Gears
Problem Description
To satisfy the fundamental law
of gearing, the gear proles
are cut to an involute curve.
Section 2.5 Spur Gears
16
Chapter 2 Sketching
Section 2.5 Spur Gears
[1] The driving
gear rotates
clockwise.
[8] Line of action (common
normal of contacting gears).
The pressure angle is 20o.
[2] The driven
gear rotates
counterclockwise.
[3] Pitch circle
rp = 2.5 in.
[4] Pitch circle
of the driving
[6] Contact
point (pitch
point).
[5] Line of
centers.
[7] Common
tangent of the
pitch circles.
[9] Addendum
ra = 2.75 in.
[12] The llet
has a radius of
0.1 in.
[10]
Dedendum
rd = 2.2 in.
[11] The shaft has a
radius of 1.25 in.
17
Chapter 2 Sketching
Techniques/Concepts
Draw>Construction Point
Draw>Spline
Modify>Replicate
Constraints>Perpendicular
Section 2.5 Spur Gears
18
Chapter 2 Sketching
Section 2.6 Microgripper
Section 2.6
Microgripper
Problem Description
[1] Gripping
direction.
[2] Actuation
direction.
[3] SMA
actuator.
[4] Glass
bead.
19
Chapter 2 Sketching
Section 2.6 Microgripper
92
32
D30
Unit: m
212
Thickness: 300 m
R45 R25
144
176
280
480
400
47
87
77
140
20
20
Chapter 2 Sketching
Techniques/Concepts
Constraints>Equal Radius
Copy bodies (Mirror)
Create new sketch
Constraints>Tangent
Multiple parts
Section 2.6 Microgripper
21
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Basement FootingDokument42 SeitenBasement FootingSocrates Palomino GamboaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Drawing from the Beginning: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionVon EverandEngineering Drawing from the Beginning: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Geometric Algebra for Computer Science (Revised Edition): An Object-Oriented Approach to GeometryVon EverandGeometric Algebra for Computer Science (Revised Edition): An Object-Oriented Approach to GeometryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 8 RevisionDokument4 SeitenUnit 8 Revisionl wanningNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oriented Projective Geometry: A Framework for Geometric ComputationsVon EverandOriented Projective Geometry: A Framework for Geometric ComputationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- High-Performance Gradient Elution: The Practical Application of the Linear-Solvent-Strength ModelVon EverandHigh-Performance Gradient Elution: The Practical Application of the Linear-Solvent-Strength ModelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catia V5 R20 BasicsDokument27 SeitenCatia V5 R20 BasicsHarika Sonnathi100% (1)
- Chapter02 PDFDokument21 SeitenChapter02 PDFHourglass1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 02Dokument21 SeitenChapter 02Làm Đồ Án ThuêNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 02Dokument21 SeitenChapter 02HECTORNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 02Dokument21 SeitenChapter 02ronnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANSYS Workbench - SketchingDokument81 SeitenANSYS Workbench - SketchingDaniel HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ansys Workbench 13: Theory - Applications - Case StudiesDokument51 SeitenAnsys Workbench 13: Theory - Applications - Case StudiesimamtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finite Element Simulations: With ANSYS Workbench 15Dokument54 SeitenFinite Element Simulations: With ANSYS Workbench 15Andres HerbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter05 PDFDokument12 SeitenChapter05 PDFpuppdeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ansys Chapter 05Dokument12 SeitenAnsys Chapter 05Tran Van TienNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 3D Solid Modeling 1Dokument18 SeitenChapter 4 3D Solid Modeling 1Tran Van TienNoch keine Bewertungen
- With ANSYS Workbench 2021: Finite Element SimulationsDokument55 SeitenWith ANSYS Workbench 2021: Finite Element SimulationsTirth ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Arm Clamp AssemblyDokument123 SeitenModel Arm Clamp AssemblyDavid Rios CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Ended LabDokument6 SeitenOpen Ended LabIsmail AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolidWorks Modeling TechniquesDokument26 SeitenSolidWorks Modeling TechniquesStevenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D Solid Modeling Chapter: Beam Bracket, Cylinder Cover, Lifting ForkDokument18 Seiten3D Solid Modeling Chapter: Beam Bracket, Cylinder Cover, Lifting ForkAbu Bakr M. SaeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 05Dokument12 SeitenChapter 05mafevi90Noch keine Bewertungen
- CATIA V5 Sketcher TutorialDokument29 SeitenCATIA V5 Sketcher TutorialsalehmeiabadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAD Notes by Mr. Kilaku.Dokument54 SeitenCAD Notes by Mr. Kilaku.nattydreadfathelahNoch keine Bewertungen
- With ANSYS Workbench 2019: Finite Element SimulationsDokument55 SeitenWith ANSYS Workbench 2019: Finite Element Simulationstadele10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Autocad Tutorial: (Introductory Level)Dokument70 SeitenAutocad Tutorial: (Introductory Level)AmexTesfayeKoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To: Autodesk InventorDokument34 SeitenIntroduction To: Autodesk InventorutpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building a Teapot in SolidThinkingDokument25 SeitenBuilding a Teapot in SolidThinkingjjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cad 2Dokument13 SeitenCad 2Seb testaccountNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-Part Design and SketcherDokument8 Seiten3-Part Design and SketcherTiga002Noch keine Bewertungen
- 03 - Overview of Linework and Modify ToolsDokument73 Seiten03 - Overview of Linework and Modify ToolsJoão José Zani MateussiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 3D Simulations 1Dokument12 SeitenChapter 5 3D Simulations 1Darshan SoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 3D Simulations Mesh Controls Stress AnalysisDokument12 SeitenChapter 5 3D Simulations Mesh Controls Stress AnalysisAlvaro Fernandez VillarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Objectives: The Sketching EnvironmentDokument31 SeitenLearning Objectives: The Sketching EnvironmentCatherine Nur KomaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Axis Standard CAD Rev 2 - V28Dokument17 Seiten3 Axis Standard CAD Rev 2 - V28Fatima NayabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bim Training For Engineer PDFDokument31 SeitenBim Training For Engineer PDFPhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mesh Modeling AutoCAD 2010Dokument6 SeitenMesh Modeling AutoCAD 2010arutapub100% (1)
- Linear Static Analysis of a Plate with a HoleDokument243 SeitenLinear Static Analysis of a Plate with a HoleTomoyuki TadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A2 - Modal - Analysis (Analyst)Dokument50 SeitenA2 - Modal - Analysis (Analyst)Tomoyuki TadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Machine Design & CAD-II Lab (MEEN-3238)Dokument9 SeitenDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Machine Design & CAD-II Lab (MEEN-3238)Sarmad HafeezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry Model of A 3-D Clevis: Workshop 2Dokument16 SeitenGeometry Model of A 3-D Clevis: Workshop 2hfathollahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- For Autocad 3dDokument241 SeitenFor Autocad 3dVinayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part and Assembly Modeling: With Solidworks 2014Dokument123 SeitenPart and Assembly Modeling: With Solidworks 2014Tâm NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed CAD Modeling of 2 Linear and 3 Rotary AxisDokument27 SeitenDetailed CAD Modeling of 2 Linear and 3 Rotary AxisMuhammad FurqanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AutoCAD 3DDokument33 SeitenAutoCAD 3DDane AgoyaoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-Pat Design FundamentalsDokument187 Seiten3-Pat Design Fundamentalskishore99939Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 7 Math Paper 2 Mid Year Examination 2019Dokument6 SeitenGrade 7 Math Paper 2 Mid Year Examination 2019peterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autodesk Fusion 360: Sketch: Launch VideoDokument7 SeitenAutodesk Fusion 360: Sketch: Launch VideoCarlos OrtegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LS04 - Tapered PlateDokument21 SeitenLS04 - Tapered PlateArles SintiawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catia v5Dokument32 SeitenCatia v5Jeevesh PrasoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge O Level: Mathematics (Syllabus D) 4024/11Dokument20 SeitenCambridge O Level: Mathematics (Syllabus D) 4024/11Hina HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Siemens NX class no. 1 create 3D cuboid holesDokument2 SeitenSiemens NX class no. 1 create 3D cuboid holesMichał WoźniakNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Axis Pro CAD Rev 2Dokument24 Seiten3 Axis Pro CAD Rev 2Fatima NayabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sketch and Model a W16x50 Steel BeamDokument1 SeiteSketch and Model a W16x50 Steel BeamRayGaintNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANSYS SpaceClaim Mixing Elbow WorkshopDokument14 SeitenANSYS SpaceClaim Mixing Elbow WorkshopTanishk KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- NX 9 for Beginners - Part 3 (Additional Features and Multibody Parts, Modifying Parts)Von EverandNX 9 for Beginners - Part 3 (Additional Features and Multibody Parts, Modifying Parts)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Smoothing of Multivariate Data: Density Estimation and VisualizationVon EverandSmoothing of Multivariate Data: Density Estimation and VisualizationBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Autodesk 3ds Max 2014 Essentials: Autodesk Official PressVon EverandAutodesk 3ds Max 2014 Essentials: Autodesk Official PressNoch keine Bewertungen
- NASA-CR-112236 Adhesive Bonded Single Lap JointsDokument116 SeitenNASA-CR-112236 Adhesive Bonded Single Lap JointsNuno MoreiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Guidelines For Adhesive-Bonded Joint Design: Lord User InstructionsDokument2 SeitenGeneral Guidelines For Adhesive-Bonded Joint Design: Lord User InstructionsAnonymous oTrMzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shell BucklingDokument3 SeitenShell Bucklingkhudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solution ADokument2 SeitenSolution Akhudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- ContactDokument2 SeitenContactkhudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geomtry 1Dokument11 SeitenGeomtry 1khudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- JointDokument5 SeitenJointkhudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shell LinearDokument3 SeitenShell Linearkhudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- JointDokument5 SeitenJointkhudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- JointDokument5 SeitenJointkhudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- Static 3Dokument4 SeitenStatic 3khudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- Upper BondDokument11 SeitenUpper Bondkhudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- solu Solcontrol, On Antype, StaticDokument2 Seitensolu Solcontrol, On Antype, Statickhudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- GeomatryDokument11 SeitenGeomatrykhudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- GeometryDokument6 SeitenGeometrykhudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- SolutionDokument2 SeitenSolutionkhudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- 41 PDFDokument4 Seiten41 PDFkhudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solu and PostDokument3 SeitenSolu and Postkhudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S002074030400147X Main PDFDokument17 Seiten1 s2.0 S002074030400147X Main PDFkhudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- FE Lab 1 PDFDokument17 SeitenFE Lab 1 PDFkhudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sakin 2016Dokument13 SeitenSakin 2016khudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- AnsysTutorial Warwick PDFDokument15 SeitenAnsysTutorial Warwick PDFkhudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- TB F4 PDFDokument12 SeitenTB F4 PDFkhudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- Resm2015 30me1205Dokument17 SeitenResm2015 30me1205khudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- Investigation of Springback of Metallic Sheets at Small StrainsDokument17 SeitenInvestigation of Springback of Metallic Sheets at Small Strainskhudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- Yanagimoto2007 PDFDokument4 SeitenYanagimoto2007 PDFkhudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rolla V Ver.7 PDFDokument10 SeitenRolla V Ver.7 PDFkhudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- Toros PDFDokument6 SeitenToros PDFkhudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wang 2013Dokument7 SeitenWang 2013khudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen