Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
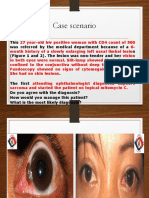
Allergic Conjunctivitis
Hochgeladen von
Letisha RahmadinaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Allergic Conjunctivitis
Hochgeladen von
Letisha RahmadinaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Allergic conjunctivitis
February 8th, 2012 |
Author: Kantatasamsara
Allergic conjunctivitis:
Allergic conjunctivitis may be classified into the followings :
1. Simple Allergic conjunctivitis
2. Vernal conjunctivitis
3. Atopic conjunctivitis
4. Phlyctenular conjunctivitis
5. Giant papillary conjunctivitis
Allergic rhino conjunctivitis /Simple Allergic conjunctivitis:
1.Acute allergic rhinoconjunctivitis
2.seasonal allergic conjunctivitis ( hay fever), with onset during
the spring and summer .
3.perennial allergic conjunctivitis causes symptoms through out
the year with exacerbation in the autumn .
Diagnosis:
Presentation
Symtomps
Transient,acute attacks of redness, watering and itching.
Associated with sneezing and nasal discharge
Signslid oedemachemosis and a papillary reaction
Treatment:
Mast cell satbilizers
Antihistamines
Combined antihistamines and mast cell stabilizers
Steroids
Vernal kerato conjunctivitis:
Vernal
Keratoconjunctivitis is a bilateral, recurrent, disorder in which IGE and cell mediated
immune mechanisms plays important roles.It primarily affects boys and usually
presents in the first decade of life. 95% of cases remit by the late teens and the
remainder develops atopic keratoconjunctivitis.Classification:
o
Palpebral disease primarily involves the upper tarsal conjunctiva.
Limbal disease typically affects black and Asian people.
Mixed has features of both palpebral and limbal disease.
Diagnosis:
Symptoms consists of intense itching, which may be associated with
lacrimation,photophobia, a foreign body sensation, burning and thick mucoid
discharge
Palpebral disease
Diffuse papillary hypertrophy on the superior tarsus
Macropapillae(1mm)(cobblestones)
Giant papillae
Limbal disease
Gelatinous papillae on the limbal conjunctiva that may be associated with
discrete white spots at their apices(Trantas dots)
In tropical regions limbal disease may be very severe
Keratopathy
Punctate epithelial erosions
Epithelial macroerosions
Shield ulcer and plaque
Pseudogenerontoxon
Perpheral superficial vascularization
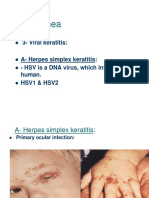
Herpes simplex keratirtis
Treatment:
o
o
Topical
Mast cell stabilizers
Antihistamines
Steroids
Acetylcysteine
Ciclosporin
Supratarsal steroid injection
Systemic
Immunosupressive agent
Oral antihistamines
Surgery
Superficial keratectomy
Amniotic membrance overlay graft
Atopic kerato conjunctivitis:
Atopic keratoconjunctivitis is a rare bilateral and symmetrical disease that typically
develops in young men following a long history of severe atopic dermatitis.
Diagnosis:
o
o
Symptomps are similar to VKC but often more severe and unremitting.
Eyelids
Red,thickened,macerated and fissured lids with chronic staphylococcal
blephiaritis and madarosis.
Tightening of the facial skin may cause lower lid ectropion and epiphora.
Conjunctiva
Micropapillary conjunctivitis
Giant papillae
Scarring and infiltration
Cicatricial conjunctivitis
Symblepharon
Keratopathy:
Punctate epithelial erosions
Persistent epithelial defect
Prediposing to keratoconus
Treatment:
Topical
Mast cell stabilizers
Ketorolac
Antihistamines
Steroids
Acetylcysteine
Ciclosporin
Antibiotics
Supratarsal steroid injection
Systemic antihistamines
Antibiotics
Ciclosporin
Phlyctenular conjunctivitis:
It is an allergicreaction of the conjunctiva caused by endogenous bacterial toxins and
characterised by bleb or nodule formation near the limbus.
o
o
Aetiology:
Tuberculo-protien
Toxins from staphylo-coccus or streptococcus.
Toxins from intestinal parasites.
Clinical types:
Phyctenular conjunctivitis
Phlyctenular kerato-conjunctivitis.
Phlyctenular keratitis.
Symptoms:
Redness with formation of bleb.
Irritation and lacrimation.
Pain and photophobia.
Signs:
One or more,small ,round and raised nodule at or near the limbus
Localised bubar congestion
No conjunctival discharge.
Secondary infection.
Complications:
Phlyctenular keratitis
Fascicular ulcer
Superficial phlyctenular pannus.
Ring ulcer.
Investigations:
To detect tuberculosis:
Sputum for AFB.
Blood for TLC,DLC,ESR.
X-ray chest.
Mantoux test.
ENT consultation to exclude chronic tonsilitis or adentis.
Stool for OPC.
Conjunctival swab and corneal scraping.
Treatment:
Corticosteroid eye drop.
In case of secondary infection, first treat bacterial conjunctivitis,by local
antibiotic drops and then treat with local cortico-steroid drops.
When cornea involved-atropin(1%) eye oinment
Improvement of the nutritional status
Treatement of causal factors.
Treatement of tuberculosis
Treatement of tonsilitis or adenitis
Antihelmintics for intestinal parasites.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Diseases of CorneaDokument170 SeitenDiseases of CorneaLavanya MadabushiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CONJUNCTIVITISDokument67 SeitenCONJUNCTIVITISNauli Panjaitan86% (7)
- Three-Phase SCR Battery Charger Installation GuideDokument20 SeitenThree-Phase SCR Battery Charger Installation GuideJohnTPNoch keine Bewertungen
- EVA and MVADokument19 SeitenEVA and MVATanveer Ahmad100% (1)
- Respiratory Medicine 1 50Dokument33 SeitenRespiratory Medicine 1 50Ahmed Kh. Abu WardaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burns SeminarDokument66 SeitenBurns SeminarPratibha Thakur100% (1)
- FLSPfister IB05000 I GBTRWSD0216 MailDokument26 SeitenFLSPfister IB05000 I GBTRWSD0216 MailLuis Angel BusturiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Follicular Conjunctivitis and Allergic ConjunctivitisDokument7 SeitenChronic Follicular Conjunctivitis and Allergic ConjunctivitisTiodora Wike DsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Konjungtivitis Dan KeratitisDokument117 SeitenKonjungtivitis Dan KeratitisResti Puteri ApriyuslimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ophthalmology - Diseases of ConjunctivaDokument11 SeitenOphthalmology - Diseases of ConjunctivajbtcmdtjjvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allergic Conjunctivitis: History Is ImportantDokument17 SeitenAllergic Conjunctivitis: History Is ImportantAnnisa RahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Referat KonjungtivitisDokument21 SeitenReferat KonjungtivitisWyendae CliquersNoch keine Bewertungen
- The ConjunctivaDokument63 SeitenThe ConjunctivaMariam QaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allergic Eye Diseases MSRDokument11 SeitenAllergic Eye Diseases MSRnafilNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConjunctivitisDokument51 SeitenConjunctivitisIsraa AlaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConjunctivaDokument85 SeitenConjunctivaMuhammad AboAlasaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laporan Kasus Keratokonjungtivitis Atopik Dengan Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency - ViorasusiDokument10 SeitenLaporan Kasus Keratokonjungtivitis Atopik Dengan Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency - Viorasusimade dharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disorders of The Conjunctiva Lec 6Dokument6 SeitenDisorders of The Conjunctiva Lec 6Moneer MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConjunctivitisDokument15 SeitenConjunctivitisbismahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ocular Allergy Esen Karamursel Akpek, MDDokument8 SeitenOcular Allergy Esen Karamursel Akpek, MDAndri SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pemicu 2 "Ada Apa Dengan Mataku?": Adrian Pratama - 405100018 - Blok PenginderaanDokument82 SeitenPemicu 2 "Ada Apa Dengan Mataku?": Adrian Pratama - 405100018 - Blok PenginderaanRilianda SimbolonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mata MerahDokument119 SeitenMata MerahAzwanHamdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vernal KeratoconjunctivitisDokument13 SeitenVernal KeratoconjunctivitisAswathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- P ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Dokument48 SeitenP ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Nauli PanjaitanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09conjunctival Infections 13-12-07Dokument55 Seiten09conjunctival Infections 13-12-07ari rujatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConjunctivaDokument40 SeitenConjunctivaSarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Mulya Dita ParamitaDokument12 SeitenJurnal Mulya Dita ParamitamulyaditaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013 Article 19-VKC PDFDokument16 Seiten2013 Article 19-VKC PDFmentariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbial Keratitis: Causes, Symptoms, Signs and ManagementDokument56 SeitenMicrobial Keratitis: Causes, Symptoms, Signs and ManagementRanveerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 792 Viral Protozoal Corneal UlcerDokument33 Seiten792 Viral Protozoal Corneal UlcerMounika PapireddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis: - Dr. Zulfiqar AliDokument30 SeitenVernal Keratoconjunctivitis: - Dr. Zulfiqar AliAsad FrazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vernal ConjungtivitisDokument34 SeitenVernal ConjungtivitisNadine WangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuliah SMTR VDokument117 SeitenKuliah SMTR VHorakhty PrideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of ConjunctivitisDokument20 SeitenTypes of ConjunctivitisAnonymous 9lmlWQoDm8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eye Emergency: DR Abdelmoniem SaeedDokument63 SeitenEye Emergency: DR Abdelmoniem SaeedYousef Al-AmeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conjunctivitis Guide: Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentDokument77 SeitenConjunctivitis Guide: Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentJade MonrealNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corneal Infections: HundumaDokument40 SeitenCorneal Infections: HundumaHawwi IsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conjunctivitis and Other Ocular Lesions Opthalmology ClassDokument43 SeitenConjunctivitis and Other Ocular Lesions Opthalmology ClassJaikrit SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anterior Segment ManifestationDokument25 SeitenAnterior Segment ManifestationNatnaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis: Mast Cell StabilizersDokument1 SeiteVernal Keratoconjunctivitis: Mast Cell StabilizersIntan MayangsariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical App Red Eye Without Blurred VisionDokument38 SeitenClinical App Red Eye Without Blurred VisionPriskila SamanthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angular ConjunctivitisDokument12 SeitenAngular ConjunctivitisGhaniRahmaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Focus: Chronic Allergic Eye DiseaseDokument2 SeitenFocus: Chronic Allergic Eye DiseaseBal QieshNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 - Ocularsurface2022Dokument76 Seiten2 - Ocularsurface2022MERAYM TRABLSINoch keine Bewertungen
- Grodno State Medical University: Assistant Lecturer of The Department of OphthalmologyDokument37 SeitenGrodno State Medical University: Assistant Lecturer of The Department of Ophthalmologypriti089Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis: Fact or Fiction - True or False?Dokument1 SeiteVernal Keratoconjunctivitis: Fact or Fiction - True or False?elisabethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blefaritis EarlyDokument28 SeitenBlefaritis EarlyPaomo Zhixia EarlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conjunctivitis - Dita LSDokument17 SeitenConjunctivitis - Dita LSMeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal KeratitisDokument2 SeitenJurnal Keratitisanggun pratissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cornea PDFDokument24 SeitenCornea PDFMariam QaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConjunctivitisDokument27 SeitenConjunctivitisGAURAVNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 EczemaDokument5 Seiten2 Eczemaحسين طاهر حاتم طاهرNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conjunctiva Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument101 SeitenConjunctiva Anatomy and PhysiologyPurva KeswaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuliah Blok Mata: Halida Wibawaty Infection Immunology Subdivision Department of Ophthalmology RSUD DR Moewardi SurakartaDokument51 SeitenKuliah Blok Mata: Halida Wibawaty Infection Immunology Subdivision Department of Ophthalmology RSUD DR Moewardi SurakartaMuhammad Nur SidiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis (VKC)Dokument19 SeitenVernal Keratoconjunctivitis (VKC)api-3742497Noch keine Bewertungen
- Red Eye - Student VersionDokument69 SeitenRed Eye - Student VersionKreshnik HAJDARINoch keine Bewertungen
- Allergic Conjunctivitis Guide: Types, Symptoms & TreatmentDokument7 SeitenAllergic Conjunctivitis Guide: Types, Symptoms & TreatmentDicki Pratama HolmesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allergic ConjunctivitisDokument33 SeitenAllergic ConjunctivitisNor Faezah Abd HamidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuliah InfeksiDokument88 SeitenKuliah InfeksiuupupupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conjunctivitis by Asma GulDokument36 SeitenConjunctivitis by Asma GulAbdul SamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acanthamoeba Keratitis: DR Saransh Jain 08/06/2015Dokument42 SeitenAcanthamoeba Keratitis: DR Saransh Jain 08/06/2015Defayudina Dafilianty RosatariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viral Keratitis: Current ConceptsDokument8 SeitenViral Keratitis: Current ConceptsDini MayrisdayaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 375 1 FullDokument7 Seiten375 1 FullLetisha RahmadinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09 Aj 0235Dokument1 Seite09 Aj 0235Letisha RahmadinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 341 FullDokument12 Seiten341 FullLetisha RahmadinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute AppendicitisDokument1 SeiteAcute AppendicitisAllen AykayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethics Zoo EssayDokument2 SeitenEthics Zoo EssayChanel SalinasNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of PharmaDokument4 SeitenList of PharmaJamielle SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shavuot 5774Dokument4 SeitenShavuot 5774Andrea KingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tle 7 - 8 Curriculum MapDokument11 SeitenTle 7 - 8 Curriculum MapKristianTubagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMB4519R9v06-3238 12ports (LB 4T, PCS-2.6G 4T Dual Beam) 2.6m Twin BeamDokument3 SeitenAMB4519R9v06-3238 12ports (LB 4T, PCS-2.6G 4T Dual Beam) 2.6m Twin BeamMIGUEL PEREDA QUIJANONoch keine Bewertungen
- Children's Test Anxiety Scale (CTASDokument10 SeitenChildren's Test Anxiety Scale (CTASSchahyda ArleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Concepts Good Side and Bad Side of HumansDokument9 SeitenThe Concepts Good Side and Bad Side of HumansFAITHINGODMISSIONARIESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guillermo Waco v. People Homicide RulingDokument1 SeiteGuillermo Waco v. People Homicide RulingCandelaria QuezonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cottonhill - Red Collection PDFDokument33 SeitenCottonhill - Red Collection PDFVioricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Bank Accounts Registration FormDokument2 SeitenMultiple Bank Accounts Registration FormAjith JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cricket War .TextDokument2 SeitenThe Cricket War .TextNikita SyrotiukNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAOKEN Comparison With J&JDokument3 SeitenLAOKEN Comparison With J&JMario Alfonso MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- HLF Sharing Fitness Business CooperationDokument17 SeitenHLF Sharing Fitness Business Cooperationbhardwajharsh2706Noch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Toolbox Project ProposalDokument33 SeitenSafety Toolbox Project ProposalShaffizi Boboy100% (1)
- 2021 Rival IQ Social Media Benchmark ReportDokument132 Seiten2021 Rival IQ Social Media Benchmark ReportVu Thu TrangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plateau Pressure Ventilation MeasurementDokument1 SeitePlateau Pressure Ventilation MeasurementImtiaz AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annotated Bibliography For Elder AbuseDokument6 SeitenAnnotated Bibliography For Elder Abuseapi-302577490Noch keine Bewertungen
- A.686 (17) Cod AlarmeDokument39 SeitenA.686 (17) Cod Alarmeciocioi iancuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Developmental Psychology - Socioemotional Development in Middle & Late ChildhoodDokument56 SeitenDevelopmental Psychology - Socioemotional Development in Middle & Late ChildhoodAlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- B Fire BehaviorDokument39 SeitenB Fire BehaviorDon VitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dasar Genetik GandumDokument282 SeitenDasar Genetik GandumAlekkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Palm Avenue ApartmentsDokument6 SeitenPalm Avenue Apartmentsassistant_sccNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evonik-BREAK THRU Brochure Microbials EN Asset 2214205Dokument5 SeitenEvonik-BREAK THRU Brochure Microbials EN Asset 2214205李雷Noch keine Bewertungen
- Confined Space Planning ChecklistDokument3 SeitenConfined Space Planning ChecklistKB100% (1)
- Shell Alexia 40 cylinder oil designed for IMO 2020 complianceDokument2 SeitenShell Alexia 40 cylinder oil designed for IMO 2020 complianceStefas DimitriosNoch keine Bewertungen