Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
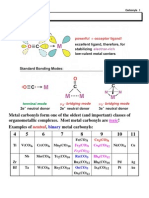
P-Acceptor Ligands - Table of Properties
Hochgeladen von
ch_ymyaaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
P-Acceptor Ligands - Table of Properties
Hochgeladen von
ch_ymyaaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CO
Carbonyl: -donor, strong -acceptor.
Terminal (1850-2100 cm-1), 2-bridging (1700-1850 cm-1) or 3-bridging (1600-1700 cm-1).
For free CO, (CO) = 2143 cm-1.
CS
Thiocarbonyl: better -donor and better -acceptor than CO.
Terminal (1160-1410 cm-1), 2-bridging (1100-1160 cm-1) or 3-bridging (1040-1080 cm-1).
For free CS (not stable at room temperature), (CS) = 1273 cm-1.
Synthesis of thiocarbonyl complexes from MLx + CS2/PR3 or MLx2- + Cl2C=S.
NO
Nitrosyl: redox active linear NO+ (1600-1850 cm-1) or bent N=O- ( 1500-1700 cm-1)
NO+ is isoelectronic with CO: worse -donor, better -acceptor.
Nitrosyls can be terminal or bridging. Synthesis from NO gas, NO+ PF6- or ClNO.
A related pair of redox active ligands are R-NN+ (diazonium) and R-N=N- (diazenide)
N2
Dinitrogen: isoelectronic with CO Worse -donor and much worse -acceptor than CO.
A poor ligand, and very unreactive due to extremely strong NN triple bond. N-N bond
dissociation energies: NN (946 kJmol-1), HN=NH (414 kJmol-1), H2N-NH2 (159 kJmol-1).
(N2) for free N2 = 2331 cm-1 (Raman). (N2) for LxM(N2) = 700-2200 cm-1.
In complexes N2 often reduced to N22- or N24- - use low valent early TM, lanthanide or actinide
complexes {e.g. (R2N)3NbIII,R2TiIVCl2+Na/Hg, Cp*2SmII or (R2N)3UIII(THF)}.
Huge interest in converting N2 to useful N-containing compounds e.g. NH3. Plants do this at RT
and 1 atm pressure. Haber-Bosch process (120 million Tonnes p.a.) Ru/C cat., 400 oC, 200 atm.
CN-
Cyanide: isoelectronic with CO, but in some ways more like a halide than CO.
Good -donor, only a moderate -acceptor. (CN) for LxM(CN) useful.
Better at stabilizing metals in high oxidation states than those in low oxidation states.
CNR Isonitrile or Isocyanide (Stench !): isoelectronic with CO but much larger dipole moment.
M-CN-R almost always linear. Generally a stronger -donor and a weaker -acceptor than
CO (depends on R), but more able to adjust to suit the metal than CO.
Unlike CO, metal coordination can either raise or lower (CN) (2000-2200 cm-1)
because the HOMO of CNR is much more antibonding than that of CO.
PR3
Phosphines -donors and -acceptors.
No useful IR handle, but 31P-NMR is almost as easy to run as 1H NMR.
Huge variety of phosphines available - Can just pick one with the desired steric and electronic
properties. C. A. Tolman, Chem. Rev., 1977, 313.
Related ligands: P(OR)3 = phosphites (worse -donors, better -acceptors), AsR3 = arsine
(slightly worse ligands, lone pair not as available for bonding as in PR3)
Ligands Isoelectronic With CO
CS (thiocarbonyl) better -donor and better -acceptor
than CO.
N2 a poor ligand (much worse -donor and -acceptor)
typically reduced in its complexes
CN- good -donor, OK -acceptor more similar to a
halide than CO.
CNR (isocyanide or isonitrile) similar to CO but can
tune the steric and electronic properties. More reactive for
insertion chemistry.
NO and NNR redox active ligands (linear NO+ or bent
NO-) can change the total electron count of a complex
(what would you expect for [Cr(NO)4] ?).
..
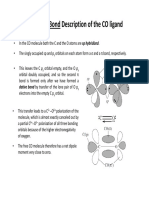
Linear Nitrosyl (NO+)
(M-N-O ~ 180o)
Bent Nitrosyl
(NO-)
(M-N-O ~ 120o)
..
N
..
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Tese Beatbox - Florida PDFDokument110 SeitenTese Beatbox - Florida PDFSaraSilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sla At&tDokument2 SeitenSla At&tCésar Lainez Lozada TorattoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbonyls PDFDokument10 SeitenCarbonyls PDFMaheshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap03 CarbonylsDokument10 SeitenChap03 CarbonylsAPLCTNNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHR410 Chapter 2Dokument36 SeitenPHR410 Chapter 2pulock.paulNoch keine Bewertungen
- IR OrganometallicDokument21 SeitenIR OrganometallicYanti Yana HalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- IC - Lecture 6BDokument13 SeitenIC - Lecture 6BDusuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infrared SpectrosDokument30 SeitenInfrared Spectrosifebriandewi87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Publication 3 2208 1587Dokument63 SeitenPublication 3 2208 1587Tharakeshwari MuraliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infrared SpectrosDokument63 SeitenInfrared SpectrosAsim Alaa Al SalehiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH221 10Dokument28 SeitenCH221 10ankushtoppo25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Spec Ir NMR Spectra TablesDokument15 SeitenSpec Ir NMR Spectra TablesMah NovaesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complexes With Multiple Metal-Carbon Bonds: Metal Carbenes and CarbynesDokument22 SeitenComplexes With Multiple Metal-Carbon Bonds: Metal Carbenes and Carbynesfarhan rivaldiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Organometallic Chem 01-4Dokument21 SeitenIntroduction To Organometallic Chem 01-4Aparna DuggiralaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0302 紅外線光譜儀 孫仲銘老師Dokument47 Seiten0302 紅外線光譜儀 孫仲銘老師周浩銘Noch keine Bewertungen
- Metal CarbonylsDokument9 SeitenMetal Carbonylsadarsh abcdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Org A No Met PDFDokument9 SeitenOrg A No Met PDFSandipan SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1950 - Colthup - J Opt Soc Am - Spectra-Structure Correlations in The Infra-Red RegionDokument4 Seiten1950 - Colthup - J Opt Soc Am - Spectra-Structure Correlations in The Infra-Red Regionvitoribeiro90Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3.3 CHM622 NMRDokument42 Seiten3.3 CHM622 NMRsharifah sakinah syed soffianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Carbonyls May Be Mononuclear or PolynuclearDokument48 SeitenMetal Carbonyls May Be Mononuclear or PolynuclearcoolrulzNoch keine Bewertungen
- IR Spectroscopy by Tejas SahooDokument31 SeitenIR Spectroscopy by Tejas Sahootejassahoo123Noch keine Bewertungen
- 10 03 2006 Biophysics 2Dokument30 Seiten10 03 2006 Biophysics 2api-3696530Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Interpretation of Infrared SpectraDokument3 SeitenIntroduction To Interpretation of Infrared Spectrachinnirao100% (4)
- 2 PraktIPATerpadu-IR SpectrosDokument32 Seiten2 PraktIPATerpadu-IR Spectrosvsvsuresh2099Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Introduction To Hydrocarbons-1Dokument47 Seiten1 - Introduction To Hydrocarbons-1Alvis MwangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- C-13 NMR and DEPTDokument41 SeitenC-13 NMR and DEPTV G Viju Kumar100% (1)
- 2 PraktIPATerpadu-IR SpectrosDokument32 Seiten2 PraktIPATerpadu-IR SpectrosSurya SimamoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coordination ChemistryDokument33 SeitenCoordination ChemistryGOVIND RANJAN80% (5)
- 1 - Introduction To HydrocarbonsDokument56 Seiten1 - Introduction To HydrocarbonsPaul NderebaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) With Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) AnalysisDokument5 SeitenScanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) With Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) AnalysisAjeeth KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case in Point: Tetrahedral Vs Octahedral ComplexesDokument33 SeitenCase in Point: Tetrahedral Vs Octahedral ComplexesShubham KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- IR SpectrosDokument44 SeitenIR SpectrosVansh YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- IR Spectra Structural Prediction of Organic CompoundsDokument40 SeitenIR Spectra Structural Prediction of Organic CompoundsBharat SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Co Ordination 1Dokument33 SeitenCo Ordination 1Nivi RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- 424 Spectra TablesDokument19 Seiten424 Spectra TablespradeepiitdNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 - TransitionMetalDokument37 Seiten11 - TransitionMetaltuyenvip441999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4 IR Spectrum AnalysisDokument43 SeitenLecture 4 IR Spectrum AnalysiskhadijahhannahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infrared Spectroscopy: Concepts and TheoriesDokument55 SeitenInfrared Spectroscopy: Concepts and Theoriesdead_knightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 5 UpdateDokument20 SeitenLec 5 UpdateMa. Salma Kirsten CayabyabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbenes 3Dokument20 SeitenCarbenes 3assquimicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 212: Physical Analytical ChemistryDokument22 SeitenChem 212: Physical Analytical ChemistrysamuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- UGSemsterSyllabus Chemistry 6Sem614Chemistry English InorganicOrganicPhysicalChemistryDokument168 SeitenUGSemsterSyllabus Chemistry 6Sem614Chemistry English InorganicOrganicPhysicalChemistryAnil GugulothNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metalcarbonyls 180405141857Dokument17 SeitenMetalcarbonyls 180405141857Biswajit RoutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atyabrata Endh MSC Part I (2017-18) Department of Chemistry Berhampur University, Odisha, IndiaDokument17 SeitenAtyabrata Endh MSC Part I (2017-18) Department of Chemistry Berhampur University, Odisha, IndiaDr. Md. Ehtesham Ul HoqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 (2) Veto of Life He Our Pitch orDokument27 Seiten5 (2) Veto of Life He Our Pitch orStephenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caligan Probset1Dokument5 SeitenCaligan Probset1Jeff Tristan CaliganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spectroscopy ProblemsDokument16 SeitenSpectroscopy Problemsnvithyarajan6872100% (2)
- Soft & Hard Acids - Bases, and Molecular Geometry PDFDokument9 SeitenSoft & Hard Acids - Bases, and Molecular Geometry PDFAtul GautamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organometallic ChemistryDokument90 SeitenOrganometallic Chemistrytharun thennarasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Interpretation of Infrared SpectraDokument3 SeitenIntroduction To Interpretation of Infrared SpectraBenni WewokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uv-Visible SpectrosDokument71 SeitenUv-Visible SpectrosAshutoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inorganic Chemistry SummaryDokument8 SeitenInorganic Chemistry SummaryClara1212Noch keine Bewertungen
- Raw Material Analysis-IRDokument58 SeitenRaw Material Analysis-IRDilla Wulan NingrumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Orbital of Chemisorbed Carbon Monoxide: GeohgeDokument6 SeitenMolecular Orbital of Chemisorbed Carbon Monoxide: GeohgeLuis M. MolinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACS Study GuideDokument3 SeitenACS Study Guidemyst8ry03513Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wk12a Complex StabilityDokument30 SeitenWk12a Complex Stabilityaanfebrianto1993Noch keine Bewertungen
- NMR Hly09Dokument44 SeitenNMR Hly09Giang NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13-C NMR-09Dokument27 Seiten13-C NMR-09M Nur M. MahmudNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHMBD 449 - Organic Spectral: AnalysisDokument40 SeitenCHMBD 449 - Organic Spectral: AnalysisIleana ManciuleaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonVon EverandSolid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (4)
- Coordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972Von EverandCoordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972A. B. P. LeverNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnnleaveDokument2 SeitenAnnleavech_ymyaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SicleaveDokument1 SeiteSicleavech_ymyaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Travelling ExpensesDokument1 SeiteTravelling Expensesch_ymyaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FraappDokument2 SeitenFraappch_ymyaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition of Dependent ChildDokument1 SeiteDefinition of Dependent Childch_ymyaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sounds GoodDokument1 SeiteSounds Goodch_ymyaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nano SilverDokument3 SeitenNano Silverch_ymyaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Have You Gotten The Message On Cholesterol?: Resource For Option #10Dokument1 SeiteHave You Gotten The Message On Cholesterol?: Resource For Option #10ch_ymyaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 31-35. P1 閲讀理解Dokument9 Seiten31-35. P1 閲讀理解ch_ymyaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 26-30. P1 閲讀理解Dokument11 Seiten26-30. P1 閲讀理解ch_ymyaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Python: - To Start, Input Your Commands HereDokument5 SeitenPython: - To Start, Input Your Commands Herech_ymyaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bromination ExperimentDokument9 SeitenBromination Experimentch_ymyaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wades Rules 2Dokument5 SeitenWades Rules 2ch_ymyaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC 16 Colorimetric Analysis For Lab NotebookDokument7 SeitenAC 16 Colorimetric Analysis For Lab Notebookch_ymyaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Experiment To Find Out The Melting Point of Chocolate: Some Hints For Drawing Your Graph..Dokument3 SeitenAn Experiment To Find Out The Melting Point of Chocolate: Some Hints For Drawing Your Graph..ch_ymyaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conduction Convection Radiation NotesDokument13 SeitenConduction Convection Radiation Notesch_ymyaa100% (3)
- Calzone or Pizza Bender LabDokument1 SeiteCalzone or Pizza Bender Labch_ymyaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beef JerkyDokument2 SeitenBeef Jerkych_ymyaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peter G. NELSON: Modified Lewis TheoryDokument4 SeitenPeter G. NELSON: Modified Lewis Theorych_ymyaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hanwha Q Cells Data Sheet Qpeak L-g4.2 360-370 2017-10 Rev02 NaDokument2 SeitenHanwha Q Cells Data Sheet Qpeak L-g4.2 360-370 2017-10 Rev02 NazulfikarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH-5 Further Percentages AnswersDokument5 SeitenCH-5 Further Percentages AnswersMaram MohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Five Reasons Hazards Are Downplayed or Not ReportedDokument19 SeitenFive Reasons Hazards Are Downplayed or Not ReportedMichael Kovach100% (1)
- SCERT Kerala State Syllabus 9th Standard English Textbooks Part 1-1Dokument104 SeitenSCERT Kerala State Syllabus 9th Standard English Textbooks Part 1-1Athulya ThondangattilNoch keine Bewertungen
- SafetyRelay CR30Dokument3 SeitenSafetyRelay CR30Luis GuardiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultracold Atoms SlidesDokument49 SeitenUltracold Atoms SlideslaubbaumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mecha World Compendium Playbooks BWDokument12 SeitenMecha World Compendium Playbooks BWRobson Alves MacielNoch keine Bewertungen
- XII CS Material Chap7 2012 13Dokument21 SeitenXII CS Material Chap7 2012 13Ashis PradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- KLA28 ProductsapplicationpresetDokument2 SeitenKLA28 ProductsapplicationpresetcarxmozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Importance of Skill Based Education-2994Dokument5 SeitenImportance of Skill Based Education-2994João Neto0% (1)
- Simon Ardhi Yudanto UpdateDokument3 SeitenSimon Ardhi Yudanto UpdateojksunarmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Rates (Nh-15 Barmer - Sanchor)Dokument118 SeitenAnalysis of Rates (Nh-15 Barmer - Sanchor)rahulchauhan7869Noch keine Bewertungen
- EMD Question Bank II 2Dokument4 SeitenEMD Question Bank II 2Soham MisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIIMS 2015 Solved PaperDokument436 SeitenAIIMS 2015 Solved PaperSurya TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Universal Ultrasonic Generator For Welding: W. Kardy, A. Milewski, P. Kogut and P. KlukDokument3 SeitenUniversal Ultrasonic Generator For Welding: W. Kardy, A. Milewski, P. Kogut and P. KlukPhilip EgyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quotation of Suny PDFDokument5 SeitenQuotation of Suny PDFHaider KingNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Comparative Study of Public Private Life Insurance Companies in IndiaDokument5 SeitenA Comparative Study of Public Private Life Insurance Companies in IndiaAkansha GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Education: Template No. 1 Teacher'S Report On The Results of The Regional Mid-Year AssessmentDokument3 SeitenDepartment of Education: Template No. 1 Teacher'S Report On The Results of The Regional Mid-Year Assessmentkathrine cadalsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day6 7Dokument11 SeitenDay6 7Abu Al-FarouqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catheter Related InfectionsDokument581 SeitenCatheter Related InfectionshardboneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alfa Week 1Dokument13 SeitenAlfa Week 1Cikgu kannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circular ConvolutionDokument3 SeitenCircular Convolutionseeksudhanshu1Noch keine Bewertungen
- COK - Training PlanDokument22 SeitenCOK - Training PlanralphNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18-MCE-49 Lab Session 01Dokument5 Seiten18-MCE-49 Lab Session 01Waqar IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Based On PSA 700 Revised - The Independent Auditor's Report On A Complete Set of General Purpose Financial StatementsDokument12 SeitenBased On PSA 700 Revised - The Independent Auditor's Report On A Complete Set of General Purpose Financial Statementsbobo kaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DirectionDokument1 SeiteDirectionJessica BacaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Img 20201010 0005Dokument1 SeiteImg 20201010 0005Tarek SalehNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0012 Mergers and Acquisitions Current Scenario andDokument20 Seiten0012 Mergers and Acquisitions Current Scenario andJuke LastNoch keine Bewertungen