Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Sepsis Updated Algorithm
Hochgeladen von
ThanhLeCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Sepsis Updated Algorithm
Hochgeladen von
ThanhLeCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
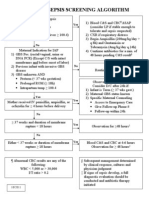
Evaluation and Management of Possible Neonatal Sepsis
( 35 weeks Gestation During the First Few Hours of Life)
Maternal GBS Positive (unless Cesarean delivery without
labor with membranes intact)
Status:
OR
Unknown and GBS risk factors present
(Box 1)
Baby with signs of
possible sepsis, not
clearly improving
(Box 2)
No
intrapartum
fever and
ROM < 18h
<4h
intrapartum
antibiotics
Baseline
CBC + CRP
Baby with signs of
possible sepsis, not
clearly improving
(Box 2)
Baby well or
clearly improving
in first 2 h (Box 2)
Maternal temp 100.4F
(38C) or ROM 18h or
clinically diagnosed
chorioamnionitis
Baseline
CBC + CRP
Blood and
CSF culture,
antibiotics
(Box 4)
Blood culture
and antibiotics,
repeat labs in 12
to 24h (Box 4)
Antibiotics at
least 7 to 10d
(based on
clinical
course,
laboratory
values and
culture
results)
Antibiotics can
be discontinued
after 48h if
culture negative,
labs normal or
normalize
quickly and
benign clinical
course)
No Chorioamnionitis
or fever
ROM 18h or
Maternal Temp of
100.4 to 101.4 in
presence of epidural
ROM <18h
Baseline
CBC + CRP
Normal
Observe at
least 48h, no
antibiotics
(unless baby
develops
signs of
possible
sepsis)
Baby well or
clearly improving
in first 2 h (Box 2)
Chorioamnionitis or
Maternal temp 100.4F(38C)
without epidural or 101.5F
(38.6C) with epidural
>4h
intrapartum
antibiotics
Screening
CBC + CRP
Abnormal
(Box 3)
Negative
OR
Positive with Cesarean delivery without
labor with membranes intact
OR
Unknown with no GBS risk factors (Box 1)
Screening
CBC + CRP
Abnormal
(Box 3)
Routine
Newborn
Care
Normal
Blood and
CSF culture,
antibiotics
(Box 4)
Blood culture
and antibiotics
(Box 4), repeat
labs in 12 to 24h
Antibiotics at
least 48h to
10d (based
on clinical
course,
laboratory
values and
culture
results)
Antibiotics can
be discontinued
after 48h if
culture negative,
labs normal or
normalize
quickly and
benign clinical
course)
Repeat labs
in 12 to 24h
(Box 3)
Observe at
least 48h
No antibiotics
(unless baby
develops
signs of
possible
sepsis)
(Box 2)
Box 1. Group B Streptococcus Risk Factors
1. Delivering at <37 weeks' gestation
2. Intrapartum temperature >=100.4F (>=38.0C)
3. Rupture of membranes for >18 hours
4. Previous infant with invasive GBS disease
5. GBS bacteriuria during the current pregnancy
Box 2.
Signs of Possible Neonatal Sepsis: tachypnea, grunting, cyanosis, oxygen requirement,
apnea, persistent temperature <36.5 or >37.5, hypotonia, poor feeding, persistent unexplained
hypoglycemia
Baby well or clearly improving means clear and rapid improvement during the first 2
hours of life, no residual signs by 2 hours of age, and no worsening of any signs.
Box 3. Normal Lab Values
1. CRP: normal < 0.5 mg/dL (at UIHC, other hospitals may use different values)
2. CBC: normal I:T ratio at birth < 0.16 (although some use a cutoff of 0.20)
I:T ratio = (immature forms) / (total neutrophils + immature forms).
Also total neutrophil count should be within normal limits according to age (see nomogram at
http://www.uihealthcare.com/depts/med/pediatrics/iowaneonatologyhandbook/infection/referenc
erange.html)
Box 4. Antibiotics
1. Ampicillin 100 mg/kg/dose IV q12h.
2. Gentamicin 4 mg/kg/dose IV q24h.
Get a trough gentamicin level before the 2nd dose. If > 1.0, hold and check at 36 h. If < 1.0 at
36h, give q 36h. If still > 1.0 at 36h, hold and check at 48 h and give q 48h if < 1.0.
References
Benitz et al. Risk factors for early-onset Group B Streptococcal sepsis. Pediatrics 1999;
103:77e.
Escobar et al. Neonatal sepsis workups in infants >= 2000 grams at birth. Pediatrics 2000;
106:256.
Schrag et al. Prevention of perinatal Group B Streptococcal disease. MMWR 2002;51:1.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Newborn Sepsis Clinical Practice GuidelineDokument2 SeitenNewborn Sepsis Clinical Practice GuidelineAgus WijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newborn Sepsis GuidelineDokument2 SeitenNewborn Sepsis GuidelineAmelia ArnisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal SepsisDokument31 SeitenNeonatal Sepsisanwar jabariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre-eclampsia, (Pregnancy with Hypertension And Proteinuria) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandPre-eclampsia, (Pregnancy with Hypertension And Proteinuria) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal Jaundice PathwayDokument35 SeitenNeonatal Jaundice PathwayMcmac YangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal ObservationsDokument3 SeitenNeonatal ObservationsMuhammad Bayu Zohari HutagalungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Problems: in Newborn InfantDokument94 SeitenCommon Problems: in Newborn InfantAhmad JustNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOP Neonatal SepsisDokument3 SeitenSOP Neonatal SepsisEidi IdhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- NICE 2021 Assessing and Managing The Risk of Early Onset SepsisDokument4 SeitenNICE 2021 Assessing and Managing The Risk of Early Onset Sepsisradualina26Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3.children DiseasesDokument90 Seiten3.children DiseasesMahmoud SuleimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 - Sepsis AlgorithmDokument1 Seite6 - Sepsis Algorithmapi-221111168Noch keine Bewertungen
- PR 2, Neonatal PeriodDokument67 SeitenPR 2, Neonatal PeriodDaly DaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Guide JaundiceDokument2 SeitenStudent Guide JaundiceAnna StacyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Neonatal SepsisDokument30 SeitenManagement of Neonatal SepsisRam krishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Neonatal Sepsis: Niki Kosmetatos, MD Anthony Piazza, MD J. Devn Cornish, MDDokument30 SeitenManagement of Neonatal Sepsis: Niki Kosmetatos, MD Anthony Piazza, MD J. Devn Cornish, MDiniidzniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visual Summary On Neonatal Infection Determining The Need For Antibiotic Treatment of Babies Within 72 Hours of Birth PDF 9078464413Dokument2 SeitenVisual Summary On Neonatal Infection Determining The Need For Antibiotic Treatment of Babies Within 72 Hours of Birth PDF 9078464413walaa alsharanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care During Prenatal PeriodDokument7 SeitenNursing Care During Prenatal Periodsands32Noch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Practice Guideline On Neonatal Sepsis: Summarized by Dr. Catherine Chua October 2012Dokument3 SeitenClinical Practice Guideline On Neonatal Sepsis: Summarized by Dr. Catherine Chua October 2012Joey CuayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Neonatal ProblemsDokument32 SeitenCommon Neonatal ProblemsbrhomzalatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ectopic PregnancyDokument54 SeitenEctopic Pregnancypatriciaatan1497Noch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal Jaundice Pathway PDFDokument35 SeitenNeonatal Jaundice Pathway PDFarjunaquellNoch keine Bewertungen
- NICU Standing Orders KFAFHDokument36 SeitenNICU Standing Orders KFAFHallysonviernes100% (1)
- Askep Anak SupriyadiDokument13 SeitenAskep Anak Supriyadiputi bungsuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 - Preterm Labour+PROMDokument27 Seiten10 - Preterm Labour+PROMاحمد احمدNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Features and Management of Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia in Term and Near Term InfantsDokument16 SeitenClinical Features and Management of Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia in Term and Near Term InfantstatadhNoch keine Bewertungen
- NICU ProtocolDokument75 SeitenNICU ProtocolCatherine Lee100% (6)
- Preterm Labour & Premature Rupture of Membrane: Dr. Mashael Shebaili Consultant Ob/Gyn Assistant ProfessorDokument27 SeitenPreterm Labour & Premature Rupture of Membrane: Dr. Mashael Shebaili Consultant Ob/Gyn Assistant ProfessorarajorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fever: Your Next Friend Request: Robert P. Olympia, MD, FAAPDokument96 SeitenFever: Your Next Friend Request: Robert P. Olympia, MD, FAAPDavid LadinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Intrapartum Newborn CareDokument31 SeitenEssential Intrapartum Newborn CareJohn Christopher LucesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fever Without A Source in The 1 - To 3-Month-Old Infant Case FileDokument2 SeitenFever Without A Source in The 1 - To 3-Month-Old Infant Case Filehttps://medical-phd.blogspot.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal JaundiceDokument23 SeitenNeonatal JaundiceAsad M AminNoch keine Bewertungen
- QR Management of Neonatal Jaundice (Second Edition) PDFDokument8 SeitenQR Management of Neonatal Jaundice (Second Edition) PDFOlayinka AwofoduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Penugasan Morning Report Pediatric - H1A021103 - Andi Muhammad Al Fatih HaqDokument17 SeitenPenugasan Morning Report Pediatric - H1A021103 - Andi Muhammad Al Fatih HaqPentolNoch keine Bewertungen
- NNJ by DR MadhuDokument59 SeitenNNJ by DR MadhuNabrazz SthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 - Preterm Labour+PROMDokument27 Seiten10 - Preterm Labour+PROMSemon YohannesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal Assessment of SepsisDokument1 SeiteMaternal Assessment of SepsisCamilo Almanza GloriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- B R A H M S PCT: Procalcitonin (PCT) Reference Values in NeonatologyDokument2 SeitenB R A H M S PCT: Procalcitonin (PCT) Reference Values in NeonatologyNgai29Noch keine Bewertungen
- High Risk NewbornDokument21 SeitenHigh Risk Newbornnaga maniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosis of Pregnancy - SamyaDokument58 SeitenDiagnosis of Pregnancy - Samyaragulraj6699Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCGDokument91 SeitenNCGhesham1978Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case StudyDokument8 SeitenCase StudyMelody Jane PardilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Penilaian Status GiziDokument86 SeitenPenilaian Status GiziAnna MardiyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Neonatal Problems 2016Dokument161 SeitenCommon Neonatal Problems 2016Dejen TakeleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preterm Labour: Muhammad Hanif Final Year MBBSDokument32 SeitenPreterm Labour: Muhammad Hanif Final Year MBBSArslan HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recent - Neonatal JaundiceDokument30 SeitenRecent - Neonatal JaundiceBibek DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal Jaundice Lecture,,By DR Kassahun GirmaDokument25 SeitenNeonatal Jaundice Lecture,,By DR Kassahun GirmaKassahun Girma GelawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standards of Care in ServiceDokument7 SeitenStandards of Care in ServiceLucian CaelumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative and QualitativeDokument4 SeitenQuantitative and QualitativekukadiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity No. 10 Qualitative HCG DeterminationDokument9 SeitenActivity No. 10 Qualitative HCG DeterminationCruz JenniferNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid Eval JCDokument8 SeitenMid Eval JCiglesiasowenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trabajo Final de InglésDokument9 SeitenTrabajo Final de Inglésliuvas Boizán CobasNoch keine Bewertungen
- PD2 Final Exam MergedDokument35 SeitenPD2 Final Exam MergedJohn TecsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jaundice PresentationDokument33 SeitenJaundice Presentationmbishara20100% (1)
- HCG Strip (OneStep)Dokument2 SeitenHCG Strip (OneStep)Rita WidaningsihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jaundice in The Newborns: Division of Neonatology, Department of Pediatrics All India Institute of Medical SciencesDokument23 SeitenJaundice in The Newborns: Division of Neonatology, Department of Pediatrics All India Institute of Medical Sciencesbubble_inNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antenatal CareDokument46 SeitenAntenatal CareKIPA SHRESTHANoch keine Bewertungen
- Fever With Focus in Well Appearing Child - 3yearsDokument15 SeitenFever With Focus in Well Appearing Child - 3yearsShenillee BurgessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arizona, Utah & New Mexico: A Guide to the State & National ParksVon EverandArizona, Utah & New Mexico: A Guide to the State & National ParksBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- The Bahamas a Taste of the Islands ExcerptVon EverandThe Bahamas a Taste of the Islands ExcerptBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Japanese Gardens Revealed and Explained: Things To Know About The Worlds Most Beautiful GardensVon EverandJapanese Gardens Revealed and Explained: Things To Know About The Worlds Most Beautiful GardensNoch keine Bewertungen
- New York & New Jersey: A Guide to the State & National ParksVon EverandNew York & New Jersey: A Guide to the State & National ParksNoch keine Bewertungen
- South Central Alaska a Guide to the Hiking & Canoeing Trails ExcerptVon EverandSouth Central Alaska a Guide to the Hiking & Canoeing Trails ExcerptBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Naples, Sorrento & the Amalfi Coast Adventure Guide: Capri, Ischia, Pompeii & PositanoVon EverandNaples, Sorrento & the Amalfi Coast Adventure Guide: Capri, Ischia, Pompeii & PositanoBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)