Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
It Can Change Alternating Current Into Direct Current and at The Same Time Can Control The Amount of Powerfed To The Load
Hochgeladen von
Aris Setyawan0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
32 Ansichten2 Seitennbn
Originaltitel
Scr
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldennbn
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
32 Ansichten2 SeitenIt Can Change Alternating Current Into Direct Current and at The Same Time Can Control The Amount of Powerfed To The Load
Hochgeladen von
Aris Setyawannbn
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
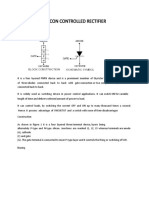
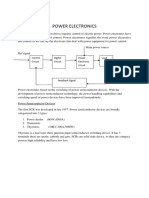
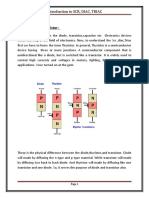
SCR is a silicon based semiconductor device with four layers of alternating P and N-type
material, which is used in electrical circuits for switching operation.
It can change alternating current into direct current and at the same time can control the amount
of powerfed to the load
SCR is consist on four layer of semiconductor which forms PNPN or NPNP
structure, it has tree junction J1, J2 and J3 and also three terminals, the anode
terminal of Silicon Control Rectifier SCR is connected to the P-Type of material
of PNPN structure and the cathode terminal is connected to the N-Type layer
of the Silicon Control Rectifier while the gate of the Silicon Control Rectifier
SCR is connected to the P-Type of material near to the cathode. An SCR is
turned on by applying a pulse to its gate terminal. Gate terminal for a
controlling input signal.
To turn ON the Silicon Control Rectifier SCR we apply clock pulse at the gate
terminal which called triggering of Silicon Control Rectifier, but when the
Silicon Control Rectifier SCR turned ON, now if we remove the triggering
voltage, the Silicon Control Rectifier SCR will remain in ON state. This voltage
is called Firing voltage
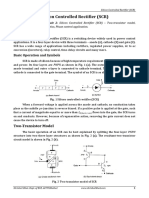
The Silicon Control Rectifier SCR start conduction when it is forward biased.
For this purpose the cathode is kept at negative and anode at positive. When
positive clock pulse is applied at the gate the SCR turns ON.When forward
bias voltage is applied to the Silicon Control Rectifier SCR, the junction J1 and
J3 become forward bias while the junction J2 become reverse bias. When we
apply a clock pulse at the gate terminal, the junction J2 become forward bias
and the Silicon Control Rectifier SCR start conduction.The Silicon Control
Rectifier SCR turn ON and OFF very quickly, At the OFF state the Silicon
Control Rectifier SCR provide infinity resistance and in ON state, it offers very
low resistance, which is in the range of 0.01O to 1O.
Reverse blocking: In this state the thyristor blocks the current in the same
way as that of a reverse biased diode.
Forward blocking: In this state the thyristor operation is such that it blocks
forward current conduction that would normally be carried by a forward
biased diode.
Forward conducting: In this state the thyristor has been triggered into
conduction. It will remain conducting until the forward current drops below a
threshold value known as the holding current.
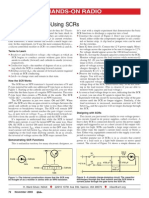
Gate connected directly to its own anode through a diode; nearly complete
half-wave current through load.
We can delay the triggering of the SCR, however, by inserting some
resistance into the gate circuit, thus increasing the amount of voltage drop
required before enough gate current triggers the SCR. In other words, if we
make it harder for electrons to flow through the gate by adding a resistance,
the AC voltage will have to reach a higher point in its cycle before there will
be enough gate current to turn the SCR on.
Resistance inserted in gate circuit; less than half-wave current through load.
By making the series gate resistor variable, we can make adjustments to the
time-proportioned power: Increasing the resistance raises the threshold level,
causing less power to be delivered to the load. Decreasing the resistance
lowers the threshold level, causing more power to be delivered to the load.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Silicon Controlled Rectifier DefinitionDokument10 SeitenSilicon Controlled Rectifier DefinitionishmamNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELECTRON DEVICES-Power DevicesDokument58 SeitenELECTRON DEVICES-Power DevicesSekar GanapathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Silicon Controlled RectifierDokument9 SeitenSilicon Controlled RectifierMahendraNath Reddy ENoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Power Electronics DevicesDokument14 SeitenIntroduction To Power Electronics DevicesahmedsaeedobiedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ece014 - Electronics 3 - Experiment 1Dokument9 SeitenEce014 - Electronics 3 - Experiment 1John Wilfredd CurimoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power ElectronicsDokument17 SeitenPower ElectronicsGanesan KandasamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PE Unit-1 PDFDokument29 SeitenPE Unit-1 PDFNaveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rohini 96440522279Dokument4 SeitenRohini 96440522279Swapnil AmbadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1Dokument9 SeitenExperiment 1John Wilfredd CurimoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control SCR firing angle using gate resistorDokument12 SeitenControl SCR firing angle using gate resistorplokplokplokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Semiconductor DevicesDokument40 SeitenSpecial Semiconductor DevicesJairus OnkwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sillicon Controlled Rectifier Lab ReoprtDokument6 SeitenSillicon Controlled Rectifier Lab ReoprtMuhammad Mushtaq100% (2)
- Chapter 3 Power SupplyDokument23 SeitenChapter 3 Power SupplyBricksoe NgwenyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Silicon-Controlled Rectifiers: EE 140 Industrial ElectronicsDokument22 SeitenSilicon-Controlled Rectifiers: EE 140 Industrial Electronicssaber marriotte durimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BE 5 UnitDokument23 SeitenBE 5 Unit08sunnyjaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forward Blocking ModeDokument10 SeitenForward Blocking ModeSmithi SureshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5Dokument38 SeitenChapter 5Markos NiguseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Battery Charger Circuit Using SCRDokument5 SeitenBattery Charger Circuit Using SCRankitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Silicon Controlled RectifierDokument9 SeitenSilicon Controlled RectifierFarishat Nusabbee An Nafs100% (1)
- Thyristor: Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR)Dokument9 SeitenThyristor: Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR)Vlad V WalachiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IECD Capsule NotesDokument59 SeitenIECD Capsule NotesANANTHU PRADEEPNoch keine Bewertungen
- POWER ELECTRONICsDokument120 SeitenPOWER ELECTRONICsJeji HirboraNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCR Power Control Circuit: SCS: Motor Start/stop Circuit, An Equivalent Circuit With Two TransistorsDokument5 SeitenSCR Power Control Circuit: SCS: Motor Start/stop Circuit, An Equivalent Circuit With Two TransistorsMark Kenneth Apuyan100% (1)
- POWER ELECTRONICS DEVICES AND CIRCUITSDokument111 SeitenPOWER ELECTRONICS DEVICES AND CIRCUITSnazibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indus Lecture 2 PartialDokument69 SeitenIndus Lecture 2 PartialIris Jean Mosquera100% (1)
- Silicon Controlled Rectifiers: Chapter - 15Dokument3 SeitenSilicon Controlled Rectifiers: Chapter - 15lvsaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison Between BJT, FET & Thyristor: Intruder AlarmDokument26 SeitenComparison Between BJT, FET & Thyristor: Intruder AlarmRojan Pradhan100% (1)
- Power Electronics & Drives: Unit: 1 Power Semiconductor DevicesDokument24 SeitenPower Electronics & Drives: Unit: 1 Power Semiconductor DevicesTapobroto ChatterjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2Dokument22 SeitenUnit 2SUSHMAGUPTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics ControlDokument19 SeitenPower Electronics ControlMohan KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics: Control Circuit Digital Circuit Power Electronic Circuit LoadDokument13 SeitenPower Electronics: Control Circuit Digital Circuit Power Electronic Circuit LoadNayon RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics and PLC: SCHEME/YEAR:C-16/3 YEAR/5 SEM Subject Code: Ee-504Dokument76 SeitenPower Electronics and PLC: SCHEME/YEAR:C-16/3 YEAR/5 SEM Subject Code: Ee-504rathina4careerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power UNIT I PDFDokument39 SeitenPower UNIT I PDFNoor WaleedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyristors: Bidirectional Trigger Diode (DIAC)Dokument16 SeitenThyristors: Bidirectional Trigger Diode (DIAC)anthonyrobertxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide to Thyristor DevicesDokument30 SeitenGuide to Thyristor DevicesNaty SeyoumNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10-17 SCR Into, CommutationDokument45 Seiten10-17 SCR Into, CommutationAdnan MagsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Silicon Controlled RectifierDokument8 SeitenSilicon Controlled RectifierTrisha Camille NerieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Thyristors PDFDokument9 SeitenIntroduction To Thyristors PDFAnnie BordsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electronics (18ELN14/18ELN24) - Silicon Controlled Rectifier (Module 2)Dokument5 SeitenBasic Electronics (18ELN14/18ELN24) - Silicon Controlled Rectifier (Module 2)Shrishail BhatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20 Talking ElectronicsDokument23 Seiten20 Talking ElectronicsBalaki SrikanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20 Talking ElectronicsDokument23 Seiten20 Talking ElectronicsJohn Mike SardengNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20 Talking ElectronicsDokument23 Seiten20 Talking ElectronicsAXLLE RHOESS DOMUGHO. ELLOREGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment: Trigering of SCRDokument7 SeitenAssignment: Trigering of SCRAb CNoch keine Bewertungen
- THYRISTORDokument25 SeitenTHYRISTORandreasmagaka11Noch keine Bewertungen
- SCR Power Control Circuit ExplainedDokument6 SeitenSCR Power Control Circuit ExplainedEric BiscochoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCR Power Control CircuitDokument8 SeitenSCR Power Control CircuitRyan Joseph BalmacedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Silicon Controlled Rectifier SCR - Two Transistor Model - Operating PrincipleDokument24 SeitenSilicon Controlled Rectifier SCR - Two Transistor Model - Operating PrinciplesixfacerajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Silicon-Controlled Rectifier: A High Power SCRDokument8 SeitenSilicon-Controlled Rectifier: A High Power SCRPaarthibba KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pe PPT PDFDokument268 SeitenPe PPT PDFtushar agale100% (1)
- Batangas State University Alangilan - Main Campus Ii Electrical and Computer Engineering DepartmentDokument15 SeitenBatangas State University Alangilan - Main Campus Ii Electrical and Computer Engineering DepartmentKarenMacalaladTanangNoch keine Bewertungen
- DET40073 - Topic 1Dokument54 SeitenDET40073 - Topic 1KuhaanProNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCR MechatronicsDokument50 SeitenSCR MechatronicsBefu HailuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power ElectronicsDokument11 SeitenPower ElectronicsRAHUL MOINoch keine Bewertungen
- Unidirectional ThyristorDokument5 SeitenUnidirectional ThyristorArvin Dexter De CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment #10-Using SCRS: Hands-On RadioDokument2 SeitenExperiment #10-Using SCRS: Hands-On RadioAnonymous ptCa270Uy2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Silicon Controlled RectifierDokument13 SeitenSilicon Controlled RectifierdhanshreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semiconductor Power Switching DevicesDokument30 SeitenSemiconductor Power Switching Devicesबृजभूषणशर्माNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCR, Traic, Diac ReportDokument19 SeitenSCR, Traic, Diac ReportPravin Gareta60% (5)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- DMBS Asgnmt 3Dokument2 SeitenDMBS Asgnmt 3abhi404171Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case 3:09 CV 01494 MODokument13 SeitenCase 3:09 CV 01494 MOAnonymous HiNeTxLMNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Year Pak Studies (English Medium)Dokument134 Seiten2nd Year Pak Studies (English Medium)MUHAMMAD HASAN RAHIMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Draft Certificates Bg. Terang 306 - 7,557. 258mt Mt-2Dokument5 SeitenDraft Certificates Bg. Terang 306 - 7,557. 258mt Mt-2BOBY RAHMAN PURBANoch keine Bewertungen
- The Philosophy of EmoDokument2 SeitenThe Philosophy of EmoTed RichardsNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Tribological WaysDokument516 SeitenNew Tribological Waysskippytheclown100% (2)
- Interpretative Translation Theory EvaluationDokument13 SeitenInterpretative Translation Theory EvaluationAnastasia MangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Techno ReadDokument11 SeitenTechno ReadCelrose FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC Physics P2 2013 JuneDokument20 SeitenCSEC Physics P2 2013 JuneBill BobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sap HCM loclalization-EGDokument124 SeitenSap HCM loclalization-EGrania abdelghanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Copticmanuscript 00 CoelDokument468 SeitenCopticmanuscript 00 Coelbavly barsomNoch keine Bewertungen
- SkipTheFlip Physical PDFDokument230 SeitenSkipTheFlip Physical PDFSebi100% (4)
- (1964) AC 763 Help: House of Lords Chandler and OthersDokument22 Seiten(1964) AC 763 Help: House of Lords Chandler and OthersShehzad HaiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Gaona BrianDokument218 Seiten1 Gaona BrianElias Nicol100% (1)
- Philo 12Dokument2 SeitenPhilo 12Rachel LaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- PAG 03.1 - Determination of ResistivityDokument3 SeitenPAG 03.1 - Determination of ResistivityjmsonlNoch keine Bewertungen
- How The Government Was Formed After Prophet MuhammadDokument48 SeitenHow The Government Was Formed After Prophet MuhammadMUSALMAN BHAINoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study on Student Budgeting HabitsDokument41 SeitenA Study on Student Budgeting Habitsbornak BonalasNoch keine Bewertungen
- AntimonyDokument72 SeitenAntimony沈益Noch keine Bewertungen
- Essays in ExistentialismDokument4 SeitenEssays in Existentialismafibaixzyhpqmc100% (2)
- SF3 - 2022 - Grade 8 SAMPLEDokument2 SeitenSF3 - 2022 - Grade 8 SAMPLEANEROSE DASIONNoch keine Bewertungen
- IntroDokument1 SeiteIntroaravinthr1989Noch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Job Interview Tips For IntrovertsDokument5 Seiten5 Job Interview Tips For IntrovertsSendhil RevuluriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dissertation Le Juge Administratif Et Le Droit InternationalDokument8 SeitenDissertation Le Juge Administratif Et Le Droit InternationalPayPeopleToWritePapersWestValleyCityNoch keine Bewertungen
- 99 Names of Allah SWT and Mohammed (PBUH)Dokument11 Seiten99 Names of Allah SWT and Mohammed (PBUH)api-26870382100% (1)
- Teresa R. Ignacio, Represented by Her Attorney-In-fact, Roberto R. Ignacio, Petitioner, V. Office of The City Treasurer of Quezon City, Et. Al.Dokument2 SeitenTeresa R. Ignacio, Represented by Her Attorney-In-fact, Roberto R. Ignacio, Petitioner, V. Office of The City Treasurer of Quezon City, Et. Al.Pam Otic-ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Call HandlingDokument265 SeitenCall HandlingABHILASHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Management Accounting: ConceptsDokument47 SeitenAdvanced Management Accounting: ConceptsGEDDIGI BHASKARREDDYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Petitioner Respondent: Civil Service Commission, - Engr. Ali P. DaranginaDokument4 SeitenPetitioner Respondent: Civil Service Commission, - Engr. Ali P. Daranginaanika fierroNoch keine Bewertungen