Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
MGW Route Oveflow Towards BSC PDF
Hochgeladen von
anne_lize0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
36 Ansichten1 SeiteLoad sharing algorithm based on the Round Robin method is applied. A usable MG is An MG that is available, not manually blocked or gracefully locked, appropriate from MG congestion control point of view. An MG is considered as congested if its Media Gateway congestion (MC) value is greater than zero.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
MGW route oveflow towards BSC.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenLoad sharing algorithm based on the Round Robin method is applied. A usable MG is An MG that is available, not manually blocked or gracefully locked, appropriate from MG congestion control point of view. An MG is considered as congested if its Media Gateway congestion (MC) value is greater than zero.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
36 Ansichten1 SeiteMGW Route Oveflow Towards BSC PDF
Hochgeladen von
anne_lizeLoad sharing algorithm based on the Round Robin method is applied. A usable MG is An MG that is available, not manually blocked or gracefully locked, appropriate from MG congestion control point of view. An MG is considered as congested if its Media Gateway congestion (MC) value is greater than zero.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
MGW route oveflow towards BSC
Facts from available docs:
During the selection of an MG (Media Gateway) from an MGG (Media Gateway
Group) a load sharing algorithm based on the Round Robin method is applied.
According to this algorithm the MGs of an MGG are arranged in a circular list where
the last selected MG is marked. In a subsequent selection attempt towards the MGG
the search for a usable MG (see 3rd point for meaning) starts from the MG next to the
last selected MG. If an MG is finally selected from that MGG it is marked as being the
last selected. In this way an even load distribution is implemented among the MGs
of an MGG.
During call setup MSC selects a media gateway from the BSC media gateway group
and attempts to seize a circuit on the route connected to that media gateway. If the
circuit seizure is not successful then MSC performs media gateway reselection
from the BSC media gateway group excluding the already attempted media
gateways. Reselection may be repeated until all the possible media gateways in the
BSC media gateway group have been attempted.
A usable MG is an MG that is available, not manually blocked or gracefully locked,
appropriate from MG congestion control point of view, with the proper MG profile
that match the received required capabilities and is not indicated to be excluded from
re-selection. For an emergency call or call requesting High Probability of Completion
(HPC) an MG is usable regardless of whether it is congested or not. If an MG is
already used in a call then it is usable for the specific call regardless of whether it is
congested, manually blocked or gracefully locked.
An MG is considered as congested if its Media Gateway Congestion (MC) value is
greater than zero. A congested MG will be selected only for a fraction of new calls
proportional to the value of its MC.
The load control function is implemented in the MGC (MSC-S) and regulates the
traffic load towards the MGs that the MGC controls. The objective of the load control
function is to maintain a high throughput during long-lasting overload. The regulation
is based on that the MGC decreases its traffic load towards MGs corresponding to
congested signalling routes as well as towards MGs that are congested. The traffic
reduction towards an MG is controlled by its MC.
Analysis of the above points:
Traffic distribution between MGWs to a BSC is evenly distributed according to a load
sharing algorithm. It would seem that the MSC continues with this even distribution
even though the other route is congested and in that case a MGW reselection is
performed (after unsuccessful seizure). Overall MGW congestion (according to an MC
value) is considered rather than route congestion when selecting the MGW. I cannot
ascertain if the same call is retained or lost during MGW reselection in case of an
unsuccessful seizure attempt.
Recommendation:
It is appropriate to have equal number of circuits to each MGW route towards a
particular BSC. Equal number of circuits will avoid unbalanced route utilization and
congestion towards one MGW route while the other route is not congested.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Introduction To Dialogic Continuous Speech Processing: Application NoteDokument11 SeitenIntroduction To Dialogic Continuous Speech Processing: Application Noteanne_lizeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Here Are Some Tips To Remember When Storing and Using FoodsDokument2 SeitenHere Are Some Tips To Remember When Storing and Using Foodsanne_lizeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cause CodesDokument7 SeitenCause Codesanne_lizeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conversion Calculators For Power and VSWRDokument3 SeitenConversion Calculators For Power and VSWRStarLink1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Dialogic Continuous Speech Processing: Application NoteDokument11 SeitenIntroduction To Dialogic Continuous Speech Processing: Application Noteanne_lizeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model TrafficDokument36 SeitenModel Trafficanne_lizeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spatiotemporal Interference Rejection Combining: David Ast Ely and BJ Orn OtterstenDokument21 SeitenSpatiotemporal Interference Rejection Combining: David Ast Ely and BJ Orn OtterstenAminreza PournorouzNoch keine Bewertungen
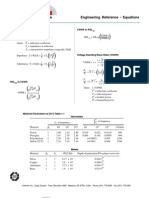
- Engineering Reference - Equations: Voltage Reflection Coefficient VSWR To RSLDokument5 SeitenEngineering Reference - Equations: Voltage Reflection Coefficient VSWR To RSLanne_lizeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Specialized Epic EVO 2021Dokument3 SeitenSpecialized Epic EVO 2021MTB-VCONoch keine Bewertungen
- LCD panel and module replacement parts for saleDokument1 SeiteLCD panel and module replacement parts for saleValeria bolañosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me 2403 Power Plant Engineering - Short Question and AnswersDokument16 SeitenMe 2403 Power Plant Engineering - Short Question and AnswersBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0100CT1901 Sec-23 102520202Dokument120 Seiten0100CT1901 Sec-23 102520202Chandra SekaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine TimeDokument11 SeitenMachine TimeFRANCIS THOMASNoch keine Bewertungen
- F. M. 1Dokument3 SeitenF. M. 1Aashish PardeshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTML5 Element Cheatsheet 2019Dokument1 SeiteHTML5 Element Cheatsheet 2019vVvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acha Teff ThresherDokument62 SeitenAcha Teff ThresherTANKO BAKO100% (2)
- Export Promotion Councils - Final UpdatedDokument14 SeitenExport Promotion Councils - Final UpdatedUtkarsh SaxenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Culata JD 6466Dokument4 SeitenCulata JD 6466TECNOTRAC AldanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PLAXIS Tutorial ManualDokument124 SeitenPLAXIS Tutorial ManualPeteris Skels100% (2)
- Tugas Dinamika Struktur Shape Function - Kelompok 6Dokument8 SeitenTugas Dinamika Struktur Shape Function - Kelompok 6Mochammad Choirul RizkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PBV20N2 Service Manual PDFDokument244 SeitenPBV20N2 Service Manual PDFJack Norhy100% (1)
- MELHORES SITES DE INFOPRODUTOS PLR E SUAS RANKS NO ALEXADokument8 SeitenMELHORES SITES DE INFOPRODUTOS PLR E SUAS RANKS NO ALEXAAlexandre Silva100% (2)
- Abrasive Cleaning SystemDokument4 SeitenAbrasive Cleaning SystemSulfikar SalimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wulf 2018Dokument12 SeitenWulf 2018Nida iqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- By Himanshu Panwar Asst. Prof. Civil Engineering Department AkgecDokument34 SeitenBy Himanshu Panwar Asst. Prof. Civil Engineering Department AkgecAlok0% (1)
- D4. SBS Iran PDFDokument10 SeitenD4. SBS Iran PDFMohammed QaderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Manuscript Word TemplateDokument4 SeitenScience Manuscript Word TemplatepopularsodaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Miniature Maglev Using Hybrid MagnetsDokument4 SeitenDesign of Miniature Maglev Using Hybrid MagnetsErmin FazlicNoch keine Bewertungen
- VisQ Queue Manager System Guide Version 10.3Dokument27 SeitenVisQ Queue Manager System Guide Version 10.3MSC Nastran Beginner100% (1)
- Project Report PDFDokument4 SeitenProject Report PDFPradeep VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BUK9Y53-100B DatasheetDokument12 SeitenBUK9Y53-100B Datasheetisomeso21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Definitions of CEC2017 Benchmark Suite Final Version UpdatedDokument34 SeitenDefinitions of CEC2017 Benchmark Suite Final Version Updatedpc100% (1)
- WFT Composite PlugsDokument11 SeitenWFT Composite Plugsahmad haqkim muhamad malackNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS en 50160 2007Dokument24 SeitenBS en 50160 2007Pepe Eulogio OrtízNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASV Posi-Track PT-80 Track Loader Parts Catalogue Manual PDFDokument14 SeitenASV Posi-Track PT-80 Track Loader Parts Catalogue Manual PDFfisekkkdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green Finance For Green GrowthDokument24 SeitenGreen Finance For Green GrowthSreejith BhattathiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compressive Strength, Chloride Diffusivity and Pore Structure of High Performance Metakaolin and Silica Fume ConcreteDokument8 SeitenCompressive Strength, Chloride Diffusivity and Pore Structure of High Performance Metakaolin and Silica Fume ConcreteAboalmaail AlaminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lot Inspection Report For LPG New CylindersDokument3 SeitenLot Inspection Report For LPG New CylindersJagannath MajhiNoch keine Bewertungen