Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Bio 11 - Handout For Lectures 1-6 (Summary)
Hochgeladen von
Steffi Gatdula0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
95 Ansichten1 SeiteHandout for Bio 11
Originaltitel
Bio 11 - Handout for Lectures 1-6 (Summary)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenHandout for Bio 11
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
95 Ansichten1 SeiteBio 11 - Handout For Lectures 1-6 (Summary)
Hochgeladen von
Steffi GatdulaHandout for Bio 11
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
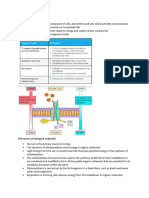
Figure 10.
23
MAKE CONNECTIONS
The Working Cell
This figure illustrates how a generalized plant cell
functions, integrating the cellular activities you
learned about in Chapters 510.
Movement Across Cell Membranes
(Chapter 7)
DNA
Nucleus
Energy Transformations in the Cell:
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
(Chapters 810)
mRNA
9 Water diffuses into and out of the cell
directly through the plasma membrane and
by facilitated diffusion through aquaporins.
See Figure 7.1.
7 In chloroplasts, the process of photosynthesis uses the energy
Nuclear
pore
10 By passive transport, the CO2 used in
of light to convert CO2 and H2O to organic molecules, with
O2 as a by-product. See Figure 10.22.
photosynthesis diffuses into the cell and the
O2 formed as a by-product of photosynthesis
diffuses out of the cell. Both solutes move
down their concentration gradients.
See Figures 7.10 and 10.22.
8 In mitochondria, organic molecules are broken down by
Protein
3
Ribosome
Protein
in vesicle
cellular respiration, capturing energy in molecules of ATP,
which are used to power the work of the cell, such as
protein synthesis and active transport. CO2 and H2O are
by-products. See Figures 8.98.11, 9.2, and 9.16.
Rough endoplasmic
reticulum (ER)
mRNA
CO2
in chloroplast
H2O
Protein
synthesis of mRNA, which moves to the
cytoplasm. See Figures 5.23 and 6.9.
in the cytosol or binds to the rough ER. Proteins
are synthesized. See Figures 5.23 and 6.10.
Exocytosis (shown in step 5) and endocytosis
move larger materials out of and into the cell.
See Figures 7.9 and 7.19.
7 Photosynthesis
Vesicle
forming
Golgi
apparatus
1 In the nucleus, DNA serves as a template for the
2 mRNA attaches to a ribosome, which remains free
by ATP) is used to transport a solute against
its concentration gradient. See Figure 7.16.
Vacuole
Flow of Genetic Information in the Cell:
DNA
RNA
Protein (Chapters 57)
11 In active transport, energy (usually supplied
ATP
Organic
molecules
6
Plasma
membrane
O2
3 Proteins and membrane produced by the rough
ER flow in vesicles to the Golgi apparatus, where
they are processed. See Figures 6.15 and 7.9.
ATP
ATP
4 Transport vesicles carrying proteins pinch off
11
M A K E C O N N E C T I O N S The first enzyme that functions in glycolysis is hexokinase. In this plant cell, describe the entire process
from the Golgi apparatus. See Figure 6.15.
5 Some vesicles merge with the plasma membrane,
releasing proteins by exocytosis. See Figure 7.9.
by which this enzyme is produced and where it functions, specifying the locations for each step. (See Figures 5.18, 5.23, and 9.9.)
10
6 Proteins synthesized on free ribosomes stay in
the cell and perform specific functions; examples
include the enzymes that catalyze the reactions
of cellular respiration and photosynthesis. See
Figures 9.7, 9.9, and 10.19.
Transport
pump
ATP
Cellular respiration
in mitochondrion
9
A N I M AT I O N
Cell wall
O2
Visit the Study Area in
MasteringBiology for BioFlix 3-D Animations
in Chapters 6, 7, 9, and 10. BioFlix Tutorials can
also be assigned in MasteringBiology.
CO2
206
UNIT TWO
H2O
The Cell
Biology 11 Exam 1
CHAPTER 10
Photosynthesis
207
/steffigatdula/
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Aircraft Classifications - RfsDokument69 SeitenAircraft Classifications - RfsPaulo SouzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ap Biology Exam Review Questions OnlyDokument20 SeitenAp Biology Exam Review Questions Onlyapi-57781915100% (1)
- Gen Bio Module 1Dokument18 SeitenGen Bio Module 1Mark Kenneth CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipeline Shore Approach Design Case Study PDFDokument10 SeitenPipeline Shore Approach Design Case Study PDFJohn RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 2 Cells Membranes Energy Metabolism Biol101 f13Dokument8 SeitenExam 2 Cells Membranes Energy Metabolism Biol101 f13api-249772989Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 HL Bio Exam AnswersDokument3 Seiten2016 HL Bio Exam AnswersEricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pirates A Dungeon World SourcebookDokument14 SeitenPirates A Dungeon World SourcebookLloyd Collins100% (1)
- Fersa Solutions - ZF 16Dokument66 SeitenFersa Solutions - ZF 16Julio Harold Urquizo RojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 8 Study GuideDokument4 SeitenCH 8 Study Guideapi-3423342160% (1)
- Marine PollutionDokument29 SeitenMarine PollutionSarah Rivera100% (1)
- Air India ProjectDokument26 SeitenAir India Projectjenkin100% (2)
- ASM Orals Questions - KrishnaDokument3 SeitenASM Orals Questions - KrishnaVarun Agrawal100% (1)
- Chem 31.1 Midterms Reviewer Experiment 1: Solubility of Organic CompoundsDokument6 SeitenChem 31.1 Midterms Reviewer Experiment 1: Solubility of Organic CompoundsSteffi GatdulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RR 12-99Dokument16 SeitenRR 12-99doraemoanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Completely Compiled BiologyDokument236 SeitenCompletely Compiled BiologyKyu9930100% (1)
- Belt Stacker BSDokument69 SeitenBelt Stacker BSRahmat HidayatNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM 40.1 BUFFER REVIEWDokument5 SeitenCHEM 40.1 BUFFER REVIEWSteffi GatdulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Manuel For L1 - Xplorer CherokeeDokument16 SeitenUser Manuel For L1 - Xplorer CherokeeIonut Gabriel GavrilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOL 112 Practice Final December 2012Dokument15 SeitenBIOL 112 Practice Final December 2012SeoAm HurNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Biology Essay QuestionsDokument3 SeitenIB Biology Essay QuestionsMadeeha KalsekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Figure 14-5the Relationship Between Mitochondria and MicrotubulesDokument6 SeitenFigure 14-5the Relationship Between Mitochondria and MicrotubulesDewi simangunsongNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 9 Reading GuideDokument15 SeitenCH 9 Reading GuideKapil NathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions of The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum: Synthesis of Proteins On Membrane-Bound Versus Free RibosomesDokument7 SeitenFunctions of The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum: Synthesis of Proteins On Membrane-Bound Versus Free RibosomesDanie MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 - Study Guide - AP BiologyDokument6 SeitenUnit 3 - Study Guide - AP BiologyMishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Þ CC) C' (CC& +C++C: CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCDokument12 SeitenÞ CC) C' (CC& +C++C: CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCgauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- DP2 HomeworkDokument3 SeitenDP2 HomeworkMouga MaevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP BIO EXAM ESSAY Q'SDokument37 SeitenAP BIO EXAM ESSAY Q'SBeatrice MallariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breakdown of GlucoseDokument2 SeitenBreakdown of GlucoseJAYLEN TRACEYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chromatophore Manuscript Final 03 24 19Dokument25 SeitenChromatophore Manuscript Final 03 24 19SigmundNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitochondria: Mitochondria and Oxidative Phosphorylation Molecular Mechanisms of Electron Transport and Proton PumpingDokument55 SeitenMitochondria: Mitochondria and Oxidative Phosphorylation Molecular Mechanisms of Electron Transport and Proton Pumpingnokate konkoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- UG S5 Cell Bio & Mol Bio Scheme Jan 2023Dokument13 SeitenUG S5 Cell Bio & Mol Bio Scheme Jan 2023beatriceelistenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Questions02 03Dokument7 SeitenAnswer Questions02 03yo-chengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 06Dokument39 SeitenChapter 06NnleinomNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATP PRODUCTION IN CELLULAR RESPIRATIONDokument24 SeitenATP PRODUCTION IN CELLULAR RESPIRATIONCLIER GEROMALANoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisDokument2 SeitenCellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisDonna O.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jesse Science DocumentDokument7 SeitenJesse Science Documentapi-260887014Noch keine Bewertungen
- Confidential: ATP SynthetaseDokument5 SeitenConfidential: ATP SynthetaseazszahNoch keine Bewertungen
- easter-revision-day-1-work-book-1712165354Dokument31 Seiteneaster-revision-day-1-work-book-1712165354robinsonbryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18 Quarter 1 Module 18-AEROBICDokument22 Seiten18 Quarter 1 Module 18-AEROBICTheresa Rebullos BileNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerobic Respiration RevisionDokument10 SeitenAerobic Respiration RevisionJenny JanssonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Achilike Sbi Assignment 1Dokument6 SeitenAchilike Sbi Assignment 1skillsj123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Signaling Study GuideDokument19 SeitenCell Signaling Study GuideSamuel Schatzman100% (1)
- Cellular Respiration: MitochondriaDokument8 SeitenCellular Respiration: MitochondriaMaryRoseTrajada100% (1)
- Bioenergetics and Metabolism - MitochondrionDokument5 SeitenBioenergetics and Metabolism - Mitochondrionpaul catalinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 3 PhotosynthesisDokument39 Seiten8 3 PhotosynthesisKhin (Darin) Hnin PhyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artificial Photosyntetic Cell Samuel Nature 2019Dokument10 SeitenArtificial Photosyntetic Cell Samuel Nature 2019José Antonio Silva NetoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 Study Guide - VMDokument4 SeitenChapter 9 Study Guide - VMVM27340% (1)
- Cell respiration and the structure of mitochondriaDokument16 SeitenCell respiration and the structure of mitochondria한서현Noch keine Bewertungen
- Genes and Health: Activity 2.23 Check Your Notes For Topic 2Dokument6 SeitenGenes and Health: Activity 2.23 Check Your Notes For Topic 2DennisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materi Minggu 5Dokument84 SeitenMateri Minggu 5HafizahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap. 6B Enzymes: - Introduction To Enzymes - How Enzymes Work - Enzyme Kinetics As An Approach ToDokument28 SeitenChap. 6B Enzymes: - Introduction To Enzymes - How Enzymes Work - Enzyme Kinetics As An Approach ToRock SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular Respiration Model SHODokument4 SeitenCellular Respiration Model SHODeana Amira MontgomeryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure and Function Matching KEYDokument3 SeitenCell Structure and Function Matching KEYJustin Lin100% (1)
- IISC Bangalore PH.D Entrance Question Paper 2013Dokument0 SeitenIISC Bangalore PH.D Entrance Question Paper 2013Abhay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- REVISION 3Dokument27 SeitenREVISION 3Biology BảoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Figure 5-9: Punnett Square Depicting The Cross Between A Homozygous Dominant and A Heterozygous OrganismDokument15 SeitenFigure 5-9: Punnett Square Depicting The Cross Between A Homozygous Dominant and A Heterozygous OrganismRumana AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- FullDokument72 SeitenFullCamille FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Biology Syllabus CurriculumDokument17 SeitenIB Biology Syllabus Curriculumju5940Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 5 Reading WorksheetDokument3 SeitenChap 5 Reading WorksheetSarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bmotor BioenergyDokument12 SeitenBmotor BioenergydsecondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- As Biology Unit 2 Key Terms and DefinitionsDokument6 SeitenAs Biology Unit 2 Key Terms and DefinitionsVIctoriakayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen Bio 1 Second QTR Module RevisedDokument37 SeitenGen Bio 1 Second QTR Module RevisedMichaela CasabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Respiration Lab BackgroundDokument4 SeitenCell Respiration Lab Backgroundapi-553676905Noch keine Bewertungen
- LECTURE 4 CARBOHYDRATE-GLYCOLYSISDokument20 SeitenLECTURE 4 CARBOHYDRATE-GLYCOLYSISBiology BảoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy and RespirationDokument11 SeitenEnergy and Respirationririrachma fitriahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 BiochemistryDokument29 SeitenModule 2 BiochemistryLaarnie LinggayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry Lect 5 2011 Colour 2 Slides Per PageDokument11 SeitenBiochemistry Lect 5 2011 Colour 2 Slides Per Pageyr0668Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Level Biology Unit 7 Notes on Respiration and PhotosynthesisDokument18 SeitenA Level Biology Unit 7 Notes on Respiration and PhotosynthesisJody-Ann Mears0% (1)
- Biochemistry II Notes - Module 1Dokument32 SeitenBiochemistry II Notes - Module 1lalcala2Noch keine Bewertungen
- 73aeb33f-6dd9-4f48-b8b4-feb351a95529Dokument9 Seiten73aeb33f-6dd9-4f48-b8b4-feb351a95529layanhaliloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self-Assembly: From Surfactants to NanoparticlesVon EverandSelf-Assembly: From Surfactants to NanoparticlesRamanathan NagarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 - Methods in The Study of BiologyDokument3 Seiten4 - Methods in The Study of BiologySteffi GatdulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDRI TablesDokument7 SeitenPDRI TablesCamille Chen100% (1)
- 3D - Life Structure, Function and Control (Cell Cycle)Dokument8 Seiten3D - Life Structure, Function and Control (Cell Cycle)Steffi GatdulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3C - Life Structure, Function and Control (Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration)Dokument6 Seiten3C - Life Structure, Function and Control (Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration)Steffi GatdulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3B - Life Structure, Function and Control (Cell Parts, Functions and Types)Dokument8 Seiten3B - Life Structure, Function and Control (Cell Parts, Functions and Types)Steffi GatdulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3A - Life Structure, Function and Control (Chemistry of Life and Cell)Dokument7 Seiten3A - Life Structure, Function and Control (Chemistry of Life and Cell)Steffi GatdulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 & 2 - Concept and Manifestations of LifeDokument5 Seiten1 & 2 - Concept and Manifestations of LifeSteffi GatdulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fine File DataDokument1 SeiteFine File DataFusi ChobokoaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP50 Installation PlusDokument142 SeitenAP50 Installation PlusPeterJBloomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Megatrail Owner S ManualDokument14 SeitenMegatrail Owner S ManualDownhillnewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transportation in KarnatakaDokument51 SeitenTransportation in KarnatakaBidyut RayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Freight Rate - Informal/Formal Entry: Forwarding Charges Amount Local ChargesDokument2 SeitenAir Freight Rate - Informal/Formal Entry: Forwarding Charges Amount Local ChargesCarmelita BulawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2017 Glider Kit FlyerDokument2 Seiten2017 Glider Kit FlyerHuaman Chavez Jesus AngelNoch keine Bewertungen
- PC 1-3 Wheel-Rail Interaction Fundamentals WRI 2017 - 20170604Dokument109 SeitenPC 1-3 Wheel-Rail Interaction Fundamentals WRI 2017 - 20170604Hà Tiến ĐôngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abb Indian Railways PDFDokument6 SeitenAbb Indian Railways PDFDeepak GehlotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Otc 6488Dokument6 SeitenOtc 6488marranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Edwin HWoodruff ASelectionDokument25 Seiten1 Edwin HWoodruff ASelectionEswar StarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCM 2015 Understanding SCM RevisedDokument40 SeitenSCM 2015 Understanding SCM RevisedsumeetpatnaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultrasonic Testing of Discontinuties of Metal of Gear Blanks of Rolling StockDokument7 SeitenUltrasonic Testing of Discontinuties of Metal of Gear Blanks of Rolling StockEswin Paico de la CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ten CodesDokument2 SeitenTen CodesLhye CarmonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 18 - Pavement DesignDokument18 SeitenChapter 18 - Pavement DesignDiyoke HenryNoch keine Bewertungen
- EM 1110-2-503 - Design of Small Water Systems - WebDokument83 SeitenEM 1110-2-503 - Design of Small Water Systems - WebPDHLibraryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Considerations in Planning The Construction StagingDokument58 SeitenConsiderations in Planning The Construction StagingHenry TuraldeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tendernotice 1 59 Aq9jzhDokument2 SeitenTendernotice 1 59 Aq9jzhkawatgharerNoch keine Bewertungen
- KTM LC4 400 - LsemilDokument50 SeitenKTM LC4 400 - LsemilAngel VázquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stainless Steel Evaporator Engineering ManualDokument52 SeitenStainless Steel Evaporator Engineering ManualGerber GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sati, 2011Dokument147 SeitenSati, 2011Muhammad ArshadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 National Steel Corporation vs. CA, 283 SCRA 45Dokument35 Seiten10 National Steel Corporation vs. CA, 283 SCRA 45blessaraynesNoch keine Bewertungen