Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
National Tuberculosis Program
Hochgeladen von
gecalian0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
23 Ansichten2 SeitenCHN
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCHN
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
23 Ansichten2 SeitenNational Tuberculosis Program
Hochgeladen von
gecalianCHN
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
National Tuberculosis Program
Vision: A country where TB is no longer a public health problem.
Mission: Ensure that TB DOTS services are available, accessible, and
affordable to the communities in collaboration with the LGUs and other partners.
Signs and Symptoms
General signs and symptoms include:
Fever
Chills
night sweats
loss of appetite
weight loss
fatigue
Significant nail clubbing may also occur
Diagnosis Test
Diagnosing active tuberculosis based merely on signs and symptoms is difficult,
as is diagnosing the disease in those who are immunosuppressed. A diagnosis of TB
should, however, be considered in those with signs of lung disease or constitutional
symptoms lasting longer than two weeks. A chest X-ray and multiple sputum cultures for
acid-fast bacilli are typically part of the initial evaluation. Interferon- release assays and
tuberculin skin tests are of little use in the developing world. IGRA have similar
limitations in those with HIV.
A definitive diagnosis of TB is made by identifying M. tuberculosis in a clinical
sample (e.g. sputum, pus, or a tissue biopsy). However, the difficult culture process for
this slow-growing organism can take two to six weeks for blood or sputum culture. Thus,
treatment is often begun before cultures are confirmed.
Nucleic acid amplification tests and adenosine deaminase testing may allow
rapid diagnosis of TB. These tests, however, are not routinely recommended, as they
rarely alter how a person is treated. Blood tests to detect antibodies are not specific or
sensitive, so they are not recommended.
Treatment with side effects
Different medications used to treat tuberculosis are associated with specific side effects:
Isoniazid may make you feel tired or nauseous or make you lose your appetite. It can
cause numbness or tingling in your hands or feet, but this is rare in well-nourished
people.
Rifampicin can reduce the effectiveness of the contraceptive pill and some other
medications. It is important to advise the doctor who prescribes your TB treatment about
any other medicines you are taking. Women taking the contraceptive pill may need to
discuss other forms of contraception with their general practitioner or an advisor at a
family planning clinic. If you have lens implants or wear soft contact lenses, inform your
doctor, as rifampicin can stain them. Rifampicin will cause a pinkish/orange
discolouration of your urine, saliva and sweat. This side effect is harmless so you should
not be concerned.
Ethambutol or Myambutol can cause visual problems. Your eyesight will be checked
during treatment, but you should stop taking the medication if your vision is affected and
call your doctor straight away.
Pyrazinamide can lead to nausea and a loss of appetite. It is usually only taken for
the first two to three months of treatment. Consult with your doctor if you develop
unexplained rashes, fever, aches or joint pains.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Assignment in Community Health Nursing Savarez Aliza Grace F. BSN II-ADokument4 SeitenAssignment in Community Health Nursing Savarez Aliza Grace F. BSN II-AYUBaromNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary TBDokument2 SeitenPulmonary TBPrincess Gwyneth MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- TB PamphletDokument2 SeitenTB PamphletMuhammad Kamal0% (1)
- NNTHDokument6 SeitenNNTHGuezil Joy DelfinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Susceptibility of AntimicrobialDokument3 SeitenSusceptibility of AntimicrobialbeleifheozNoch keine Bewertungen
- FRSTDokument12 SeitenFRSTGuezil Joy DelfinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plans: Nursing Diagnosis and Assessment, Nursing Interventions GuideVon EverandNursing Care Plans: Nursing Diagnosis and Assessment, Nursing Interventions GuideBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- IBONG ADARNA at RigoreDokument2 SeitenIBONG ADARNA at RigoreRomel RigoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Causative Agent: Mycobacterium TuberculosisDokument20 SeitenCausative Agent: Mycobacterium TuberculosisDivya TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study For TuberculosisDokument7 SeitenCase Study For TuberculosisGabbii CincoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FFTHDokument13 SeitenFFTHGuezil Joy DelfinNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 4 - DIAGNOSIS Part 1Dokument3 SeitenUNIT 4 - DIAGNOSIS Part 1Anonymous Wfl201YbYoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Botulism: Physical ExamDokument13 SeitenBotulism: Physical ExamAlexandria P. OrcajadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tuberculosis: by Rohma XI A2, Roll No.-2Dokument15 SeitenTuberculosis: by Rohma XI A2, Roll No.-2fur ballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infliximab: Drug Treatment InformationDokument7 SeitenInfliximab: Drug Treatment InformationAlin-Ionuț SălcianuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ciclosporin Update June 2020 - Lay Reviewed June 2020Dokument6 SeitenCiclosporin Update June 2020 - Lay Reviewed June 2020Gee B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Infliximab Update April 2016 - Lay Reviewed March 2016Dokument6 SeitenInfliximab Update April 2016 - Lay Reviewed March 2016Naveed KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TuberculosisDokument10 SeitenTuberculosisagnescheruseryNoch keine Bewertungen
- USMLE Step 3 Lecture Notes 2021-2022: Internal Medicine, Psychiatry, EthicsVon EverandUSMLE Step 3 Lecture Notes 2021-2022: Internal Medicine, Psychiatry, EthicsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (9)
- Moderate To Severe Psoriasis: Biologic Drugs: Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-alpha) BlockersDokument8 SeitenModerate To Severe Psoriasis: Biologic Drugs: Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-alpha) BlockersGabriellaSepthendriPutriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Management Review 2023-2024: Volume 2: USMLE Step 3 and COMLEX-USA Level 3Von EverandClinical Management Review 2023-2024: Volume 2: USMLE Step 3 and COMLEX-USA Level 3Noch keine Bewertungen
- April Health UpdateDokument3 SeitenApril Health UpdateNcediswaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ObjectivesDokument6 SeitenObjectivesElaine Jean UayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TB AssignmentDokument12 SeitenTB AssignmentKieth Roland PalosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIG COVID19 GuideDokument20 SeitenAIG COVID19 Guidedinesh kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- COV GuideDokument20 SeitenCOV GuidepuNoch keine Bewertungen
- LDN Information PackDokument17 SeitenLDN Information PackkindheartedNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETHAMBUTOLDokument2 SeitenETHAMBUTOLXerxes DejitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lupus: Natural Treatment Protocols for Complete RecoveryVon EverandLupus: Natural Treatment Protocols for Complete RecoveryNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Essential Kidney Disease Cookbook: Over 150 Delicious Kidney-Friendly Meals to Ensure You Manage Your Kidney DiseaseVon EverandThe Essential Kidney Disease Cookbook: Over 150 Delicious Kidney-Friendly Meals to Ensure You Manage Your Kidney DiseaseNoch keine Bewertungen
- MDR-TB Patient Education Flipchart FilipinoDokument23 SeitenMDR-TB Patient Education Flipchart FilipinoUnica Ija N RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mold Illness Diet: A Beginner's 3-Week Step-by-Step Guide to Healing and Detoxifying the Body through Diet, with Curated Recipes and a Sample Meal PlanVon EverandMold Illness Diet: A Beginner's 3-Week Step-by-Step Guide to Healing and Detoxifying the Body through Diet, with Curated Recipes and a Sample Meal PlanBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris ArifDokument6 SeitenTugas Bahasa Inggris ArifAldila PuspaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Heal Your Gut Naturally in 90 Days!Von EverandIrritable Bowel Syndrome: Heal Your Gut Naturally in 90 Days!Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tuberculosis, Diabetes, CancerDokument21 SeitenTuberculosis, Diabetes, CancerCarolina Calle HerreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Covid-19 Info DriveDokument61 SeitenCovid-19 Info DriveMac MacapilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agranulocytosis, A Simple Guide to The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandAgranulocytosis, A Simple Guide to The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- TB Hiv CoinfectionDokument29 SeitenTB Hiv CoinfectionVinobhachowdary DondapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hiv Co-Morbidities, Ois and NcdsDokument49 SeitenHiv Co-Morbidities, Ois and NcdszawadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSN3-9A Tuberculosis or TBDokument4 SeitenBSN3-9A Tuberculosis or TBenelrahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Management Review 2023-2024: Volume 1: USMLE Step 3 and COMLEX-USA Level 3Von EverandClinical Management Review 2023-2024: Volume 1: USMLE Step 3 and COMLEX-USA Level 3Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris MarselinaDokument6 SeitenTugas Bahasa Inggris MarselinaAldila PuspaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Advisory For VolunteersDokument4 SeitenHealth Advisory For VolunteersHerbert Q. CarpioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Clindamycin, Ipatropium BromideDokument8 SeitenDrug Study Clindamycin, Ipatropium Bromidepaupaulala100% (2)
- Epilepsy - Case StudyDokument11 SeitenEpilepsy - Case StudyHarry Sivia100% (3)
- Selpi Tiara Ariska TranslateDokument18 SeitenSelpi Tiara Ariska TranslateSelpi TiaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Ana Claudia Domene's Multiple Sclerosis and (lots of) Vitamin DVon EverandSummary of Ana Claudia Domene's Multiple Sclerosis and (lots of) Vitamin DNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatty Liver Detox Cleanse: A Beginner's 3-Week Step-by-Step Guide to Managing Fatty Liver Symptoms Including Fatigue with Recipes and a Meal PlanVon EverandFatty Liver Detox Cleanse: A Beginner's 3-Week Step-by-Step Guide to Managing Fatty Liver Symptoms Including Fatigue with Recipes and a Meal PlanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Thesis PDFDokument8 SeitenMycobacterium Tuberculosis Thesis PDFrebeccabordescambridge100% (2)
- Lpu - St. Cabrini School of Health Sciences, Inc.: College of Allied MedicineDokument11 SeitenLpu - St. Cabrini School of Health Sciences, Inc.: College of Allied MedicineRaven TeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dengue Fever Health TeachingDokument9 SeitenDengue Fever Health TeachingChris Tine CaccamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastritis: Is An, Irritation, or Erosion of The Lining of The - It Can Occur Suddenly (Acute) or Gradually (Chronic)Dokument26 SeitenGastritis: Is An, Irritation, or Erosion of The Lining of The - It Can Occur Suddenly (Acute) or Gradually (Chronic)Teodora AlexandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- TreatmentDokument2 SeitenTreatmentAngelica GuintoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes TuberculosisDokument6 SeitenLecture Notes TuberculosisDENNIS N. MUÑOZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris NoraDokument6 SeitenTugas Bahasa Inggris NoraAldila PuspaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument8 SeitenNursing Care PlanVincent QuitorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Granulomatosis polyangiitis, (Wegener Granulomatosis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandGranulomatosis polyangiitis, (Wegener Granulomatosis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition of DiagnosisDokument42 SeitenDefinition of DiagnosisgecalianNoch keine Bewertungen
- CA Labs 9th AbgDokument2 SeitenCA Labs 9th AbggecalianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnostic TestDokument23 SeitenDiagnostic TestgecalianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication DisorderDokument3 SeitenCommunication DisordergecalianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Possible DrugsDokument8 SeitenPossible DrugsgecalianNoch keine Bewertungen
- DrugDokument36 SeitenDruggecalian100% (1)
- Drug StudyDokument34 SeitenDrug StudygecalianNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 NCP CompileDokument21 Seiten14 NCP CompilegecalianNoch keine Bewertungen
- TopicDokument2 SeitenTopicgecalianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument23 SeitenDrug StudyEdward Baes33% (3)
- Anxiolytics: What Are Anti-Anxiety Drugs?Dokument4 SeitenAnxiolytics: What Are Anti-Anxiety Drugs?Dr-Mohamed EssawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Geneology Tree: Felix PablitoDokument1 SeiteMy Geneology Tree: Felix PablitogecalianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Related Nursing TheoryDokument1 SeiteRelated Nursing TheorygecalianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument60 SeitenDrug StudygecalianNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Teaching Plan On Dengue FeverDokument1 SeiteA Teaching Plan On Dengue FevergecalianNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Tuberculosis ProgramDokument2 SeitenNational Tuberculosis ProgramgecalianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Published-Pdf-327-6-10. IJZAB ID No. 327 PDFDokument6 SeitenPublished-Pdf-327-6-10. IJZAB ID No. 327 PDFIJZABNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Emergencies and First AidDokument54 SeitenMedical Emergencies and First AidCeleste Coronel Dela Cruz100% (2)
- Update PMDT GuidelineDokument53 SeitenUpdate PMDT GuidelineTanto RusnantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homoeopathic Rmedy For ShockDokument2 SeitenHomoeopathic Rmedy For ShockSuhas IngaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Katak PDFDokument5 SeitenJurnal Katak PDF31122007Noch keine Bewertungen
- 18XX OutlawDokument4 Seiten18XX OutlawConnor BrassfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sitting Fox: Materials KeyDokument7 SeitenSitting Fox: Materials KeyVerónica TNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.movers Pratice Test - RW Part 1 - 2Dokument20 Seiten2.movers Pratice Test - RW Part 1 - 2Ngoc Huyen HoangNoch keine Bewertungen
- XtendaDokument2 SeitenXtendaAlexis CoronadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magical Pets v2.0 EnglishDokument2 SeitenMagical Pets v2.0 EnglishKing EntropyNoch keine Bewertungen
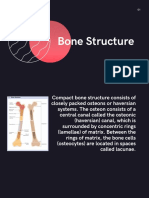
- Topic PPT Bone StructureDokument14 SeitenTopic PPT Bone StructureMoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- For Other Uses, See .: Frog (Disambiguation)Dokument6 SeitenFor Other Uses, See .: Frog (Disambiguation)Mari Creon A. BaumgardnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Norma BasalisDokument10 SeitenNorma BasalisArshad hussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- CrocodilesDokument3 SeitenCrocodilesPeculiarMemoriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Report of Nereis (Neanthes) Virens (Sars) An Epitoky Polychaete Worm From Middle Strait, Baratang, Andaman Island, IndiaDokument6 SeitenFirst Report of Nereis (Neanthes) Virens (Sars) An Epitoky Polychaete Worm From Middle Strait, Baratang, Andaman Island, IndiaresearchinbiologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Easy Kitten With Heart Amigurumi PDF Free PatternDokument6 SeitenEasy Kitten With Heart Amigurumi PDF Free PatternSandra100% (1)
- Letters From A Father To His Daughter CompressDokument84 SeitenLetters From A Father To His Daughter CompressThaw ThawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fish and Inverts of UtilaDokument4 SeitenFish and Inverts of UtilaMarx Lenin Nieto CcalleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 3 EVS Question Bank 1Dokument8 SeitenClass 3 EVS Question Bank 1ᴅᴇᴇᴘ ᴘʀᴀᴋᴀsʜ ᴍᴏᴅɪ xɪ-ᴅNoch keine Bewertungen
- Triangles of The NeckDokument65 SeitenTriangles of The NeckPaulo Duata100% (3)
- The Badness Within HimDokument6 SeitenThe Badness Within HimSteven Colin0% (1)
- W.a.S.P. Stage AnticsDokument7 SeitenW.a.S.P. Stage AnticsAndré LuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- TESTDokument5 SeitenTESTnoralizaaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEW ETHICS NNNNNNNNN)Dokument12 SeitenNEW ETHICS NNNNNNNNN)Mulugeta100% (1)
- The Wax # 9Dokument54 SeitenThe Wax # 9Emmanuel MilwaukeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIT1012 Human-Anatomy-And-Physiology ETH 1 AC37Dokument2 SeitenBIT1012 Human-Anatomy-And-Physiology ETH 1 AC37Vignesh AiyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kamasutra LengkapDokument104 SeitenKamasutra LengkapTjap TjoeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ImpressionDokument7 SeitenImpressionAnnisa Nur AmalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animals SimilesDokument1 SeiteAnimals SimilesacademiaedelNoch keine Bewertungen