Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
HRM, 437 Assessment Week
Hochgeladen von
SantoshKumarOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
HRM, 437 Assessment Week
Hochgeladen von
SantoshKumarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
HRM, 437 ASSESSMENT WEEK
where the banks would open branches. None of the three banks had till then any
branches (except for the sole attempt and that too a brief one by the Bank of Bengal
at Mirzapore in 1839) despite the way that the agreement had issued them such
power. In any case, when the three organization gatherings were ensured of the free
usage of government
Treasury equalities at spots where they would open branches, they set out on
branch advancement at a speedy pace. By 1876, the branches, workplaces and sub
associations of the three organization banks secured an expansive segment of the
genuine parts and an impressive parcel of the inland trade concentrates in India.
While the Bank of Bengal had eighteen branches including its head office, general
branches and sub workplaces, the Banks of Bombay and Madras had fifteen each.
Bank of Madras Note Dated 1861 for Rs.10
Organization Banks Act
The organization Banks Act, which came into operation on 1 May 1876, brought the
three organization banks under an ordinary statute with similar imprisonments on
business. The prohibitive relationship of the Government was, nevertheless, finished,
however the banks continued holding charge of general society commitment working
environments in the three organization towns, and the power of a bit of the
organization counterbalances. The Act moreover stipulated the making of Reserve
Treasuries at Calcutta, Bombay and Madras into which wholes over the foreordained
minimum conforms ensured to the organization banks at simply their head working
environments were to be held up. The Government could provide for the
organization banks from such Reserve Treasuries however the last could look upon
them more demonstration of generosity some assistance than as a benefit.
Bank of Madras
The decision of the Government to keep the surplus changes in Reserve Treasuries
outside the run of the mill control of the organization banks and the related decision
not to guarantee slightest government equalities at new places where branches were
to be opened effectively checked the advancement of new branches after 1876. The
pace of expansion saw in the before decade fell firmly but, by virtue of the Bank of
Madras, it continued on an inconspicuous scale as the advantages of that bank were
basically gotten from trade scattered among different port towns and inland centers
of the organization.
India saw fast commercialisation in the last quarter of the nineteenth century as its
rail line framework stretched out to cover all the critical locale of the country. New
watering framework sorts out in Madras, Punjab and Sind revived the procedure of
progress of subsistence items into cash trims, a section of which felt that it somehow
into the outside organizations. Tea and coffee farms changed far reaching reaches
of the eastern Terais, the inclines of Assam and the Nilgiris into regions of
endowment cultivating second to none. All these achieved the expansion of India's
all inclusive trade more than six-fold. The three organization banks were both
beneficiaries and promoters of this commercialisation change as they got the chance
to be incorporated in the financing of essentially every trading, amassing and mining
activity in the sub-landmass. While the Banks of Bengal and Bombay were involved
with the financing of tremendous current amassing business ventures, the Bank of
Madras went into the financing of broad propelled gathering organizations, the Bank
of Madras went into the financing of little scale business endeavors in a way which
had no parallel some place else. At any rate, the three banks were completely
banned from any business including outside exchange. Not simply was such
business considered unsafe for these banks, which held government stores, it was
moreover expected that these banks getting a charge out of government bolster
would offer uncalled for contention to the exchange banks which had by then
interfaced India. This shirking continued till the making of the Reserve Bank of India
in 1935.
Bank of Bombay
Organization Banks of Bengal
The Presidency Banks of Bengal, Bombay and Madras with their 70 branches were
met fit as a fiddle the Imperial Bank of India. The triad had been changed into a
stone landmark and a creature among Indian business banks had risen. The new
bank handled the triple piece of a business bank, an agent's bank and a speculator
to the organization.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Table of Penalties For Crimes Committed Under The Revised Penal CodeDokument6 SeitenTable of Penalties For Crimes Committed Under The Revised Penal CodeElaine Grace R. AntenorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nivea Case StudyDokument15 SeitenNivea Case StudyShreyas LigadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power of The High Courts To Transfer CasesDokument2 SeitenPower of The High Courts To Transfer CasesShweta ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Kurdistan Worker's Party (PKK) in London-Countering Overseas Terrorist Financing andDokument28 SeitenThe Kurdistan Worker's Party (PKK) in London-Countering Overseas Terrorist Financing andrıdvan bahadırNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogue of CCP Publications 2021Dokument75 SeitenCatalogue of CCP Publications 2021marcheinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Republic Act. 10157Dokument24 SeitenRepublic Act. 10157roa yusonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 MTB - TG SB Q1 W5Dokument10 Seiten2 MTB - TG SB Q1 W5Rodrigo100% (1)
- Fearing GodDokument5 SeitenFearing GodAnonymous d79K7PobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal Acctng CasesDokument108 SeitenLegal Acctng CasesJerry Barad SarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Plan FinalDokument28 SeitenBusiness Plan FinalErica Millicent TenecioNoch keine Bewertungen
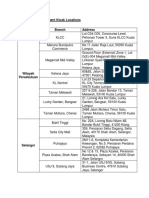
- Debit Card Replacement Kiosk Locations v2Dokument3 SeitenDebit Card Replacement Kiosk Locations v2aiaiyaya33% (3)
- (Faisal Iqbal) (HM322 Pre Mid Assignment)Dokument10 Seiten(Faisal Iqbal) (HM322 Pre Mid Assignment)Wajid AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- City Development PlanDokument139 SeitenCity Development Planstolidness100% (1)
- Urban Planning PHD Thesis PDFDokument6 SeitenUrban Planning PHD Thesis PDFsandracampbellreno100% (2)
- Nationalization of Industries by 1971Dokument2 SeitenNationalization of Industries by 1971alamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opening PrayersDokument2 SeitenOpening PrayersKathleen A. Pascual100% (1)
- ΛΙΣΤΑ ΕΜΦIΑΛΩΜΕΝΩΝ ΝΕΡΩΝDokument8 SeitenΛΙΣΤΑ ΕΜΦIΑΛΩΜΕΝΩΝ ΝΕΡΩΝΕλενη ΧιονηNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marxism and Brontë - Revenge As IdeologyDokument8 SeitenMarxism and Brontë - Revenge As IdeologyJonas SaldanhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aquarium Aquarius Megalomania: Danish Norwegian Europop Barbie GirlDokument2 SeitenAquarium Aquarius Megalomania: Danish Norwegian Europop Barbie GirlTuan DaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ObliconDokument3 SeitenObliconMonica Medina100% (2)
- File:///d - /... SER/Desktop/LABOR LAW/Cases/G.R. No. 196036, October 23, 2013 - ELIZABETH M..TXT (8/24/2020 9:55:51 PM)Dokument6 SeitenFile:///d - /... SER/Desktop/LABOR LAW/Cases/G.R. No. 196036, October 23, 2013 - ELIZABETH M..TXT (8/24/2020 9:55:51 PM)Russ TuazonNoch keine Bewertungen
- BlompmDokument208 SeitenBlompmswiftvishnulalNoch keine Bewertungen
- European Decarb Industry Report ICFDokument52 SeitenEuropean Decarb Industry Report ICFGitan ChopraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 137684-1980-Serrano v. Central Bank of The PhilippinesDokument5 Seiten137684-1980-Serrano v. Central Bank of The Philippinespkdg1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- SJDM Es Smepa Board 2020-2021Dokument5 SeitenSJDM Es Smepa Board 2020-2021Loreto Capitli MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Action Plans and Alignment GuideDokument13 SeitenStrategic Action Plans and Alignment GuideAbeer AzzyadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kukurija: Shuyu KanaokaDokument10 SeitenKukurija: Shuyu KanaokaMarshal MHVHZRHLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purpose of Schooling - FinalDokument8 SeitenPurpose of Schooling - Finalapi-257586514Noch keine Bewertungen
- FY2011 Sked CDokument291 SeitenFY2011 Sked CSunnyside PostNoch keine Bewertungen
- 55WeekScheduleforFOUNDATION Pouyrogram-CrackiasDokument21 Seiten55WeekScheduleforFOUNDATION Pouyrogram-CrackiasThowheedh MahamoodhNoch keine Bewertungen