Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Volume 2 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Karthik Kala KondaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Volume 2 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Karthik Kala KondaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Volumes and Areas
Page 1 of 3
Volumes and Areas
The Grid | Volume command is used to compute net volumes, cut and fill volumes, planar areas, and surface areas. The
computation results are displayed in the grid volume report. The results can be saved as an ASCII text file, in Rich Text
Format, or can be pasted into the clipboard.
Volume calculations are performed on solids defined by an upper and lower surface. The upper and lower surfaces are
defined by a grid file or a plane of constant Z level. When two grid files are specified for the upper and lower surfaces, the
grid files must have the same number of rows and columns and the same X and Y limits. The upper surface does not have
to be above the lower surface at all points; the upper surface may dip below the lower surfaces in some locations. Blanked
regions on either the upper or the lower surface are excluded from consideration during the volume calculations.
Volume results are provided in cubic units based on the units of the input grid file.
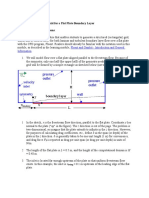
Volume Accuracy Example
This grid has a highly irregular surface and
is a poor candidate for volume calculations.
These two grids are based on the same data but created at different grid densities.
The grid on the right is a better candidate for obtaining accurate volume
information because it is a much more smooth and dense grid.
Volume calculations are generated for each grid cell. In areas where the surface is tilted at the top or bottom of a grid cell,
Surfer approximates the volume of the prism at the top or bottom of the grid cell column. For very coarse grids, the prisms
can contain a significant volume. Volume calculations become more accurate as the density of the grid is increased
because the relative size of the prisms is reduced compared to the size of the associated column. Grids with significant
"noise" or with highly irregular surfaces are poor candidates for volume calculations.
Calculating Volumes and Areas
Use the Grid | Volume command to calculate net volumes, cut and fill volumes, planar areas, and surface areas.
mk:@MSITStore:C:\Program%20Files\Golden%20Software\Surfer%2011\Surfer.CHM::... 12/12/2014
Volumes and Areas
Page 2 of 3
1.
Click the Grid | Volume command.
2.
In the Open Grid dialog, specify the name of the grid file to use in the volume and area calculations. This can be the
grid file for either the upper or the lower surface.
3.
Click OK and the Grid Volume dialog is displayed. The specified grid file is shown for both the upper and lower surface.
4.
Specify the Upper Surface and Lower Surface parameters.
The
button displays information about the grid file used in the volume calculations. The information includes
the grid size, the minimum and maximum XYZ values contained in the grid file, and statistics. If the grid file is large,
click OK in the message box that appears to create a detailed grid report or click the Cancel button to create a
shorter, less detailed grid report.
The Grid File option is used to specify a grid to use as the upper or lower surface. To use the grid file for the
surface, click the Grid File option. To change the grid file for either the upper or lower surface, click the Grid File
option and click the
button to select another grid file.
The Constant option is used to specify the level of the planar surface to use as the upper or lower surface. Specify
the level of the planar surface by entering the value into the Z = box. The specified value is in Z data units.
5.
If the X, Y, and Z units are different, the resulting volume calculations are meaningless. If, for example, your XY values
are in meters but your Z values are in feet, the volume results are square meters times feet, rather than cubic units. Z
Scale Factor can be used to adjust for this problem. In this example, setting the Z Scale Factor to 0.3048 (number of
meters in a foot) results in cubic meters for volume calculations. You will need to know the conversion factor to use this
field.
6.
Click OK in the Grid Volume dialog and the results are displayed in a report.
7.
Click File | Save As to save the report, or you can copy the information to the clipboard and paste it into another
application.
Use the Grid | Volume command to calculate net volumes, cut and fill volumes, planar areas, and surface areas.
Grid Volume Dialog
Click the Grid | Volume command to open the Open Grid dialog. Select a grid file and click Open to open the Grid
Volume dialog.
Specify grid volume options in the Grid Volume dialog.
Upper Surface and Lower Surface Grid Information
The
button displays information about the grid file used in the volume calculations. The information includes the grid
size, the minimum and maximum X, Y, and Z values contained in the grid file, and statistics. If the grid file is large, click OK
in the message box that appears to create a detailed grid report or click Cancel to create a shorter, less detailed grid report.
Grid File
The Grid File option is used to specify a grid to use as the upper or lower surface. To use the grid file for the surface, click
mk:@MSITStore:C:\Program%20Files\Golden%20Software\Surfer%2011\Surfer.CHM::... 12/12/2014
Volumes and Areas
Page 3 of 3
the Grid File option. To change the grid file for either the upper or lower surface, click the Grid File option, and then click the
button to open the Open Grid dialog. Select another grid file and click the Open button. The new grid file is now
displayed in the Grid File box.
Constant Z
The Constant option is used to specify the level of the planar surface to use as the upper or lower surface. Specify the level
of the planar surface by entering the value into the Z = box. The specified value is in Z data units.
Units
If the X, Y, and Z units are different, the resulting volume calculations are meaningless. If, for example, your X, Y values are
in meters but your Z values are in feet, the volume results are square meters times feet, rather than cubic units. Z Scale
Factor can be used to adjust for this problem. In this example, setting the Z Scale Factor to 0.3048 (number of meters in a
foot) results in cubic meters for volume calculations. You will need to know the conversion factor to use this field.
3
A grid with X, Y, and Z units in feet, the units for the results are: Net Volume = (feet * feet * feet) or ft .
Grid Report
Click OK in the Grid Volume dialog and the results are displayed in the Grid Volume Report. Use File | Save As to save
the report, or you can copy the information to the clipboard and paste it into another application.
See Also
Introduction to Volumes, Areas, Cross Sections
Calculating the Volume of a Lake
Calculating the Volume of a Blanked Grid
Calculating the Volume between Two Surfaces
Grid Volume Report
Send comments about this topic.
mk:@MSITStore:C:\Program%20Files\Golden%20Software\Surfer%2011\Surfer.CHM::... 12/12/2014
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Image Histogram: Unveiling Visual Insights, Exploring the Depths of Image Histograms in Computer VisionVon EverandImage Histogram: Unveiling Visual Insights, Exploring the Depths of Image Histograms in Computer VisionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Secrets of Access Database Development and ProgrammingVon EverandSecrets of Access Database Development and ProgrammingBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- nrcs142p2 032035Dokument10 Seitennrcs142p2 032035Muhammad Abdul FattahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surfer 8 Geology TutorialDokument22 SeitenSurfer 8 Geology TutorialEdin DivovićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Software SGeMSDokument26 SeitenTutorial Software SGeMSEdi Setiawan100% (3)
- Us Soilsv3Dokument10 SeitenUs Soilsv3Abdelhak AlmNoch keine Bewertungen
- S-Gems Tutorial Notes: Hydrogeophysics: Theory, Methods, and ModelingDokument26 SeitenS-Gems Tutorial Notes: Hydrogeophysics: Theory, Methods, and ModelingmarcialcolosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paquete Geometry LatexDokument63 SeitenPaquete Geometry LatexSaul Yahua HumpireNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Geometry Package: Hideo Umeki Hideo - Umeki@toshiba - Co.jp 2000/06/28 (v2.3)Dokument22 SeitenThe Geometry Package: Hideo Umeki Hideo - Umeki@toshiba - Co.jp 2000/06/28 (v2.3)Ajuchán EliezerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D WireframesDokument6 Seiten3D WireframesaymeneNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Computer AreaDokument2 SeitenHow To Computer AreaYa SamolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Raster Tutorial ArcgisDokument21 SeitenRaster Tutorial ArcgisMihai MereNoch keine Bewertungen
- MESYS Shaft CalculationDokument28 SeitenMESYS Shaft CalculationZoebairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual SurferDokument19 SeitenManual SurferVincent NeyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical Analysis Using Gnumeric: Entering Data and Calculating ValuesDokument18 SeitenStatistical Analysis Using Gnumeric: Entering Data and Calculating ValuesandriuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frequency of Simulation Results File WritingDokument4 SeitenFrequency of Simulation Results File WritingpotriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Step 1: Aster or SRTM?: Downloading and Importing Dem Data From Aster or SRTM ( 30M Resolution) Into ArcmapDokument6 SeitenStep 1: Aster or SRTM?: Downloading and Importing Dem Data From Aster or SRTM ( 30M Resolution) Into ArcmapAmel BoumesseneghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2261 PDFDokument30 Seiten2261 PDFTessfaye Wolde GebretsadikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carry & Makeup: The ProcessDokument11 SeitenCarry & Makeup: The ProcessGonzalesEscobarFabricioNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS3D Plotting Tips 200407Dokument4 SeitenMS3D Plotting Tips 200407Kenny CasillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volumes and Slope Area: 11.1 OverviewDokument19 SeitenVolumes and Slope Area: 11.1 OverviewbirukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aashto RigidDokument99 SeitenAashto RigidArbiel GhumlasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sigma Getting StartedDokument4 SeitenSigma Getting StartedsemuwembaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hoja de Calculo AASHTO 98Dokument96 SeitenHoja de Calculo AASHTO 98Ricardo FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aashto RigidDokument99 SeitenAashto RigidAbu DabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aashto RigidDokument99 SeitenAashto Rigidaklilu ayalewNoch keine Bewertungen
- AASHTO Supplement, Rigid Pavement DesignDokument91 SeitenAASHTO Supplement, Rigid Pavement DesignAlvaro HerbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erdas Imagine - Querying and EditingDokument4 SeitenErdas Imagine - Querying and EditingmikejpbNoch keine Bewertungen
- GUIA 98 (Version 1)Dokument89 SeitenGUIA 98 (Version 1)Efraín CórdovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AASHTO - Rigid CopiedDokument83 SeitenAASHTO - Rigid CopiedrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- AASHTO - Rigid Pavement DesignDokument83 SeitenAASHTO - Rigid Pavement DesignBenedict OgbaghaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diseño Aashto 98 Pav Rigi.Dokument83 SeitenDiseño Aashto 98 Pav Rigi.Danitza Rosario Sucasaca MamaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computational Domain - Overview: WizardDokument5 SeitenComputational Domain - Overview: WizardsantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tufts GIS Tip Sheet Working With Elevation DataDokument4 SeitenTufts GIS Tip Sheet Working With Elevation DataFlor TsukinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plotting: Graph LayersDokument32 SeitenPlotting: Graph LayersSyd BarrettNoch keine Bewertungen
- Whaem Quick Start GuideDokument11 SeitenWhaem Quick Start GuideAlexandre SerafiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ternarias Triangulo J.GDokument76 SeitenTernarias Triangulo J.GAicrag JehisbellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial SpatialDokument19 SeitenTutorial SpatialRicardo GomesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minescape Form Help: Form Name: Form UsageDokument4 SeitenMinescape Form Help: Form Name: Form UsageAhmad FudelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reporting Mesh StatisticsDokument18 SeitenReporting Mesh StatisticsTech MitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Step by Step GuideDokument5 SeitenStep by Step GuideSourav SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Create An Earthwork Construction PlanDokument5 SeitenTo Create An Earthwork Construction Planသံသရာ ခရီးသည္Noch keine Bewertungen
- GIS Tutorial For Watershed DelineationDokument6 SeitenGIS Tutorial For Watershed Delineationashenafi negusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Erosion ModellingDokument20 SeitenSoil Erosion ModellingRheza FirmansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Railway Curves 13Dokument15 SeitenRailway Curves 13vpmohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rigid PavementDokument83 SeitenRigid PavementdonnybtampubolonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tri Plot - v1 4 2Dokument82 SeitenTri Plot - v1 4 2Elvis Jesús Espíritu Espíritu100% (1)
- Scrubber 2Dokument18 SeitenScrubber 2molszewNoch keine Bewertungen
- A01 Catenary and Wave SystemsDokument15 SeitenA01 Catenary and Wave SystemshuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tecplot 360 Quick Reference GuideDokument12 SeitenTecplot 360 Quick Reference Guidechewbacca11Noch keine Bewertungen
- What's New in FEMAPDokument79 SeitenWhat's New in FEMAPkvpaok4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gambit - Generation of Grid For A Flat Plate Boundary LayerDokument6 SeitenGambit - Generation of Grid For A Flat Plate Boundary LayerAngga HartonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vmerwade@purdue - Edu: Handling Raster Data For Hydrologic ApplicationsDokument10 SeitenVmerwade@purdue - Edu: Handling Raster Data For Hydrologic ApplicationsGeo SpatialistNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRADISTAT-1 (Danau)Dokument222 SeitenGRADISTAT-1 (Danau)AndryTiraskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11-Zonal Statistics in ArcGIS 2009Dokument7 Seiten11-Zonal Statistics in ArcGIS 2009dolceannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AASHTO Supplement, Rigid Pavement Design v2Dokument91 SeitenAASHTO Supplement, Rigid Pavement Design v2Juan Jose Gutierrez VidalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flagging An Interval Table With 3dm InterceptsDokument12 SeitenFlagging An Interval Table With 3dm InterceptsRozalia PengoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NX 9 for Beginners - Part 2 (Extrude and Revolve Features, Placed Features, and Patterned Geometry)Von EverandNX 9 for Beginners - Part 2 (Extrude and Revolve Features, Placed Features, and Patterned Geometry)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Building Material Estimates and Rates Build Up: Second EditionVon EverandBuilding Material Estimates and Rates Build Up: Second EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solidworks 2018 Learn by Doing - Part 3: DimXpert and RenderingVon EverandSolidworks 2018 Learn by Doing - Part 3: DimXpert and RenderingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Miryalaguda 09a 04 2021 ModelDokument1 SeiteMiryalaguda 09a 04 2021 ModelKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ground Floor Plan: Shop - F2 21'0" X 9'7 "Dokument1 SeiteGround Floor Plan: Shop - F2 21'0" X 9'7 "Karthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lack of Fit Temparature StressDokument1 SeiteLack of Fit Temparature StressKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 44x60 RCC Drawing Model (Details)Dokument1 Seite44x60 RCC Drawing Model (Details)Karthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 40' Wide Road: Shop1 Shop2 Shop3 Shop4 Shop5Dokument1 Seite40' Wide Road: Shop1 Shop2 Shop3 Shop4 Shop5Karthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- StadiumDokument1 SeiteStadiumKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leads KosgiDokument1 SeiteLeads KosgiKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sta ReportDokument3 SeitenSta ReportKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathabramanapalli Nallacheruv 26-1-15-ModelDokument1 SeitePathabramanapalli Nallacheruv 26-1-15-ModelKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data PDFDokument3 SeitenData PDFKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roof DismantlingDokument1 SeiteRoof DismantlingKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design EndDokument1 SeiteDesign EndKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Madaram Konambaiocheruv ModelDokument1 SeiteMadaram Konambaiocheruv ModelKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narasayapalli Pealknulkunta ModelDokument1 SeiteNarasayapalli Pealknulkunta ModelKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Talakondapalli Ramireddykunta ModelDokument1 SeiteTalakondapalli Ramireddykunta ModelKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jangareddypalli Ravancheruv ModelDokument1 SeiteJangareddypalli Ravancheruv ModelKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Venkatraopet Peddacheruv ModelDokument1 SeiteVenkatraopet Peddacheruv ModelKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Madaram Veeralakunta-ModelDokument1 SeiteMadaram Veeralakunta-ModelKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Settipalli Veerannacheruv: PLOT No: 81/145 Sri Venkateshwar NagarDokument1 SeiteSettipalli Veerannacheruv: PLOT No: 81/145 Sri Venkateshwar NagarKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Velugurlathanda Thetakunta ModelDokument1 SeiteVelugurlathanda Thetakunta ModelKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gokaram Checkdam ModelDokument1 SeiteGokaram Checkdam ModelKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jangareddypalli Burugukunta ModelDokument1 SeiteJangareddypalli Burugukunta ModelKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jangareddypalli Burugukunta ModelDokument1 SeiteJangareddypalli Burugukunta ModelKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chekunthala Abrajcheruv 29-2-15-ModelDokument1 SeiteChekunthala Abrajcheruv 29-2-15-ModelKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ankuthotapalli Yerrikunta1!02!15 ModelDokument1 SeiteAnkuthotapalli Yerrikunta1!02!15 ModelKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irvin Kothacheruv ModelDokument1 SeiteIrvin Kothacheruv ModelKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH: 9030469971 PH: 9030469971: Surveyed by Surveyed byDokument1 SeitePH: 9030469971 PH: 9030469971: Surveyed by Surveyed byKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anmangal Suryasamadram 28-01-15-ModelDokument1 SeiteAnmangal Suryasamadram 28-01-15-ModelKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mission Kakatiya: Irvin Kokal Cheruv Amangal (M) Mahabub Nagar (Dist)Dokument1 SeiteMission Kakatiya: Irvin Kokal Cheruv Amangal (M) Mahabub Nagar (Dist)Karthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Konapur Ura Kunta - 1!2!15-ModelDokument1 SeiteKonapur Ura Kunta - 1!2!15-ModelKarthik Kala KondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting Information Systems: Basic Concepts and Current Issues 4th Edition Robert L. HurtDokument29 SeitenAccounting Information Systems: Basic Concepts and Current Issues 4th Edition Robert L. HurtJamieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exhibitor 35804 PDFDokument36 SeitenExhibitor 35804 PDFulton1237624Noch keine Bewertungen
- Zones of Protection and Dead or Blind Zone in Power SystemDokument4 SeitenZones of Protection and Dead or Blind Zone in Power SystemkarthikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aircraft Refuelling HoseDokument4 SeitenAircraft Refuelling HoseBimo IndroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ponds and Aerated LagoonsDokument24 SeitenPonds and Aerated LagoonsGabriella AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Report 2017 English PDFDokument90 SeitenAnnual Report 2017 English PDFanand.srajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moi PDFDokument3 SeitenMoi PDFSACHINNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market Consumer Perception Mahindra ThesisDokument95 SeitenMarket Consumer Perception Mahindra ThesisHarmeet singh100% (1)
- FDTP brochure-EC 3354 Signals and Systems 2023Dokument2 SeitenFDTP brochure-EC 3354 Signals and Systems 2023Principal RVSETGI,DindigulNoch keine Bewertungen
- JSP BasicsDokument41 SeitenJSP BasicsSandeep KavuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- NJ Res Chapter10Dokument10 SeitenNJ Res Chapter10Anonymous bVFHovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calipers, Possible Errors in Measurements.: Kushal DhunganaDokument11 SeitenCalipers, Possible Errors in Measurements.: Kushal Dhunganauploadz upNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of FiberDokument33 SeitenApplication of FiberReem OmerNoch keine Bewertungen
- ND3361 Lesson 11 Ipatch 360 Hardware Jul 13 PDFDokument40 SeitenND3361 Lesson 11 Ipatch 360 Hardware Jul 13 PDFJosel ArevaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- One BookDokument29 SeitenOne BookOnebookNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report of Apollo 201 Review BoardDokument2.540 SeitenReport of Apollo 201 Review BoardBob Andrepont100% (2)
- Medellin Castillo Zaragoza Siqueiros2019 - Article - DesignAndManufacturingStrategi PDFDokument16 SeitenMedellin Castillo Zaragoza Siqueiros2019 - Article - DesignAndManufacturingStrategi PDFajay d1212Noch keine Bewertungen
- TR200 Surface Tester ManualDokument3 SeitenTR200 Surface Tester Manualprasadjoshi781429Noch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Aging in Bituminous MixesDokument15 SeitenEffect of Aging in Bituminous MixesyadavameNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volvo (Dem) and Haldex: History, Function, Diagnosis and RepairsDokument6 SeitenVolvo (Dem) and Haldex: History, Function, Diagnosis and RepairsNecsaszNorbertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liebherr Hydraulic Components For Heavy Duty On Highway Engines Application Flyer Es WebDokument4 SeitenLiebherr Hydraulic Components For Heavy Duty On Highway Engines Application Flyer Es WebDaniel Castillo PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidebook 184Dokument1 SeiteGuidebook 184Anonymous 7GOnu0xeuCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Summary: Semiconductor MC68HC11A8 MC68HC11A1 MC68HC11A0 8-Bit MicrocontrollersDokument45 SeitenTechnical Summary: Semiconductor MC68HC11A8 MC68HC11A1 MC68HC11A0 8-Bit MicrocontrollersElias CoronelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Music Frequency Cheat SheetDokument1 SeiteMusic Frequency Cheat SheetLeonel Molina AlvaradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jar Test Lab Report Environmental EngineeringDokument7 SeitenJar Test Lab Report Environmental EngineeringNur Hazimah100% (1)
- Guide To Single Point Moorings Old PDFDokument456 SeitenGuide To Single Point Moorings Old PDFsarifin100% (1)
- 5.2.1 Red AlertsDokument4 Seiten5.2.1 Red AlertsCursedDiamondsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alfonso, Michael John Agaser 202005047MN0 Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering Enrolled SubjectsDokument1 SeiteAlfonso, Michael John Agaser 202005047MN0 Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering Enrolled SubjectsMJA.AlfonsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Bendable and Wearable Cardiorespiratory Monitoring Device Fusing Two Noncontact Sensor PrinciplesDokument10 SeitenA Bendable and Wearable Cardiorespiratory Monitoring Device Fusing Two Noncontact Sensor PrinciplesMd arshatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundation Engineering Shot NotesDokument21 SeitenFoundation Engineering Shot NotesSejal VermaNoch keine Bewertungen