Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Table of English Tenses: Tense Use Signal Words
Hochgeladen von
Adriana MuresanOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Table of English Tenses: Tense Use Signal Words
Hochgeladen von
Adriana MuresanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
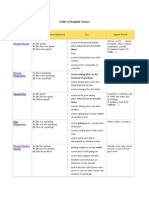
Table of English Tenses
Tense
Affirmative/Negative/Ques
tion
Use
Simple Present
Present
Continuous
Simple Past
A: He speaks.
N: He does not speak.
Q: Does he speak?
A: He is speaking.
N: He is not speaking.
Q: Is he speaking?
A: He spoke.
N: He did not speak.
Q: Did he speak?
action set by a timetable or
schedule
action taking place in the
moment of speaking
action taking place only for a
limited period of time
action arranged for the future
action in the past taking place
once, never or several times
actions taking place one after
another
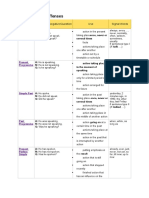
Past Continuous
A: He was speaking.
N: He was not speaking.
Q: Was he speaking?
action in the present taking
place once, never or several
times
facts
actions taking place one after
another
action taking place in the
middle of another action
action going on at a certain
time in the past
actions taking place at the
same time
action in the past that is
interrupted by another action
Signal Words
always, every ,
never, normally, often,
seldom, sometimes,
usually
if sentences type I (If I
talk, )
at the moment, just,
just now, Listen!,
Look!, now, right now
yesterday, 2 minutes
ago, in 1990, the
other day, last Friday
if sentence type II (If I
talked, )
when, while, as long
as
Present Perfect
Simple
A: He has spoken.
N: He has not spoken.
Q: Has he spoken?
Present Perfect
Continuous
Past Perfect
Simple
Past Perfect
Continuous
A: He has been speaking.
N: He has not been speaking.
Q: Has he been speaking?
A: He had spoken.
N: He had not spoken.
Q: Had he spoken?
A: He had been speaking.
N: He had not been speaking.
Q: Had he been speaking?
putting emphasis on the
result
action that is still going on
action that stopped recently
finished action that has an
influence on the present
action that has taken place
once, never or several times
before the moment of
speaking
putting emphasis on the
course or duration (not the
result)
action that recently stopped
or is still going on
finished action that influenced
the present
action taking place before a
certain time in the past
sometimes interchangeable
with past perfect continuous
putting emphasis only on the
fact (not the duration)
action taking place before a
certain time in the past
sometimes interchangeable
with past perfect simple
putting emphasis on the
duration or course of an
action
already, ever, just,
never, not yet, so far,
till now, up to now
all day, for 4 years,
since 1993, how
long?, the whole week
already, just, never,
not yet, once, until
that day
if sentence type III (If I
had talked, )
for, since, the whole
day, all day
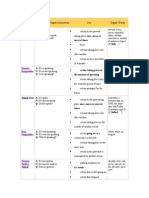
Future I Simple
Future I Simple
A: He will speak.
N: He will not speak.
Q: Will he speak?
(going to)
A: He is going to speak.
N: He is not going to speak.
Q: Is he going to speak?
Future I
Continuous
A: He will be speaking.
N: He will not be speaking.
Q: Will he be speaking?
Future II Simple
A: He will have spoken.
N: He will not have spoken.
Q: Will he have spoken?
Future II
Continuous
A: He will have been speaking.
N: He will not have been
speaking.
Q: Will he have been speaking?
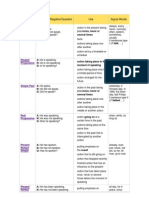
Conditional I
Simple
A: He would speak.
N: He would not speak.
Q: Would he speak?
Conditional I
Continuous
A: He would be speaking.
N: He would not be speaking.
Q: Would he be speaking?
Conditional II
Simple
A: He would have spoken.
N: He would not have spoken.
Q: Would he have spoken?
A: He would have been
speaking.
N: He would not have been
speaking.
Q: Would he have been
assumption with regard to the
future
decision made for the future
Conditional II
Continuous
action in the future that
cannot be influenced
spontaneous decision
conclusion with regard to the
future
action that is going on at a
certain time in the future
action that is sure to happen
in the near future
action that will be finished at
a certain time in the future
action taking place before a
certain time in the future
in a year, next ,
tomorrow
If-Satz Typ I (If you ask
her, she will help you.)
assumption: I think,
probably, perhaps
in one year, next
week, tomorrow
in one year, next
week, tomorrow
by Monday, in a week
for , the last couple
of hours, all day long
if sentences type II
(If I were you, I would
go home.)
if sentences type III
(If I had seen that, I
would have helped.)
putting emphasis on the
course of an action
action that might take place
action that might take place
putting emphasis on the
course / duration of the action
action that might have taken
place in the past
action that might have taken
place in the past
puts emphasis on the course /
duration of the action
speaking?
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- EMMS SpecificationsDokument18 SeitenEMMS SpecificationsAnonymous dJtVwACc100% (2)
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideVon EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aircraft ChecksDokument10 SeitenAircraft ChecksAshirbad RathaNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Tense ChartDokument4 SeitenEnglish Tense Chartdieba105Noch keine Bewertungen
- C ClutchesDokument131 SeitenC ClutchesjonarosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument4 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentXorianopoulou SofiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IEC-60721-3-3-2019 (Enviromental Conditions)Dokument12 SeitenIEC-60721-3-3-2019 (Enviromental Conditions)Electrical DistributionNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Tenses and Adjective ComparisonDokument39 SeitenEnglish Tenses and Adjective ComparisonSam TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument4 SeitenTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordsanon1000Noch keine Bewertungen
- English TensesDokument4 SeitenEnglish TensesAgung ArdyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English TensesDokument2 SeitenTable of English TensesMariana Crăciun100% (1)
- 2.0 - SITHKOP002 - Plan and Cost Basic Menus Student GuideDokument92 Seiten2.0 - SITHKOP002 - Plan and Cost Basic Menus Student Guidebash qwertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer Behaviour Towards AppleDokument47 SeitenConsumer Behaviour Towards AppleAdnan Yusufzai69% (62)
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: PresentRaj KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English TensesDokument4 SeitenTable of English TensesKashif WakeelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument3 SeitenTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsAbdulaziz2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English TensesDokument3 SeitenTable of English TensesGonzalo AstorgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Present: I Talk, )Dokument3 SeitenSimple Present: I Talk, )Krupesh PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Chart ExplainedDokument3 SeitenTense Chart ExplainedKiki MulqiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table TensesDokument4 SeitenTable TensesmariminniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questio N Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument5 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Questio N Use Signal Words: Simple PresentFitrie RnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentSorin Mihai VassNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument4 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDenis SăndicăNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verb Tense Overview With ExamplesDokument5 SeitenVerb Tense Overview With ExamplesSaulo ZunigaNoch keine Bewertungen
- English TensesDokument2 SeitenEnglish TensesGustavo SteffenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English TensesDokument3 SeitenTable of English TensesShoba DevarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Tenses ChartDokument3 SeitenEnglish Tenses ChartAndreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TensesDokument5 SeitenTensesGanesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English Tenses in 40 CharactersDokument3 SeitenTable of English Tenses in 40 CharactersAndrea Paredes GuerreroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordshpeter195798Noch keine Bewertungen
- Summary Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument1 SeiteSummary Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsCTMundialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chart of English TensesDokument2 SeitenChart of English TensesNorafiqah Rifhan RamlanNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Tenses Table and ChartDokument6 SeitenEnglish Tenses Table and ChartRatmi 'Bundanya Rena'Noch keine Bewertungen
- Present Simple Tense GuideDokument3 SeitenPresent Simple Tense GuidePavlina HaralampievaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/ Use Signal Words: Ifi TalkDokument4 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/ Use Signal Words: Ifi Talkshel087Noch keine Bewertungen
- TenseDokument3 SeitenTenseMădălina RădulescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument3 SeitenTenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordsyingying1102Noch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument3 SeitenTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsTaris TallasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument6 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentTigercubx9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Present SimpleDokument4 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Present SimpleRobertaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English TensesDokument3 SeitenTable of English TensesCristina-Raluca RuşeţNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentMariana PasatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentVeronica BurdujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Tense Verbs and Their UsesDokument3 SeitenPresent Tense Verbs and Their UsesLyana LorenzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument2 SeitenTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDebyPuspitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentRuxanda RusuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument4 SeitenTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsthirtysecondsmarsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present tense verbs guideDokument4 SeitenPresent tense verbs guideZandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentHazel-mae LabradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentJavier J SalazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Presentdddiana21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Present: I Talk, )Dokument2 SeitenSimple Present: I Talk, )romina5_13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Timpuri LeDokument3 SeitenTimpuri LemadybyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Present: TalkedDokument4 SeitenSimple Present: TalkedDangVanTamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Positive/negative/question Usage Signal WordsDokument4 SeitenTense Positive/negative/question Usage Signal WordsMyriam GGoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TensesDokument18 SeitenTensesNora Mestiri100% (1)
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument1 SeiteTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentVlasta LoncaricNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verb Tense Use Example: Present Simple ... Present Continuous ..Dokument4 SeitenVerb Tense Use Example: Present Simple ... Present Continuous ..charanpalsinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Tense TableDokument5 SeitenEnglish Tense TablekaterynavelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple TenseDokument13 SeitenSimple TenseChad HayesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple Presentgulzar72Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pronouns Subject Pronouns Object Pronouns Possessive Adjectives Possessive Pronouns Reflexive PronounsDokument5 SeitenPronouns Subject Pronouns Object Pronouns Possessive Adjectives Possessive Pronouns Reflexive PronounsRasyidy 'Eddy' AliasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentLecherooMendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English TensesDokument5 SeitenTable of English TensesMaria CristianNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAC-Documentation-Tool Session 2Dokument4 SeitenLAC-Documentation-Tool Session 2DenMark Tuazon-RañolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Design of Flexible Pavement Using Coir GeotextilesDokument126 Seiten01 Design of Flexible Pavement Using Coir GeotextilesSreeja Sadanandan100% (1)
- Galvanometer: Project Prepared By:-Name - Pragati Singh Class - Xii A AcknowledgementDokument11 SeitenGalvanometer: Project Prepared By:-Name - Pragati Singh Class - Xii A AcknowledgementANURAG SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.2 Probability DistributionDokument38 Seiten3.2 Probability Distributionyouservezeropurpose113Noch keine Bewertungen
- Raychem Price ListDokument48 SeitenRaychem Price ListramshivvermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bethany Getz ResumeDokument2 SeitenBethany Getz Resumeapi-256325830Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Dean GR6211 Fall 2018 Columbia University: - Choice Theory'Dokument5 SeitenMark Dean GR6211 Fall 2018 Columbia University: - Choice Theory'bhaskkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Citizenship Initiative To Better Support The 21 Century Needs of StudentsDokument3 SeitenDigital Citizenship Initiative To Better Support The 21 Century Needs of StudentsElewanya UnoguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interna Medicine RheumatologyDokument15 SeitenInterna Medicine RheumatologyHidayah13Noch keine Bewertungen
- VNC Function Operation InstructionDokument11 SeitenVNC Function Operation InstructionArnaldo OliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hardware Purchase and Sales System Project ProfileDokument43 SeitenHardware Purchase and Sales System Project Profilesanjaykumarguptaa100% (2)
- Scholars of Hadith Methodology in Dealing With The Two Sahihs: The Criticized Ahadith As A Model. Ammar Ahmad Al-HaririDokument37 SeitenScholars of Hadith Methodology in Dealing With The Two Sahihs: The Criticized Ahadith As A Model. Ammar Ahmad Al-HaririSalah KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Programming InterfaceDokument12 SeitenApplication Programming InterfacesorinproiecteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accidental PoisoningDokument3 SeitenAccidental PoisoningBRUELIN MELSHIA MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daughters of The Storm by Kim Wilkins - Chapter SamplerDokument32 SeitenDaughters of The Storm by Kim Wilkins - Chapter SamplerHarlequinAustraliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delhi Public School: Class: XI Subject: Assignment No. 3Dokument1 SeiteDelhi Public School: Class: XI Subject: Assignment No. 3Aman Kumar BhagatNoch keine Bewertungen
- France: French HistoryDokument16 SeitenFrance: French HistoryMyroslava MaksymtsivNoch keine Bewertungen
- ArtigoPublicado ABR 14360Dokument14 SeitenArtigoPublicado ABR 14360Sultonmurod ZokhidovNoch keine Bewertungen
- STEM Spring 2023 SyllabusDokument5 SeitenSTEM Spring 2023 SyllabusRollins MAKUWANoch keine Bewertungen
- Panasonic TC-P42X5 Service ManualDokument74 SeitenPanasonic TC-P42X5 Service ManualManager iDClaimNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNT Audit Cash CountDokument2 SeitenDNT Audit Cash CountAnonymous Pu7TnbCFC0Noch keine Bewertungen
- StsDokument10 SeitenStsSamonte, KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motivations for Leaving Public Accounting FirmsDokument33 SeitenMotivations for Leaving Public Accounting Firmsran0786Noch keine Bewertungen
- EMECH 2 MarksDokument18 SeitenEMECH 2 MarkspavanraneNoch keine Bewertungen