Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
MasterCard Assessment
Hochgeladen von
PalluRajuCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
MasterCard Assessment
Hochgeladen von
PalluRajuCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Coursera - Foundations of Business Strategy - Final Project - Roberto.Pierantoni@GMail.
com June 2015
MASTERCARD STRATEGIC ANALYSIS
Final Project of Coursera course "Foundations of Business Strategy"
Author: Roberto Pierantoni Roberto.Pierantoni@GMail.com
June 2015
Coursera - Foundations of Business Strategy - Final Project - Roberto.Pierantoni@GMail.com June 2015
- Executive Summary -
MasterCard (MC) is the second largest electronic payments processor by purchase volume behind Visa in the
world. MasterCard does not issue credit cards directly, but licenses its brand to banks, who then issue cobranded cards (such as the Chase MasterCard). MasterCard makes money by charging merchant fees on
individual transactions and by charging the credit card issuers licensing fees and a small percentage of the
total dollar amount spent on each card.
The ability to grow the business is influenced by personal consumption expenditure growth, driving cash and
checks toward electronic forms of payment, increasing MasterCard's share in electronic payments and
providing value-added products and services. MasterCard drives growth by growing, diversifying and
building our business.
MasterCard focus on growing the core businesses globally, including growing credit, debit, prepaid and
commercial products and solutions and increasing the number of payment transactions process, with focus
on:
- diversifying the customer base by working with partners such as governments and digital and
mobile providers;
- encouraging use of the products and solutions in areas that provide new opportunities for
electronic payments, such as transit and person-to-person transfers;
- driving acceptance at small merchants and merchants who have not historically accepted
MasterCard products;
and
- broadening financial inclusion for the unbanked and underbanked.
MasterCard works with merchants to help them enable new sales channels, create better purchase
experiences, increase revenues and fight fraud. MasterCard's partner with large digital and mobile providers
and telecommunication companies to support their digital payment solutions with our technology, expertise
and security protocols. MasterCard helps national and local governments drive increased financial inclusion
and efficiency, reduce costs, increase transparency to reduce crime and corruption and advance social
programs. For consumers, MasterCard provides better, safer and more convenient ways to pay. MasterCard
provides financial institutions with solutions to help them increase revenue and increase preference for their
MasterCard-branded products.
The nature of competitive rivalry in the industry is very high. All five Porter's force is very aggressive and
MasterCard could be considered an incumbent actor of this industry. The barriers to entry are the same as
the network economy. The difficult is create the network acquirer and the customer base. Actually, the
technology barrier is low. The attractiveness of industry is very high. The payment ecosystem business is
growing with a two digits increase every year.
Coursera - Foundations of Business Strategy - Final Project - Roberto.Pierantoni@GMail.com June 2015
The current competitive position of MasterCard Corporation is very enviable. Few costs, high earnings, few
real competitors (VISA, American Express) and high barriers to entry by processes and agreements with all
actors of transaction. MasterCard created a several division with specific goal, in order to create and
maintain a competitive advantage sustainable. The MasterCard brand is to 88 position on this year's Best
Global Brands ranking. The innovation strategy is a must in MasterCard, but no real impressive and
disruptive new idea is output out in recent years.
The industry structure are changing. Consumers are embracing mobile in large numbers and are clearly
showing their preference for the convenience and simplicity of transacting on the mobile anywhere, anytime
and on any device. Banks continue to possess inherent strengths. They have large customer bases; vast
amounts of customer and transaction data; and strong capabilities to execute payments securely all of
which are difficult to replicate quickly by newcomers.
THE RECOMMENDATION is to invest in the developing of new form of e-payment, in particular in mobile
payment. MasterCard brand must to be associated to this easy, natural and secure new way of payment.
Actually the QR-Code is the best way to get the greatest number of users. In the future, when the NFC
smartphone penetration will reached critical mass, the NFC will replace the QR-Code.
A massive marketing campaign in order to create the need to pay with smartphone to masses and the
economic incentives to customers and acquirer banks, it will create a distinctive success. Otherwise the
spectrum of new forms of payment, offered by the incumbent as Google, Apple, PayPal or othes, can easily
disintermediation process created and currently dominated by MasterCard.
Coursera - Foundations of Business Strategy - Final Project - Roberto.Pierantoni@GMail.com June 2015
OVERVIEW
MasterCard (MC) is a technology company in the global payments industry that connects consumers,
financial institutions, merchants, governments and businesses worldwide, enabling them to use electronic
forms of payment instead of cash and checks. As the operator of what MC believes is the worlds fastest
payments network, MC facilitates the processing of payment transactions, including authorization, clearing
and settlement, and deliver related products and services. MC makes payments easier and more efficient
by creating a wide range of payment solutions and services using MC family of well-known brands,
including MasterCard, Maestro and Cirrus. MC also provides value-added offerings such as loyalty and
reward programs, information services and consulting. MasterCard network is designed to ensure safety
and security for the global payments system. A typical transaction on MC network involves four participants
and MC: cardholder, merchant, issuer (the cardholders financial institution) and acquirer (the merchants
financial institution). MC generates revenue by charging fees to issuers and acquirers for providing
transaction processing and other payment-related products and services, as well as by assessing these
customers based primarily on the dollar volume of activity, or gross dollar volume (GDV), on the cards
and other devices that carry MasterCard brands.
VISION: A world beyond cash.
MISSION: Every day, everywhere, MasterCard uses his technology and expertise to make payments safe,
simple and smart.
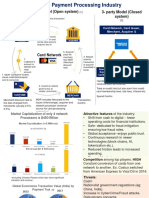
INDUSTRY ANALYSIS
MasterCard competes in the global payments industry against all forms of payment including:
Cash and Check. Cash and check continue to represent the most widely-used forms of payment,
constituting approximately 85% of the worlds retail payment transactions. However, electronic forms
of payment are increasingly displacing paper forms of payment around the world, benefiting electronic
payment brands.
Coursera - Foundations of Business Strategy - Final Project - Roberto.Pierantoni@GMail.com June 2015
General Purpose Payment Networks. MC competes worldwide with payment networks such as Visa,
American Express and Discover, among others. Among global networks, Visa has significantly greater
volume than MC does. Outside of the United States, networks such as JCB in Japan and UnionPay in
China have leading positions in their domestic markets. In the case of UnionPay, it operates the sole
domestic payment switch in China. In addition, several governments are promoting, or considering
promoting, local networks for domestic processing.
Debit Cards. MC compete with ATM and point-of-sale debit networks in various countries, such as
Interlink, Plus and Visa Electron (owned by Visa Inc.), Star (owned by First Data Corporation),
NYCE (owned by FIS), and Pulse (owned by Discover), in the United States; Interac in Canada; EFTPOS
in Australia; and Bankserv in South Africa. In addition, in many countries outside of the United States,
local debit brands serve as the main domestic brands, while MasterCard brands are used mostly to
enable cross-border transactions, which typically represent a small portion of overall transaction
volume.
Three-Party Payments Networks. MC competitors include operators of proprietary three-party
payments networks, such as American Express and Discover, that have direct acquiring relationships
with merchants and direct issuing relationships with account holders. These competitors have certain
competitive advantages over four-party payments systems such as MC. Among other things, these
networks do not require formal interchange fees to balance payment system costs between the issuing
and acquiring sides of their business, even though they have the ability to internally transfer costs in a
manner similar to interchange fees. As a result, to date, operators of three-party payments networks
have generally avoided the same regulatory and legislative scrutiny and litigation challenges MC faces.
Coursera - Foundations of Business Strategy - Final Project - Roberto.Pierantoni@GMail.com June 2015
Competition for Customer Business. MC competes intensely with other payments networks for
customer business. Globally, financial institutions typically issue both MasterCard and Visa-branded
payment products, and MC competes with Visa for business on the basis of individual portfolios or
programs. In addition, a number of MC customers issue American Express and/or Discover-branded
payment cards in a manner consistent with a four-party system. MC continues to face intense
competitive pressure on the prices MasterCard charge their issuers and acquirers, and MC seeks to
enter into business agreements with them through which MC offers incentives and other support to
issue and promote MC payment products. MC also competes for non-financial institution partners,
such as merchants, governments and telecommunication companies.
Third-Party Processors. MC faces competition, and potential displacement, from transaction processors
throughout the world, such as First Data Corporation and Total System Services, Inc., which MC is
seeking to enhance their networks that link issuers directly with point-of-sale devices for payment
transaction authorization and processing services.
Alternative Payments Systems and New Entrants. As the global payments industry becomes more
complex, MC may face increasing competition from emerging payment providers. Many of these
providers have developed payments systems focused on online activity in e-commerce and mobile
channels, however they either have or may expand to other channels. These competitors include digital
wallet providers such as PayPal, AliPay and Amazon, merchants (via CurrenC, a merchant-owned mobile
commerce network), mobile operator services, services such as mPesa, handset manufacturers, and
cryptocurrencies. MasterCard competes with these providers in some circumstances, but in some cases
they may also be our customers or partner with us.
MasterCard competitive advantages includes the highly-adaptable network that MC believes is the worlds
fastest, his adoption of innovative products and platforms like MasterPass, his leadership of industry efforts
on fraud reduction such as EMV migration and tokenization, and his MasterCard Advisors group dedicated
solely to the payments industry. MC expanded on-soil presence in 12 individual markets and a heightened
focus on working with governments has improved his ability to serve a broad array of participants in global
payments.
6
Coursera - Foundations of Business Strategy - Final Project - Roberto.Pierantoni@GMail.com June 2015
PORTERS FIVE FORCES ANALYSIS
Bargaining power of customers: HIGH
Payments have become expensive, time-consuming and opaque. High churn, low switching costs and a
plethora of substitute solutions from alternate providers are attracting consumers to these newer players
who are providing an alternate digital experience.
Threat of substitute products or services: HIGH
The mobile phone has become a disruptive payments platform for new innovations and is attempting to
replace cash and checks. Some of the recently launched products have the potential to disrupt the
payments industry, namely P2P payments, mobile wallets, mobile check deposits, pre-loaded cards, digital
currencies, smart ATMs, among others. The above innovations, amongst others, address the current
inefficiencies in the payments marketplace and can provide a superior digital experience to consumers.
Bargaining power of suppliers: HIGH
The several decade-old payment infrastructures especially in advanced countries are an impediment to
supporting real time payments. There is a lack of transparency in the current settlement process with the
value of free float enjoyed by banks continues to remain very high. Unable to support innovation, various
stakeholders are looking at alternate approaches to improve the current system. Countries like Australia
are building new payment platforms that will transition to a real time system. Without a modern payments
infrastructure at banks, the market is open for new players for greater disruption, while also rapidly making
the current systems redundant. A number of players are already innovating in this area such as Dwolla,
Square, PayPal, ClearXchange and virtual currencies like Bitcoin, all with the capability to build an alternate
payments infrastructure.
Threat of new entrants: HIGH
The payments industry has become a hotbed for innovation with new players wanting to upstage the
traditional ones and dominate the market quickly. They come from varied industries ranging from startups,
telcos, card companies, supermarket chains, technology companies and de-nova banks, offering simpler
functionality through an exciting digital experience that appeals to everyone including the millennials.
Many see greater opportunities in the payments data to generate advertisement revenues. A number of
these players are today offering everything from debit cards, checking and savings accounts to money
transfers and small business lending outside of traditional banking.
Rivalry amongst existing competitors: HIGH
The competitive rivalry in payments has intensified over the past year with banks, card companies, telcos,
de-nova banks, payment companies, supermarket chains and large technology companies all trying to
engage with the consumer, with traditional players trying to hold on to their customers in spite of the many
frictions that exist in their offerings. Card companies like Visa, MasterCard, and American Express are
looking at opening up their market through new offerings based on pre-paid cards, mobile wallets, among
others. PayPal continues to dominate the payments settlement business. clearXchange, a network of four
of the seven largest U.S. banks operates a P2P network for its member banks, while Western Union and
MoneyGram maintain their domination in the remittance business.
As one can see, Porters five forces analysis implies an approaching digital disruption that could
fundamentally transform the payments industry. A number of players from diverse industries are trying to
influence the outcome of this marketplace in the backdrop of a rising customer preference for greater selfservice in an increasingly integrated digital and physical world. And banks are running the risk of being
relegated to back-office utilities thereby losing their customer touch points
Coursera - Foundations of Business Strategy - Final Project - Roberto.Pierantoni@GMail.com June 2015
MASTERCARDS CAPABILITIES
MasterCard have several division in order to create a competitive advantage sustainable:
MasterCard Advisors. MasterCard Advisors is a global professional services group which provides
proprietary analysis, datadriven consulting and marketing services solutions to help clients optimize,
streamline and grow their businesses. With analyses based on billions of anonymous transactions
processed globally, MC leverages aggregated information and a consultative approach to help financial
institutions, merchants, media companies, governments and other organizations grow their businesses or
otherwise achieve efficiencies.
Global Products & Solutions (GP&S) is the division responsible for the key differentiating products and
solutions that MasterCard delivers to its customers. Drives the management, development, and
commercialization of core payment solutions (Commercial, Consumer Credit, Debit, Prepaid, and Integrated
Processing Solutions) globally to create a sustainable competitive advantage for MasterCard and its
customers. Emerging Payments consists of MasterCards products and solutions in the areas of eCommerce, Mobile, P2P, PayPass/Transit, inControl, Bill Payment, Chip, and the Mobile Payment Solutions
(Smart Hub) joint venture.
Loyalty and Rewards Solutions. MC provides MasterCard cardholders with a variety of benefits and
services, including a scalable rewards platform that enables issuers to provide their consumers with
personalized offers and rewards, access to a global airline lounge network, global and local concierge
services, individual insurance coverages, emergency card replacement, emergency cash advance services
and a 24-hour cardholder service center. For merchants, MC provides targeted offers and rewards
campaigns and management services for publishing offers, as well as opportunities for holders of co-brand
or loyalty cards and rewards program members to obtain reward points faster. MC support these services
with program management capabilities.
Marketing. MC manages and promotes his brands through advertising, promotions and sponsorships, as
well as digital, mobile and social media initiatives, in order to increase consumer preference for MC brands
and usage of products. MC sponsors a variety of sporting, entertainment and charity-related marketing
properties to align with consumer segments important to MS and thei customers. MasterCard's advertising
plays an important role in building brand visibility, usage and overall preference among cardholders
globally. The Priceless advertising campaign, which has run in 53 languages in 112 countries worldwide,
promotes MasterCard usage benefits and acceptance, markets MasterCard payment products and
solutions and provides MasterCard with a consistent, recognizable message that supports the brand around
the globe. MC have extended the Priceless brand to focus on consumers spending preferences - Priceless
Cities provides cardholders in 35 cities across all of their regions with access to special experiences and
offers, Priceless Causes provides cardholders with opportunities to support philanthropic causes, and
Priceless Surprises provides cardholders with unexpected unique experiences when they use their cards
Coursera - Foundations of Business Strategy - Final Project - Roberto.Pierantoni@GMail.com June 2015
REFERENCE SOURCES
MasterCard Annual Report 2014,
http://www.ezodproxy.com/mastercard/2015/ar/images/MasterCard-AR2014.pdf
Impending Disruption in the Payment Marketplace Should Retail Banks be Worried? - A Validation
Using Porters Five Forces Framework
http://www.tcs.com/SiteCollectionDocuments/White-Papers/Disruption-Payment-0614-1.pdf
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- MasterCard ReportDokument17 SeitenMasterCard Reportjhernandez12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mastercard AssignmentDokument37 SeitenMastercard AssignmentAnastasia EgorovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mastercard CaseStudyDokument20 SeitenMastercard CaseStudyapi-3757737Noch keine Bewertungen
- Credit Card Marketing: Bank of AmericaDokument3 SeitenCredit Card Marketing: Bank of AmericaHamna ShahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lending ClubDokument2 SeitenLending ClubNaman JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Debit CardDokument16 SeitenDebit CardAvinash Sahu100% (1)
- Payments Industry - SLIDE DECK 05.12.2017Dokument361 SeitenPayments Industry - SLIDE DECK 05.12.2017Nat Banyatpiyaphod100% (2)
- Mobile Wallets 101Dokument23 SeitenMobile Wallets 101Anonymous wcqkliGtjNoch keine Bewertungen
- E Wallet User MasterCardDokument12 SeitenE Wallet User MasterCardFlaviub23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Paytm Wallet - Group5DDokument23 SeitenMarketing Paytm Wallet - Group5DAdwait Deshpande100% (1)
- Banking As A Service A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandBanking As A Service A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signet PayDokument10 SeitenSignet Paychakshina gupta100% (1)
- Management Presentation MastercardDokument31 SeitenManagement Presentation Mastercardapi-460871523Noch keine Bewertungen
- Xiaomi Inc in Consumer Electronics (World)Dokument31 SeitenXiaomi Inc in Consumer Electronics (World)sourabhNoch keine Bewertungen
- FileTransferMethods MasterCardDokument6 SeitenFileTransferMethods MasterCardChristopher Attard100% (2)
- MasterCard JJDokument7 SeitenMasterCard JJjohnjamgochianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Payment GatewaysDokument11 SeitenPayment GatewaysAnmol Agarwal100% (1)
- Paytm Case StudyDokument11 SeitenPaytm Case StudyShriraj BamneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deconstructing Digital Only Banking Model A Proposed Policy Roadmap For India FINALDokument44 SeitenDeconstructing Digital Only Banking Model A Proposed Policy Roadmap For India FINALVenke JayakanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-4.4-Payment GatewaysDokument8 SeitenUnit-4.4-Payment GatewaysShivam SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- MasterCard Regional Pricing BulletinDokument4 SeitenMasterCard Regional Pricing Bulletinsoricel23Noch keine Bewertungen
- AfterpayDokument6 SeitenAfterpaykunwar showvhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visa Master CardDokument10 SeitenVisa Master CardsirvashsharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mastercard: A Leading Company in Diversity: Kristin SampleDokument20 SeitenMastercard: A Leading Company in Diversity: Kristin SamplejanedohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research MethodologyDokument34 SeitenResearch MethodologySangeetaLakhesar80% (5)
- b2b Gift Card Market StudyDokument14 Seitenb2b Gift Card Market StudyPriyanshu RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CITIBANKDokument7 SeitenCITIBANKSreeramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alliance Governance at Klarna: Managing and Controlling Risks of An Alliance PortfolioDokument9 SeitenAlliance Governance at Klarna: Managing and Controlling Risks of An Alliance PortfolioAbhishek SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Credit CardDokument51 SeitenCredit CardSmita JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wells FargoDokument9 SeitenWells Fargomnikolic167% (3)
- RBC Mobile WalletDokument2 SeitenRBC Mobile WalletsruthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIS CardLifecycleManagement StrategyDokument35 SeitenFIS CardLifecycleManagement Strategygautam_hariharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Credit Card Market in IndiaDokument62 SeitenCredit Card Market in IndiaDavid BarlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retail Management Assignment - PrintDokument22 SeitenRetail Management Assignment - PrintSian HweiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Citibank: Launching The Credit Card in Asia Pacific: Erica Baumann Paul Davis Nathan Hahn Rebecca Leeds Lauren LettieriDokument30 SeitenCitibank: Launching The Credit Card in Asia Pacific: Erica Baumann Paul Davis Nathan Hahn Rebecca Leeds Lauren Lettierisiddus1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Payment Gateways in IndiaDokument14 SeitenPayment Gateways in IndiaDeepak SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Credit Card Industry in IndiaDokument28 SeitenCredit Card Industry in IndiaAk SahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer Perception and Attitude Towards Credit Card UsageDokument20 SeitenConsumer Perception and Attitude Towards Credit Card UsageSARATH KUMAR DNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paypal Case WriteupDokument3 SeitenPaypal Case WriteupAaras VasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Survey of Popularity of Credit Cards Issued by Different BanksDokument3 SeitenSurvey of Popularity of Credit Cards Issued by Different Bankspritam0000100% (2)
- Mobey Forum Whitepaper Prepaid Mobile WalletDokument32 SeitenMobey Forum Whitepaper Prepaid Mobile Walletmanu_130381Noch keine Bewertungen
- Master Card Credit Authorization SimulatorDokument220 SeitenMaster Card Credit Authorization SimulatorСергій Глоба80% (5)
- Payment Gateway DetailsDokument9 SeitenPayment Gateway DetailsArvind SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Payments 101: Credit and Debit Card Payments: Key Concepts and Industry IssuesDokument16 SeitenPayments 101: Credit and Debit Card Payments: Key Concepts and Industry IssuesShiv PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- MasterCard and Paypass Case Study The Hong Kong Airport ExpressDokument10 SeitenMasterCard and Paypass Case Study The Hong Kong Airport ExpressNguyễn Thị Kiều DiễmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Payments Industry - Card ProcessingDokument5 SeitenPayments Industry - Card ProcessingShriya Chandrakar100% (1)
- Cineplex Report PDFDokument60 SeitenCineplex Report PDFSean MooreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brac Bank Credit Card ChargeDokument1 SeiteBrac Bank Credit Card ChargeMehedi HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MasterCard RulesDokument360 SeitenMasterCard RulesEzeamama ChimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chip Card Terminolgy Explained PDFDokument15 SeitenChip Card Terminolgy Explained PDFMuhammad Asad Bin Faruq100% (1)
- Mobile WalletDokument2 SeitenMobile WalletHimanshu KoliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pocket Rocket PayTmDokument16 SeitenPocket Rocket PayTmNikhil Negi100% (1)
- MasterCard Merchant RulesDokument268 SeitenMasterCard Merchant Rulesfayazm100% (1)
- American Express CompanyDokument10 SeitenAmerican Express CompanygjjkvhjjklhkjkjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apple ACCC SubmissionDokument65 SeitenApple ACCC SubmissionMikey Campbell100% (1)
- Merchant Fees Guide 1Dokument8 SeitenMerchant Fees Guide 1Winston BoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mastercard Case: To-Do List: 1. Strategic PositionDokument8 SeitenMastercard Case: To-Do List: 1. Strategic PositionTomás RodriguesNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOSCMT MastercardDokument5 SeitenDOSCMT MastercardRewati BulusuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 3 - Master CardDokument4 SeitenGroup 3 - Master CardArpit MalviyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MasterCard GL CompanyDokument2 SeitenMasterCard GL CompanyRamneek SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEMS Assignment 22-09-14Dokument1 SeiteMEMS Assignment 22-09-14PalluRajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix D' Conduct Rules: Commencement & ApplicationDokument10 SeitenAppendix D' Conduct Rules: Commencement & ApplicationPalluRajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment of orDokument4 SeitenAssignment of orPalluRajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 Return Calculation SlidesDokument45 SeitenLecture 1 Return Calculation Slidesjong190920_881290942Noch keine Bewertungen
- FreeVibrations Freestudy Co UkDokument0 SeitenFreeVibrations Freestudy Co Ukdeepak_dce_meNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development of Empirical Models From Process Data: - An Attractive AlternativeDokument27 SeitenDevelopment of Empirical Models From Process Data: - An Attractive AlternativeJamel CayabyabNoch keine Bewertungen
- PGP IPRS Audited Report 2014Dokument19 SeitenPGP IPRS Audited Report 2014Roshan MohammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apping Guide InternDokument6 SeitenApping Guide InternPalluRajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crochrane J. (2005) Time Series For Macroeconomics and FinanceDokument136 SeitenCrochrane J. (2005) Time Series For Macroeconomics and FinanceDipki KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DataDokument12 SeitenDataPalluRajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Press Release - Summer Placements 2013 15Dokument3 SeitenPress Release - Summer Placements 2013 15PalluRajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- NotesDokument68 SeitenNotescoonyu1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Internship AbroadDokument9 SeitenInternship AbroadAnkit BharthanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pillar and Wall-Mounted Slewing Jib Cranes: Move MoreDokument18 SeitenPillar and Wall-Mounted Slewing Jib Cranes: Move MoreEgemen AkbulutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kroger Vendor General Parcel Air LTL TL Routing InstructionsDokument4 SeitenKroger Vendor General Parcel Air LTL TL Routing InstructionsReetika ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gulfood Exhibitor List - N 3Dokument14 SeitenGulfood Exhibitor List - N 3Lupu CarmenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development of Plastic Cards Market - Past, Present and Future Scenario in Indian BanksDokument10 SeitenDevelopment of Plastic Cards Market - Past, Present and Future Scenario in Indian BanksVivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Company Case ArgosDokument5 SeitenCompany Case ArgosssclhtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ice Cream ProjectDokument40 SeitenIce Cream ProjectAsif BashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active DetergentDokument16 SeitenActive DetergentRAZIA SULTANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carrefour's Glocal Strategies in TaiwanDokument16 SeitenCarrefour's Glocal Strategies in TaiwanBom TangwiboonpanichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retail Marketing AssignmentDokument26 SeitenRetail Marketing AssignmentOlga GordeevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datawarehouse Interview Quesion and AnswersDokument230 SeitenDatawarehouse Interview Quesion and Answersabraham_sse1594100% (1)
- FDI in Retail in IndiaDokument7 SeitenFDI in Retail in Indiark85mishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bullwhip EffectDokument8 SeitenBullwhip Effectsatu20Noch keine Bewertungen
- RAtio AnalysisDokument16 SeitenRAtio AnalysisThéotime HabinezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Content Delivery NetworkDokument3 SeitenContent Delivery Networkshibanim-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Abante, Jr. vs. Lamadrid Bearing & Parts Corp.Dokument1 SeiteAbante, Jr. vs. Lamadrid Bearing & Parts Corp.Ron DecinNoch keine Bewertungen
- External Environmental AnalysisDokument19 SeitenExternal Environmental AnalysisHale Bulasan100% (1)
- Unit 3 P1 Marketing Techniques Ansoff Matrix NotesDokument2 SeitenUnit 3 P1 Marketing Techniques Ansoff Matrix NotesAlfie_Armstrong100% (1)
- 2014 CatalogDokument390 Seiten2014 CatalogAna Mabel GuevaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questionnaire: Mysore Sandal Soap Products With Reference To Bangalore Market". IDokument4 SeitenQuestionnaire: Mysore Sandal Soap Products With Reference To Bangalore Market". ISuraj Seshan100% (4)
- Outlet SelectionDokument23 SeitenOutlet SelectionSatyajeet SumanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fashion CycleDokument39 SeitenFashion Cycleabhishek_sinha100% (1)
- EU GDPR Opportunities For Grocery RetailDokument24 SeitenEU GDPR Opportunities For Grocery RetailOpen Data Institute100% (1)
- 1 4Dokument20 Seiten1 4pepelocura2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5Dokument6 SeitenChapter 5tomalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Raw Data NielsenDokument7 SeitenRaw Data Nielsenanon_362077100Noch keine Bewertungen
- RitealDokument20 SeitenRitealajaybabukmNoch keine Bewertungen
- 849 FullDokument13 Seiten849 FullAnsuf WicaksonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bingo MKTG StrategyDokument35 SeitenBingo MKTG StrategyShelly SinghalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advertising Barbell.: Ni Kenkoy (The Misadventures of Kenkoy) Created byDokument4 SeitenAdvertising Barbell.: Ni Kenkoy (The Misadventures of Kenkoy) Created byJoana Mae GabasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Mining and Data Warehouse BYDokument12 SeitenData Mining and Data Warehouse BYapi-19799369100% (1)