Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Femle Reproduction Outline
Hochgeladen von
Nhung NguyenOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Femle Reproduction Outline
Hochgeladen von
Nhung NguyenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The Female Reproductive System - RMC
Perineum
Diamond-shaped area between the medial thighs
o Anteriorly (really superiorly) by the pubic symphysis
o Laterally by the ischial tuberosities
o Posteriorly (inferior) by the coccyx.
2 distinct triangle bases
o
Imaginary horizontal line extending b/w the ischial tuberosities
Anterior triangle, or Urogenital triangle
o Contains the urethral and vaginal orifices in females
o Contains the base of the penis and the scrotum in males.
Posterior triangle, or Anal triangle
o Location of the anus in both sexes.
Boundaries of Female Perineum External Genitalia = Vulva
Mons pubis Hair covered Fat Pad
Medial aspects (insides) of the thighs
Gluteal folds
The superior end of the Intergluteal Cleft
the cleft b/w the buttocks (tip of the coccyx is palpable)
Up until 6 wk of lifethere is no differentiation of sex
-clitoris and glans penis have the same precursor
Pelvic Diaphragm (in the pelvic triagles)
Levator Ani and Coccygeus muscles make up Pelvic Floor Muscles Diaphragm
Levator Ani made up of 3-Muscles:
Puborectalis Pubis & Rectus
Pubococcygeus
Iliococcygeus
o The anal aperture goes through it
Supports pelvic organs
Seals inferior opening of bony pelvis (muscular floor)
Lifts to help release (or not release) feces during defecation
Anatomy of Female Reproductive System
Peritoneum = The peritoneum is the serous membrane that forms the lining of the abdominal cavity or the coelom
Peritoneum Folds around the various pelvic organs and creates two major dead-end recesses, or pouches.
o Anterior vesicouterine pouch forms the space b/w the uterus and the urinary bladder
o Posterior rectouterine pouch forms the space b/w the uterus anteriorly and the rectum posteriorly
More commonly known as Pouch of Douglas Cul-de-sac of Peritoneum b/w Uterus &
Cervix
Primary sex organs of the female are the OVARIES.
Accessory sex organs include
o Uterine tubes
o Uterus,
o Vagina,
o Clitoris
o Mammary glands.
Peritoneal Folds/ Ligaments
Mesovarium:
o Double folds of Peritoneum
o Attaches Ovaries to broad ligament
Broad ligament
o Peritoneum that Drapes over the uterus
o Extends from lateral uterine fold to wall of pelvis
o Holds Ovaries and Uterine Tubes
o Mesosalpinx Peritoneum covering over Uterine Tubes
(which are part of the uterus)
Round Ligament
o From uterus through the inguinal canal Labia Majora of ext. genitalia
The Female Reproductive System - RMC
Ovarian ligament
o Ovary to superior margin of uterus
Suspensory ligament
o Ovary to pelvic wall
Superficial Pouch (Didnt Discuss)
B/w inferior fascia of UG diaphragm and membranous layer of superficial fascia (Colles Fascia)
Contains:
o Superficial transverse perineal muscle & Ischiocavernosus and bulbospongiosus muscles
o Cura of penis or clitoris
o Perineal Nerve
o Internal pudenal artery and vein
Deep Perineal Space (Pouch) (Didnt Discuss)
B/w superior and inferior fascia of UG Diaphragm
Contents:
o Deep transverse perineal muscle
o Sphincter & Membraneous part of urethra
o Bulbourethral glands
o Branches of internal pudenal vessels
o Pudenal nerve
OVARY
Production of Gametes and Hormones
Posterior to broad ligament (Mesovarium)
o Broad: a fold of peritoneum; Drapes over reproductive organs
Suspensory & ovarian ligaments anchor
o Suspensory- to lateral wall of pelvis
o Ovarian- to uterus
Blood supply by Ovarian Artery
***Venous drainage
o Right Gonadal Vein empties into Inferior Vena Cava!
o Left Gonadal Vein empties into Left RENAL Vein! empties into IVC
Composed of Ovarian Follicles (sac-like)
Structures of ovarian follicle:
o Oocyte Stimulated by FSH
o Follicular cells Forming Ovarian Follicles
Homologous to testes
Vasculature of Ovaries
o Ovarian artery from ab. Aorta enters suspensory ligaments and branches through mesovarium
o Veins drain via pampiniform plexi
The Female Reproductive System - RMC
Lymphatics of Ovaries
o Follow ovarian blood vessels, ascend to lumbar lymph nodes
Innervation of Ovaries Both Sympathetic & Parasympathetic
o Parasympathetic from pelvic splanchnic nerves
o Afferent fibers enter spinal cord through T10 and T11 nerves
UTERUS (includes cervix, fallopian tube)
Located b/w Urinary Bladder and Rectum
Organ of gestation
Intraperiotneal (broad ligament)
Anteverted (leans forward) at junction of cervix and vagina
Anteflexed (bends) at cervix and body
Hollow organ
Support of the Uterus
Pelvis floor muscles: Pelvic & Urogenital Diaphragm
Round Ligaments: Lateral Uterus through Inguinal canal to Labia Majora
o Maintain Anteverted position
Transverse Cervical Ligaments (Cardinal): Lateral Cervix and Vagina to pelvic wall
Uterosacral Ligaments: Inferior/Lateral Uterus to Sacrum
o Cardinal and Uterosacral Ligaments are thickenings of subserous fascia and smooth muscle
Functions:
Implantation (pre-embryo), Nourishment (embryo/fetus), Ejects fetus, & Menstruation (Actually Uterine
Bleeding!)
o Organogenesis First 56 days after fertilization; After that, all organs have developed, and
growth continues.
o Site for Implantation: pre-embryo implants to inner uterine wall and connects to its lining
o Supports, protects, and nourishes the developing embryo/fetus
Forms vascular connection with uterine wall develops into placenta
o Ejects fetus at birth after maternal oxytocin levels increase contractions of labor
o Site of Menstruation
If oocyte not fertilized or after birth muscular wall contracts and sheds inner lining
Regions of the Uterus
Fundus: (dome shaped) Rounded portion superior & anterior to uterine tube entrance
o A non-impregnated Uterus is a Pelvic Organ!
o During pregnancy, Fundus becomes Abdominal Organ!
Body: Main portion; cavity is triangular
Isthmus: Constricted region b/w body and cervix
Cervix: Narrow portion which joins to vagina
o Cervical canal
o Internal Os opening to Isthmus
o External Os opening to Vagina
Uterine Layers/ Wall of the Uterus
The Female Reproductive System - RMC
Perimetrium: Serosa Outer Layer; Peritoneum and thin connective tissue; Continuous with broad ligament
(because its part of the peritoneum)
Myometrium: Smooth Muscle; Middle Layer; becomes distended during pregnancy (muscle cells increase in
size and number)
Endometrium: Hormone sensitive (Estrogen & Progesterone); Growth cycles b/w puberty and menopause
(this is the layer that will shed during menstration)
o Two layers: Stratum Basalis & Stratum Functionalis
S. Functionalis builds up each month (ovarian hormones)
o Uterine glands secret glycoproteins into uterine cavity (nutrients for potential zygote)
o At Menstruation: func. layers self digest; Spiral Arteries kink and constrict so cells die
o Just before menstrual flow, Spiral Arteries open wide, capillaries burst and func. layer sloughs off.
Oxitocin = only hormone with a positive feedback that creates uterine contraction
Blood Supply: Uterine (from internal iliac), Vaginal, and Ovarian (from abdominal aorta) arteries ***HIGHLY
VASCULARIZED FOR REPRODUCTION!!! KNOW ARTERIES!!!
Arcuate, the straight arteries, then squiggly arteries into the endometrium
UTERINE TUBES (Fallopian tubes/oviductspart of the uterus)
Extend laterally from both sides of uterus toward ovaries
o Does NOT physically attach to Ovaries
W/in and Suspended by Broad Ligament
Homologous to Vas Deferens Tubular Structure
Receives Ovulated Oocyte
o ~3 to 5 days for Pre-Embryo to reach lumen of Uterus!!!
PARTS: Inside Lined with Mucosa (Simple Ciliated Columnar)
Muscularis Serosa (Made up of MESOSALPINX)
o Infundibulum Flared end of tube
Fimbriae = finger like projections at distal end
o **Ampulla Long, Wide portion
Where Secondary Oocyte is FERTILIZED
o Isthmus Narrow, attach to uterus
o Cilia line walls of tubes (move oocyte towards uterus)
o Interstitial Segment
Blood supply via Ovarian and Uterine Arteries
Drainage to Lumbar Lymph Nodes
Nerve supply from Ovarian and Uterine Plexi
Cilia and Non-Ciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium
o Ciliary movement and periodic peristaltic contractions move ova
o Secretion of nutrient substances
VAGINA
The Female Reproductive System - RMC
Muscles related to the vagina:
o Pubovaginalis (part of levator ani)
o External Urethral Sphincter Muscle
o Urethrovaginal Sphincter Muscle
o Bulbospongiosus Muscle
Lymphatic Drainage of the Vagina (important in this location because its an
opening to the outside)
o Superior: internal and external iliac nodes
o Middle: internal iliac nodes
o Inferior: sacral and common iliac nodes; superficial inguinal nodes
**Parasym and Sym both innervate the vagina
External Genitalia
***Collectively called the VULVA (or Pudendum)
Mons pubis Fatty Hair Covered Area overlying pubic symphysis
Labia Majora Homologous to Scrotum
o Outer skin pigmented
Sweat, sebaceous glands
Hairs present after puberty
o Inner Skin Pink (no pubic hair)
Thick-walled, Fibromuscular Tube The Organ of Copulation
Forms the inferior-most region of female reproductive tract
~10cm in length in an adult female
Connects uterus w/ outside of the body anteroventrally (functions as Birth Canal)
Passageway for Menstruation
HIGHLY VASCULARIZED (Uterine, Vaginal, Pudendal Arteries) & invested w/ Lymphatic Vessels
Its relatively thin, distensible wall consists of 3 tunics:
o Inner Mucosa (Thrown into RUGAE) Middle Muscularis & Outer Adventitia (NOT Serosa!...bc its not
an intra-abdominal organ (like the esophagus))
From Cervix (~ 90 degree angle) to Exterior of Body (Vestibule)
o Vestibule is region b/w labia minora
Posterior to Urethra & Anterior to Rectum
Hymen Mucous Membrane over entry (Embryonic Remnant)
Fornices Pocket surrounding Uterine Cervix (surgical access to pelvic cavity; location of birth control
device)
Labia minora
o No hair, no fat
o Core of spongy connective tissue containing erectile tissue and many blood vessels
o Contains Vestibule Potential space b/w Labia; Enclosed by Labia Majora
Contains Openings: Urethral & Vaginal Orifices, & Vestibular Glands (Bartholin's Glands)
o Posterior forms frenulum of clitoris
Clitoris located where Labia Minora meets Anteriorly
o Prepuce External/Anterior fold of the Labia Minora that forms a hood like Covering over the Clitoris
Glans clitoris
Two Crura (each is a crus)
Two Corpora Cavernosa (Just like the Penis, the Clitoris has Two Corpora)
o Frenulum of clitoris
o Contains erectile tissue, homologous to penis
Four purposes include:
o Sensory & Erectile tissue
o Directs the flow of urine
o Prevents entry of foreign material
o Padding
Greater vestibular gland
o Under or behind bulb of vestibule
o Homologous to bulbourethral gland
The Female Reproductive System - RMC
o
o
Secretes mucus
Drained by duct into vestibule (b/w labia minora and hymen)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
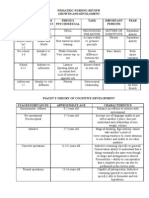
- 1 Growth and DevelopmentDokument7 Seiten1 Growth and DevelopmentMaica LectanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial NervesDokument6 SeitenCranial Nervesvienny kayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiologic and Psychologic Changes During PregnancyDokument12 SeitenPhysiologic and Psychologic Changes During Pregnancyyannie100% (1)
- Guide To History TakingDokument55 SeitenGuide To History TakingGabriella Hild100% (1)
- Medex Exam Writeups PageDokument9 SeitenMedex Exam Writeups Pageaahmad87Noch keine Bewertungen
- OB - Normal Labor and DeliveryDokument51 SeitenOB - Normal Labor and DeliveryJosh Matthew Rosales33% (3)
- PEDS Final Questions ATI Questions and AnswersDokument14 SeitenPEDS Final Questions ATI Questions and Answersianshirow834Noch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal and Infancy PeriodDokument10 SeitenNeonatal and Infancy PeriodJoji Santa MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identify The Heart Rhythm Represented in The Following EKG StripsDokument3 SeitenIdentify The Heart Rhythm Represented in The Following EKG StripsJelly BeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal Medicine Review QuestionsDokument50 SeitenLegal Medicine Review QuestionsAngelique Mae Mortejo Salarza100% (2)
- Elderly ProblemsDokument4 SeitenElderly ProblemsWilliam Ezekiel JUju CustodioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midwifery Lab ManualDokument56 SeitenMidwifery Lab Manualgladz25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wits Obstetrics 2008Dokument134 SeitenWits Obstetrics 2008Muvenn Kannan100% (1)
- Developmental Stages - Infant To AdolescentDokument6 SeitenDevelopmental Stages - Infant To AdolescentGeguirra, Michiko SarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Nursing Edited)Dokument1 SeitePediatric Nursing Edited)Dominique RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- HPS Tylenol PedsDokument3 SeitenHPS Tylenol PedsEvelynn Gallardo100% (1)
- Neurologic DysfunctionDokument75 SeitenNeurologic DysfunctionNur SanaaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Newborn ExaminationDokument132 SeitenThe Newborn ExaminationdevilstNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Cardiovascular DisordersDokument9 SeitenPediatric Cardiovascular Disorderscayla mae carlos0% (1)
- UntitledDokument41 SeitenUntitledvioletdeocaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Born Care 1Dokument12 SeitenNew Born Care 1Tsuyoshi BangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 NewbornDokument123 Seiten2 NewbornANNIE SHINE MAGSACAYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assisting in Insertion of Intrauterine Contraceptive DeviceDokument4 SeitenAssisting in Insertion of Intrauterine Contraceptive DeviceRini Robert100% (1)
- Vital Signs: Aurora Roslin Samosa, Man RNDokument57 SeitenVital Signs: Aurora Roslin Samosa, Man RNAlexander DontonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mcqs - Obstetrics and Gynaecology (For Post Graduate Preparing For FNB and Professionals) Obstetrics and GynaecologyDokument27 SeitenMcqs - Obstetrics and Gynaecology (For Post Graduate Preparing For FNB and Professionals) Obstetrics and GynaecologyAnonymous kQCQ30Rq5ONoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Nurse in ObstetricsDokument6 SeitenRole of Nurse in ObstetricsSridevi DevarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Swine PPT 2012Dokument99 SeitenSwine PPT 2012ዘንገና ቲዩብNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abigail Domingo Physical AssessmentDokument87 SeitenAbigail Domingo Physical AssessmentVenus Maui RoqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peds Exam 3Dokument61 SeitenPeds Exam 3Katie Morgan EdwardsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asthma That Disappears Between Ages 6-8 - Bronchioles Grew & Resolved The AsthmaDokument27 SeitenAsthma That Disappears Between Ages 6-8 - Bronchioles Grew & Resolved The Asthmasimonedarling100% (1)
- Dermpath Cheat SheetDokument2 SeitenDermpath Cheat SheetBob LoblawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Growth and Development ToddlersDokument3 SeitenUnderstanding Growth and Development ToddlersSimranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ob Study PacketDokument85 SeitenOb Study PacketEagles171100% (2)
- Insulin ChartDokument1 SeiteInsulin ChartChristian BagaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Systems ANDREADokument7 SeitenReview of Systems ANDREAAndrea Dora OrtalizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parenting Styles: - Dictatorial or AuthoritarianDokument45 SeitenParenting Styles: - Dictatorial or AuthoritarianCourseTree LearningNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric NursingDokument17 SeitenPediatric NursingMark Ray A. EspinozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skills Checklist (HCA and Mental Health) - Copy (1710)Dokument2 SeitenSkills Checklist (HCA and Mental Health) - Copy (1710)Mohammad Tayyab KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cesarean Section PrimaryDokument33 SeitenCesarean Section PrimaryKazvin Carl PeraltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal Ob NotesDokument103 SeitenMaternal Ob NotesBoris OrbetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical-Surgical Nursing: Perioperative OverviewDokument24 SeitenMedical-Surgical Nursing: Perioperative OverviewSheena Ann L. LLarenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flash Cards Vocab For Exam 1. Jarvis CH 1-3, 8, 9, 12, 13http - P.quizlet - Com - Settitle Health Assessment Vocab For Exam 1Dokument22 SeitenFlash Cards Vocab For Exam 1. Jarvis CH 1-3, 8, 9, 12, 13http - P.quizlet - Com - Settitle Health Assessment Vocab For Exam 1tipredd100% (1)
- Tracheostomy Care SkillsDokument8 SeitenTracheostomy Care Skillshoangt2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Safe and Effective Care EnvironmentDokument8 SeitenSafe and Effective Care Environmentgretch_carreonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signs and Symptoms of AbuseDokument4 SeitenSigns and Symptoms of AbusefranjoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- BreastfeedingDokument20 SeitenBreastfeedingThe Rat83% (6)
- AH2 Hesi ReviewDokument46 SeitenAH2 Hesi ReviewJamie Antonini Grant100% (1)
- HESI 2015 Maternal New Born Specialty AnswersDokument2 SeitenHESI 2015 Maternal New Born Specialty AnswersAnaGranara100% (3)
- Head To Toe Assessment GuideDokument2 SeitenHead To Toe Assessment GuideSara SabraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jennifer Portillo Health Assessment VocabularyDokument9 SeitenJennifer Portillo Health Assessment VocabularyJennifer PortilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wet To Damp DressingDokument2 SeitenWet To Damp DressingCarrie TranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autonomic DrugsDokument2 SeitenAutonomic DrugsDouglas Greg CookNoch keine Bewertungen
- CheatsheetDokument2 SeitenCheatsheetSiddaq SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study 2Dokument3 SeitenCase Study 2jamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDokument16 SeitenAutonomic Nervous SystemmogibsfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antepartal Fetal Assessment: Developed by D. Ann Currie, R.N.,M.S.NDokument38 SeitenAntepartal Fetal Assessment: Developed by D. Ann Currie, R.N.,M.S.NismailalviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Which Signs and Symptoms Would The Nurse Expect To Assess in A Newborn WithDokument1 SeiteWhich Signs and Symptoms Would The Nurse Expect To Assess in A Newborn WithjamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diabetes Continence1Dokument3 SeitenDiabetes Continence1Anonymous C7H7wS6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Suffixes and PrefixesDokument2 SeitenSuffixes and PrefixesNiksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Brochure Health ScienceDokument2 SeitenFinal Brochure Health Scienceapi-313269355Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gemp3 Paediatric Clinical Examination SkillsDokument13 SeitenGemp3 Paediatric Clinical Examination SkillsAnna-Tammy HumanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Growth &development ShaluDokument36 SeitenGrowth &development ShaluNIRANJANA SHALININoch keine Bewertungen
- UWorld Sim Assessment 1Dokument3 SeitenUWorld Sim Assessment 1vsalardaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatrics PDFDokument15 SeitenPediatrics PDFLouis FortunatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3120 Midterm Study GuideDokument43 Seiten3120 Midterm Study Guidemicheala12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric AsthmaDokument8 SeitenPediatric AsthmaBoris SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bone Cancer Chart 2012Dokument8 SeitenBone Cancer Chart 2012BigBoostingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intake and Output (I&O) : Key TerminologyDokument5 SeitenIntake and Output (I&O) : Key TerminologyJack KeurigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activ Care List of Day Care TreatmentsDokument7 SeitenActiv Care List of Day Care TreatmentsHarish HuddarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fpp-Obstetric & Gynaecology ProcedureDokument8 SeitenFpp-Obstetric & Gynaecology ProcedureNurul FarhanahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Drills TwoDokument15 SeitenTest Drills TwoSeanmarie CabralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unitive and Procreative Health Procreation, Creation and EvolutionDokument9 SeitenUnitive and Procreative Health Procreation, Creation and EvolutionJustJ ThingsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post Term PregnancyDokument22 SeitenPost Term PregnancyDarianne HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rcog2018 3ad0b1b NORMALDokument1 SeiteRcog2018 3ad0b1b NORMALberlianroma100% (1)
- Complicated Labor and DeliveryDokument226 SeitenComplicated Labor and Deliveryrhimineecat71100% (1)
- Natural and Artificial Methods of ContraceptionDokument40 SeitenNatural and Artificial Methods of ContraceptionelynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differentiation Between True and False Labor ContractionDokument10 SeitenDifferentiation Between True and False Labor Contractionpearl joy holleroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Utama Kelompok 1 (Position in Labour)Dokument9 SeitenJurnal Utama Kelompok 1 (Position in Labour)retnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre Natal Care Book BasedDokument9 SeitenPre Natal Care Book BasedAngelaTrinidadNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Shape and Dimensions of The Human Vagina As Seen in Three-Dimensional Vinyl Polysiloxane CastsDokument5 SeitenThe Shape and Dimensions of The Human Vagina As Seen in Three-Dimensional Vinyl Polysiloxane CastsgaboinklNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materials and Equipments For Physical AssessmentDokument2 SeitenMaterials and Equipments For Physical AssessmentJANEDOE101100% (1)
- Patho BabyDokument7 SeitenPatho BabyNicklaus RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- پارتوگرافDokument49 Seitenپارتوگرافdr jai gurungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vulva Vagina Uterus - MODIFIED PDFDokument141 SeitenVulva Vagina Uterus - MODIFIED PDFBatool SherbiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Early Pregnancy Loss in Emergency MedicineDokument14 SeitenEarly Pregnancy Loss in Emergency MedicineMuhammad RezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student'S Gynaecology Notes: For Students, by StudentsDokument45 SeitenStudent'S Gynaecology Notes: For Students, by StudentsAdli IsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pregnancy With Prolapse Utery PDFDokument2 SeitenPregnancy With Prolapse Utery PDFAnwar Mahnan QomariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mummification Maceration PyometraDokument16 SeitenMummification Maceration PyometrafeyisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Three-Dimensional Sonographic Findings of A Cervical PregnancyDokument4 SeitenThree-Dimensional Sonographic Findings of A Cervical PregnancyEdwin AtencioNoch keine Bewertungen