Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Bio Transformation Is The Chemical Modification
Hochgeladen von
selva17cpOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Bio Transformation Is The Chemical Modification
Hochgeladen von
selva17cpCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Biotransformation is the chemical modification (or modifications) made by an
organism on a chemical compound. If this modification ends in mineral
compounds like CO2, NH3+ or H2O, the biotransformation is called mineralisation.
Biotransformation means chemical alteration of chemicals such as (but not
limited to) nutrients, amino acids, toxins, or drugs in the body. It is also needed
to render nonpolar compounds polar so that they are not reabsorbed in renal
tubules and are excreted.
Precipitation is the formation of a solid in a solution or inside another solid
during a chemical reaction or by diffusion in a solid. When the reaction occurs in a
liquid, the solid formed is called the precipitate, and the liquid remaining above
the solid is called the supernate. Powders derived from precipitation have also
historically been known as flowers.
Centrifugation is a process that involves the use of the centrifugal force for the
separation of mixtures, used in industry and in laboratory settings. More-dense
components of the mixture migrate away from the axis of the centrifuge, while less-
dense components of the mixture migrate towards the axis. Chemists and biologists
may increase the effective gravitational force on a test tube so as to more rapidly
and completely cause the precipitate ("pellet") to gather on the bottom of the tube.
The remaining solution is properly called the "supernate" or "supernatant liquid".
The supernatant liquid is then either quickly decanted from the tube without
disturbing the precipitate, or withdrawn with a Pasteur pipette.
Crystallization is the (natural or artificial) process of formation of solid crystals
precipitating from a solution, melt or more rarely deposited directly from a gas.
Crystallization is also a chemical solid-liquid separation technique, in which mass
transfer of a solute from the liquid solution to a pure solid crystalline phase occurs.
Protocols for centrifugation typically specify the amount of acceleration to be applied to the
sample, rather than specifying a rotational speed such as revolutions per minute. The acceleration
is often quoted in multiples of g, the standard acceleration due to gravity at the Earth's surface.
This distinction is important because two rotors with different diameters running at the same
rotational speed will subject samples to different accelerations.
Since the motion is circular the acceleration can be calculated as the product of the radius and the
square of the angular velocity. Traditionally named "Relative centrifugal force" (RCF), it is the
measurement of the acceleration applied to a sample within a centrifuge and it is measured in
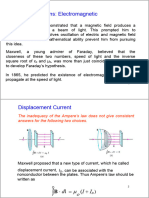
units of gravity (times gravity or × "g"). It is given by
where
is earth's gravitational acceleration,
is the rotational radius,
is the rotating speed, measured in revolutions per unit of time.
When the rotational speed is given in revolutions per minute (RPM) and the rotational radius is
expressed in centimetres (cm) the above relationship becomes
is the rotational radius measured in centimetres (cm),
is rotating speed measured in revolutions per minute (RPM).
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Use of Mattsson's Solution of PH 7.2 To Evaluate The Stress-Corrosion Cracking Susceptibility of Copper-Zinc AlloysDokument3 SeitenUse of Mattsson's Solution of PH 7.2 To Evaluate The Stress-Corrosion Cracking Susceptibility of Copper-Zinc AlloysGrato Jr SingcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Variant Analysis PPT 27.02.2013Dokument25 SeitenVariant Analysis PPT 27.02.2013UMMID WashimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systematic Toxicological Screening Using The ACQUITY UPLC I-Class/Xevo TQ-S MicroDokument4 SeitenSystematic Toxicological Screening Using The ACQUITY UPLC I-Class/Xevo TQ-S MicrokgvtgNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCC 5Dokument1 SeiteSCC 5TasmanijskaNemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory and PracticeDokument22 SeitenTheory and PracticeBryan Ramirez100% (1)
- 2012 Env Drill Comp Fluids Dir PDFDokument25 Seiten2012 Env Drill Comp Fluids Dir PDFWilson WanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 - Maxwell's Equations - Sks - 1Dokument15 Seiten2 - Maxwell's Equations - Sks - 1Shakawat Hossain ShifatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Science: Quarter 2 - Module 13: Special Theory of RelativityDokument24 SeitenPhysical Science: Quarter 2 - Module 13: Special Theory of RelativitykimkimkimaaangNoch keine Bewertungen
- CYD505Dokument5 SeitenCYD505yasuluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Free SilicaDokument2 SeitenEffect of Free SilicaHazem DiabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Birla Instritute of Technology & Science, Pilani, Pilani Campus Chemical Engineering DepartmentDokument2 SeitenBirla Instritute of Technology & Science, Pilani, Pilani Campus Chemical Engineering DepartmentVaibhav SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Mine Drainage Quality Prediction of Surface Coal Mine Rock Samples With Humidity Column Test-3-10Dokument8 SeitenThe Mine Drainage Quality Prediction of Surface Coal Mine Rock Samples With Humidity Column Test-3-10Fanteri Aji DharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Co2 EvaporatorsDokument7 SeitenDesign Co2 EvaporatorsYutt Watt100% (1)
- Coal Sampling and Analysis Standards - ccc235 PDFDokument123 SeitenCoal Sampling and Analysis Standards - ccc235 PDFAparkenthonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q13&14Dokument2 SeitenQ13&14Izzah HzmhNoch keine Bewertungen
- WTA 11.9-S-SE DN15-125 NewDokument2 SeitenWTA 11.9-S-SE DN15-125 NewShah Rizal AbidNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Chemistry (CHEM.1012) Chapter 1 and 2 PPT - Yibrehu Bogale - Academia - EduDokument1 SeiteGeneral Chemistry (CHEM.1012) Chapter 1 and 2 PPT - Yibrehu Bogale - Academia - EduMalkamu JankoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual MaDokument21 SeitenManual MaSergio RecabarrenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loctite 5182Dokument3 SeitenLoctite 5182ccorp0089Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2022-JEE Advanced Booster Test-2 SolutionsDokument14 Seiten2022-JEE Advanced Booster Test-2 SolutionsDivyansh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment On AstrophysicsDokument5 SeitenAssignment On AstrophysicsNarayanan Elatchoumy PadyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Data Sheet: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakingDokument12 SeitenSafety Data Sheet: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakingthjamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atmospheric AerosolsDokument24 SeitenAtmospheric Aerosolsh_guthrieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 1 (A) HSBDokument6 SeitenWeek 1 (A) HSBBeyonce SkekelNoch keine Bewertungen
- EPAS NC II Rating Sheet CoreDokument12 SeitenEPAS NC II Rating Sheet CoreDhena H Rasul Sabdula100% (1)
- Heat Transfer: Precious Arlene Villaroza-MelendrezDokument46 SeitenHeat Transfer: Precious Arlene Villaroza-MelendrezMark Jake Rodriguez0% (1)
- Discussions On IE Irodov's Problems in General Physics Arihant Books ArihantBooksDokument2 SeitenDiscussions On IE Irodov's Problems in General Physics Arihant Books ArihantBooksShootingStarPhotonsNoch keine Bewertungen
- M1Dokument5 SeitenM1Mavis WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- FTIRDokument79 SeitenFTIRshruti shahNoch keine Bewertungen