Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
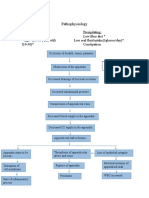
Drug Study For Fracture
Hochgeladen von
itsmeayaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Drug Study For Fracture
Hochgeladen von
itsmeayaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
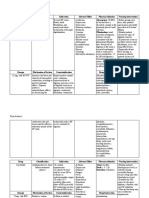
Pre-op medications
Generic name
Cefazolin
Brand
Name
Ancef
Classification
Therapeutic: Antiinefectives
1g/IVTT/OD
Pharmacologic: First
generation
cephalosphorins
Ranitidine
50mg IVTT
Zanta
c
Therapeutic:
Anti-ulcer agents
Pharmacologic:
Mechanism of
action
Bind to bacterial
cell wall
membrane,
causing cell death.
Active against
many grampositive cocci
including:
Streptococcus
pneumoniae,
Group A betahemolytic
streptococci;
Penicillinasproducing
staphylococci.
Inhibits the
action of
histamine at the
H2 receptor site
Indication
Skin & skin structure
infections; bone & joint
infections
Treatment and
prevention of heartburn,
acid indigestion, and
sour stomach.
Adverse effects
CNS:
Seizures (high doses)
GI:
Pseudomembranous colitis,
diarrhea, nausea, vomiting,
cramps
GU:
Interstitial nephritis
DERM:
Rashes, urticaria
HEMAT:
Blood dyscrasias, hemolytic
anemia
LOCAL:
Pain at IM site, phlebitis at IV
site
MISC:
Allergic reactions including
Anaphylaxis and Serum
sickness, superinfection
CNS:
Confusion, dizziness,
drowsiness, hallucinations,
headache
Nursing consideration
Assess patient for infection (vital
signs; appearance of surgical site,
urine; WBC) at beginning and during
therapy.
Before initiating therapy, obtain a
history to determine previous use of
and reactions to penicillins or
cephalosphorins. Persons with a
negative history of penicillin
sensitivity may still have an allergic
response.
Obtain specimens for culture and
sensitivity before initiating therapy.
Observe patient for signs and
symptoms of anaphylaxis (rash,
pruritis, laryngeal edema, wheezing).
Discontinue drug and notify physician
or other health care professional
immediately if these problems occur.
Keep epinephrine, an antihistamine,
and resuscitation equipment close by in
case of anaphylactic reaction.
Assess patient for epigastric or
abdominal pain and frank or occult
blood in the stool, emesis, or gastric
aspirate.
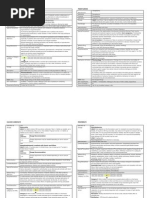
Metoclopromide
Clopr
a
Histamine H2
antagonists
located primarily
in gastric parietal
cells, resulting in
inhibition of
gastric acid
secretion.
In addition,
ranitidine bismuth
citrate has some
antibacterial
action against H.
pylori.
Therapeutic:
Antiemetic
Potent central
dopamine receptor
antagonist.
Structurally
related to
procainamide but
has little
10mg IVTT
Pharmacologic:
direct-acting
cholinergic
(parasympathomimetic
CV:
Arrhythmias
GI:
Altered taste, black tongue,
constipation, dark stools,
diarrhea, drug-induced hepatitis,
nausea
GU:
Decreased sperm count,
impotence
ENDO:
Gynecomastia
HEMAT:
Agranulocytosis, Aplastic
Anemia, neutropenia,
thrombocytopenia
LOCAL:
Pain at IM site
MISC:
Hypersensitivity reactions,
vasculitis
To facilitate intubation of
small bowel;
symptomatic treatment
of gastroesophageal
reflux.
CNS: restlessness,
drowsiness,
fatigue,insomia,
dizziness,anxiety
CV: tansient hypertension
GI: nausea and diarrhea
Nurse should know that it may cause
false-positive results for urine protein;
test with sulfosalicylic acid.
Inform patient that it may cause
drowsiness or dizziness.
Inform patient that increased fluid
and fiber intake may minimize
constipation.
Be aware that during early
treatment period, serum
aldosterone may be elevated;
after prolonged administration
periods, it returns to
pretreatment level.
Lab tests: Periodic serum
Midazolam
15mg tab
Therapeutic:
Anti-anxiety agents,
sedative/hypnotics
Pharmacologic:
benzodiazepines
antiarrhythmic or
anesthetic activity.
Exact mechanism
of action not clear
but appears to
sensitize GI
smooth muscle to
effects of
acetylcholine by
direct action.
Physiologic
Mechanism
Short-term
sedation
Postoperative
amnesia
Pharmacologic
Mechanism
Acts at many
levels of the CNS
to produce
generalized CNS
depression.
Effects may be
mediated by
GABA, an
inhibitory
neurotransmitter.
Preprocedural sedation.
Aids in the induction of
anesthesia and as part of
balanced anesthesia.
drowsiness
confusion
problems with balance
and movement
slowed reflexes
slowed breathing and
heartbeat
coma (loss of
consciousness for a
period of time)
electrolyte.
Monitor for possible
hypernatremia and
hypokalemia, especially if
patient has CHF or cirrhosis.
Assess level of sedation and level of
consciousness throughout and for 2-6
hr following administration.
Monitor BP, pulse and respiration
continuously during IV administration.
Oxygen and resuscitative equipment
should be immediately available.
If overdose occurs, monitor pulse,
respiration , and BP continuously.
Maintain patent airway and assist
ventilation as needed. If hypotension
occurs, treatment includes IV fluids,
repositioning and vasopressors.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- PNF PatternsDokument19 SeitenPNF PatternsDany VirgilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sexual Disorders ParaphiliaDokument32 SeitenSexual Disorders Paraphiliaitsmeaya0% (1)
- Post Abortion CareDokument35 SeitenPost Abortion CareNatukunda DianahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Development: FDA's Definition of A New DrugDokument11 SeitenDrug Development: FDA's Definition of A New DrugSophie MendezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendicitis PathophysiologyDokument2 SeitenAppendicitis PathophysiologyitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Pancreatitis: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & TreatmentDokument3 SeitenAcute Pancreatitis: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & TreatmentitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- War Wounds: Basic Surgical Management: The Principles and Practice of The Surgical Management of Wounds Produced by Missiles or ExplosionsDokument48 SeitenWar Wounds: Basic Surgical Management: The Principles and Practice of The Surgical Management of Wounds Produced by Missiles or ExplosionsInternational Committee of the Red Cross86% (7)
- Coping With Stress Senior HighDokument23 SeitenCoping With Stress Senior HighJulienne Rose Penaranda Saballa100% (1)
- Dimenhydrinate PDFDokument2 SeitenDimenhydrinate PDFWindy SengiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatrics Pediatrics Pediatrics Pediatrics Pediatrics: Pediatrics Pediatrics Pediatrics Pediatrics PediatricsDokument2 SeitenPediatrics Pediatrics Pediatrics Pediatrics Pediatrics: Pediatrics Pediatrics Pediatrics Pediatrics PediatricsBobet Reña100% (2)
- DRUG STUDY Allopurinol (Purinase)Dokument2 SeitenDRUG STUDY Allopurinol (Purinase)DennMarkTaponNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Status ExaminationDokument4 SeitenMental Status Examinationitsmeaya100% (3)
- DRUG STUDY EpinephrineDokument2 SeitenDRUG STUDY EpinephrineCarlo Francisco D. Canto78% (9)
- Drug StudyDokument9 SeitenDrug Studykcbabee0333% (3)
- Drug Study of Ceftriaxone & RowatinexDokument5 SeitenDrug Study of Ceftriaxone & RowatinexLorina Lynne ApelacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument9 SeitenDrug StudyJonica CamposNoch keine Bewertungen
- San Pedro Hospital of Davao City, Inc.: Nurses' NotesDokument2 SeitenSan Pedro Hospital of Davao City, Inc.: Nurses' NotesSophia Jay LaurieNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - FatigueDokument3 SeitenNCP - Fatigueitsmeaya100% (1)
- Nifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyDokument5 SeitenNifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyAllyne GavinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acceptance of Dying A Discourse Analysis of Palliative Care LiteratureDokument8 SeitenAcceptance of Dying A Discourse Analysis of Palliative Care LiteratureMauricio MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- KetorolacDokument5 SeitenKetorolacMichelle Ann P. NacuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument13 SeitenDrug StudyAldrin Ian Oraza AlpeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug study cilostazol intermittent claudicationDokument2 SeitenDrug study cilostazol intermittent claudicationart_mutantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amoxicillin Nursing ConsiderationsDokument3 SeitenAmoxicillin Nursing ConsiderationsNico DonatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug mechanism indication contraindication side effects nursingDokument1 SeiteDrug mechanism indication contraindication side effects nursinghahahahaaaaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DioxelDokument1 SeiteDioxelJosselle Sempio CalientaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DuphalacDokument2 SeitenDuphalacianecunarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug AnalysisDokument8 SeitenDrug AnalysisJonie Vince SañosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- COLCHICINE pptx1800128929Dokument15 SeitenCOLCHICINE pptx1800128929April Mergelle LapuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study: Name of Drug Action Indication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityDokument4 SeitenDrug Study: Name of Drug Action Indication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityBel CortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Ko ToDokument4 SeitenDrug Study Ko ToGian Carlo FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 66 Drug AnaDokument3 Seiten66 Drug AnaAlexa RoqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biperiden Generic and Brand Names, Uses, Side EffectsDokument1 SeiteBiperiden Generic and Brand Names, Uses, Side EffectsMFQ.RN100% (2)
- DS (Fenofibrate)Dokument5 SeitenDS (Fenofibrate)Mary April MendezNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUGS Study OrigDokument17 SeitenDRUGS Study OrigKiersten Karen Policarpio Verina100% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbigail BascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cefazolin Sodium AncefDokument1 SeiteCefazolin Sodium AncefKristi WrayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study FinalDokument5 SeitenDrug Study FinalJackie Ann Marie DapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discharge PlanDokument4 SeitenDischarge PlanVillanueva NiñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Cushing's SyndromeDokument5 SeitenDrug Study Cushing's SyndromeSelena MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument8 SeitenDrug StudyRizzi DeveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atropine SulfateDokument1 SeiteAtropine SulfateTrishaaMayolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chromium Picolinate Drug StudyDokument1 SeiteChromium Picolinate Drug StudyjoellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DS (Calcium + Vit. D)Dokument6 SeitenDS (Calcium + Vit. D)Mary April MendezNoch keine Bewertungen
- NafarinDokument2 SeitenNafarinianecunar100% (2)
- Metoclopramide Drug Study: Uses, Side Effects, Nursing ConsiderationsDokument2 SeitenMetoclopramide Drug Study: Uses, Side Effects, Nursing ConsiderationsJohn Paolo Tamayo OrioNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUG-STUDY - BALLON, Karlo CDokument6 SeitenDRUG-STUDY - BALLON, Karlo CMelinda Cariño BallonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Stugeron and Kalium DuruleDokument1 SeiteDrug Study Stugeron and Kalium DuruleawesomedawnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing and Treating Post-Operative HypothermiaDokument2 SeitenAssessing and Treating Post-Operative HypothermiaJayrelle D. SafranNoch keine Bewertungen
- CefoperazoneDokument3 SeitenCefoperazoneBaim FarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument10 SeitenDrug Studyjho_26100% (2)
- AtroventDokument2 SeitenAtroventKatie McPeekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study - AmlodipineDokument1 SeiteDrug Study - AmlodipineDanielle Marie SamblacenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apixaban 5 PDFDokument2 SeitenApixaban 5 PDFWanie Al-basriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument5 SeitenDrug StudyBridgette ArañesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ItoprideDokument2 SeitenItoprideLesValenzuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LacipilDokument2 SeitenLacipilianecunarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chn-Herbal MedicineDokument5 SeitenChn-Herbal MedicineBSN 1-N CASTRO, RicciNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discharge Plan CapDokument3 SeitenDischarge Plan Capalexander abasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudiesDokument16 SeitenDrug Studiesvitcloud23100% (2)
- Ertapenem (Invanz)Dokument1 SeiteErtapenem (Invanz)Adrianne BazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- D50WDokument1 SeiteD50WElizalde Husband100% (1)
- Solu-Cortef (Hydrocortisone)Dokument3 SeitenSolu-Cortef (Hydrocortisone)E100% (2)
- Example of Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenExample of Drug Studydonna mae junioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug AnalysisDokument3 SeitenDrug AnalysisAbby BorabienNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayDokument4 SeitenMetronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayCrisyl LipawenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument4 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJhoizel VenusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument4 SeitenDrug StudyXio PauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verapamil HCLDokument3 SeitenVerapamil HCLMae Ann Bueno CastillonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cefuroxime Anti-Bacterial CephalosporinDokument9 SeitenCefuroxime Anti-Bacterial CephalosporinDustin JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- GENERIC NAME: Ranitidine BRAND NAME: Zantac CLASSIFICATION Therapeutic: Anti-Ulcer AgentsDokument4 SeitenGENERIC NAME: Ranitidine BRAND NAME: Zantac CLASSIFICATION Therapeutic: Anti-Ulcer Agentsehnna50% (2)
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Drug'S Effect Nsg. ConsiderationDokument2 SeitenDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Drug'S Effect Nsg. ConsiderationKatrina PonceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrointestinal System: Antihistamine Half-Life: Onset: Peaks: DurationDokument3 SeitenGastrointestinal System: Antihistamine Half-Life: Onset: Peaks: DurationsyerlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acetylcysteine, Phenytoin, Gentamicin, Captopril, Pilocarpine Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokument7 SeitenAcetylcysteine, Phenytoin, Gentamicin, Captopril, Pilocarpine Nursing ResponsibilitieseyesidphNoch keine Bewertungen
- Promoting Activity Tolerance in a Patient with CoughDokument3 SeitenPromoting Activity Tolerance in a Patient with CoughitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patient Classification Systems: A GuideDokument69 SeitenPatient Classification Systems: A GuideitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Philippines Pantawid Pamilyang Pilipino ProgramDokument2 SeitenImpact of Philippines Pantawid Pamilyang Pilipino Programitsmeaya0% (1)
- Acute GlomerulonephritisDokument4 SeitenAcute GlomerulonephritisitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study FormatDokument1 SeiteDrug Study FormatitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kwashiorkor and MarasmusDokument2 SeitenKwashiorkor and Marasmusitsmeaya100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan General Objective: To Promote Safety Through Prevention of The Spread of InfectionDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan General Objective: To Promote Safety Through Prevention of The Spread of InfectionitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food Safety ChecklistDokument2 SeitenFood Safety ChecklistitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benner's TheoryDokument15 SeitenBenner's TheoryitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnorexicDokument15 SeitenAnorexicitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnorexicDokument15 SeitenAnorexicitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Appearance: The: Patient Was On Semi Fowler's Position During Assessment and Body Weakness Was NotedDokument9 SeitenGeneral Appearance: The: Patient Was On Semi Fowler's Position During Assessment and Body Weakness Was NoteditsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- External HemorrhoidsDokument61 SeitenExternal HemorrhoidsitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cues Problem Physiologic Behavioral: Date Identified: July 19, 2016 Subjective CuesDokument2 SeitenCues Problem Physiologic Behavioral: Date Identified: July 19, 2016 Subjective CuesitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benner's TheoryDokument15 SeitenBenner's TheoryitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Red Blood CellsDokument3 SeitenRed Blood CellsitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subjective Cues:: IndependentDokument4 SeitenSubjective Cues:: IndependentitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Or ObjectivesDokument1 SeiteOr ObjectivesitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chole Lithia SisDokument4 SeitenChole Lithia SisitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generic Name Brand Name Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indications Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokument1 SeiteGeneric Name Brand Name Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indications Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilitiesitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Staff Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokument3 SeitenStaff Nursing ResponsibilitiesitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Staff Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokument3 SeitenStaff Nursing ResponsibilitiesitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IntroductionDokument1 SeiteIntroductionitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GNFDokument2 SeitenGNFitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin Is The Largest Organ of The Human BodyDokument4 SeitenSkin Is The Largest Organ of The Human BodyitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capstone PosterDokument1 SeiteCapstone Posterapi-273438577Noch keine Bewertungen
- CLOZE TEST Discovery Could Ease Blood ShortageDokument2 SeitenCLOZE TEST Discovery Could Ease Blood ShortageKarsan Ayaz MaierNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICNCDRS Blindness Registry FormDokument4 SeitenICNCDRS Blindness Registry FormAprilAngeliRobleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical History QuestionnaireDokument3 SeitenMedical History QuestionnaireSachitra Nirman MalwatteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Causes of Foamy UrineDokument12 SeitenCauses of Foamy UrineAishwariyaaAngelinaStephenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature Review For Specimen Labeling and Blood BankDokument3 SeitenLiterature Review For Specimen Labeling and Blood Bankapi-236445988Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adult Grip Strength Norms For The Baseline Digital DynamometerDokument25 SeitenAdult Grip Strength Norms For The Baseline Digital DynamometerOmar Escalante DíazNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Shouldice Repair: Robert Bendavid, MDDokument14 SeitenThe Shouldice Repair: Robert Bendavid, MDmarquete72Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Airway ManagementDokument98 SeitenBasic Airway ManagementRani Salsabilah100% (1)
- Management of Head InjuryDokument27 SeitenManagement of Head InjuryrosybashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parotid Tumors and Other Salivary Gland TumorsDokument41 SeitenParotid Tumors and Other Salivary Gland Tumorsdrhiwaomer100% (9)
- Dr. Steven Corwin LetterDokument2 SeitenDr. Steven Corwin LetterJonathan LaMantiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastritis PDFDokument6 SeitenGastritis PDFsrimardiahkusumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Pendukung 2Dokument13 SeitenJurnal Pendukung 2Eko PrasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disclosures: Kori Dewing, DNP, ARNP Virginia Mason Medical Center October 29, 2013Dokument3 SeitenDisclosures: Kori Dewing, DNP, ARNP Virginia Mason Medical Center October 29, 2013Alexander Diaz ZuletaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guillian-Barre Syndrome: Renalyn Galache Gladys Gegare BSN-3BDokument18 SeitenGuillian-Barre Syndrome: Renalyn Galache Gladys Gegare BSN-3BGLadys GegareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preoperative Diagnosis of A Third Root Canal in First and Second Maxillary Premolars A Challenge For The ClinicianDokument7 SeitenPreoperative Diagnosis of A Third Root Canal in First and Second Maxillary Premolars A Challenge For The ClinicianS S Saad SaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- TriageDokument42 SeitenTriageNic JiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shock Resident LectureDokument38 SeitenShock Resident Lecturepapermate9293Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4 Medical Terminology PDFDokument38 SeitenLecture 4 Medical Terminology PDFAhmed KhaledNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychiatry IntroductionDokument26 SeitenPsychiatry IntroductionMunir AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen