Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Prolong Labour
Hochgeladen von
NishaThakuriOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Prolong Labour
Hochgeladen von
NishaThakuriCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Prolong Labour
Definition
The prolonged labour is defined when the combined duration of the first and second stage
of labour is more than the arbitary time limit of 18 hours. Labour is considered prolonged when
the cervical dilatation rate is less than 1cm/hr and descent of the presenting part is <1cm/hr for a
period of minimum 4 hours observations. It is calculated from mothers subjective estimate of
onset of true labour.
Prolonged latent phase: the latent phase is from onset of regular painful contraction with
cervical dilatation upto 4cm. If cervix is not dilated beyond 4cm for 8 hours of regular
contraction is considered as prolonged latent phase.
Prolonged active phase: the active phase is period from cervical dilatation 4-10cm.
Regular painful contractions with cervical dilatation more than 4cm last longer than 12
hour is considered as prolonged active phase. If the cervical dilatation arrests more than 2
hours is considered as abnormal.
Cervix is fully dilated and woman has urge to push but no descent is called prolonged
expulsive phase.
The second stage is considered prolonged if it lasts for more than 2 hours in primigravida
and 1 hours in multipara.
Causes of prolonged labour
First stage: failure to dilate cervix is due toi. Fault in power:- abnormal uterine contraction such as uterine inertia or hypotonic uterine
dysfunction (common), incordinate uterine contraction or hypertonic uterine dysfunction.
ii. Fault in the passage:- contracted pelvis, cervical dystocia, pelvic tumour or even in full
bladder, minor degree of pelvic contraction.
iii. Fault in the passenger:- malposition (OP) and malpresentation (face, brow), congenital
anomalies of the fetus (hydrocephalus), deflexed head.
iv. Others:- injudicious (early) administration of sedatives and analgesic before the active labour
begins.
Second stage
Fault in power:- uterine inertia, inability to bear down, epidural analgesia, constriction
ring.
Fault in the passage:- CPD, Contracted pelvis, android pelvis, soft tissue pelvic tumour,
undue resistance of the pelvic floor or perineum due to spasm or old scarring.
Fault in the passenger:- malposition, malpresentation , big baby, congenital
malformation of the baby.
Sign and symptoms
Labor extend for more than 18 hours
The rate of cervical dilatation is less than 1cm/hour in primigravida and less than 1.5
cm/hour in multipara in first stage of labor.
There may be slow descent of head or non descend of presenting part even after full
dilatation of cervix.
Patient looks exhausted and distressed
Pain may be more on the radiating to the thighs rather than within abdomen due to
pressure on muscle and ligaments.
Pulse rate often high
The uterus is tender on palpation does not relax fully between contraction.
Variable degree of moulding and caput formation is cephalic presentation.
Fetal distress may develop.
Membranes may or may not rupture.
Ketoacidosis may develop due to prolong starvation.
Risk of prolonged labour
Fetal risk
Hypoxia due to decreased uteroplacental circulation.
Intrauterine infection
Intracranial stress or hemorrhage following prolonged stay on perineum
Increased operative delivery
Increased risk of perinatal loss
Mother risk
Maternal distress
Intrauterine infection
Trauma and injuries in birth canal eg cervical tear, rupture of uterus
PPH
Postpartum infection or puerperal sepsis
Subinvolution
Diagnosis
History of prolonged labour
Abdominal examination
Per vaginal examination
Partograph- recording of maternal and fetal condition.
Intranatal radiography.
Management of Prolonged Latent Phase
If the woman has been in the latent phase for more than 8 hours and there is little sign of
progress, reasses the situation by assessing the cervix as follows:
If there has been no change in cervical dilatation or effacement and no fetal distress,
review the diagnosis. She may not be in labour.
If any changes in cervical effacement or dilatation, membrane should be ruptured and
labour should induced.
The woman should assessed every 4 hourly
If she has not been enterd in active phase after 8 hours of induction, delivered by
caesarean section
If there is sign of infection immediately augment the labour with oxytocin and antibiotics
should be given like ampicilin and gentamycin untill delivery.
If not delivered vaginally delivered by caesarean section and continue antibiotics plus
metronidazole for 48 hours
Management of Prolonged Active Phase
If there is no sign of CPD and good contraction with membrane intact, ruptured the
membrane artificially.
Assess uterine contraction
- If contractions are inefficient ( <3contraction in 10 minutes lasting less than 40 sec)
suspect inadequate uterine activity and refer to higher center.
- If contraction are efficient(3 or more contractions in 10 minute lasting more than 40 sec)
suspect CPD, malposition or malpresentation and refer to higher level.
Continue to moniter maternal and fetal wellbeing and progress of labour.
Encourage the womans birth companion to give adequate support.
Explain all procedure to the woman.
Provide supportive, encouraging atmosphere for the birth.
Encourage her to empty her bladder regularly.
Encourage breathing technique.
Mangement of prolonged expulsive phase
If malpresentation and obvious obstruction have been excluded, augment labour with
oxytocin.
If there is no descent (fetal head is at 0 or -2 station) after augmentation delivery by
vaccum extraction or forceps or symphysiotomy.
Abnormal Uterine Contraction
Normal labour is characterized by coordinated uterine contraction associated with
progressive dilatation of the cervix and descent of the fetal head within the specified time limit.
Any deviation of the normal pattern of uterine contraction affecting the course of labour is
termed as disordered or abnormal uterine action.
Etiology of abnormal uterine contraction
Elderly primigravidae
Prolonged pregnancy
Over distended uterus due to twins or hydramnious
Psychological factor
Contracted pelvis
Malpresentation
Full bladder
Injudious administration of sedatives, analgesics and oxytocics
Premature attempt of vaginal delivery or attempted instrumental delivery under
anesthesia.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Prolonged Labour: Causes, Diagnosis and ManagementDokument24 SeitenProlonged Labour: Causes, Diagnosis and ManagementSanthosh.S.U100% (1)
- Prolonged Labour: Causes, Signs and ManagementDokument36 SeitenProlonged Labour: Causes, Signs and ManagementQuay Kar Ying100% (3)
- Abnormal Uterine ActionDokument96 SeitenAbnormal Uterine ActionN. Siva100% (2)
- Managing Obstetrical Emergencies & Its ChallengesDokument58 SeitenManaging Obstetrical Emergencies & Its Challengessanthiyasandy100% (1)
- OccipitoposteriorDokument11 SeitenOccipitoposteriorVijith.V.kumar100% (1)
- Birth Canal Injuries: Causes, Types, Prevention and ManagementDokument67 SeitenBirth Canal Injuries: Causes, Types, Prevention and ManagementnamitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstructed LabourDokument11 SeitenObstructed Labourabhay jain100% (2)
- BreechDokument38 SeitenBreechsanthiyasandy100% (2)
- Breast Complications in PuerperiumDokument24 SeitenBreast Complications in Puerperiumvincentsharon100% (9)
- Physiological Processes in Second Stage of LabourDokument32 SeitenPhysiological Processes in Second Stage of Labournamita100% (1)
- Cephalo Pelvic DispoportionDokument12 SeitenCephalo Pelvic DispoportionN. Siva100% (1)
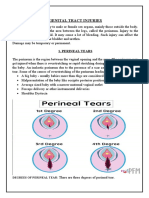
- Genital Tract InjuriesDokument19 SeitenGenital Tract InjuriesMarvella Nongkhar100% (1)
- Mechanism of LabourDokument15 SeitenMechanism of Labourangel panchalNoch keine Bewertungen
- STAGES OF LABOURDokument37 SeitenSTAGES OF LABOURJude Martin100% (1)
- Physiological Changes of Pregancy. NEW VERSION-For BSC Nursing StudentsDokument107 SeitenPhysiological Changes of Pregancy. NEW VERSION-For BSC Nursing StudentsKripa Susan100% (2)
- Antenatal CareDokument19 SeitenAntenatal CareIshika RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 1 Induction of Labour PowerPointDokument18 SeitenGroup 1 Induction of Labour PowerPointgeorgeloto12100% (3)
- Elderly PrimiDokument7 SeitenElderly PrimiAnnapurna Dangeti67% (3)
- Definition of Contracted Pelvis and Factors Affecting LabourDokument19 SeitenDefinition of Contracted Pelvis and Factors Affecting LabourAuri SururyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Occipito Posterior PositionDokument52 SeitenOccipito Posterior PositionVijith.V.kumar100% (3)
- Perineal and Cervical TearsDokument43 SeitenPerineal and Cervical TearsN. SivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology of Normal LabourDokument41 SeitenPhysiology of Normal LabourEric Mayo Dagradi KabatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Woman During First Stage of Labour Management of Woman During First Stage of LabourDokument21 SeitenManagement of Woman During First Stage of Labour Management of Woman During First Stage of LabourKinjal Vasava67% (3)
- Post Partum Hemorrhage (PPH)Dokument77 SeitenPost Partum Hemorrhage (PPH)Aparna LaxmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Government College of Nursing Jodhpur (Raj.) : Procedure On-Cordiotocography Subject-Obstetrics & Gynecology Specialty-IDokument6 SeitenGovernment College of Nursing Jodhpur (Raj.) : Procedure On-Cordiotocography Subject-Obstetrics & Gynecology Specialty-Ipriyanka100% (1)
- Uterine MalformationsDokument6 SeitenUterine MalformationssubashikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minor Ailments During PregnancyDokument47 SeitenMinor Ailments During PregnancyDiablo GoliathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Premature LabourDokument29 SeitenPremature LabourSanthosh.S.U100% (1)
- Elderly Primigravida, Adolescent Pregnancy, Grand MultiparaDokument3 SeitenElderly Primigravida, Adolescent Pregnancy, Grand MultiparamercyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoulder DystociaDokument20 SeitenShoulder DystociaFaridahMaksumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cephalo Pelvic Disproportion (CPD) & Contracted PelvisDokument45 SeitenCephalo Pelvic Disproportion (CPD) & Contracted Pelvisbinipsamuel250% (1)
- Mechanism of LabourDokument18 SeitenMechanism of LabournamithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Stage of Labour ExplainedDokument5 SeitenFirst Stage of Labour ExplainedSucharita PandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- INDUCTION OF LABOUR: METHODS & PROTOCOLSDokument8 SeitenINDUCTION OF LABOUR: METHODS & PROTOCOLSgeorgeloto12100% (1)
- Obs Vaginal ExaminationDokument15 SeitenObs Vaginal Examinationaparna shamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normal Labor Essential Factors Elements of Uterine Contractions & Physiology of 1 Stage of LaborDokument88 SeitenNormal Labor Essential Factors Elements of Uterine Contractions & Physiology of 1 Stage of LaborAswathy Aswathy100% (1)
- Obg - 15.4.20 (Afternoon) Unit 10 - Birth InjuriesDokument102 SeitenObg - 15.4.20 (Afternoon) Unit 10 - Birth InjuriesElakkiyaanu64 Elakkiyaanu64100% (3)
- Cervical DystociaDokument22 SeitenCervical DystociaBaldau TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of PuerperiumDokument22 SeitenManagement of Puerperiumannu panchalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normal PuerperiumDokument3 SeitenNormal PuerperiumarunshreerajendranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstructed LaborDokument43 SeitenObstructed LaborNyangara Rajabu0% (2)
- New NORMAL PUERPERIUMDokument21 SeitenNew NORMAL PUERPERIUMvarshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition:-The Partograph Is A Simple Chart orDokument12 SeitenDefinition:-The Partograph Is A Simple Chart orBharat ThapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Induction of Labour: A Guide to Methods and ManagementDokument18 SeitenInduction of Labour: A Guide to Methods and ManagementNihal ZaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Destructive OperationDokument8 SeitenDestructive OperationNishaThakuri100% (4)
- Face Presentation: Diagnosis, Mechanism and ManagementDokument6 SeitenFace Presentation: Diagnosis, Mechanism and ManagementNishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fetal Skull and Maternal Pelvis LandmarksDokument28 SeitenFetal Skull and Maternal Pelvis LandmarksAshwanee Jharia0% (1)
- Minor Disorders of Newborn and Its ManagementDokument3 SeitenMinor Disorders of Newborn and Its Managementarun26198891% (11)
- Care of Low Birth Weight BabiesDokument102 SeitenCare of Low Birth Weight Babiesvarshasharma050% (2)
- CPD and Contracted PelvisDokument55 SeitenCPD and Contracted PelvisShaells JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iugr FinalDokument35 SeitenIugr Finalsanthiyasandy100% (3)
- Abnormal Uterine ActionDokument64 SeitenAbnormal Uterine ActionKanimozhi Kasinathan100% (1)
- Physiology of Normal LabourDokument29 SeitenPhysiology of Normal LabournamitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Partograph DR OdofinDokument61 SeitenPartograph DR OdofinEkiran BabajideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetrical Emergencies Maternity NursingDokument100 SeitenObstetrical Emergencies Maternity Nursingsanthiyasandy100% (4)
- Government College of Nursing Jodhpur: Presentation ON Prolonged LabourDokument6 SeitenGovernment College of Nursing Jodhpur: Presentation ON Prolonged Labourpriyanka100% (2)
- Abnormal Labor and Dystocia: Prolonged Labor, Obstructed Labor, Shoulder DystociaDokument50 SeitenAbnormal Labor and Dystocia: Prolonged Labor, Obstructed Labor, Shoulder DystociaNorliana Jaafar0% (1)
- Prolonged LabourDokument47 SeitenProlonged LabourBharat ThapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dysfunctional Labor As One of The Intrapartal ComplicationsDokument23 SeitenDysfunctional Labor As One of The Intrapartal ComplicationsKenje Kate AgripoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Proposal o NishaDokument14 SeitenResearch Proposal o NishaNishaThakuri100% (1)
- QuestionnaireDokument7 SeitenQuestionnaireNishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Knowledge Regarding Oxytocin Administration Among Nurses in Phect NepalDokument1 SeiteKnowledge Regarding Oxytocin Administration Among Nurses in Phect NepalNishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Destructive OperationDokument8 SeitenDestructive OperationNishaThakuri100% (4)
- Forcep DeliveryDokument26 SeitenForcep DeliveryNishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix B: The Work Plan of The Research StudyDokument1 SeiteAppendix B: The Work Plan of The Research StudyNishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiological Changes During 2nd Stage of LaborDokument5 SeitenPhysiological Changes During 2nd Stage of LaborNishaThakuri100% (4)
- Normal Labor Process in 4 StagesDokument19 SeitenNormal Labor Process in 4 StagesNishaThakuri100% (1)
- Physiological Changes During 1st Stage of LaborDokument18 SeitenPhysiological Changes During 1st Stage of LaborNishaThakuri90% (39)
- Normal Labor Process in 4 StagesDokument19 SeitenNormal Labor Process in 4 StagesNishaThakuri100% (1)
- Normal LaborDokument8 SeitenNormal LaborNishaThakuri100% (2)
- Breeech PresentationDokument3 SeitenBreeech PresentationNishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- ResponsibilityDokument5 SeitenResponsibilityNishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Mid BDokument11 SeitenCurriculum Mid BNishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fetal CirculationDokument4 SeitenFetal CirculationNishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal of Perinatal and Neonatal NursingDokument1 SeiteJournal of Perinatal and Neonatal NursingNishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- First AidDokument87 SeitenFirst AidNishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Mid ADokument10 SeitenCurriculum Mid ANishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- PERINATAL PATIENT SAFETY: Management of Oxytocin For Labor Induction and Augmentation MCN, The American Journal of Maternal/Child NursingDokument2 SeitenPERINATAL PATIENT SAFETY: Management of Oxytocin For Labor Induction and Augmentation MCN, The American Journal of Maternal/Child NursingNishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Failure To Initiate and Sustain Breathing at Birth Is Called Birth AsphyxiaDokument21 SeitenFailure To Initiate and Sustain Breathing at Birth Is Called Birth AsphyxiaNishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- College MGMT Kamhson GroupDokument11 SeitenCollege MGMT Kamhson GroupNishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newborn Resuscitation StepsDokument34 SeitenNewborn Resuscitation StepsNishaThakuri100% (2)
- Change ProcessDokument7 SeitenChange ProcessNishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal DeathsDokument4 SeitenMaternal DeathsNishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDokument5 SeitenNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentNishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exogenous Oxytocin Is A Powerful Uterine StimulantDokument2 SeitenExogenous Oxytocin Is A Powerful Uterine StimulantNishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- The UK All Party Parliamentary Group On Population, Development and Reproductive Health Parliamentary Hearings Into Maternal MorbidityDokument2 SeitenThe UK All Party Parliamentary Group On Population, Development and Reproductive Health Parliamentary Hearings Into Maternal MorbidityNishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- American Journal of Obstetrics and GynecologyDokument1 SeiteAmerican Journal of Obstetrics and GynecologyNishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxytocin drug formsDokument8 SeitenOxytocin drug formsNishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis Proposal DraftDokument20 SeitenThesis Proposal DraftNishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Practice QuestionsDokument22 SeitenNursing Practice QuestionsJune DumdumayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digoxin Therapeutic Range and Signs of ToxicityDokument118 SeitenDigoxin Therapeutic Range and Signs of Toxicitybeautifulme031690Noch keine Bewertungen
- Family Nursing Care Plan: (A Case Study of Paglingayen Family)Dokument9 SeitenFamily Nursing Care Plan: (A Case Study of Paglingayen Family)Adrian MallarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narcotics Anonymous Meeting 3Dokument6 SeitenNarcotics Anonymous Meeting 3api-401390929Noch keine Bewertungen
- Colonic InertiaDokument20 SeitenColonic InertiaAndina Destiyani PutriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feeding larvae to predatory bug nymphsDokument4 SeitenFeeding larvae to predatory bug nymphsEvawaty Sri UlinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hazelnuts - 7 Benefits of These Heart-Healthy, Brain-Boosting Nuts - DRDokument18 SeitenHazelnuts - 7 Benefits of These Heart-Healthy, Brain-Boosting Nuts - DRRajib DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Care of New BornDokument25 SeitenCare of New BornNirupama KsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Personality Development Course Navi MumbaiDokument2 SeitenBest Personality Development Course Navi MumbaiGurpreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Health CH 2Dokument6 SeitenMental Health CH 2Gina GiammalvoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16.MDR-XDR TBDokument18 Seiten16.MDR-XDR TBLinna SriwaningsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amenorrhea - Algorithm & DifferentialsDokument9 SeitenAmenorrhea - Algorithm & DifferentialsItharshan IndreswaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- EFN - PPTX 3Dokument9 SeitenEFN - PPTX 3Suheni Khotimah IndrianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absen Metod!!!Dokument4 SeitenAbsen Metod!!!Haris Pratama RebornNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Plan On Newborn ScreeningDokument8 SeitenTeaching Plan On Newborn ScreeningQueenie Sicco100% (1)
- Schizophrenia: Causes, Types, and Nursing CareDokument32 SeitenSchizophrenia: Causes, Types, and Nursing CareNasriah Macadato100% (1)
- MMPI-2 Validity ScalesDokument7 SeitenMMPI-2 Validity ScalesEspíritu Ciudadano50% (2)
- Nimesulide ODTDokument10 SeitenNimesulide ODTMihai SebastianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Analysis SchizophreniaDokument2 SeitenCase Analysis Schizophreniamark OrpillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Morris Fishbein - How the AMA Enemy Fought American Health InnovationsDokument9 SeitenMorris Fishbein - How the AMA Enemy Fought American Health InnovationsuncoveringconsciousNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 A Randomized Clinical Trial of Manual Therapy For Cervico Brachial Pain Syndrome A Pilot StudyDokument8 Seiten1 A Randomized Clinical Trial of Manual Therapy For Cervico Brachial Pain Syndrome A Pilot StudyCassie RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- DrugsDokument17 SeitenDrugsQais ShaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rincian Tagihan ObatDokument18 SeitenRincian Tagihan Obatganesha trengginasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The EyeDokument8 SeitenThe Eyezyrine jhen100% (1)
- RN review nuggets: Essential fundamentals of nursingDokument32 SeitenRN review nuggets: Essential fundamentals of nursingr.a.g.Noch keine Bewertungen
- New Zealand School of Acupuncture and TraditionalDokument12 SeitenNew Zealand School of Acupuncture and Traditionalfann80100% (1)
- Carob (Ceratonia siliqua): Mechanism of Action and PharmacologyDokument7 SeitenCarob (Ceratonia siliqua): Mechanism of Action and PharmacologyMonica BotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cervical CancerDokument16 SeitenCervical CancerChoi Gong JuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health10 LM U1Dokument38 SeitenHealth10 LM U1Che CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enviro-Flo, Inc. Enviro-Chlor Tablet Chlorinator: Installation & Owner'S ManualDokument7 SeitenEnviro-Flo, Inc. Enviro-Chlor Tablet Chlorinator: Installation & Owner'S ManualSteve DennisNoch keine Bewertungen