Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Glassware
Hochgeladen von
Iti ChauhanCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Glassware
Hochgeladen von
Iti ChauhanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
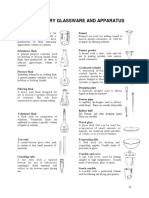
The mortar (/mrtr/) is a bowl, typically made of hard wood, ceramic or stone.
The pestle (/psl/) is a heavy club-shaped object, the end of which is used for
crushing and grinding. The substance to be ground is placed in the mortar and
ground, crushed or mixed with the pestle.
Mortars and pestles were traditionally used in pharmacies to crush various
ingredients prior to preparing an extemporaneous prescription.
Mortars and pestles are used to :
reduce the particle size of powders
Grind crystal into powder form
Mix powders
Mix powder and liquids
Make emulsions
Beakers
A beaker is a common container in most labs. It is used for mixing, stirring, and heating
chemicals. Most beakers have a spout on the rim to aid in pouring. There is a lip that runs around
the rim. They also commonly have markings to measure the volume they contain. However, a
beaker is not precise when measuring liquids. Beakers come in a wide range of sizes.
Funnel
This is just like any other funnel except designed to be used in a laboratory setting. These can be
made of plastic or glass. Usually, they have either a short stem or a long stem, depending on
what they are needed for. There are several sizes that can be chosen from based on the amount
of liquid that needs to go through them quickly.
Graduated Cylinder
This is a primary measuring tool for the volume of a liquid. There are several markings up and
down the length of the container with specific increments. These come in many sizes. The
smaller they are, the more specific the volume measurements will be.
Volumetric Flasks
A volumetric flask is a round flask with a long neck and a flat bottom. These are used to measure
an exact volume of liquid. There is a small line on the neck that indicates where these are to filled
to (Use the bottom of the meniscus). They come with special caps that will not let anything in or
out.
Pipettes
There are a large variety of pipettes designed to accomplish specific goals. However, they are all
for measuring an exact volume of liquid and placing it into another container.
Spatulas and Scoopulas
Spatulas and scoopulas are for scooping solid chemicals. The typical use for these in a lab is
scooping chemical out of its original container onto a weigh boat so that it can be weighed on a
balance.
Bunsen Burner
A Bunsen burner is a mechanical apparatus that is connected to a flammable gas source. There
is a knob to adjust the amount of gas flow and a rotating collar that controls airflow. These both
must be adjusted to get an ideal flame for heating purposes. The burner is lit with a striker
Erlenmeyer Flasks
This flask was named after its inventor in 1861, but can also be called a conical flask. It has a
narrow neck and expands as you go toward its base. This allows easy mixing and swirling of the
flask without too much risk of spilling. The narrow opening also allows for the use of a rubber or
glass stopper. It can easily be clamped to a ring stand as well as heated or shaken mechanically.
Once again the marks on the side are meant primarily for estimation rather than precision.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chemistry Lab Mysteries, Fun Laboratory Tools! Chemistry for Kids - Children's Analytic Chemistry BooksVon EverandChemistry Lab Mysteries, Fun Laboratory Tools! Chemistry for Kids - Children's Analytic Chemistry BooksBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Lab Equipment BSCrim Organic - AutosavedDokument130 SeitenLab Equipment BSCrim Organic - Autosavedangelo aquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mason Jar Lunches: 50 Pretty, Portable Packed Lunches (Including) Delicious Soups, Salads, Pastas & MoreVon EverandMason Jar Lunches: 50 Pretty, Portable Packed Lunches (Including) Delicious Soups, Salads, Pastas & MoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name Description PictureDokument4 SeitenName Description PictureHazel AjeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Chemistry GuideDokument17 SeitenA Chemistry GuideEllen CristyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Equipment Flame Brass Glass Stainless Steel AluminiumDokument9 SeitenLaboratory Equipment Flame Brass Glass Stainless Steel AluminiumKenneth P PablicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Laboratory Tools & Important Scientific EquipmentsDokument2 SeitenCommon Laboratory Tools & Important Scientific Equipmentsblinz95Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab EquipmentDokument8 SeitenLab EquipmentMathew YoyakkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Laboratory GlasswareDokument3 SeitenCommon Laboratory GlasswareRegina SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maintaining Accuracy and PrecisionDokument6 SeitenMaintaining Accuracy and PrecisionAkshit ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Know Your Lab Equipments: Test TubeDokument9 SeitenKnow Your Lab Equipments: Test TubeWelly Boss HwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS MTDokument3 SeitenBS MTGenrev LisondraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Tubes - A Glass Tube Where One End Is Open And: (Type Here)Dokument5 SeitenTest Tubes - A Glass Tube Where One End Is Open And: (Type Here)dean2O6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Glassware For Qualitative UsesDokument4 SeitenGlassware For Qualitative UsesAnneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory ApparatusDokument17 SeitenLaboratory Apparatuszena100% (1)
- A List of Chemistry Laboratory Apparatus and Their UsesDokument15 SeitenA List of Chemistry Laboratory Apparatus and Their Usesjohn erick camotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Laboratory EquipmentDokument2 SeitenCommon Laboratory EquipmentYuan BrionesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory ApparatusDokument3 SeitenLaboratory ApparatusRacky Carag100% (2)
- Equipment in Chemistry LaboratoryDokument5 SeitenEquipment in Chemistry LaboratoryIstiva AmeiliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phar 205Dokument156 SeitenPhar 205billhaddNoch keine Bewertungen
- A List of Chemistry Laboratory Apparatus and Their Uses: Sign inDokument17 SeitenA List of Chemistry Laboratory Apparatus and Their Uses: Sign inMaggyNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEAKERS Are Made Up of TemperedDokument12 SeitenBEAKERS Are Made Up of TemperedmnmrznNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab ApparatusDokument29 SeitenLab ApparatusEpoditmas SeyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Glassware and Apparatus LSMDokument4 SeitenLaboratory Glassware and Apparatus LSMShiina Mashiro100% (1)
- Lab Equipment and UsesDokument2 SeitenLab Equipment and UsesReka FuentesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Chemistry Apparatus AaaaDokument4 SeitenBasic Chemistry Apparatus Aaaahoranlovely5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab0ratory Equipment and ToolsDokument40 SeitenLab0ratory Equipment and ToolsJane AndaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LaboratoryapparatussespptDokument39 SeitenLaboratoryapparatussespptMapeh EditingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Laboratory EquipmentDokument50 SeitenCommon Laboratory EquipmentChristian Josh EspedillonNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Chemistry GuideDokument15 SeitenA Chemistry GuideAnil YusufNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Chemistry GuideDokument19 SeitenA Chemistry GuideAnil YusufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity No 1Dokument9 SeitenActivity No 1Mary Cuba GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM2212 - ESTANOCO - SAMUEL.M. - Activity 1 LABORATORY EQUIPMENTDokument6 SeitenCHEM2212 - ESTANOCO - SAMUEL.M. - Activity 1 LABORATORY EQUIPMENTSam EstanocoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commonly Encountered Equipment in The Chemistry LaboratoryDokument9 SeitenCommonly Encountered Equipment in The Chemistry Laboratorysadiqah mushtaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab0ratory Equipment and ToolsDokument40 SeitenLab0ratory Equipment and ToolsJane AndaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipet. It Has Only OneDokument3 SeitenPipet. It Has Only OneAytona Villanueva PearlNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Chemistry Laboratory Apparatus and Their UsesDokument15 SeitenList of Chemistry Laboratory Apparatus and Their UsescruiserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 Week 1 Lesson 2Dokument3 SeitenGrade 8 Week 1 Lesson 2alleynekenisha5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report - Basic Chemistry EquipmentDokument6 SeitenLab Report - Basic Chemistry EquipmentDexter ClamohoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab - Inst: Pipet. It Has Only OneDokument3 SeitenLab - Inst: Pipet. It Has Only OneAytona Villanueva PearlNoch keine Bewertungen
- KumiDokument29 SeitenKumimonike07Noch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Instrument: Pipet. It Has Only OneDokument3 SeitenLaboratory Instrument: Pipet. It Has Only OneAytona Villanueva PearlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipet. It Has Only OneDokument3 SeitenPipet. It Has Only OneAytona Villanueva PearlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory ApparatusDokument41 SeitenLaboratory ApparatusReygil CapunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory E: Pipet. It Has Only OneDokument3 SeitenLaboratory E: Pipet. It Has Only OneAytona Villanueva PearlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipet. It Has Only OneDokument3 SeitenPipet. It Has Only OneAytona Villanueva PearlNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4Dokument4 Seiten4julie anne ricaforteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pictures Description UsesDokument4 SeitenPictures Description UsesRanice Krizelle LomibaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Equip: Pipet. It Has Only OneDokument3 SeitenLaboratory Equip: Pipet. It Has Only OneAytona Villanueva PearlNoch keine Bewertungen
- See More All Lab BurnersDokument6 SeitenSee More All Lab BurnersApolloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ana Video 1Dokument6 SeitenAna Video 1Lu'lu Abdi Aziiz HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Laboratory ApparatusDokument21 SeitenCommon Laboratory ApparatusMaria Kristelle Alejandro PaltaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Equipment: Pipet. It Has Only OneDokument3 SeitenLaboratory Equipment: Pipet. It Has Only OneAytona Villanueva PearlNoch keine Bewertungen
- A List of Chemistry Laboratory Apparatus and Their UsesDokument8 SeitenA List of Chemistry Laboratory Apparatus and Their UsesStephen HenryNoch keine Bewertungen
- A List of Basic Chemistry ApparatusDokument15 SeitenA List of Basic Chemistry ApparatusSyrille Lubigan AlarconNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM Lab ApparatusDokument4 SeitenCHEM Lab ApparatusHannah Gwynette SamonteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apparatus Description UsesDokument6 SeitenApparatus Description UsesVenus De GraciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab ApparatusesDokument39 SeitenLab ApparatusespidoghislaineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identification of Laboratory 1Dokument15 SeitenIdentification of Laboratory 1kimberlymapagalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Laboratory Apparatus Equipment and Their UseDokument26 SeitenCommon Laboratory Apparatus Equipment and Their UseEli JahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Features of Community PharmacyDokument5 SeitenDesign Features of Community PharmacyIti ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure BacteriaDokument42 SeitenStructure BacteriaIti Chauhan100% (3)
- LipidsDokument23 SeitenLipidsIti ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patient CounsellingDokument5 SeitenPatient CounsellingIti Chauhan80% (5)
- Over The Counter DrugDokument5 SeitenOver The Counter DrugIti ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- India Otc Pharma Profile 2011Dokument10 SeitenIndia Otc Pharma Profile 2011Sulabh MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Who Trs 908-Annex9Dokument12 SeitenWho Trs 908-Annex9Poorvi KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scope of PharmacistDokument6 SeitenScope of PharmacistIti ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- A WHO GuideDokument100 SeitenA WHO Guidej.k.kumar92% (13)
- MixingDokument52 SeitenMixingIti Chauhan100% (3)
- Organization and StructureDokument3 SeitenOrganization and StructureIti ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Baptismal DelayDokument20 SeitenBaptismal DelayfiohdiohhodoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xiaopan OS: DescriptionDokument1 SeiteXiaopan OS: DescriptionMan SavliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chinese MedicineDokument16 SeitenChinese MedicineTrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1422-Article Text-3684-1-10-20211104Dokument57 Seiten1422-Article Text-3684-1-10-20211104f.kpobi1473Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bsee 36: Survey of English and American Literature Learning Material 2: Introduction To Literary Theories and CriticismDokument4 SeitenBsee 36: Survey of English and American Literature Learning Material 2: Introduction To Literary Theories and CriticismCarlosNorielCabanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method For Determination of Iron Folic Acid & Vitamin B12 in FRK - 07.11.2023Dokument17 SeitenMethod For Determination of Iron Folic Acid & Vitamin B12 in FRK - 07.11.2023jonesbennetteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions 1Dokument3 SeitenQuestions 1krp_212003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Repeater Panel User GuideDokument24 SeitenRepeater Panel User Guideamartins1974Noch keine Bewertungen
- Entropy (Information Theory)Dokument17 SeitenEntropy (Information Theory)joseph676Noch keine Bewertungen
- Andre Bazin, The Ontology of The Photographic Image From His Book What Is Cinema Vol. IDokument8 SeitenAndre Bazin, The Ontology of The Photographic Image From His Book What Is Cinema Vol. IAnkit LadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upsa Y5 2023Dokument8 SeitenUpsa Y5 2023Faizal AzrinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept MapDokument1 SeiteConcept Mapapi-402935758Noch keine Bewertungen
- Preliminary Exam (Primark)Dokument4 SeitenPreliminary Exam (Primark)Zybel RosalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Fluid StaticsDokument26 SeitenChapter 2 Fluid StaticsSoban Malik100% (1)
- Pyrethroids April 11Dokument15 SeitenPyrethroids April 11MadhumithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Samsung LN55C610N1FXZA Fast Track Guide (SM)Dokument4 SeitenSamsung LN55C610N1FXZA Fast Track Guide (SM)Carlos OdilonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fastener Torque Charts: Phone: 1-800-558-2808 Fax: 1-800-553-8769Dokument2 SeitenFastener Torque Charts: Phone: 1-800-558-2808 Fax: 1-800-553-8769KOMATSU SHOVELNoch keine Bewertungen
- Itf EssayDokument18 SeitenItf EssayTharshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- G-00-1169 - Grade Designation For Low Carbon Hot Rolled Steel Sheets Used in Automotive Applications - Rev 4Dokument7 SeitenG-00-1169 - Grade Designation For Low Carbon Hot Rolled Steel Sheets Used in Automotive Applications - Rev 4Prince Ali50% (2)
- Gunnar Fischer's Work On Ingmar Bergman's The Seventh Seal and Wild StrawberriesDokument6 SeitenGunnar Fischer's Work On Ingmar Bergman's The Seventh Seal and Wild StrawberriesSaso Dimoski100% (1)
- Final Project Part-3 Marketing PlanDokument8 SeitenFinal Project Part-3 Marketing PlanIam TwinStormsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estimation of Measurement Uncertainty For Electrical Conductivity in WaterDokument4 SeitenEstimation of Measurement Uncertainty For Electrical Conductivity in WaterMaruthi KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Title Format: ITU-T Recommendation Q.713Dokument4 SeitenGlobal Title Format: ITU-T Recommendation Q.713Pravesh Kumar ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lux Level Calculation: WILSON ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING BOOKS (Simplified Edition 2020)Dokument1 SeiteLux Level Calculation: WILSON ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING BOOKS (Simplified Edition 2020)Wilson (Electrical Engineer)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Altium Designer Training For Schematic Capture and PCB EditingDokument248 SeitenAltium Designer Training For Schematic Capture and PCB EditingAntonio Dx80% (5)
- Consumer Perception Towards WhatsappDokument72 SeitenConsumer Perception Towards WhatsappRaj KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Exploration: Magnetism (Find Gizmo Icon On Eclass)Dokument4 SeitenStudent Exploration: Magnetism (Find Gizmo Icon On Eclass)Abdel Majeed Tuffaha0% (1)
- Theoretical & Conceptual Framework (RESEARCH)Dokument3 SeitenTheoretical & Conceptual Framework (RESEARCH)Rizza Manabat PacheoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jahnteller Effect Unit 3 2017Dokument15 SeitenJahnteller Effect Unit 3 2017Jaleel BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- 160 78-m1Dokument70 Seiten160 78-m1George100% (7)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeVon EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincVon EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (137)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactVon EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideVon EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Chemistry: A Modern IntroductionVon EverandFundamentals of Chemistry: A Modern IntroductionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeVon EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsVon EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolVon EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (90)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsVon EverandTribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionVon EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Ingredients: A Visual Exploration of 75 Additives & 25 Food ProductsVon EverandIngredients: A Visual Exploration of 75 Additives & 25 Food ProductsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodVon EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (20)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableVon EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (22)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsVon EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (146)
- Bioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookVon EverandBioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsVon EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactVon EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (14)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsVon EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)