Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
PT3 Science Chapter 20 Excretion
Hochgeladen von
Spike ChingyenOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
PT3 Science Chapter 20 Excretion
Hochgeladen von
Spike ChingyenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
PT3 Science Chapter 20: Excretion
3.1 Human Excretion
1. What is Excretion ?
It is the removal of metabolic waste products from the
body.
2. Metabolism means all chemical reactions that take place
in the body.
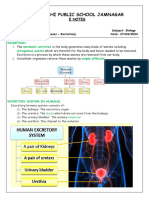
3. The removal of waste products from the body is carried out by
excretory organs , which are the skin, the
lungs and the kidneys.
a. The skin
i. Excrete water, mineral salts and some urea
when a person sweats.
ii. Sweat is salty.
iii. Sweat gland, sweat duct, sweat pore
iv. The body sweats more on a hot day.
v. The evaporation of sweat cools the skin
and the body.
b. The lungs
i. During respiration, waste products such as carbon
dioxide and water are produced.
ii. These waste products are removed from lungs during
gaseous exchange.
c. The kidneys
i. Main excretory organ to remove urea.
ii. Urea is a waste product formed in the liver from excess
amino acids in the body.
iii. Urea is removed in urine.
iv. Urine contains urea, water and mineral salts.
4. The importance of excretion
a. Metabolic wastes will become toxic if accumulated in human
body.
b. Waste products will damage some organs in human body.
c. If an illness persists, death can take place.
d. Waste products must be eliminated through excretion in order to
maintain a healthy body.
5. Excess carbon dioxide will increase the breathing rate.
Excess urea is toxic is toxic to human body.
By removing excess water and mineral salts, the kidneys help
maintain the chemical composition, water and pH balance of the
body.
3.2 The Urinary System in Man
1. The kidneys are located in the back of abdominal cavity.
2. The liver removes excess amino acids from the blood by converting
them into urea which is excreted by the kidneys.
PT3 Science
Page 1
PT3 Science Chapter 20: Excretion
3. The flow of urea into urinary system starts from the kidneys through
the Ureters to the Bladder, and lastly to the
Urethra. From urethra, it is removed as urine through the
penis or opening.
4. Function of each part in urinary system.
Structure
Aorta
Renal vein
Renal artery
Kidney
Ureter
Bladder
Function
The main blood vessel that brings blood from the heart
to the kidney.
The blood vessel that carries blood without waste
products from kidney.
The blood vessel that brings waste products to the
kidney.
An excretory organ that removes wastes like urea,
water and mineral salts from blood.
The tube that carries urine from the kidney to the
bladder.
Temporary store for the urine before it is removed.
The tube that brings urine from the bladder to the penis
or opening for removal.
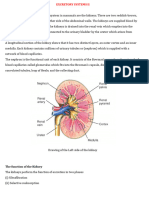
5. Structure of kidney
a. It is bean-shaped. Each kidney is approximately the
Urethra
size of fist.
b. There is a thick layer of fat cover and protect each kidney.
c. The outer, transparent coat of the kidney is called the
capsule. It is a tough membrane.
d. When kidney is cut longitudinally, it can be seen two
parts:
i. Darker outer part Cortex
1. One third of the kidney
ii. Lighter inner part Medulla
1. Medulla forms several pyramids which open into
a sac-like cavity called the Pelvis.
2. From the pelvis, a long, narrow tube, the ureter,
leads to the bladder.
6. Functions of the kidney
a. The kidneys filter waste from the blood.
PT3 Science
Page 2
PT3 Science Chapter 20: Excretion
b. The kidneys also regulate the water (reabsorption of
water) and chemical balance in the body.
7. Two stages or filtration system
a. First filtration water, mineral salts, sugar and waste
products are filtered as blood passes through the kidneys.
b. Second filtration performed in blood capillaries. Most of
the mineral salts and sugar are returned to the
circulatory system.
8. The amount of water that is reabsorbed depends on the amount of
water required by the body.
a. If the body system has too much water reabsorption of
water will be less, the urine will be diluted.
b. If the body system needs more water water will be
reabsorbed into the blood, the urine will be concentrated.
9. The kidneys control the chemical composition of the blood and
play a regulatory role .
a. The blood vessel that brings blood containing waste products
to the kidneys is the Renal Artery.
b. The blood vessel that brings clean blood away from the
kidneys is the Renal Vein.
c. Substances that pass from the blood into the kidneys are
Urea, Glucose, Amino Acids, Mineral Salts and Water.
d. Substances which are reabsorbed into blood from the kidneys
are Glucose and Amino Acids.
i. Glucose energy source
ii. Amino acids body building
e. The urine contains mineral salts, water and urea.
10.The importance of maintaining healthy kidneys
a. Toxic substances such as mercury , lead , arsenic /,
and insecticides can damage the kidneys.
b. Food that is too salty and sweet is also harmful for kidneys.
11.High intake of salt will affect the water balance, causing hypertension
. A high concentration of salt in blood may lead to the formation
of Kidney Stones, which can cause kidney failure .
12.Too much sugar in our blood will ultimately cause Diabetes .
13.Drinking eight glasses of plain water daily and regular exercise
will help improve the blood circulation to and from the kidneys.
14.Kidney failure is treated through dialysis or kidney transplants
.
15.Dialysis is a technique of separating particles of different sizes. A liquid
mixture is passed through a partially permeable membrane
.
a. Dialysis machine works on the principle of diffusion.
Substances move from an area of high concentration to an
area of low concentration across a partially permeable
membrane.
b. A tube is connected to an artery in the arm of a patient, to
allow blood to flow along the tube and enter the dialysis
machine.
PT3 Science
Page 3
PT3 Science Chapter 20: Excretion
c. Blood from the artery flows through the semi-permeable
membrane of the tube. These tubes are immersed in a
dialysis solution called Dialysate.
d. Waste products such as excess water, urea and salts and
other impurities diffuse out from the blood through the pores
of the semi-permeable membrane into the dialysate.
e. The blood with waste products removed goes back into the
vein of the patient.
f. The patient must be connected to the dialysis machine for
about four hours each time, needed two or three times a
week.
3.3 Excretion of Plants
1. The waste products of plants are water, carbon dioxide, oxygen,
mineral salts and nitrogenous wastes .
a. Water and carbon dioxide produced during respiration are
used in photosynthesis.
b. Only small amount of oxygen produced during photosynthesis
is used for respiration.
c. Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuses into the air through the
stomata in the leaves.
d. Excess water is removed as water vapour during
transpiration.
2. Mineral salts remain in the plant as crystals.
a. Minerals like silicon salts are deposited in the leaves of
plants of the grass family. Silicon salts strengthen the leaf
blades.
3. Plants have little nitrogenous waste products, which are usually
converted into harmless granules which are retained in the plant cells.
a. Examples of nitrogenous waste are Flower and Leaf
Pigments .
b. Most pigments are alkaloids which are extremely
poisonous.
c. Some alkaloids can be extracted to produce medicines.
d. Drugs like morphine, opium and cocaine are poisonous.
PT3 Science
Page 4
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Asme Section Viii Div.1Dokument87 SeitenAsme Section Viii Div.1balu100% (7)
- Kidney Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandKidney Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOC 315 - Biochemistry of Food Processing Lecture NotesDokument55 SeitenBIOC 315 - Biochemistry of Food Processing Lecture NotesPerry MasonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 1 PhysicsDokument75 SeitenForm 1 PhysicsClinton ChikengezhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 1 UpDokument102 Seiten6 1 Upsoraandreea20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analytic Geometry Siceloff Wentworth Smith EditedDokument296 SeitenAnalytic Geometry Siceloff Wentworth Smith EditedÁkos Harkai100% (1)
- Form 2 Science Mock Test (Sem 1 Term 1)Dokument5 SeitenForm 2 Science Mock Test (Sem 1 Term 1)Spike ChingyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- PT3 Science Chapter 19 Blood Circulation and TransportDokument8 SeitenPT3 Science Chapter 19 Blood Circulation and TransportSpike ChingyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Excretion in Humans (Edited)Dokument59 SeitenIGCSE Excretion in Humans (Edited)elizabethNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Chemistry Chapter 1Dokument7 SeitenIGCSE Chemistry Chapter 1Spike ChingyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mirror Equation WorksheetDokument1 SeiteMirror Equation WorksheetSpike Chingyen100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Periodic Table of ElementsDokument3 SeitenChapter 4 Periodic Table of ElementsSpike Chingyen100% (1)
- Sop For GcmsDokument3 SeitenSop For GcmsDrMd IdrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elastomer PropertiesDokument72 SeitenElastomer PropertiesBashu PoudelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Honeycomb Kevlar 49 (Hexcel)Dokument3 SeitenHoneycomb Kevlar 49 (Hexcel)Julia GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 8Dokument7 SeitenChemistry Form 4 Chapter 8Suriati Bt A Rashid67% (6)
- Asme B30.9 - FinalDokument3 SeitenAsme B30.9 - FinalDavidNaulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem16 LE3 SamplexDokument3 SeitenChem16 LE3 SamplexmariemfranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch-8 Excretion in Animals & PlantsDokument4 SeitenCh-8 Excretion in Animals & PlantsRonnith NandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excretory System HoDokument4 SeitenExcretory System HodoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolic Wastes and Excretion in the Urinary SystemDokument20 SeitenMetabolic Wastes and Excretion in the Urinary SystemQazi QaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life Processes - ExcretionDokument4 SeitenLife Processes - ExcretionRajvir tradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0610 Biology EXCRETIONDokument27 Seiten0610 Biology EXCRETIONMunir LakhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2.43: Excretion: Removal of Waste Products of MetabolismDokument20 SeitenUnit 2.43: Excretion: Removal of Waste Products of MetabolismxspiirONoch keine Bewertungen
- Excretory System by Macalin Axmed OmaarDokument9 SeitenExcretory System by Macalin Axmed OmaarAhmed OmaarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - ExcretionDokument3 SeitenChapter 3 - ExcretionSuntharan MuniandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regulation of Body FluidsDokument5 SeitenRegulation of Body FluidsAlwìn GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excretion - Excretion Is The Removal of The Metabolic Wastes of An Organism. Wastes That AreDokument10 SeitenExcretion - Excretion Is The Removal of The Metabolic Wastes of An Organism. Wastes That ArejoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExcretionDokument2 SeitenExcretionSD card 32 gbNoch keine Bewertungen
- S3 Biology HOMEOSTASIS Notes - pdf417539Dokument26 SeitenS3 Biology HOMEOSTASIS Notes - pdf417539SsebuumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excretory SystemDokument21 SeitenExcretory SystemAnin BertNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Excretory System-14: How Organs Filter and Remove WastesDokument11 SeitenThe Excretory System-14: How Organs Filter and Remove WastesDrAli Al-FendiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Excretory Systems: Kidneys, Lungs, Skin Remove WastesDokument31 SeitenThe Excretory Systems: Kidneys, Lungs, Skin Remove WastesRolly Toledo NoarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExcretoryUrinary System2023Dokument34 SeitenExcretoryUrinary System2023staycool070112Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Excretory SystemDokument11 SeitenThe Excretory Systemapi-3759646100% (2)
- 10 BiologyDokument5 Seiten10 BiologyLegend 77 FFNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excretion KDBDokument82 SeitenExcretion KDBKiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology #10 Excretion and OsmoregulationDokument5 SeitenBiology #10 Excretion and OsmoregulationAkili ArmaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 ExcretionDokument11 Seiten6 ExcretionAnasatcia Mcpherson 9c FNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Homeostasis & ExcretionDokument142 SeitenHuman Homeostasis & ExcretionJharell CaravlhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excretory SystemDokument61 SeitenExcretory Systemalayca cabatanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zoo 1 Excretion and OsmoregulationDokument17 SeitenZoo 1 Excretion and OsmoregulationMaheshkumar KalalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excretory SystemDokument19 SeitenExcretory SystemElliz DoctoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Excretion NotesDokument8 SeitenBiology Excretion NotesAshleigh JarrettNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExcretionDokument36 SeitenExcretionMeet vermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excretion: The KidneysDokument7 SeitenExcretion: The KidneysLulu BandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.2.3 Excretory Systems IiDokument4 Seiten2.2.3 Excretory Systems Iigodswaykwa14Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plant and human excretion systems explainedDokument9 SeitenPlant and human excretion systems explainedJoy FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Notes IGCSE Excretion NoteDokument9 SeitenBiology Notes IGCSE Excretion NoteCorina HuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Excretory System: Back To TopDokument10 SeitenThe Excretory System: Back To TopDANIA PURNAMANoch keine Bewertungen
- Excretion Andosmoregulationppt09 10Dokument76 SeitenExcretion Andosmoregulationppt09 10Carl Agape DavisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory System (Lungs) : Excretes Carbon Dioxide 3. Integumentary System (Skin) : Excretes Water, SaltsDokument2 SeitenRespiratory System (Lungs) : Excretes Carbon Dioxide 3. Integumentary System (Skin) : Excretes Water, SaltsAbdallah AlasalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excretory Products and Their EliminationDokument6 SeitenExcretory Products and Their EliminationHarshit AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- IX Biology Unit on Excretion and Kidney FunctionDokument21 SeitenIX Biology Unit on Excretion and Kidney Functionpraneeth satishNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExcretionDokument39 SeitenExcretionJennifer J. Pascua100% (1)
- HomeostasisDokument10 SeitenHomeostasisSiddhesh YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excretory SystemDokument39 SeitenExcretory Systemaditya varteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 8 Revision NotesDokument5 SeitenClass 10 Biology Chapter 8 Revision NotesOm KapoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExcretoryDokument31 SeitenExcretoryAnime tingzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of Human Urinary SystemDokument5 SeitenStudy of Human Urinary SystemKʀɩsʜʌŋ ĸʀ ƦoƴNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excretory Organ PDF Invertebrates.Dokument13 SeitenExcretory Organ PDF Invertebrates.E RAMESHBABUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excretion of WaterDokument5 SeitenExcretion of WaterKamrul Alam MasumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excretion CIS VIIIDokument6 SeitenExcretion CIS VIIIelizabethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Excretion in Human BodyDokument11 SeitenIntroduction To Excretion in Human Bodyvurn5665Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Excretion in Human BodyDokument11 SeitenIntroduction To Excretion in Human Bodyvurn5665Noch keine Bewertungen
- Excretory SystemDokument6 SeitenExcretory SystemAJAYI PETERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rayan Ali - Animal ScienceDokument19 SeitenRayan Ali - Animal ScienceRayan AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExcretionDokument4 SeitenExcretiontalithaonkabetse723Noch keine Bewertungen
- ExcretionDokument4 SeitenExcretionnisha dolasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary System VocabularyDokument6 SeitenUrinary System VocabularyAgustín Bravo ArreyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExcretoryDokument31 SeitenExcretoryJevin IndaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excretory SystemDokument6 SeitenExcretory SystemDessy AnnisyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Physiology Ii: School of BiochemistryDokument15 SeitenHuman Physiology Ii: School of Biochemistrykeerthana t reddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excretion: Removal of Metabolic WasteDokument19 SeitenExcretion: Removal of Metabolic WasteLuke NancooNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Excretory System in Swine and ChickensDokument4 SeitenThe Excretory System in Swine and ChickensAbas S. AcmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 10 Excretion in Humans NotesDokument27 SeitenUNIT 10 Excretion in Humans NotescyumadripNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge Checkpoint (1113) 2009 April, P2Dokument11 SeitenCambridge Checkpoint (1113) 2009 April, P2Spike Chingyen25% (8)
- P4 Whole Numbers L1 Ex1Dokument3 SeitenP4 Whole Numbers L1 Ex1Spike ChingyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Missing Angles WorksheetDokument3 SeitenMissing Angles WorksheetSpike ChingyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Striaght LineDokument7 SeitenStriaght LineSpike ChingyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 - Mirror and Magnification EquationsDokument3 Seiten7 - Mirror and Magnification EquationsSpike ChingyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trig Circular Functions AnglesDokument2 SeitenTrig Circular Functions AnglesSpike ChingyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Science Form 4 Chapter 4Dokument5 SeitenSPM Science Form 4 Chapter 4Spike Chingyen100% (2)
- Nota FungsiDokument8 SeitenNota Fungsirhythm_no1Noch keine Bewertungen
- C3 Functions A - Questions PDFDokument1 SeiteC3 Functions A - Questions PDFSpike ChingyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- P4 Whole Numbers L1 Ex3Dokument3 SeitenP4 Whole Numbers L1 Ex3Spike ChingyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- FunctionsDokument30 SeitenFunctionsRuby WalshNoch keine Bewertungen
- C3 Functions B - Questions PDFDokument2 SeitenC3 Functions B - Questions PDFSpike ChingyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- P4 Whole Numbers L1 Ex2Dokument2 SeitenP4 Whole Numbers L1 Ex2Spike ChingyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- P4 Whole Numbers L1 Ex2Dokument2 SeitenP4 Whole Numbers L1 Ex2Spike ChingyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 The Structure of The AtomDokument1 SeiteChapter 2 The Structure of The AtomSpike Chingyen100% (1)
- Calculus - Small IncrementsDokument3 SeitenCalculus - Small IncrementsSpike ChingyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limits in CalculusDokument30 SeitenLimits in CalculusSpike ChingyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Continuity WorksheetDokument3 SeitenContinuity WorksheetSpike ChingyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch10 Momentum and CollisionsDokument30 SeitenCh10 Momentum and CollisionsSpike ChingyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- PT3 Science Chapter 18 RespirationDokument4 SeitenPT3 Science Chapter 18 RespirationSpike ChingyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Additional Mathematics SummaryDokument1 SeiteSPM Additional Mathematics SummarySpike Chingyen100% (1)
- SDS Weberfloor VB ResinDokument25 SeitenSDS Weberfloor VB ResinMaha MuflehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carboguard 893 Part B MSDSDokument11 SeitenCarboguard 893 Part B MSDSQuy RomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glydant Plus Liquid (I) 2006Dokument2 SeitenGlydant Plus Liquid (I) 2006Enrique Alberto Valenzuela Hernandez0% (1)
- Northern Cement CorporationDokument26 SeitenNorthern Cement CorporationJHuvieCLaireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes CoWinDokument3 SeitenEnzymes CoWinabinradhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waterproofing 2022Dokument8 SeitenWaterproofing 2022VR RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natural Hydrating Milk CleanserDokument1 SeiteNatural Hydrating Milk CleanserNadaNursetiyantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions Chapter 1-10Dokument107 SeitenQuestions Chapter 1-10PriyaranjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM D36D36M Standart Test Method For Softening Point of Bitumen (Ring and Ball Apparatus)Dokument5 SeitenASTM D36D36M Standart Test Method For Softening Point of Bitumen (Ring and Ball Apparatus)Yeison GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Products For Polyurethanes: Driving Comfort & DurabilityDokument8 SeitenProducts For Polyurethanes: Driving Comfort & DurabilityA MahmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delhi Public School: Subject: English CoreDokument17 SeitenDelhi Public School: Subject: English CoreVirat KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBH Metals CatalogueDokument56 SeitenMBH Metals CataloguetaichiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proposal ChlorobenzeneDokument12 SeitenProposal ChlorobenzeneDavid Akomolafe100% (1)
- This PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedDokument11 SeitenThis PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedGod is every whereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moldex3D R14 FEA Interface IntroductionDokument46 SeitenMoldex3D R14 FEA Interface IntroductionmadhukeshwartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aqua SilencerDokument18 SeitenAqua SilencerManideep AlluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coordination Compounds Cet-2Dokument2 SeitenCoordination Compounds Cet-2Amen RaipurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Wet Test Acid Radical-1Dokument5 SeitenPractical Wet Test Acid Radical-1psyxs4tsv9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Structure Determination:: Proton 1.00728 U Neutron 1.00866 U Electron 0.00055 UDokument12 SeitenStructure Determination:: Proton 1.00728 U Neutron 1.00866 U Electron 0.00055 Ufouad elferdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro ConcreteDokument4 SeitenMicro ConcreteDanie RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECC Chemical Process Pumps GuideDokument84 SeitenECC Chemical Process Pumps GuideIwan KurniawanNoch keine Bewertungen