Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ch07 SSol
Hochgeladen von
venkeeeeeOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ch07 SSol
Hochgeladen von
venkeeeeeCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
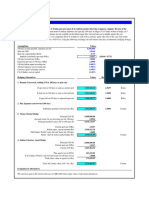
Problem 7.
1 Peso futures
Amber McClain, the currency speculator we met earlier in the chapter,sells eight June futures contracts for
500,000 pesos at the closing price quoted in Exhibit 7.1.
a. What is the value of her position at maturity if the ending spotrate is $0.12000/Ps?
b. What is the value of her position at maturity if the ending spotrate is $0.09800/Ps?
c. What is the value of her position at maturity if the ending spotrate is $0.11000/Ps?
Assumptions
Number of pesos per futures contract
Number of contracts
Buy or sell the peso futures?
Ending spot rate ($/peso)
June futures settle price from Exh7.1 ($/peso)
Spot - Futures
Value of total position at maturity (US$)
Value = - Notional x (Spot - Futures) x 8
a)
Values
500,000
8.00
Sell
b)
Values
500,000
8.00
Sell
c)
Values
500,000
8.00
Sell
$0.12000
$0.10773
$0.01227
$0.09800
$0.10773
($0.00973)
$0.11000
$0.10773
$0.00227
($49,080.00)
$38,920.00
($9,080.00)
Interpretation
Amber buys at the spot price and sells at the futures price.
If the futures price is greater than the ending spot price, she makes a profit.
Problem 7.7 How much profit -- calls?
Assume a call option on euros is written with a strike price of $1.2500/ at a premium of 3.80 per euro ($0.0380/) and with an expiration date three months from now. The
option is for 100,000. Calculate your profit or loss should you exercise before maturity at a time when the euro is traded spot at .....
Assumptions
Notional principal (euros)
Maturity (days)
Strike price (US$/euro)
Premium (US$/euro)
Ending spot rate (US$/euro)
Gross profit on option
Less premium
Net profit (US$/euro)
Net profit, total
a)
Values
100,000.00
90
$1.2500
$0.0380
$1.1000
b)
Values
100,000.00
90
$1.2500
$0.0380
$1.1500
c)
Values
100,000.00
90
$1.2500
$0.0380
$1.2000
d)
Values
100,000.00
90
$1.2500
$0.0380
$1.2500
e)
Values
100,000.00
90
$1.2500
$0.0380
$1.3000
f)
Values
100,000.00
90
$1.2500
$0.0380
$1.3500
g)
Values
100,000.00
90
$1.2500
$0.0380
$1.4000
$0.0000
($0.0380)
($0.0380)
$0.0000
($0.0380)
($0.0380)
$0.0000
($0.0380)
($0.0380)
$0.0000
($0.0380)
($0.0380)
$0.0500
($0.0380)
$0.0120
$0.1000
($0.0380)
$0.0620
$0.1500
($0.0380)
$0.1120
($3,800.00)
($3,800.00)
($3,800.00)
($3,800.00)
$1,200.00
$6,200.00
$11,200.00
Problem 7.11 U.S. dollar/euro
Pricing Currency Options on the Euro
A U.S.-based firm wishing to buy
or sell euros (the foreign currency)
Value
$1.2480
$1.2500
1.453%
2.187%
1.000
365.00
10.500%
Call option premium (per unit fc)
Put option premium (per unit fc)
(European pricing)
c
p
Call option premium (%)
Put option premium (%)
c
p
Spot rate (domestic/foreign)
Strike rate (domestic/foreign)
Domestic interest rate (% p.a.)
Foreign interest rate (% p.a.)
Time (years, 365 days)
Days equivalent
Volatility (% p.a.)
Variable
S0
X
rd
rf
T
A European firm wishing to buy
or sell dollars (the foreign currency)
Variable
S0
Value
0.8013
0.8000
2.187%
1.453%
1.000
365.00
10.500%
$0.0461
$0.0570
c
p
0.0366
0.0295
3.69%
4.57%
c
p
4.56%
3.68%
X
rd
rf
T
Copyright 2004, Barbara S. Petitt and Michael H. Moffett, Thunderbird, The American Graduate School of International Management.
Problem 7.12 U.S. dollar/Japanese yen
Pricing Currency Options on the Japanese yen
A Japanese firm wishing to buy
or sell dollars (the foreign currency)
Value
JPY 105.64
JPY 100.00
0.089%
1.453%
1.000
365.00
12.000%
Call option premium (per unit fc)
Put option premium (per unit fc)
(European pricing)
c
p
Call option premium (%)
Put option premium (%)
c
p
Spot rate (domestic/foreign)
Strike rate (domestic/foreign)
Domestic interest rate (% p.a.)
Foreign interest rate (% p.a.)
Time (years, 365 days)
Days equivalent
Volatility (% p.a.)
Variable
S0
X
rd
rf
T
A U.S.-based firm wishing to buy
or sell yen (the foreign currency)
Variable
S0
X
rd
rf
T
s
Value
$0.0095
$0.0100
1.453%
0.089%
1.000
365.00
12.000%
JPY 7.27
JPY 3.06
c
p
$0.0003
$0.0007
6.88%
2.90%
c
p
3.06%
7.27%
Copyright 2004, Barbara S. Petitt and Michael H. Moffett, Thunderbird, The Garvin School of International Management.
A Japanese firm wishing to sell U.S. dollars would need to purchase a put on dollars. The put option premium listed above is JPY3.06/$.
Put option premium (JPY/US$)
Notional principal (US$)
Total cost (JPY)
JPY 3.06
$750,000
JPY 2,297,243
Problem 7.13 Euro/Japanese yen
Pricing Currency Options on the Euro/Yen Crossrate
A Japanese firm wishing to buy
or sell euros (the foreign currency)
Value
JPY 133.89
JPY 136.00
0.088%
2.187%
0.247
90.00
10.000%
Call option premium (per unit fc)
Put option premium (per unit fc)
(European pricing)
c
p
Call option premium (%)
Put option premium (%)
c
p
Spot rate (domestic/foreign)
Strike rate (domestic/foreign)
Domestic interest rate (% p.a.)
Foreign interest rate (% p.a.)
Time (years, 365 days)
Days equivalent
Volatility (% p.a.)
Variable
S0
X
rd
rf
T
A European firm wishing to buy
or sell yen (the foreign currency)
Variable
S0
X
rd
rf
T
s
Value
0.0072
0.0074
2.187%
0.088%
0.247
90.00
10.000%
JPY 1.50
JPY 4.30
c
p
0.0001
0.0002
1.12%
3.21%
c
p
1.30%
2.90%
Copyright 2004, Barbara S. Petitt and Michael H. Moffett, Thunderbird, The Garvin School of International Management.
A European-based firm like Legrand (France) would need to purchase a put option on the Japanese yen. The company wishes a strike rate of
0.0072 euro for each yen sold (the strike rate) and a 90-day maturity. Note that the "Time" must be entered as the fraction of a 365 day year, in
this case, 90/365 = 0.247.
Put option premium (euro/JPY)
Notional principal (JPY)
Total cost (euro)
0.0002
JPY 10,400,000
2,167.90
Problem 7.14 U.S. dollar/British pound
Pricing Currency Options on the British pound
A U.S.-based firm wishing to buy
or sell pounds (the foreign currency)
Value
$1.8674
$1.8000
1.453%
4.525%
0.493
180.00
9.400%
Call option premium (per unit fc)
Put option premium (per unit fc)
(European pricing)
c
p
Call option premium (%)
Put option premium (%)
c
p
Spot rate (domestic/foreign)
Strike rate (domestic/foreign)
Domestic interest rate (% p.a.)
Foreign interest rate (% p.a.)
Time (years, 365 days)
Days equivalent
Volatility (% p.a.)
Variable
S0
X
rd
rf
T
A British firm wishing to buy
or sell dollars (the foreign currency)
Variable
S0
X
rd
rf
Value
0.5355
0.5556
4.525%
1.453%
0.493
180.00
9.400%
$0.0696
$0.0306
c
p
0.0091
0.0207
3.73%
1.64%
c
p
1.70%
3.87%
Copyright 2004, Barbara S. Petitt and Michael H. Moffett, Thunderbird, The Garvin School of International Management.
Call option premiums for a U.S.-based firm buying call options on the British pound:
180-day maturity ($/pound)
90-day maturity ($/pound)
Difference ($/pound)
$0.0696
$0.0669
$0.0027
The maturity doubled while the option premium rose only about 4%.
Problem 7.15 Euro/British pound
Pricing Currency Options on the British pound/Euro Crossrate
A European firm wishing to buy
or sell pounds (the foreign currency)
Value
1.4730
1.5000
4.000%
4.160%
0.247
90.00
11.400%
Call option premium (per unit fc)
Put option premium (per unit fc)
(European pricing)
c
p
Call option premium (%)
Put option premium (%)
c
p
Spot rate (domestic/foreign)
Strike rate (domestic/foreign)
Domestic interest rate (% p.a.)
Foreign interest rate (% p.a.)
Time (years, 365 days)
Days equivalent
Volatility (% p.a.)
Variable
S0
X
rd
rf
T
A British firm wishing to buy
or sell euros (the foreign currency)
Variable
S0
X
rd
rf
Value
0.6789
0.6667
4.160%
4.000%
0.247
90.00
11.400%
0.0213
0.0487
c
p
0.0220
0.0097
1.45%
3.30%
c
p
3.24%
1.42%
Copyright 2004, Barbara S. Petitt and Michael H. Moffett, Thunderbird, The Garvin School of International Management.
When the euro's interest rate rises from 2.072% to 4.000%, the call option premium on British pounds rises:
Call option on pounds when euro interest is 4.000%
Call option on pounds when euro interest is 2.072%
Change, an increase in the premium
0.0213
0.0189
0.0213
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Bus 322 Tutorial 5-SolutionDokument20 SeitenBus 322 Tutorial 5-Solutionbvni50% (2)
- Chap08 Pbms SolutionsDokument25 SeitenChap08 Pbms SolutionsDouglas Estrada100% (1)
- Sallie Schnudel speculates on Singapore dollar appreciationDokument25 SeitenSallie Schnudel speculates on Singapore dollar appreciationveronika100% (1)
- MBF13e Chap08 Pbms - FinalDokument25 SeitenMBF13e Chap08 Pbms - FinalBrandon Steven Miranda100% (4)
- BUS322Tutorial5 SolutionDokument20 SeitenBUS322Tutorial5 Solutionjacklee191825% (4)
- DerivativeDokument16 SeitenDerivativeShiro Deku100% (1)
- Foreign Exchange Market InsightsDokument12 SeitenForeign Exchange Market InsightsRuiting Chen100% (1)
- Finance - Module 7Dokument3 SeitenFinance - Module 7luckybella100% (1)
- Summer 2021 FIN 6055 New Test 2Dokument2 SeitenSummer 2021 FIN 6055 New Test 2Michael Pirone0% (1)
- BUS322Tutorial8 SolutionDokument10 SeitenBUS322Tutorial8 Solutionjacklee1918100% (1)
- FX II PracticeDokument10 SeitenFX II PracticeFinanceman4Noch keine Bewertungen
- FNE306 Assignment 6 AnsDokument9 SeitenFNE306 Assignment 6 AnsCharles MK ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap12 Pbms MBF12eDokument10 SeitenChap12 Pbms MBF12eBeatrice BallabioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11Dokument2 SeitenChapter 11atuanaini0% (1)
- Sallie Schnudel currency option choicesDokument1 SeiteSallie Schnudel currency option choicesSamer100% (1)
- Problem 11.3Dokument1 SeiteProblem 11.3SamerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 3 Tutorial ProblemsDokument6 SeitenWeek 3 Tutorial ProblemsWOP INVESTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 6 ProblemsDokument5 SeitenChap 6 ProblemsCecilia Ooi Shu QingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 8.1 Peregrine Funds - JakartaDokument5 SeitenProblem 8.1 Peregrine Funds - JakartaAlexisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ex - TransExposure SOLDokument5 SeitenEx - TransExposure SOLAlexisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pbm7 2Dokument1 SeitePbm7 2jordi92500Noch keine Bewertungen
- FC options vs futures; Nick Leeson's unauthorized trading at Barings BankDokument5 SeitenFC options vs futures; Nick Leeson's unauthorized trading at Barings BankMohd Hafeez NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument5 SeitenUntitledsuperorbitalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.18 East Asiatic CompanyDokument2 Seiten6.18 East Asiatic Companydummy yummyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SS - 08partDokument11 SeitenSS - 08partMrudul KotiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBF14e Chap02 Monetary System PbmsDokument13 SeitenMBF14e Chap02 Monetary System PbmsKarlNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBF14e Chap05 FX MarketsDokument20 SeitenMBF14e Chap05 FX MarketsHaniyah Nadhira100% (1)
- P&G India hedges Japanese yen payableDokument17 SeitenP&G India hedges Japanese yen payableNguyễn Gia Phương Anh100% (1)
- Problem 19.1 Trefica de Honduras: Assumptions ValuesDokument2 SeitenProblem 19.1 Trefica de Honduras: Assumptions ValueskamlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Total Inflow Total Outflow Net Inflow or Ouftlow Expected Exchange Rate Net Inflow or Outflow As Measured in US Dollars British PoundsterlingDokument3 SeitenTotal Inflow Total Outflow Net Inflow or Ouftlow Expected Exchange Rate Net Inflow or Outflow As Measured in US Dollars British Poundsterlingcatarina alexandriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch14 P13 Build A ModelDokument6 SeitenCh14 P13 Build A ModelRayudu Ramisetti0% (2)
- Feenstra Intlecon3e SM Ch13econ Ch02macroDokument6 SeitenFeenstra Intlecon3e SM Ch13econ Ch02macroSebastian BrilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Currency Risk HedgingDokument12 SeitenCurrency Risk Hedginggilli1tr100% (1)
- MBF14e Chap06 Parity Condition PbmsDokument23 SeitenMBF14e Chap06 Parity Condition PbmsKarl100% (18)
- Chap07 Pbms MBF12eDokument22 SeitenChap07 Pbms MBF12eBeatrice Ballabio100% (1)
- CHP 6Dokument8 SeitenCHP 6Nicky Supakorn100% (1)
- Chapter 12 SolutionsDokument11 SeitenChapter 12 SolutionsEdmond ZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blade's CaseDokument8 SeitenBlade's CaseEly HarunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blades Case Exposure to International Flow of FundsDokument1 SeiteBlades Case Exposure to International Flow of FundsWulandari Pramithasari50% (2)
- Solnik & Mcleavey - Global Investment 6th EdDokument5 SeitenSolnik & Mcleavey - Global Investment 6th Edhotmail13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Siam Cement Foreign Exchange Loss on $50M Debt RepaymentDokument22 SeitenSiam Cement Foreign Exchange Loss on $50M Debt Repaymentmark leeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solnik Chapter 3 Solutions To Questions & Problems (6th Edition)Dokument6 SeitenSolnik Chapter 3 Solutions To Questions & Problems (6th Edition)gilli1trNoch keine Bewertungen
- Currency Exchange Rates ExplainedDokument5 SeitenCurrency Exchange Rates Explainedhotmail13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4-Exchange Rate DeterminationDokument21 SeitenChapter 4-Exchange Rate DeterminationMelva CynthiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solnik & McLeavey - Global Investment 6th EdDokument5 SeitenSolnik & McLeavey - Global Investment 6th Edhotmail13Noch keine Bewertungen
- BioTron Medical Foreign Exchange Risk AnalysisDokument19 SeitenBioTron Medical Foreign Exchange Risk AnalysisQurratul Asmawi100% (2)
- International FinanceDokument10 SeitenInternational FinancelabelllavistaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MID-TERM REVIEW TIPS AND PRACTICEDokument29 SeitenMID-TERM REVIEW TIPS AND PRACTICEChou mỡNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBFinance Chap06-Pbms-finalDokument20 SeitenMBFinance Chap06-Pbms-finalLinda YuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inventory Simulation Game Student HandoutDokument3 SeitenInventory Simulation Game Student HandoutRhobeMitchAilarieParelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap11 Translation PbmsDokument10 SeitenChap11 Translation Pbmskk100% (2)
- FX IV PracticeDokument10 SeitenFX IV PracticeFinanceman4100% (4)
- Sample QuestionDokument9 SeitenSample QuestionYussone Sir'YussNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW Chap 7Dokument2 SeitenHW Chap 7Thao NgoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MF 6Dokument29 SeitenMF 6Hueg HsienNoch keine Bewertungen
- MF Tutorial 6Dokument29 SeitenMF Tutorial 6Hueg Hsien0% (1)
- Chap03 Pbms MBF12eDokument15 SeitenChap03 Pbms MBF12eRoopak Rewari100% (2)
- Tutorial 5 Exercises TemplateDokument17 SeitenTutorial 5 Exercises TemplateHà VânNoch keine Bewertungen
- IFM Assignment 1Dokument15 SeitenIFM Assignment 1Azrul AzliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rangkuman UTSDokument7 SeitenRangkuman UTSscorpion182Noch keine Bewertungen
- HcacjoDokument1 SeiteHcacjovenkeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Placement Report Class 2014Dokument17 SeitenPlacement Report Class 2014Mudassir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AkzoNobel Report Report 2013 0414 Tcm9-84856Dokument218 SeitenAkzoNobel Report Report 2013 0414 Tcm9-84856venkeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aifs Case - Fin 411Dokument2 SeitenAifs Case - Fin 411Tanmay MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Report 2013Dokument145 SeitenAnnual Report 2013venkeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013 Annual Report FinalDokument64 Seiten2013 Annual Report FinalvenkeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discover Annual Report1Dokument208 SeitenDiscover Annual Report1venkeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atos 2014 Financial ReportDokument99 SeitenAtos 2014 Financial ReportvenkeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- VTSP Foundation (2015) - VCenter OverviewDokument6 SeitenVTSP Foundation (2015) - VCenter OverviewvenkeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- AkzoNobel Report 2014 en Tcm9-90769Dokument258 SeitenAkzoNobel Report 2014 en Tcm9-90769venkeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fund 4e Chap07 PbmsDokument14 SeitenFund 4e Chap07 PbmsChu Minh LanNoch keine Bewertungen
- FMCG Employer Profiles: (And Graduate Assessment Process)Dokument26 SeitenFMCG Employer Profiles: (And Graduate Assessment Process)nareshsbcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discover Annual Report1Dokument208 SeitenDiscover Annual Report1venkeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wksheet 05Dokument18 SeitenWksheet 05venkeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 q4 Foi Xls v2Dokument21 Seiten2011 q4 Foi Xls v2venkeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- UhuahulhDokument1 SeiteUhuahulhvenkeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Walgreen 09Dokument16 SeitenWalgreen 09venkeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 Annual ReportDokument60 Seiten2012 Annual ReportvenkeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top 25 Summer InternshipsDokument13 SeitenTop 25 Summer InternshipsGaurav ThaparNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grennel LDokument3 SeitenGrennel LvenkeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACCT303 Chapter 9 Teaching PPDokument115 SeitenACCT303 Chapter 9 Teaching PPvenkeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 311 Session3Dokument39 Seiten311 Session3venkeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACCT303 Chapter 1 Teaching PPDokument61 SeitenACCT303 Chapter 1 Teaching PPvenkeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 13Dokument76 SeitenCH 131asdfghjkl3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Calculate Percentiles Using Z-ScoresDokument5 SeitenCalculate Percentiles Using Z-ScoresvenkeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Condensed Consolidated Statements of IncomeDokument7 SeitenCondensed Consolidated Statements of IncomevenkeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculate Percentiles Using Z-ScoresDokument5 SeitenCalculate Percentiles Using Z-ScoresvenkeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 012Dokument26 SeitenChap 012venkeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting CH 26Dokument34 SeitenAccounting CH 26venkeeeee100% (1)
- 124C1ADokument4 Seiten124C1AParthiban DevendiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Class 10 CBSE (NCERT)Dokument369 SeitenMathematics Class 10 CBSE (NCERT)LinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work MeasurementDokument15 SeitenWork MeasurementBalaji BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- SQL SlidesDokument65 SeitenSQL SlidescopsamostoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toraiz SP-16Dokument89 SeitenToraiz SP-16ScappinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virtual Retinal DisplayDokument17 SeitenVirtual Retinal Displaysaket_mnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01238-00-AD TY96 Installation ManualDokument42 Seiten01238-00-AD TY96 Installation ManualJohan SwanepoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 10 TelecommunicationsDokument7 SeitenWeek 10 TelecommunicationsGuido MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Python Notes - 1Dokument364 SeitenPython Notes - 1hopefulantonelliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loan PredictionDokument3 SeitenLoan PredictionShreyansh JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unified Modeling Language Class Diagram ..Uml)Dokument20 SeitenUnified Modeling Language Class Diagram ..Uml)Yasmeen AltuwatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument11 SeitenChapter 1bekemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compact GSM II: Installation and Application ManualDokument22 SeitenCompact GSM II: Installation and Application ManualleonardseniorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viscosity Vs ConsistencyDokument6 SeitenViscosity Vs Consistencysontakke manmathNoch keine Bewertungen
- 100 People Who Changed History and The WorldDokument400 Seiten100 People Who Changed History and The WorldManjunath.RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Influence of Ring-Stiffeners On Buckling Behavior of Pipelines UnderDokument16 SeitenInfluence of Ring-Stiffeners On Buckling Behavior of Pipelines UnderSUBHASHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ajmera - Treon - FF - R4 - 13-11-17 FinalDokument45 SeitenAjmera - Treon - FF - R4 - 13-11-17 FinalNikita KadamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signal Circuit LessonDokument1 SeiteSignal Circuit Lessonapi-208557858Noch keine Bewertungen
- JefimenkoDokument10 SeitenJefimenkoBilly M. SpragueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiziks: Basic Properties and Tools of ThermodynamicsDokument28 SeitenFiziks: Basic Properties and Tools of ThermodynamicsSURAJ PRATAP SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cylindrical Plug Gage DesignsDokument3 SeitenCylindrical Plug Gage DesignskkphadnisNoch keine Bewertungen
- CC5291-Design For Manufacture Assembly and Environments QBDokument11 SeitenCC5291-Design For Manufacture Assembly and Environments QBYuvaraj Yuvi0% (1)
- 1-Newton Second Law-ForMATDokument5 Seiten1-Newton Second Law-ForMATVAIBHAV KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- CFA Level II 3 Topics - High Yield List of QuestionsDokument4 SeitenCFA Level II 3 Topics - High Yield List of QuestionsCatalinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planetary AlignmentDokument7 SeitenPlanetary AlignmentEbn MisrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Properties of Common Liquids Solids and Foods 2Dokument2 SeitenProperties of Common Liquids Solids and Foods 2Šhëënà de LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decision Model Using ExcelDokument236 SeitenDecision Model Using Excelসামিউল ইসলাম রাজু100% (3)
- Cost Estimation TechniquesDokument41 SeitenCost Estimation TechniquessubashNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRL External CommunicationDokument3 SeitenTRL External CommunicationAyushGargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Bond Administration On Construction Project DeliveryDokument7 SeitenEffect of Bond Administration On Construction Project DeliveryOlefile Mark MolokoNoch keine Bewertungen