Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Quiz On Electromagnetism
Hochgeladen von
Neil Patrick CartajenasOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Quiz On Electromagnetism
Hochgeladen von
Neil Patrick CartajenasCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Quiz on Electromagnetism
Name: ________________________
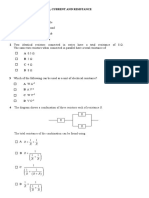
1. This diagram shows the magnetic field of
a. two wires at Y and Z both carrying electric current into the paper
b. two wires at Y and Z both carrying electric current out of the paper
c. a wire Y carrying current into the paper and a wire Z carrying current out of the paper
d. a bar magnet with N pole at Y and S pole at Z
e. a bar magnet with S pole at Y and N pole at Z
2. When the a.c. supply to the coil is switched on and left on, the iron bar will..
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
stay at the same height and vibrate
be repelled upwards from the coil and then remain stationary
move down towards the coil and then vibrate slightly
do not move at all
move down towards the coil and then up again to its starting point
3. The three lines marked X in the diagram are a symbol for
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
a capacitor
insulation
a soft iron core
a permanent magnet
a magnetic field
4. When current flows through the coil shown in the above diagram, in which of the following ways is
the iron magnetized?
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
North pole at F, South pole at G
North pole at G, South pole at F
No poles at F and G
North pole at F, North pole at G
South pole at F, South pole at G
5. Which one of the following graphs best shows the variation of the magnetic flux density along the axis
of a current carrying solenoid (the solenoid position is shown on the graph)?
6. When the magnet rotates as shown an alternating e.m.f. is generated in the coil. If the speed of
rotation is doubled
a. the voltage increases and the frequency is reduced
b. the voltage increases and the frequency doubles
c. the voltage stays the same and the frequency doubles
d. the voltage decreases and the frequency is reduced
e. the voltage decreases and the frequency doubles.
7. A transformer has 100 turns on its primary and 1000 turns on its secondary. If a 50.Hz, 100. V output
is seen at the secondary, then the
a. frequency at the primary is 5.0 Hz
b. voltage across the primary is 10.0 V
c. current in the secondary is 10 times the current in the primary
d. secondary dissipates more energy than the primary
8. The unit for electrical power is the
a. joule
b. watt
c. ohm
d. Newton
9. The current direction in the rotating coil of a simple d.c electric motoris reversed every half revolution
to
a. reverse the polarity of the field magnet
b. prevent corrosion of the brushes.
c. maintain the direction of rotation of the coil
d. provide an a.c output from the motor
10. Which of the following statements is/are correct concerning the commutator of a simple d.c electric
motor?
(1) It reverses the connections between the battery and the coil as the coil rotates.
(2) It has two conducting segments.
(3) It is connected to the battery by two brushes.
a. (1)
b. (3)
c. (1) and (2)
d. (2) and (3)
e. (1), (2) and (3)
11. Electrical energy is transmitted in the grid system at high voltages because
a. it is easier to generate high voltages than low voltages
b. energy losses are lower at high voltages
c. the resistance of the cables is lower at high voltages
d. thicker cables can be used with high voltages
12. While a magnet is being inserted into a coil the induced e.m.f. is increased if the
(1) number of turns in the coil is increased
(2) speed with which the magnet is inserted is increased
(3) opposite pole is inserted into the coil
a. (1)
b. (3)
c. (1) and (2)
d. (2) and (3)
e. (1), (2), and (3)
13. The purpose of the commutator (split ring) in the simple d.c motor is to
a. convert alternating current to direct current
b. reduce power losses
c. increase the speed of the motor
d. produce continuous motion in one direction
e. prevent sparking at the contacts with the brushes
14. If there are 2000 turns in the primary coil of a transformer and 500 turns in the secondary coil and
alternating voltage of 240 volts is applied to the primary coil, what will be the voltage in the secondary
coil?
a. 4800 V
b. 1200 V
c. 960 V
d. 60 V
e. 12 V
15. Lenzs law of electromagnetic induction may be stated as the induced effect in a circuit is in such a
direction as to oppose the change which producing it. The phrase the change which is producing it
means a change in the
a. resistance of the circuit
b. temperature of the circuit
c. material from which the circuit is made
d. magnetic flux (field) linked with the circuit
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Affidavit of EmploymentDokument1 SeiteAffidavit of EmploymentNeil Patrick CartajenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Affidavit of Employment: Charles B. RasonableDokument1 SeiteAffidavit of Employment: Charles B. RasonableNeil Patrick CartajenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deed of Sale With Assumption of MortgageDokument3 SeitenDeed of Sale With Assumption of MortgageNeil Patrick CartajenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contract of LeaseDokument9 SeitenContract of LeaseNeil Patrick CartajenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neolamarkia Cadamba (Roxb.) Bosser: (Kadamb)Dokument5 SeitenNeolamarkia Cadamba (Roxb.) Bosser: (Kadamb)Neil Patrick CartajenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alumni LetterDokument2 SeitenAlumni LetterNeil Patrick CartajenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Household Heads Training Manual v2014Dokument104 SeitenHousehold Heads Training Manual v2014Neil Patrick CartajenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines To Investigatory ProjectDokument23 SeitenGuidelines To Investigatory ProjectNeil Patrick Cartajenas60% (5)
- Laser Application (Quiz To Be Given On 2-14)Dokument8 SeitenLaser Application (Quiz To Be Given On 2-14)Neil Patrick CartajenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic and Nuclear Physics Review MaterialDokument172 SeitenAtomic and Nuclear Physics Review MaterialNeil Patrick CartajenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vetical Acceleration Problem: Vertical Acceleration Is A Constant Value. This Investigation Will Use ThatDokument2 SeitenVetical Acceleration Problem: Vertical Acceleration Is A Constant Value. This Investigation Will Use ThatNeil Patrick CartajenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Motion ProblemsDokument1 SeiteLinear Motion ProblemsNeil Patrick CartajenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building A Tall TowerDokument1 SeiteBuilding A Tall TowerNeil Patrick CartajenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Step Touch PotentialDokument6 SeitenStep Touch Potentialykh92167Noch keine Bewertungen
- ELE1502 Study BookDokument283 SeitenELE1502 Study BookMarthee BaticanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sola PaperDokument6 SeitenSola PaperPablo di PasquoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition of Electrical Terms and Electrical Units.Dokument7 SeitenDefinition of Electrical Terms and Electrical Units.julianaquino1203Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Current NotesDokument6 SeitenElectric Current Notesm.umerfaizan1895Noch keine Bewertungen
- L&T MCCB Product CatalougeDokument84 SeitenL&T MCCB Product CatalougeKishore Krishna92% (13)
- ElectroChemistry Slides PDFDokument44 SeitenElectroChemistry Slides PDFHenry OkoyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Westcar Rotofluid Catalogue - Eng 2006 (Comp)Dokument29 SeitenWestcar Rotofluid Catalogue - Eng 2006 (Comp)César Arias100% (1)
- SCR Training Manual (Chromalox)Dokument47 SeitenSCR Training Manual (Chromalox)Carlos Iván RuedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity MCQDokument14 SeitenElectricity MCQPraphul MalolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Paper 1 TZ1 HLDokument22 SeitenPhysics Paper 1 TZ1 HLBrian KwonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Vipa Hmi Touch PanelDokument48 SeitenManual Vipa Hmi Touch PanelJuan CardenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Driver Circuits - PowerGuru - Power Electronics Information PortalDokument5 SeitenDriver Circuits - PowerGuru - Power Electronics Information PortaldevchandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Electrical EngineeringDokument38 SeitenFundamentals of Electrical EngineeringnbaotuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Water Quality Monitoring System For Real Time ApplicationsDokument8 SeitenSmart Water Quality Monitoring System For Real Time ApplicationsMaruti SankannanavarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Guided Waves and Devices - R. Syms & J. Cozens - 1992 PDFDokument439 SeitenOptical Guided Waves and Devices - R. Syms & J. Cozens - 1992 PDFemanuelpoulsen80% (5)
- Wesley Stivep1 DeviceDokument60 SeitenWesley Stivep1 Devicegetit007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Application Guidelines For Aluminum Electolytic Capacitors PDFDokument19 SeitenApplication Guidelines For Aluminum Electolytic Capacitors PDFPradeep_VashistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capacitor ModelDokument18 SeitenCapacitor ModelMannal JavedNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAPORAN IP LISTRIK PASIR - Bahasa InggrisDokument55 SeitenLAPORAN IP LISTRIK PASIR - Bahasa InggrisalfonsxxxNoch keine Bewertungen
- g482 Mod 2 2 2 3 and 2 2 4 Resistance and ResistivityDokument10 Seiteng482 Mod 2 2 2 3 and 2 2 4 Resistance and Resistivityapi-236179294Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Engineering McqsDokument61 SeitenElectrical Engineering McqsMuhammad IkramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Traffic Light ControllerDokument35 SeitenAutomatic Traffic Light ControllerAmamhossain50% (2)
- Concentration Cell Batteries CorrosionDokument76 SeitenConcentration Cell Batteries Corrosionannida latifahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circui Analysis Upto 125Dokument249 SeitenCircui Analysis Upto 125AJIN RIBIA PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7Dokument7 SeitenChapter 7Taylor JammiesonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer PresentationDokument29 SeitenTransformer PresentationHannan AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Design Training Class: Line LossDokument54 SeitenElectrical Design Training Class: Line Losssri_electricalNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Voltage EngineeringDokument212 SeitenHigh Voltage EngineeringPandey d'GunnerzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Giao Trinh Cua DH Da NangDokument57 SeitenGiao Trinh Cua DH Da NangHue TranNoch keine Bewertungen