Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Scheme of Work Science Year 5
Hochgeladen von
murniOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Scheme of Work Science Year 5
Hochgeladen von
murniCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
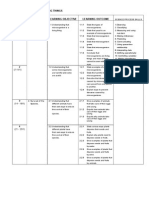
SCHEME OF WORK SCIENCE YEAR 5
SEMESTER 1
WEEK LEARNING AREAS
LEARNING OBJECTIVE
THEME : INVESTIGATING LIVING THINGS
1
2-3 JAN
1.1 Understanding that
microorganism is a living
thing.
2
6-10 JAN
3
13-17 JAN
4
20-24 JAN
1.2 Understanding that some
microorganism are harmful
and some are useful.
2. Survival of the species
5
27-30 JAN
6
4-6 FEB
2. Survival of the species
7
10-14 FEB
8
17-21 FEB
9
24-28 FEB
10
3-7 MAC
2.1 Understanding that different
animals have their own ways
to ensure the survival of their
species.
2.2 Understanding that different
plants have their own ways to
ensure the survival of their
species.
2.3 Realising the importance of
survival of the species.
3. Food Chain and Food web.
3.1 Understanding food chains.
3.2 Synthesizing food chains to
construct food web.
3.2 Synthesizing food chains to
construct food web.
LEARNING OUTCOMES
1.1.1 State types of microorganisms.
1.1.2 State that yeast is an example of microorganism.
1.1.3 State that microorganism breathes.
1.1.4 State that microorganism grows.
1.1.5 State that microorganism moves.
1.1.6 Conclude that microorganisms are living things and most of them cannot be seen with naked
eyes.
1.2.1 State examples of use of microorganisms.
1.2.2 State the harmful effects of microorganisms.
1.2.3 Describe that diseases caused by microorganisms can spread from one person to another.
1.2.4 Explain ways to prevent diseases caused by microorganisms.
2.1.1 Give examples of animals that take care of their eggs and young.
2.1.2 Explain how animals take care of their eggs and young.
2.1.3 Explain why animals take care of their eggs and young.
2.2.1 State various ways plants disperse their seeds and fruits.
2.2.2 Explain why plants need to disperse seeds or fruits.
2.2.3 Give examples of plant that disperse seeds and fruits by water.
2.2.4 Give examples of plant that disperse seeds and fruits by wind.
2.2.5 Give examples of plant that disperse seeds and fruits by animals.
2.2.6 Give examples of plant that disperse seeds and fruits by explosive mechanism.
2.2.7 Relate characteristics of seeds and fruits to the ways they are dispersed.
2.3.1 Predict what will happen if some species of animals or plants do not survive.
3.1.1 Identify animals and the food they eat.
3.1.2 Classify animals into herbivore, carnivore and omnivore.
3.1.3 Construct food chain.
3.1.4 identify producer.
3.1.5 identify consumer.
3.2.1 Construct a food web.
3.2.2 Construct food webs of different habitats.
3.2.3 Predict what will happen if there is a change in population of a certain species in a food web.
3.2.4 Explain what will happen to a certain species of animals if they eat only one type of food.
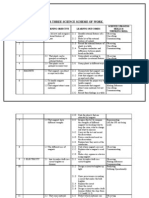
THEME : INVESTIGATING FORCE AND ENERGY
11
10-14 MAC
1. Energy.
1.1 Understanding the uses of
energy.
12
17-21 MAC
1.1.1 Explain why energy is needed.
1.1.2 Give examples where and when energy is used.
1.1.3 State various sources of energy.
PKSR 1
13
31 MAC-4
APR
14
7-11 APR
1.2 Understanding that energy
can be transformed from one
form to another.
1.3 Understanding renewable and
non-renewable energy.
1.2.1 State the various forms of energy.
1.2.2 State that energy can be transformed.
1.2.3 Give examples of appliances that make use of energy transformation.
1.3.1 State what renewable energy is.
1.3.2 State what non-renewable energy is.
1.3.3 List renewable energy resources.
1.3.4 List non-renewable energy resources.
1.3.5 Explain why we need to use energy wisely.
1.3.6 Explain why renewable energy is better than non-renewable energy.
1.3.7 Give examples on how to save energy.
1.3.8 Practice saving energy.
2.1 Knowing the sources of
electricity.
2.1.1 State the sources of electricity.
17
28 APR-2
ME
I
18
5-9 MEI
2.2 Understanding a series circuit
and a parallel circuit.
2.2.1 Identity the symbols of various components in a simple electric circuit.
2.2.2 Draw circuit diagrams.
2.2.3 Identify the difference in the arrangement of bulbs in series and parallel circuits.
19
12-16 MEI
2.3 Understanding the safety
precautions to be taken when
handling electrical
appliances.
15
14-18 APR
16
21-25 APR
2. Electricity
20
19-23 MEI
20
26-27 MEI
2.2.4 Build a series circuit.
2.2.5 Build a parallel circuit.
2.2.6 Compare the brightness of the bulbs in a series and a parallel circuit.
2.2.7 Compare the effect on the bulbs when various switches in a series circuit and a parallel
circuit are off.
2.3.1 Describe the danger of mishandling electrical appliances.
2.3.2 Explain the safety precautions to be taken when using electrical appliances.
PKSR 1
3. Light.
3.1 Understanding that light
travels in a straight line.
3.1.1 State that light travels in a straight line.
3.1.2 Give examples to verify that light travels in a straight line.
3.1.3 Describe how shadow is formed.
3.1.4 Design a fair test to find out what cause the size of a shadow to change by deciding what to
keep the same, what to change and what to observe.
3.1.5 Design a fair test to find out what factors cause the shape of a shadow to change by deciding
what to keep the same, what to change and what to observe.
28 MEI-13
JUN
21
16-20 JUN
22 & 23
23-27 JUN
30 JUN-4
JULAI
CUTI PERTENGAHAN TAHUN
3.2 Understanding that light can
be reflected.
4. Heat.
4.1 Understanding that
temperature is of indicator of
degree of hotness.
24
7-11 JULAI
25
14-18
JULAI
4.2 Understanding the effects of
heat on matter.
3.2.1 State that light can be reflected.
3.2.2 Draw ray diagrams to show reflection of light.
3.2.3 Give examples of uses of reflection of light in everyday life.
4.1.1 State that when a substance gains heat it will become warmer.
4.1.2 State that when a substance loses heat it will become cooler.
4.1.3 Measure temperature using the correct technique.
4.1.4 State the metric unit for temperature.
4.1.5 State that temperature of an object or material increases as it gains heat.
4.1.6 State that temperature of an object or material decreases as it loses heat.
4.1.7 Conclude that the temperatures is an indicator to measure hotness.
4.2.1 State that matter expands when heated.
4.2.2 State that matter contracts when cooled.
4.1.3 Give examples of the application of the principle of expansion and contraction in everyday
life.
THEME: INVESTIGATING MATERIALS
26
21-25
JULAI
27
28 JULAI-1
OGOS
28
4-8 OGOS
29&30
11-15
OGOS
18-22
OGOS
31
25-29
OGOS
32
1-5 SEPT
1. States of Matter
33 &34
8-12 SEPT
22-26
2. Acid and Alkali.
1.1 Understanding that matter
exist in the form of solid,
liquid or gas.
1.1.1 Classify objects and materials into three states of matter.
1.1.2 State the properties of solid.
1.1.3 State the properties of liquid.
CUTI HARI RAYA PUASA
1.2 Understanding that matter can
change from one state to
another.
1.1.4 State that some liquids flow faster than others.
1.1.5 State the properties of gas.
1.2.1 State that water can change its state.
1.2.2 Conclude that water can exist in any of the three states of matter.
1.2.3 Identify the processes involved when a matter changer from one state to another.
1.2.4 Identify factors that affect the rate of evaporation of water.
1.3 Understanding the water
cycle.
1.3.1 Describe how clouds are formed.
1.3.2 Describe how rain is formed.
1.3.3 Explain how water is circulated in the environment.
1.3.4 Explain the importance of water cycle.
1.4 Appreciating the importance
of water resources.
1.4.1 Give reasons why we need to keep our water resources clean.
1.4.2 Describe ways to keep our water resources clean.
2.1 Understanding the properties
of acidic, alkaline and neutral
substances.
2.1.1 Identify acidic, alkaline and neutral substances using litmus paper.
2.1.2 Identify the taste of acidic and alkaline food.
2.1.3 Conclude the properties of acidic, alkaline and neutral substances.
SEPT
THEME: INVESTIGATING THE EARTH AND THE UNIVERSE
35
29 SEPT-3
OKT
36&37
6-10 OKT
1. Constellation.
1.1 Understanding the
constellation.
2. The Earth, The Moon and
The Sun.
2.1 Understanding the
movements of the Earth, the
Moon and the Sun.
13-17 OKT
1.1.1 State what constellation is.
1.1.2 Identify constellations.
1.1.3 State the importance of constellations.
2.1.1 State that the Earth rotates on its axis.
2.1.2 State that the Earth rotates and at the same time moves round the Sun.
2.1.3 State that the Moon rotates on its axis.
2.1.4 State that the Moon rotates and at the same time moves round the Earth.
2.1.5 State that the Moon and the Earth move round the Sun at the same time.
2.1.6 Describe the changes in length and position of the shadow throughout the day.
2.1.7 Conclude that the Earth rotates on its axis from west to east.
38
20-24 OKT
CUTI HARI DEEPAVALI
39&40
27-31 OKT
2.2 Understanding the occurrence
of day and night.
2.2.1 State that it is day time for the part of the Earth facing the Sun.
2.2.2 State it is night time for the part of the Earth facing away from the Sun.
2.2.3 Explain that day and night occur due to the rotation of the Earth on its axis.
2.3 Understanding the phases of
the Moon.
2.3.1 State that the Moon does not emit light.
2.3.2 Explain that the Moon appears bright when it reflects sunlight.
2.3.3 Describe the phases of the Moon.
3-7 NOV
THEME : INVESTIGATING TECHNOLOGY
41&42
10-14 NOV
1. Strength and Stability
1.1 Knowing the shapes of objects
in structures.
1.1.1 State the shapes of objects.
1.1.2 Identify shapes in structure.
1.2.1 Identify shapes of objects that are stable.
1.2 Understanding the strength
and stability of a structure.
1.2.2 Identify the factors that affect stability of objects.
1.2.3 Explain how base area affects stability.
1.2.4 Explain how height affects stability.
1.2.5 Identify the factors that affect the strength of a structure.
1.2.6 design a model that is strong and stable.
17-21 NOV
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- EXAM Section A Closed Book 2007Dokument9 SeitenEXAM Section A Closed Book 2007Krispin Fong93% (15)
- Adaptation to Environment: Essays on the Physiology of Marine AnimalsVon EverandAdaptation to Environment: Essays on the Physiology of Marine AnimalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Science Year 5Dokument7 SeitenYearly Plan Science Year 5Aceley JainuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Science Year 5Dokument5 SeitenYearly Plan Science Year 5azmnqiinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Science Year 5Dokument7 SeitenYearly Plan Science Year 5Burhan AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Sains THN 5 - 2012Dokument9 SeitenRPT Sains THN 5 - 2012zan75Noch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Science Year 5Dokument5 SeitenYearly Plan Science Year 5wawa2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- Yearlyplanning Science Year5Dokument6 SeitenYearlyplanning Science Year5Satia KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ranc Peng Tahunan Sains Tahun 5 2014 JsuDokument8 SeitenRanc Peng Tahunan Sains Tahun 5 2014 Jsunanac_2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Theme: Investigating Living Things Learning Area Learning Objective Learning OutcomeDokument8 SeitenTheme: Investigating Living Things Learning Area Learning Objective Learning OutcomewmpejonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Specifications: Science Year 5Dokument20 SeitenCurriculum Specifications: Science Year 5hany3688_519912007Noch keine Bewertungen
- First Term Science Year 5 Yearly Plan Themes A: Investigating Living ThingsDokument24 SeitenFirst Term Science Year 5 Yearly Plan Themes A: Investigating Living ThingsXgeniusXNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT SN THN5Dokument10 SeitenRPT SN THN5Jhoster YulongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Year 5 Yearly PlanDokument7 SeitenScience Year 5 Yearly Plan惠鑫Noch keine Bewertungen
- TMK Yr2Dokument73 SeitenTMK Yr2Rosnita Abdul WahabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kontrak Latihan Murid Tahun6Dokument2 SeitenKontrak Latihan Murid Tahun6Sue Suemanie TicerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan 2011 Science Y5Dokument4 SeitenYearly Plan 2011 Science Y5Mohd ZulkarnainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theme / Learning Area / Learning Objective EkstrapolationDokument21 SeitenTheme / Learning Area / Learning Objective EkstrapolationMary Dorris JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Science Yr5 - 2011Dokument9 SeitenRPT Science Yr5 - 2011Mohd HamedanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5Dokument8 SeitenScience Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5Muhammad FarisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan STD 6 ScienceDokument3 SeitenLesson Plan STD 6 ScienceVijay ManogaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week Learning Area Learning Objectve Learnng Outcomes Scientfc Process Skills & Thinking SkillDokument7 SeitenWeek Learning Area Learning Objectve Learnng Outcomes Scientfc Process Skills & Thinking SkillDinamaniYeogesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week Topic Bil. Set Latihan Jumlah Soalan Objective StructureDokument2 SeitenWeek Topic Bil. Set Latihan Jumlah Soalan Objective StructureJeevitha SubramaniamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Science Year 5Dokument5 SeitenYearly Plan Science Year 5Anonymous RYfiBW7HNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year Planner SC Yr 6Dokument8 SeitenYear Planner SC Yr 6ccqwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated ScienceDokument6 SeitenIntegrated Scienceiteachclassroom100% (2)
- Investigating Living ThingsDokument5 SeitenInvestigating Living ThingsirisazreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- RT SN PraktikumDokument3 SeitenRT SN PraktikumNavamalar MuniandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 6 Science Budget of Work 1st To 4thDokument4 SeitenGrade 6 Science Budget of Work 1st To 4thKristine Barredo100% (5)
- Science Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5 2 0 10 First SemesterDokument10 SeitenScience Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5 2 0 10 First SemesterRaffie MuksinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Year 5 Science 2008Dokument5 SeitenYearly Plan Year 5 Science 2008marccw2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- RPT SN Y5Dokument8 SeitenRPT SN Y5vargan_ramoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Guide: Earth and Life Science SY: 2020-2021Dokument7 SeitenLearning Guide: Earth and Life Science SY: 2020-2021lj BoniolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Competencies in 5th and 6th Grade With Table of SpecificationsDokument25 SeitenScience Competencies in 5th and 6th Grade With Table of SpecificationsTerence Pelingon89% (18)
- Senarai Semak Ulangkaji Sains KSSM PT3 2019Dokument4 SeitenSenarai Semak Ulangkaji Sains KSSM PT3 2019wanted_gurlzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Competencies ScienceDokument80 SeitenCompetencies ScienceRosalyn Angcay QuintinitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jismo SCIENCE P3Dokument35 SeitenJismo SCIENCE P3Astri Mustika dewiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 2 List of Science Practicals 2021,22Dokument4 SeitenForm 2 List of Science Practicals 2021,22Harini NatashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Syllabus PDFDokument12 SeitenChemistry Syllabus PDFMaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Yearly Plan For Year ThreeDokument11 SeitenScience Yearly Plan For Year Threefarizal_scribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Budget of Work in Science 5: Iba O Este Elementary SchoolDokument1 SeiteBudget of Work in Science 5: Iba O Este Elementary SchoolCatherinei BorilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kisi-Kisi Um Ipa - For StudentsDokument2 SeitenKisi-Kisi Um Ipa - For StudentsMuhammad SyahdalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enabling and Enrichment Competencies For Science Melcs (Most Essential Learning Competencies)Dokument49 SeitenEnabling and Enrichment Competencies For Science Melcs (Most Essential Learning Competencies)Zea May BiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Science Year 3Dokument12 SeitenYearly Plan Science Year 3Awang Bakhtiar Awang SeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Syllabus 2Dokument2 SeitenCourse Syllabus 2Lovel Margarrete Lorenzo CapongcolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5Dokument9 SeitenScience Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5Annie GoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Tahunan Sains Tahun 5Dokument9 SeitenRancangan Tahunan Sains Tahun 5Som Mai EmaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan SC Year 4Dokument16 SeitenYearly Plan SC Year 4ajibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Chapter 2: Cell-The Basic Unit of LifeDokument2 SeitenScience Chapter 2: Cell-The Basic Unit of LifeWan RoziahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 5 Yearly PlanDokument14 SeitenScience 5 Yearly PlanSri GanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Budget of Work Grade 5Dokument1 SeiteBudget of Work Grade 5Maria Concepcion TuvillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investigating Living Things Year 5-Science: Week Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes VocabularyDokument8 SeitenInvestigating Living Things Year 5-Science: Week Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes VocabularyFadzliSufiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Primary 6Dokument35 SeitenScience Primary 6kadekspd42Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan Sains F1 2013Dokument8 SeitenRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan Sains F1 2013mohd nazrul nizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd Grade Science SyllabusDokument6 Seiten3rd Grade Science Syllabusepetadavid41Noch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan - Science Year 2Dokument9 SeitenYearly Plan - Science Year 2Muhammad Azrieen SamsudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Lesson Plan SC f22012Dokument4 SeitenAnnual Lesson Plan SC f22012zakiyyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Seksyen 7 Shah Alam Yearly Lesson Plan 2010 Science Form 4Dokument4 SeitenSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Seksyen 7 Shah Alam Yearly Lesson Plan 2010 Science Form 4azamuchlisaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solar-Hydrogen Energy Systems: An Authoritative Review of Water-Splitting Systems by Solar Beam and Solar Heat: Hydrogen Production, Storage and UtilisationVon EverandSolar-Hydrogen Energy Systems: An Authoritative Review of Water-Splitting Systems by Solar Beam and Solar Heat: Hydrogen Production, Storage and UtilisationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biogeochemical Cycling of Mineral-Forming ElementsVon EverandBiogeochemical Cycling of Mineral-Forming ElementsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planets and Their Atmospheres: Origin and EvolutionVon EverandPlanets and Their Atmospheres: Origin and EvolutionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Thermodynamics: Unit - IvDokument23 SeitenEngineering Thermodynamics: Unit - IvSanthosh SaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Riello 12MP 400PDokument6 SeitenRiello 12MP 400PttNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reliable Off-Grid and Mobile Energy Supply: EFOY Pro Fuel CellsDokument4 SeitenReliable Off-Grid and Mobile Energy Supply: EFOY Pro Fuel CellsRohit Kumar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boy 04 2020 CPDokument1 SeiteBoy 04 2020 CPNguyễn NgànNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogue Tu Bu MikroDokument5 SeitenCatalogue Tu Bu MikroNguyễn Văn HưngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil ReportDokument8 SeitenOil Reportashish_20kNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maximum Demand and DiversityDokument15 SeitenMaximum Demand and DiversityMahir MahmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3250 ds054 4 Light GateDokument9 Seiten3250 ds054 4 Light GateMarcosH911Noch keine Bewertungen
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Absorption Chillers ToDokument4 SeitenAdvantages and Disadvantages of Using Absorption Chillers Toأحمد صلاحNoch keine Bewertungen
- Otis Regenerative DrivesDokument2 SeitenOtis Regenerative Drivestan0314Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Energy Power & Household CircuitsDokument15 SeitenElectric Energy Power & Household CircuitsAman LilaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reciprocating Compressor Seals Partner Savings From Compressor Rod PackingDokument20 SeitenReciprocating Compressor Seals Partner Savings From Compressor Rod PackingONURNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apu Fuel Cost Saving: Type of GPU Serviceable Unserviceable Diesel Operated Type 2 1 Electrically Operated Type 0 2Dokument6 SeitenApu Fuel Cost Saving: Type of GPU Serviceable Unserviceable Diesel Operated Type 2 1 Electrically Operated Type 0 2Ras Síñĕ Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- 45CB Thermal Magnetic Electronic TripDokument23 Seiten45CB Thermal Magnetic Electronic Tripryan varonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - An Adaptive Overcurrent Protection Scheme For Distribution NetworksDokument8 Seiten1 - An Adaptive Overcurrent Protection Scheme For Distribution Networkswillian teixeira olivioNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Master Key SystemDokument143 SeitenThe Master Key Systemkicca57765100% (1)
- Lift and Escalator Motor Sizing With Calculations and ExamplesDokument22 SeitenLift and Escalator Motor Sizing With Calculations and ExamplesjayakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Design and Simulation of Voltage Source InverterDokument8 SeitenLab Design and Simulation of Voltage Source InverterIzzah NadhirahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training ISO 50008Dokument48 SeitenTraining ISO 50008Ricardo AndresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Haseeb AssignmentDokument3 SeitenHaseeb AssignmentAyeshaAmjadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2GCS638015A0070-ESI Inverter Solutions For Battery Energy Storage ApplicationsDokument28 Seiten2GCS638015A0070-ESI Inverter Solutions For Battery Energy Storage ApplicationsANDYAFANADORNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Sheet: PRO TOP1 240W 24V 10A EXDokument6 SeitenData Sheet: PRO TOP1 240W 24V 10A EXThilak PonnusamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPE Exit1Dokument5 SeitenPPE Exit1Jamiel CatapangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capacitor Bank CataloguesDokument36 SeitenCapacitor Bank Cataloguessani priadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ups2000-G 1Dokument40 SeitenUps2000-G 1hhhhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supervision RelayDokument3 SeitenSupervision RelayBassem Mostafa100% (1)
- Site Preparation para Dispensador Lobby DIEBOLD 522Dokument4 SeitenSite Preparation para Dispensador Lobby DIEBOLD 522Jose MarcosNoch keine Bewertungen
- HF-REGULATOR Electronic Regulating Ballasts For PL-T and PL-C LampsDokument3 SeitenHF-REGULATOR Electronic Regulating Ballasts For PL-T and PL-C Lampsnoel antonio RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADDC Approved Internal Wiring Contracting CompaniesDokument1 SeiteADDC Approved Internal Wiring Contracting CompaniestarikNoch keine Bewertungen