Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Syllabi For The Examination NOTE
Hochgeladen von
Souvik Das0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
16 Ansichten4 Seiteni
Originaltitel
Syllabi for the Examination NOTE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldeni
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
16 Ansichten4 SeitenSyllabi For The Examination NOTE
Hochgeladen von
Souvik Dasi
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
Syllabi for the Examination NOTE: Candidates are advised to go through the
Syllabus published in this Section for the Preliminary Examination and the
Main Examination, as periodic revision of syllabus has been done in several
subjects.
Part-A Preliminary Examination
Paper I - (200 marks) Duration: Two hours
1. Current events of national and international importance.
2. History of India and Indian National Movement.
3. Indian and World Geography - Physical, Social, Economic Geography of
India and the World.
4. Indian Polity and Governance - Constitution, Political System, Panchayati
Raj, Public Policy, Rights Issues, etc.
5. Economic and Social Development Sustainable Development, Poverty,
Inclusion, Demographics, Social Sector initiatives, etc.
6. General issues on Environmental Ecology, Bio-diversity and Climate
Change - that do not require subject specialization
7. General Science.
Paper II- (200 marks) Duration: Two hours
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Comprehension
Interpersonal skills including communication skills;
Logical reasoning and analytical ability
Decision-making and problem solving
General mental ability
Basic numeracy (numbers and their relations, orders of magnitude, etc.)
PAPER-I: Essay: Candidates may be required to write essays on multiple
topics. They will be expected to keep closely to the subject of the essay to
arrange their ideas in orderly fashion and to write concisely. Credit will be given
for effective and exact expression.
PAPER-II: General Studies- I: Indian Heritage and Culture, History and
Geography of the World and Society.
1. Indian culture will cover the salient aspects of Art Forms, Literature and
Architecture from ancient to modern times.
2. Modern Indian history from about the middle of the eighteenth century
until the present- significant events, personalities, issues
3. The Freedom Struggle - its various stages and important contributors
/contributions from different parts of the country.
4. Post-independence consolidation and reorganization within the country.
History of the world will include
events from 18th century such as
industrial revolution, world wars,
redrawal of national boundaries,
colonization, decolonization, political
philosophies like communism,
capitalism, socialism etc.- their
forms and effect on the society.
Salient features of Indian Society,
Diversity of India.
Role of women and women's
organization, population and
associated issues, poverty and
developmental issues, urbanization,
their problems and their
remedies.
Effects of globalization on Indian
society
Social empowerment, communalism,
regionalism & secularism.
Salient features of world's physical
geography.
Distribution of key natural
resources across the world
(including South Asia and the
Indian sub-continent); factors
responsible for the location of primary,
secondary, and tertiary sector
industries in various parts of
the world (including India)
Important Geophysical phenomena
such as earthquakes, Tsunami,
Volcanic activity, cyclone etc.,
geographical features and their
location- changes in critical geographical
features (including
water-bodies and ice-caps) and in
flora and fauna and the effects of
such changes.
PAPER-III
General Studies- II: Governance,
Constitution, Polity, Social Justice and
International relations.
Indian Constitution- historical
underpinnings, evolution, features,
amendments, significant
provisions and basic structure.
Functions and responsibilities of
the Union and the States, issues
and challenges pertaining to the
federal structure, devolution of
powers and finances up to local
levels and challenges therein.
Separation of powers between
various organs dispute redressal
mechanisms and institutions.
Comparison of the Indian constitutional
scheme with that of other
countries
Parliament and State Legislatures
- structure, functioning, conduct of
business, powers & privileges and
issues arising out of these.
Structure, organization and functioning
of the Executive and the
Judiciary Ministries and
Departments of the Government;
pressure groups and formal/informal
associations and their role in
the Polity.
Salient features of the
Representation of People's Act.
Appointment to various
Constitutional posts, powers,
functions and responsibilities of
various Constitutional Bodies.
Statutory, regulatory and various
quasi-judicial bodies
Government policies and interventions
for development in various
sectors and issues arising out of
their design and implementation.
Development processes and the
development industry- the role of
NGOs, SHGs, various groups and
associations, donors, charities,
institutional and other stakeholders
Welfare schemes for vulnerable
sections of the population by the
Centre and States and the performance
of these schemes;
mechanisms, laws, institutions
and Bodies constituted for the protection
and betterment of these
vulnerable sections.
Issues relating to development
1. and management of Social
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Design of Anchor Block 4 for Penstock L SectionDokument20 SeitenDesign of Anchor Block 4 for Penstock L SectionSouvik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quarter ApplicationDokument1 SeiteQuarter ApplicationSouvik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Save TreeDokument1 SeiteSave TreeSouvik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hazen Williams EquationDokument1 SeiteHazen Williams Equationanil4u29Noch keine Bewertungen
- GGFDGFFDGG 5454415154 Uijjhkjhkfjkjk 544654 KL 4k65Dokument1 SeiteGGFDGFFDGG 5454415154 Uijjhkjhkfjkjk 544654 KL 4k65Souvik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- AdvertisementDokument12 SeitenAdvertisementSabir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key DatesDokument2 SeitenKey DatesSouvik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABCGDokument4 SeitenABCGSouvik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- SL. No. Work Flow 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 1Dokument4 SeitenSL. No. Work Flow 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 1Souvik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENERGY CONSERVATION INITIATIVES AT SAMRIDDHI BHAVAN (SBILHODokument1 SeiteENERGY CONSERVATION INITIATIVES AT SAMRIDDHI BHAVAN (SBILHOSouvik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hazen Williams EquationDokument1 SeiteHazen Williams Equationanil4u29Noch keine Bewertungen
- Book Sample PageDokument4 SeitenBook Sample PageSouvik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- SI. No. Information Required: Page 1 of 2Dokument2 SeitenSI. No. Information Required: Page 1 of 2Souvik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comments Against Inspectio & Test PlanDokument2 SeitenComments Against Inspectio & Test PlanSouvik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Authorization MATRIX For CC, Plant, P.org. P.GRP During All Transactions - 2Dokument1 SeiteAuthorization MATRIX For CC, Plant, P.org. P.GRP During All Transactions - 2Souvik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Staad SpacjkertyDokument3 SeitenStaad SpacjkertySouvik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- NJKJKHJKDokument1 SeiteNJKJKHJKSouvik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- STAAD Gftfr45tDokument3 SeitenSTAAD Gftfr45tSouvik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gate 2015Dokument1 SeiteGate 2015api-261130519Noch keine Bewertungen
- Annexure: Proforma of Bank Guarantee For Contract PerformanceDokument5 SeitenAnnexure: Proforma of Bank Guarantee For Contract PerformanceSouvik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13 Civil Tech Spec No 38Dokument41 Seiten13 Civil Tech Spec No 38Rajesh Parida100% (1)
- Sika WP Shield-104 P: APP Modified Plain Finished Bituminous MembraneDokument3 SeitenSika WP Shield-104 P: APP Modified Plain Finished Bituminous MembraneSouvik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Request for Guest House Booking for 4 DaysDokument1 SeiteRequest for Guest House Booking for 4 DaysSouvik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- GHNTTHDokument1 SeiteGHNTTHSouvik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Staad SpaceDokument3 SeitenStaad SpaceVijay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cable TrencgfdhesDokument1 SeiteCable TrencgfdhesSouvik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CODE of PRACTICE For Site SupervisionDokument120 SeitenCODE of PRACTICE For Site SupervisionRaymond Kam100% (4)
- SS304 304L Data SheetDokument2 SeitenSS304 304L Data SheetPrakash KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pe789 PDFDokument12 SeitenPe789 PDFSouvik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Resignation Acceptance LetterDokument1 SeiteResignation Acceptance LetterJahnvi KanwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CELF Final ProspectusDokument265 SeitenCELF Final ProspectusDealBookNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mosaic Maker - Instructions PDFDokument4 SeitenMosaic Maker - Instructions PDFRoderickHenryNoch keine Bewertungen
- DEFCON ManualDokument13 SeitenDEFCON Manualbuyvalve100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Computer NetworksDokument32 SeitenChapter 1 - Introduction To Computer NetworksHuluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industry Life Cycle-Plant Based CaseDokument3 SeitenIndustry Life Cycle-Plant Based CaseRachelle BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
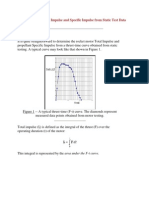
- Determining Total Impulse and Specific Impulse From Static Test DataDokument4 SeitenDetermining Total Impulse and Specific Impulse From Static Test Datajai_selvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Ology ManualDokument2 SeitenRisk Ology ManualGregoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13 Daftar PustakaDokument2 Seiten13 Daftar PustakaDjauhari NoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- SINGGAR MULIA ENGINEERING HORIZONTAL 2-PHASE SEPARATORDokument3 SeitenSINGGAR MULIA ENGINEERING HORIZONTAL 2-PHASE SEPARATORElias EliasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eship 1Dokument18 SeitenEship 1Yash SoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amended ComplaintDokument38 SeitenAmended ComplaintDeadspinNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Make Pcbat Home PDFDokument15 SeitenHow To Make Pcbat Home PDFamareshwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- C J L F S: Vinod TiwariDokument21 SeitenC J L F S: Vinod TiwariVinod TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intermediate Accounting Testbank 2Dokument419 SeitenIntermediate Accounting Testbank 2SOPHIA97% (30)
- Admission Checklist (Pre-) Master September 2021Dokument7 SeitenAdmission Checklist (Pre-) Master September 2021Máté HirschNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embedded Systems: Martin Schoeberl Mschoebe@mail - Tuwien.ac - atDokument27 SeitenEmbedded Systems: Martin Schoeberl Mschoebe@mail - Tuwien.ac - atDhirenKumarGoleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatizari Complexe - Laborator Nr. 4: Wind (M/S)Dokument1 SeiteAutomatizari Complexe - Laborator Nr. 4: Wind (M/S)Alexandru AichimoaieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leapfroggers, People Who Start A Company, Manage Its Growth Until They Get Bored, and Then SellDokument3 SeitenLeapfroggers, People Who Start A Company, Manage Its Growth Until They Get Bored, and Then Sellayesha noorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture7 PDFDokument5 SeitenLecture7 PDFrashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oscar Ortega Lopez - 1.2.3.a BinaryNumbersConversionDokument6 SeitenOscar Ortega Lopez - 1.2.3.a BinaryNumbersConversionOscar Ortega LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Road Safety GOs & CircularsDokument39 SeitenRoad Safety GOs & CircularsVizag Roads100% (1)
- Farmers InterviewDokument5 SeitenFarmers Interviewjay jariwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- M Series CylindersDokument61 SeitenM Series CylindersAndres SantanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lea 201 Coverage Topics in Midterm ExamDokument40 SeitenLea 201 Coverage Topics in Midterm Examshielladelarosa26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Liability WaiverDokument1 SeiteLiability WaiverTop Flight FitnessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Request Letter To EDC Used PE PipesDokument1 SeiteRequest Letter To EDC Used PE PipesBLGU Lake DanaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Broadband BillDokument1 SeiteBroadband BillKushi GowdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Role Can IS Play in The Pharmaceutical Industry?Dokument4 SeitenWhat Role Can IS Play in The Pharmaceutical Industry?Đức NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- UPGRADEDokument2 SeitenUPGRADEVedansh OswalNoch keine Bewertungen