Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lesson 2.3 Video Tutorials
Hochgeladen von
momathtchrOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lesson 2.3 Video Tutorials
Hochgeladen von
momathtchrCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lesson 2.
3 Functions
A. Definition of a Function
A function is a rule. A function f is a rule that assigns to each element x in a set
A exactly one element, f(x), in a set B.
Given a relation in x and y, we say y is a function of x if for every element x
in the domain, there corresponds exactly one element y in the range.
This just means that a function cant repeat any x-coordinates
A function can repeat y-coordinates
Any set of ordered pairs (x, y) is called a relation in x and y.
The set of first components in the ordered pairs is called the domain of the
relation
The set of second components in the ordered pairs is called the range of the
relation
Hint: Domain vs. Range
o D comes before R in the alphabet, just as x comes before y
o So, D goes with x and R goes with y
When you list the numbers in the Domain and Range
o List each number only ONCE
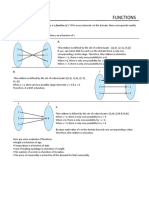
Determine if the relation defines y as a function of x. For each function,
state the domain and range. Video tutorial
1. { (-2, 5), (-1, 3), (3, 7), (4, 12)}
2. {(-4, 4), (-3, 3), (-2, 2), (-1, 1), (-4, 0)}
Lesson 2.3 Functions
B. Determining Whether an Equation is a Function
Solve the equation for y. If you get two solutions for y, the equation is not a
function.
Some equations that are NEVER a function:
o An equation that has y2 is never a function
o An equation that has represents two solutions and is not a function
Determine whether the equation defines y as a function of x.
1.
1
x2
2. y 5 3x
3. x 2y 2
4. y 3x 3 2 x 2 1
Video tutorial
C. Function Notation
When a function is defined by an equation, we often use function notation.
For example, y = 2x can be written as f x 2 x .
f is the name of the function. (It can be g(x) or h(x), etc
x is an input value from the domain of the function
f(x) is the function value (y-value) corresponding to x.
The notation f(x) is read as f of x or the value of the function f at x
A function may be evaluated at different values of x by substituting x-values
from the domain into the function.
The ordered pairs you get are the same as (x, y), but they are (x, f(x))
So, if f(5) = 10, the ordered pair is (5, 10).
Lesson 2.3 Functions
Evaluate the function at the indicated function values.
1.
f x 2 x x 1
f 0
f 1
f x 1
f 2 x
Video tutorial
f x
Lesson 2.3 Functions
f (5)
2.
Video tutorial
f ( x) 2 x 3
f ( 4)
3.
2x 1
f x
3x 5
f 0
f x h
f x 1
f 2 x
f x
Video tutorial
f x
Lesson 2.3 Functions
D. How do you find the domain?
1) Is it a fraction?
a. Set the denominator equal to zero and solve for x.
b. Domain: , ___ ___,
2) Is it an even index radical?
a. Set the inside expression 0 and solve for x.
b. Domain: ___, or it could be , ___
3) All other expressions
a. Domain is all real numbers or: ,
Find the domain of the function in interval notation.
1. f ( x) x 7
2x 1
Video tutorial #1-4
2.
2x 1
x9
3.
f ( x)
x4
x2 9
4.
f x
x
x 9
2
Lesson 2.3 Functions
5.
f ( x) t 4 Video
6.
f ( x) 3 4 x
7.
f ( x) t 2 3t
8. hz
9.
Pt
tutorial #5-9
z 3
z2
5
5t 25
Lesson 2.3 Functions
A. Increasing, Decreasing, Constant Intervals
Use the graph to find:
(a) The intercepts, if any
(b) The domain and range
(c) The intervals on which the function is increasing, decreasing or constant
1.
Video tutorial
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- IBA Test Prep MaterialDokument3 SeitenIBA Test Prep MaterialAmmar Hassan67% (9)
- Table of English Tenses PDFDokument3 SeitenTable of English Tenses PDFViviarvi100% (1)
- MAT111 Lesson 11Dokument7 SeitenMAT111 Lesson 11mykaelratlouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions PDFDokument7 SeitenFunctions PDFPaolo NaguitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 - Functions, Function Notation, Domain & RangeDokument27 SeitenLesson 1 - Functions, Function Notation, Domain & RangeJerome FresadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piccolo Sample ItemsDokument1 SeitePiccolo Sample Itemsapi-432499175Noch keine Bewertungen
- A. Definition of A Function: Video Tutorial For Parts A, B, CDokument10 SeitenA. Definition of A Function: Video Tutorial For Parts A, B, CmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Function?Dokument9 SeitenWhat Is A Function?Khaled AlanziNoch keine Bewertungen
- 000 All in One FunctionsDokument345 Seiten000 All in One FunctionsOmkar VanjariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions: One Element y in The RangeDokument7 SeitenFunctions: One Element y in The RangePaolo NaguitNoch keine Bewertungen
- FunctionsDokument33 SeitenFunctionsIrene Mae BeldaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NJC Functions Lecture Notes Teachers Edition With Tutorial and AnswersDokument43 SeitenNJC Functions Lecture Notes Teachers Edition With Tutorial and AnswersbhimabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE 1 CE Math107EDokument12 SeitenMODULE 1 CE Math107EAxl TorrilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Worksheet-Domain and RangeDokument4 SeitenMath Worksheet-Domain and RangeEducareLabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revisiting Functions: Lesson DescriptionDokument11 SeitenRevisiting Functions: Lesson DescriptionPrincess Joie RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.function - Inverse Trigonometric (English)Dokument56 Seiten8.function - Inverse Trigonometric (English)Shival KatheNoch keine Bewertungen
- LP-GenMath - Week1Dokument10 SeitenLP-GenMath - Week1Cry BeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions: A X A X +a X+a A, A,, ADokument21 SeitenFunctions: A X A X +a X+a A, A,, AMelchor Jaramilla OronosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions (J) : 1 What Is A Function?Dokument4 SeitenFunctions (J) : 1 What Is A Function?BobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Function and Its Basic PropertiesDokument5 SeitenFunction and Its Basic PropertiesMhaica L. GalagataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions: 4.1 Definition of Functions As MappingsDokument10 SeitenFunctions: 4.1 Definition of Functions As MappingsMehwish FatimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 1 General MathematicsDokument10 SeitenWeek 1 General MathematicsMarcel Baring ImperialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions: DefinitionDokument19 SeitenFunctions: DefinitionAditya BansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differentiation and Its Application Department of Mathematics NOVEMBER, 2012 Table of ContentDokument35 SeitenDifferentiation and Its Application Department of Mathematics NOVEMBER, 2012 Table of ContentFSahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 1 - General MathematicsDokument40 SeitenWeek 1 - General MathematicsSirr AustriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Transcript 1 Introduction To Functions and Piecewise Functions7Dokument14 SeitenLecture Transcript 1 Introduction To Functions and Piecewise Functions7eve lopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions (Part 1)Dokument12 SeitenFunctions (Part 1)Sachin KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 1 GMDokument41 SeitenWeek 1 GMJhanjhan BoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Mathematics Week 1 PDFDokument17 SeitenGeneral Mathematics Week 1 PDFRussiel DagohoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Met 1 Q1 PDFDokument8 SeitenMet 1 Q1 PDFShannen MonteroNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Math SHS Module 1Dokument12 SeitenGeneral Math SHS Module 1Kristian IanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 7Dokument16 SeitenUnit 7Vishwanath KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions and GraphsDokument4 SeitenFunctions and GraphsS.m. ChandrashekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions of Two Variables LimitsDokument43 SeitenFunctions of Two Variables Limitssakshiverma.hNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 Concept of A FunctionDokument10 Seiten1.1 Concept of A FunctionJoe VicenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 CalDokument10 Seiten1 CalVincent ManilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Language 0f MathDokument57 SeitenLanguage 0f MathChristian Dave Balasa100% (1)
- Lecture 1.05 - Cartesian Product and FunctionsDokument15 SeitenLecture 1.05 - Cartesian Product and FunctionsAmelia AmeliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dylan S Primeri Handouts-7Dokument13 SeitenDylan S Primeri Handouts-7Weerasak BoonwuttiwongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus Exercises With SolutionsDokument135 SeitenCalculus Exercises With Solutionssheena marieNoch keine Bewertungen
- C01 Calculus of One Variable - T1 - 1112Dokument51 SeitenC01 Calculus of One Variable - T1 - 1112Zachary NgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 5 MMWDokument40 SeitenGroup 5 MMWRailee GalvezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACS123 Functions: DR Viktor Fedun Automatic Control and Systems Engineering, C09Dokument80 SeitenACS123 Functions: DR Viktor Fedun Automatic Control and Systems Engineering, C09bala subramanianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differential Calculus: Engr. Joeydann M. TelinDokument41 SeitenDifferential Calculus: Engr. Joeydann M. TelinJoey TelinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Language of RelationsDokument25 SeitenLanguage of Relationsjerick lanojanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class NoteDokument80 SeitenClass NoteKazi prantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Some Techniques of Differentiation Under Integral Sign: Related Theorems and ApplicationsDokument40 SeitenOn Some Techniques of Differentiation Under Integral Sign: Related Theorems and Applicationsmc180403686 MUHAMMAD SHAHID MANZOORNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 (Lessons 1-4)Dokument95 SeitenChapter 3 (Lessons 1-4)Retchelle Palmero SangcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS30L7 HandoutDokument7 SeitenCS30L7 HandoutRace CariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discrete Structures L5: Functions and AlgorithmsDokument25 SeitenDiscrete Structures L5: Functions and AlgorithmsSomaiah SulaimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- FUNCTIONS pptx1Dokument57 SeitenFUNCTIONS pptx1Manuela Kassandra TribianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- JO Ao Lopes DiasDokument19 SeitenJO Ao Lopes DiasRosita Salas TuanamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions: Prepared By: Teresita P. Liwanag - ZapantaDokument38 SeitenFunctions: Prepared By: Teresita P. Liwanag - ZapantaDan CasuraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functional Equations BookDokument10 SeitenFunctional Equations BookMark ZuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week1 Introduction To Function: RelationsDokument10 SeitenWeek1 Introduction To Function: RelationsKrizha SisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.2 The Algebra of FunctionsDokument16 Seiten1.2 The Algebra of FunctionsYukiC123Noch keine Bewertungen
- NP - General Mathematics Q1W1Dokument8 SeitenNP - General Mathematics Q1W1charles stone panuncilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diff - Calc - Module-1-Functions Limits ContinuityDokument17 SeitenDiff - Calc - Module-1-Functions Limits ContinuityCiline FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Continuity One Shot #BBDokument101 SeitenContinuity One Shot #BBTanmoy Ghosh100% (1)
- Lesson 2.1 VideosDokument5 SeitenLesson 2.1 VideosmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sets and Venn Diagrams To Solve ProblemsDokument4 SeitenSets and Venn Diagrams To Solve ProblemsmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2.1 VideosDokument5 SeitenLesson 2.1 VideosmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- A. Venn Diagrams For 2 Sets: Lesson 2-3 Usingvenn Diagrams To Study Set OperationsDokument6 SeitenA. Venn Diagrams For 2 Sets: Lesson 2-3 Usingvenn Diagrams To Study Set OperationsmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- A. Infinite Sets and General TermsDokument4 SeitenA. Infinite Sets and General TermsmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jeopardy ReviewDokument27 SeitenJeopardy ReviewmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2.2 VideosDokument5 SeitenLesson 2.2 VideosmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.3 Video TutorialDokument11 Seiten7.3 Video TutorialmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4.6 Video TutorialsDokument6 SeitenLesson 4.6 Video TutorialsmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4.4 Video TutorialsDokument2 SeitenLesson 4.4 Video TutorialsmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.2 Video TutorialsDokument12 Seiten7.2 Video TutorialsmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4.5 Video TutorialsDokument4 SeitenLesson 4.5 Video TutorialsmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.1 Video TutorialsDokument14 Seiten7.1 Video TutorialsmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4.2 Video TutorialDokument7 SeitenLesson 4.2 Video TutorialmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2.7 Video TutorialsDokument4 SeitenLesson 2.7 Video TutorialsmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4.3 Video TutorialsDokument8 SeitenLesson 4.3 Video TutorialsmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3.5 Video Tutorials Rational FunctionsDokument10 SeitenLesson 3.5 Video Tutorials Rational FunctionsmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3.4 Video Tutorials Zeros of Polynomials PDFDokument23 SeitenLesson 3.4 Video Tutorials Zeros of Polynomials PDFmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hesterfield Illage: Annual Board Meeting-Your Help Is Needed!Dokument4 SeitenHesterfield Illage: Annual Board Meeting-Your Help Is Needed!momathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4.1 Video TutorialsDokument5 SeitenLesson 4.1 Video TutorialsmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3.3 Division of Polynomials PDFDokument4 SeitenLesson 3.3 Division of Polynomials PDFmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2.8 Video TutorialsDokument10 SeitenLesson 2.8 Video TutorialsmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3.2 Video Tutorials Polynomial FunctionsDokument7 SeitenLesson 3.2 Video Tutorials Polynomial FunctionsmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2.6 PDFDokument15 SeitenLesson 2.6 PDFmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- July 2014 MinutesDokument2 SeitenJuly 2014 MinutesmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 July NewsletterDokument4 Seiten2014 July NewslettermomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014-April 7 Meeting MinutesDokument9 Seiten2014-April 7 Meeting MinutesmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014-August 11 Meeting MinutesDokument8 Seiten2014-August 11 Meeting MinutesmomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pool Opening Information: Hesterfield IllageDokument2 SeitenPool Opening Information: Hesterfield IllagemomathtchrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 1 - Course OutlineDokument2 SeitenMath 1 - Course OutlineJennifer VeloriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study For Data ScienceDokument3 SeitenCase Study For Data SciencethiruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lista de Verbos Más Usados en Inglés - English Verbs - Vocabulario para Aprender InglésDokument4 SeitenLista de Verbos Más Usados en Inglés - English Verbs - Vocabulario para Aprender IngléscyudexziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speed of Writing Activity #5: Questioned Document Examination Forensic 4Dokument3 SeitenSpeed of Writing Activity #5: Questioned Document Examination Forensic 4Gregorio B. SardeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily Lesson Log: The Learner... The Learner... The Learner... The Learner..Dokument2 SeitenDaily Lesson Log: The Learner... The Learner... The Learner... The Learner..Christian Joy Magno Olarte100% (1)
- Writing in The Discipline LectureDokument31 SeitenWriting in The Discipline LectureMhel Demabogte100% (4)
- Series 0i-D (E) - V05aDokument16 SeitenSeries 0i-D (E) - V05aPaulus PramudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machingura Crispinah 2014 PDFDokument176 SeitenMachingura Crispinah 2014 PDFKupakwasheMtataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angle Postulates and Theorems LPDokument8 SeitenAngle Postulates and Theorems LPalyssa joy bagsicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Python GUI: Meher Krishna PatelDokument41 SeitenPython GUI: Meher Krishna PatelPablo Antonio Ortega LuceroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detalieri Tematice Elemente de Construcţie A Comunicǎrii Funcţii Comunicative 1Dokument7 SeitenDetalieri Tematice Elemente de Construcţie A Comunicǎrii Funcţii Comunicative 1Alina Mihaela CiubotaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cae11 - Book1Dokument80 SeitenCae11 - Book1Kristian AcolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Rivka Bar-Chaim: Can The World Really Be Hashem's Garden?Dokument1 SeiteName: Rivka Bar-Chaim: Can The World Really Be Hashem's Garden?Rivka BarChaimNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT-2 Prepared by Sathish Kumar/MitDokument16 SeitenUNIT-2 Prepared by Sathish Kumar/MitAnbazhagan Selvanathan0% (1)
- Intro Zones of Regulation PresentationDokument12 SeitenIntro Zones of Regulation PresentationMelissa Katchen100% (1)
- Grammar 10. Adjectives and Adverbs of Manner Ngoc MinhDokument4 SeitenGrammar 10. Adjectives and Adverbs of Manner Ngoc MinhMinh Phạm NgọcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paul's Mission StrategyDokument12 SeitenPaul's Mission Strategymydailyhope21Noch keine Bewertungen
- L4 Making GeneralizationsDokument17 SeitenL4 Making GeneralizationsJonalyn MempinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cahier 00Dokument6 SeitenCahier 00aggy12Noch keine Bewertungen
- TCS SD ConfigurationsDokument12 SeitenTCS SD Configurationssekhar dattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Guide To GREP Codes in Adobe InDesign-newDokument26 SeitenQuick Guide To GREP Codes in Adobe InDesign-newMark NagashNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9th Grade Math Vocabulary 1683069284Dokument2 Seiten9th Grade Math Vocabulary 1683069284BABY MARIE APASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On Data Structures and Programming Techniques (CPSC 223, Spring 2021)Dokument659 SeitenNotes On Data Structures and Programming Techniques (CPSC 223, Spring 2021)KALKA DUBEYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar HallDokument11 SeitenSeminar HallSanjaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Javascript PDFDokument22 SeitenJavascript PDFJothimani Murugesan KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tito Puente-Extention FormDokument2 SeitenTito Puente-Extention Formapi-550368270Noch keine Bewertungen
- PCAN-USB-FD UserMan EngDokument33 SeitenPCAN-USB-FD UserMan EngAndrey AbramchukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To Cauchy Sequences (Calculus)Dokument4 SeitenIntro To Cauchy Sequences (Calculus)Максим БекетовNoch keine Bewertungen