Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lab Manual
Hochgeladen von
ASWANI RAJANOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lab Manual
Hochgeladen von
ASWANI RAJANCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Electrical workshop manual
A HAND BOOK FOR
ELECTRICAL WORKSHOP
Electrical and electronics engineering dept.
SNIT adoor
SNIT ADOOR Page 1
Electrical workshop manual
CONTENTS
Part 1 General
1. Syllabus
2. Electrical engineering - An overview
3. Electric power supply system
Part 2 Study of safety devices
1. Importance of safety devices
2. Circuit breakers MCB, MCCB & RCBO (ELCB) etc
3. Earthing systems
4. Symbols
Part 3 Experiments
1. One lamp controlled by one switch
2. One lamp controlled by one switch adding plug point
3.Two lamp controlled by two switch parallel
4. One lamp controlled by one switch adding plug point and bell
5. Two lamp controlled by one switch
6.Staircase wiring
7. Godown wiring
8. Hospital wiring
9. Fluorescent lamp wiring
10.wiring of DB With ELCB and MCB
SNIT ADOOR Page 2
Electrical workshop manual
SYLLABUS
1. Study of wiring cables and electrical accessories Electrical and Electronics symbols.
2. Simple wiring circuits- A light is controlled by a single pole single throw (S.P.S.T) switch ,
addition of a plug point in the light circuit and addition of a calling bell in the wiring circuit.
3. Circuit with Fluorescent tube light
4. Circuits to control a lamp from two independent positions
5. Hospital wiring
6. Godown wiring
7. Wiring of D.B with ELCB and MCB.
8. Testing of circuits - testing of ON/OFF conditions using a tester, test lamp, and location of
phase and neutral.
SNIT ADOOR Page 3
Electrical workshop manual
Electrical engineering an overview
Electric current: - Electric currant can be termed as a continuous flow of electrons through a
conductor. One ampere is the current produced when a pressure of one volt is applied across a
circuit having one ohm resistance.
EMF: - EMF is electro motive force. Potential difference between two points in a circuit is
the electrical pressure difference required to drive a current between them. Potential
difference may be termed as voltage. Voltage of a torch battery is 1.5 V and that of
automobile battery is 12V. KSEB supply voltage for domestic installation is 240 V.
Electric power (watt):- Electric power, P = Voltage * current * Power factor Unit of electric
power is watt (W)
Electric energy:-Unit of electric energy is KWh (Kilo Watt hour) 1 unit energy = 1 KWh
KSEB provides one KWh meter at every Installation for measuring consumed energy.
Resistance is the property of a substance due to which it opposes the flow of current through
it. Unit of resistance is ohm
Resistance, R = Specific resistance * I / A
Where I is the length of material & A is the area of cross section
Effect of temperature on resistance:-When temperature increases resistance of pure metals
and Alloys increases when temperature increases resistance of electrolyte, insulators etc
decrease.
Resistance in series:-Consider three resistors connected in series, and then the total
resistance of the circuit will be the sum of the three resistors.
Ohms law:-Ohms law states that, the ratio of potential difference between any two points in a
conductor to the current flowing between them is constant.
Study of Electric Power supply
Electricity: Electricity is a form of energy. Electricity is the flow of electrons. We get
electricity, which is a secondary energy source, from the conversion of other sources of
energy, like coal, natural gas, oil, nuclear power, Hydel power and other natural sources,
which are called primary sources.
Electric power supply system
AC&DC: DC or direct current is steady current. It never changes
its direction, and AC is alternating in nature. AC voltage can be increased or decreased with
the help of transformers. By using high voltage AC, we can drastically reduce the
transmission losses. AC can be converted into DC easily but reverse is not so easy. In India
state electricity boards are the authorities to generate and distribute electric energy. KSEB
generates electric power at a voltage of 11 KV. This power is transmitted by increasing the
voltage at different levels as 33 KV, 66KV, 110 KV, 220KVor 400 KV from different
substations. At load centers this voltage again stepped down as 11 KV and a feeder network is
created. This feeder line energizes the 11KV/415V step down transformer, and from these
SNIT ADOOR Page 4
Electrical workshop manual
transformers electric supply can be given to consumers at 240V and 415 V as single phase or
three phases. All domestic and commercial consumers get electric energy from the
distribution network of concerned electricity boards. Based on the power requirements of
consumers Electricity Boards may give 3-phase connection (for high power) or single phase
connection (for low power). In the three phase connections 4 wires are provided, where as in
single-phase connection one phase and a neutral connection are provided to the consumers.
Phase to neutral voltage in our country is 230 V and phase-to-phase voltage is 400 V of
frequency 50 Hz. Most of the appliances work on single-phase supply. There are some
motors, which requires three phase supply. A KWh meter is provided at the consumer end for
measuring the electrical energy consumed. KSEB introduces different tariffs for different
consumers, as per their connected load and nature of connection.
Study of safety devices
Importance of safety devices
The safety features are inbuilt with electric power distribution. The current is to flow
through the path it is expected to pass and should not take another path through which
it is not expected to pass. Conductors made of copper or aluminium are provided across
the path for carrying the current and insulators like PVC, paper or rubber are provided
isolate the faulty circuit from the rest of the supply. The very high currents caused by short
circuit situation can cause lots of damage to electrical installation. Protective devices are
needed to break short-circuit and overload currents. Circuit breakers and fuses are protective
devices that control the power going to a particular route of wiring. In case of an overload or
a short on that circuit, the breaker or fuse trips and automatically shuts off power to that
circuit. Fuses are the commonly used protection devices to protect components like wires,
transformers electronics circuit modules against overload. The general idea of the fuse is that
it "burns fuse link" when current gets higher than it's rating and thus stops the current
flowing.
Types of safety devices
_ Fuse
_ Circuit breakers( MCB, MCCB & ELCB)
_ Earthing.
Basically two types of protections are provided in the power supply system of domestic
consumers.
1. Protection from over current.
2. Protection from leakage current due to failure of insulation or inadvertent contact with live
conductors by the user.
Over current and Short circuit
One type of situation that wiring needs to be protected against is over current. The electrical
wiring is rated for certain maximum current. If you try to pull more current through it, the
wiring will heat considerably. When the wiring heats too much, it will cause the melting of
cable insulation, cause fire if there is something flammable near cable and even melt the
copper conductors in the cable. So protection is needed to guarantee that in case of something
tries to pull too much current through mains wiring, this cannot happen for any long time
until the fuse blows and stops the current.
Every electrical circuit shall be protected against over current by suitable over current
devices. These devices could be
1. Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)
2. Moulded Case Circuit Breaker
3. Semi enclosed rewirable fuses
SNIT ADOOR Page 5
Electrical workshop manual
d. High Rupturing Capacity (HRC) fuses
Typical breaking capacities of protective devices are as follows:
HRC fuses - 80 kA
MCB - 16 kA
Rewirable fuses - 1 to 4 kA beats at a steady
FUSES
Fuse is a wire of short length having low melting point which gives protection against
excessive current. This excessive current may be due to over load or short circuit. Under
normal working condition the current flowing through the circuit is within safe limit. But
when some faults such as short circuit occurs the current exceeds the safe limit value, the fuse
wire gets heated and melts. This will cause breaking of the circuit. After one fusing operation,
fuse wire must be rewired with the 2same size wire.
This basic guide will help you decide which fuse to fit to ensure the safe use of your
household appliances.
1
Appliances up to 700 Watts = 3 Amp fuse
2
Appliances between 700 and 1000 Watts = 5 Amp fuse
3
Appliances over 1000 Watts = 13 Amp fuse
COMMON FUSE TYPES
1. Rewirable fuse
2. Cartridge fuse
3. HRC fuse
1. Rewirable fuse:
This is the cheapest method for protecting a circuit from short circuit. Wires of different
diameters made of lead and tin are used in the circuit. When large current flows these wires
melts and disconnects the faulty circuit from the rest of the supply. There are different types
of fuses. The usual type is the rewirable type in which the fuse wire is carried in a removable
fuse link (Fig. a). The fuse link is made of porcelain or other suitable insulating material. The
fuse carrier is push-fitted to the fuse base to make the connection through. An advantage of
this type is that the blown fuse wire can be replaced with negligible cost. But there is a
chance of selecting a wrong size of fuse wire. Another disadvantage with rewirable fuse is
SNIT ADOOR Page 6
Electrical workshop manual
that it may sometimes lead to fire hazards, when the fuse wire blows. The semi enclosed
rewirable fuses has the following drawbacks:
1
It normally melts on 50 % to 100 % excessive overload. The
melting current cannot be accurately predicted.
2
It takes time to rewire the fuse.
3
Standard fuse wire should be always made available.
However it is the cheapest mode of protection from short circuit.
2. Cartridge fuse
Cartridge fuse consists of a tube with metal end caps at both ends.
The tubeis usually made of glass with no filling material. The fuse wire is placed inside the
tube, connected between the end caps. Since the tube is made of glass, the fuse element can
be easily inspected for breakage. When the fuse is blown, the whole cartridge has to be
replaced. The advantages of cartridge fuses are, quick and easy replacement and the fuse
rating is marked on the end cap of the cartridge itself.Cartridge fuses are mainly: used in
various electrical and electronic equipment.
3. High Rupturing Capacity Fuse (HRC):
This is a completely enclosed cartridge type of fuse. These fuses are screwed or linked in
the circuit. Generally it is used in the high power circuits. High Rupturing Capacity (HRC)
fuse consists of a porcelain tube! with metal end caps and fixing tags. The fuse element is
SNIT ADOOR Page 7
Electrical workshop manual
held inside the tube between the end caps and the tube is filled with silica sand or granulated
quartz. When the fuse element blows, the silica inside the tube prevent the formation of an
arc, and thus avoids the possibility of fire hazards. HRC fuse links are available in a range
of 10A to 800A.
The HRC fuse has the following advantages:
1
It is very reliable.
2
It has an enclosed fuse wire, therefore no chance its arc doing any damage
to the surroundings.
3
It has low temperature rise at rated load.
4
Maintenance free.
The drawbacks are:
1
It is costly.
2
Take time to replace the fuse.
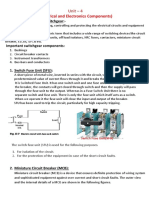
Circuit breakers
MCB and ELCB
MCB is miniature circuit breaker. It is automatic in action. When excessive current
passes through the circuit, handle of MCB will moves down and thus trips the circuit. After
one such an operation we can manually reset the supply by solving the fault in that circuit.
Thus rewiring fault size fuse wire in the case of fuse can be avoided by using MCBs. ELCB
is earth leakage circuit breaker. It protects the circuit from any leakage of current. It protects
the circuit from lightning and thunder. Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) Miniature circuit
breakers are compact devices used in distribution boards for protection against overload and
short circuit. The overload protection is achieved by a thermal trip mechanism using a
bimetallic strip. An electromagnetic trip mechanism is also incorporated for instantaneous
tripping in the event of a short circuit. When there is a sudden increase in current due to a
short circuit, the circuit should open immediately, but the bimetallic strip does not respond
quickly. In this case, the solenoid attracts the plunger and thus triggers the trip mechanism.
After clearing the fault, the MCB can be switched on manually. Fig. below shows the current
path in a typical miniature circuit breaker when it is in the 'on' position. The current passes
through a solenoid coil and a bimetallic strip.
SNIT ADOOR Page 8
Electrical workshop manual
When an overload condition persists for a few seconds, the bimetallic strip bends and triggers
the trip mechanism. The principle of operation of an MCB is based on the following two
principles.
1. Thermal operation
2. Magnetic operation
1. Thermal operation
In thermal operation, the extra heat produced by the high current warms the
bimetal strip. This results in bending the bimetallic strip and trips the operating contacts. The
thermal operation is slow. Hence, it is not suitable for speedy isconnection required to clear
fault currents. However, it is ideal for operation in the event of small but prolonged overload
currents. Thus, in general the thermal operation is suitable for opening the circuit in the event
of excessive current due to the overloaded machines.
The magnetic operation, on the other hand is suitable for protection against
high short circuit currents. This magnetic operation is due to the magnetic field set up by a
coil carrying the current, which attracts an iron part to trip the breaker when the current
becomes large enough. The magnetic operation is very fast and is used for braking fault
currents. In most cases of MCB' s, both types are provided so that overload currents and short
circuit currents are handled with the same degree. It should however be remembered that the
mechanical operation of opening the contacts takes a definite minimum time, typically 20ms,
so that there can never be the possibility of truly instantaneous operation. In many
installations, MCBs are preferred over fuses mainly because there is no need of rewiring the
fuse wire or replacing the cartridge. MCBs are available in a range of 0.5A to 63A normal
operating current and for the entire range, the, physical dimensions are almost identical.
The major advantages of MCBs are
1
Instantaneous opening of the contact on short circuit faults
2
Can be designed to operate even for very small overload currents
3
They can be quickly reset by hand
4
They cannot be reclosed if fault persist
SNIT ADOOR Page 9
Electrical workshop manual
In many cases they preferred over fuses as there is no need to rewire it.
Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker
The earth leakage circuit breaker (ELCB) is a protective device, which will
automatically trip, when there is an earth leakage within the installation. It is also known as
residual current circuit breaker (RCCB). It works on the current balance principle. The main
part is a core consisting of three windings. Here one winding carries the phase current, the
other winding carries the neutral current and the third winding to the tripping circuit. Under
normal operating conditions the net flux in the core is zero as such no emf induced in the trip
coil. However, when earth fault occurs, the phase and neutral current varies, the net flux in
the core will be different and as such, emf is induced in the trip coil and it is energized. It
then opens the circuit. The functioning of the ELCB can be checked using a switch
SNIT ADOOR Page 10
Electrical workshop manual
What is earthing /grounding?
Earthing or grounding is the term used for electrical connection to the general mass of
earth. Equipment or a system is said to be 'earthed' when it is effectively connected
to the ground with a conducting object. Earthing provides protection to personal
and equipment by ensuring operation of the protective gear and isolation of faulty
circuit during:
1
Insulation failure
2
Accidental contact
3
Lightning
strike Importance of
earthing
Earthing is necessary for proper functioning of certain equipments. Earthing is done also for
preventing the operating personal from hazardous shocks caused by the damage of the
heating appliances. Consider an electric heater connected to the supply using two-pin plug
and socket. If by some chance the heating element comes in contact with the metallic body of
the heater, the body of the heater being a conducting material will be at the same potential as
the heating coil. If a person comes and touches the body of the heater, current will flow
through his body, which will result in an electric shock.
System earthing: It is the earthing of neutrals of generating stations and substations. It is
employed to limit the voltage of live conductors with respect to potential of general mass of
earth. This is necessary to prevent failure of insulation.
Equipment earthing: Is earthing of non current carrying metal parts of electrical
equipments. As per Rules 33 and 61 of Indian Electricity Rule 1956 non-current carrying
metal parts must be earthed with two separate and distinct earth continuity conductors to an
efficient earth electrode. However equipments with double insulation need not be earthed.
Some Definitions:
Earthing: A tower/ equipments connecting to the general mass of earth by means of an
electrical conductor.
Earth Electrode: Connection to earth is achieved by electrically connecting a metal plate,
rod or other conductors or an array of conductors to the general mass of earth. This metal
plate or rod or conductor is called as "Earth electrode".
Earth lead: The conductor by which connection to earth is made.
Earth loop impedance: The total resistance of earth path including that of
conductors, earth wire, earth leads and earth electrodes at consumer end and
substation end.
Factors affecting the value of earth electrode resistance
1
Electrode material.
2
Electrode size.
3
Material and size of earth wire.
4
Moisture content of soil.
5
Depth of electrode of underground.
6
Quantity of dust and charcoal in earth pit.
SNIT ADOOR Page 11
Electrical workshop manual
Earth resistance consists of following components
1
Resistance of metal electrode
2
Contact resistance between electrode and soil
3
Resistance of soil away from electrode surface.
Distribution Board System
In distribution board system, which is most commonly adopted for
distribution of electrical energy in a building, the fuses of various circuits are grouped
together on a distribution board, some times simply known as fuse board. The two copper
strips, known as bus-bars, fixed in a distribution board of hard wood or metal case are
connected to the supply main through a linked switch so that the installation can be switched
off as a whole from both the poles of supply if required. A fuse is inserted in the + ve or phase
pole of each circuit so that each circuit is connected up through its own particular fuse. For
determination of load of an installation the following ratings maybe assumed unless the
values are known or specified.
1) Fluorescent lamps 40 watts.
2) Incandescent lamps, fans, and socket outlets 60 watts.
3) Power socket-outlets 1,000 watts.
4) Exhaust fans as per capacity of exhaust fans.
SYSTEMS OF WIRING
The types of internal wiring usually employed in our country are:
1. Cleat wiring:
In this system of internal wiring the cables used are
either VIR or PVC type. The cables are held by porcelain cleats about 6 mm above the walls
or ceiling. The cleats are mademin two halves, one base and the other cap. The base is
grooved to accommodate the cables and the cap is put over it and whole of it is then screwed
on wooden plugs (gutties) previously cemented into the wall or ceiling. Thus the cables are
firmly griped between the two halves of the cleats and secured to the supporting wall or
SNIT ADOOR Page 12
Electrical workshop manual
ceiling. The cleats used are of different sizes and different types in order to accommodate
cables of various sizes and different numbers of cables respectively. The cleats are of three
typesone groove, two grooves and three grooves to accommodate one, two, and three
cables respectively.
Advantages:
1) It is the cheapest system of internal wiring.
2) Its installation and dismantlement is easy and quick.
3) Material is recoverable after dismantlement.
4) Inspection, alterations and additions can be easily made.
5) Skill required is little.
Disadvantages:
1) It is not good looking.
2) It is quite temporary and perishes quickly.
3) The wires are exposed to mechanical injury.
4) The insulation catches dampness from the atmosphere and common salt like substance
appears on the insulation which lowers the insulation
resistance and Causes leakage. Hence this system of wiring cannot be
used in damp places.
5) Oil and smoke are injurious to VIR insulation.
Fields of Application:
The wiring of this type is very suitable for temporary installations in dry places. This is
also acceptable where appearance is not so important and cheapness is the main
consideration. This system is not suitable for use in domestic premises.
2. Wooden Casing and Capping Wiring:
The cable used in this type of wiring is either VIR or PVC or any other
approved insulated cables. The cables are carried through the wooden casing enclosures. The
casing consists of V-shaped grooves (usually two to hold the cables of opposite polarity in
different groves) and is covered at the top by means of rectangular strip of wood,known as
capping, of same width as that of casing. The capping is screwed to the casing by means of
wooden screws fixed at every 15 cm on the centre fillet. To protect the casing against white
ants first class seasoned teak wood, varnished hellac varnish is employed. Two or three cables
of same polarity (either all phases or all neutrals) may be run in one groove and in no case the
cables of opposite polarity should be run in the same groove. The casing ia usually placed 3.2
mm apart from the wall or ceiling by means of porcelain distance pieces of thickness not less
than 6.5 mm in order to keep the casing dry at the back.
SNIT ADOOR Page 13
Electrical workshop manual
3. CTS or TRS Wiring.
In this type of wiring the cables used may be single core, twin core
or three core TRS cables with a circular oval shape. Usually single core cables are preferred.
TRS cables are sufficiently chemical proof, water proof, steam proof but are slightly affected
by lubricating oils. TRS eaoles are run on well seasoned, perfectly straight and well varnished
(on all four sides) teak wood batten of thickness 10 mm at least. The width of the batten
depends upon the number and size of cables to be carried by it. The battens are available in
width of 13,19,25,31,38,44,50,56,63,69 and 75 mm. The wooden battens are secured to the
walls or ceiling by flat head wood screws to wood or other approved plugs at an interval not
exceeding 75 cm. The cables are held on the wooden batten by means of tinned brass link
clips already fixed on the batten with brass pins and spaced at an interval of 10 cm in case of
horizontal runs and 15 cm in case of vertical runs. The wiring after erection is neatly painted
with two coats of oil-less noncracking paint as specified in IS 732 and so on.
Advantages
1) Its installation is easy and quick and saving in labor largely compensate for the extra cost
of the cable.
2) Its life is long.
3) Within certain limits it is fire proof.
4) It can withstand the action of most chemicals such as acids and alkalies.
5) It is cheaper than other types of wiring except cleat wiring.
6)If the job is carried out with proper attention, it gives a nice appearance.
Disadvantages
1) Good workmanship is required to make a sound job in TRS wiring.
2) This type of wiring cannot be recommended for use in situations open
to sun or rain unless preventive steps are taken to preserve the insulation
of cables.
4. Lead Sheathed Wiring
This type of wiring employs conductors insulated with VIR and is covered
with an outer sheath of lead aluminum alloy containing about 95% lead. This metal sheath
gives protection to the cable from mechanical injury, dampness and atmospheric corrosion.
The whole lead covering is made electrically continuous and is connected to earth at the point
of entry to protect against electrolytic action due to leaking current and to provide safety
against the sheath becoming a live. The cables are run on wooden batten and fixed by means
of link clips as in TRS wiring. The great part of the cable employed is flat twin (the cable
having two insulated conductors side by side covered with red and black tape respectively
and under one flat covering of lead alloy). Three-core flat type cable is also used in certain
cases as well as single core cables under a circular sheath
of lead alloy.
Advantages
1) It provides protection against mechanical injury better than provided by
TRS wiring.
2) It is easy to fix and looks nice as it can be run in building without
damaging decoration and can be painted to suit colour scheme of the
surroundings.
3) Its life is long if proper earth continuity is maintained throughout.
4) It can be use din damp situations provided protection against moisture
effect on the ends of the cable is given.
SNIT ADOOR Page 14
Electrical workshop manual
e) It can be used in situations exposed to rain and sun provided no joint is
exposed.
Disadvantages
1) It is costlier than TRS wiring.
2) It is not suitable for places where chemical corrosion may occur.
3) In case of damage to insulation the metal sheath becomes alive and
gives shock, so as to provide safety against electrical shock it is necessary
that the sheath is properly earthed and an earth wire is run side by side
with it and all pieces are properly bounded or joined together so that not a
single cover is left unearthed.
4) Skilled labour and proper supervision is required.
5. Conduit Wiring
In this system of wiring steel tubes, known as conduits, are installed on
the surface of walls by means of saddles or pipe hooks or buried under plaster and VIR or
PVC cables are drawn into afterwards by means of a GI wire of size of about 18 SWG. In
damp situations the conduits can be spaced from the walls by means of small wooden blocks
fixed below the pipes at regular intervals. In order to facilitate drawing of wires numbers of
inspection fittings are provided along its length. The conduits should be electrically and
mechanically continuous and connected to earth at some suitable point. The conduits used for
this purpose are of two types namely (i) light gauge (or split type) conduit and heavy gauge
(or screwed type) conduit. Light gauge or split conduit with a seam along its length is used
for cheap work. It is not water tight or even damp proof and is not permitted on medium
voltage (i.e. on voltages higher than 250V). Screwed conduit (solid drawn or with welded
seam) is used for all medium voltage (250 V or 600 V) circuits and in places where good
mechanical protection and absolute protection from moisture is desired. In general the finish
of the conduit is black stove-enamelled, there being a smooth coating of enamel both on the
inside and outside surface of the tube. Galvanized conduit is also employed, especially in
damp situation when the conduit is on the surface but under ordinary conditions buried in
walls it offers little, if any, advantage over good enamelled conduits.
Advantages
1) It provides protection against mechanical damage.
2) It provides complete protection against fire due to short-circuits etc.
3) The whole system is water proof.
4) Replacement and alteration of defective wiring is easy.
5) Its life is long if the work is properly executed.
6)It is shock proof also if earthing and bonding is properly done.
Disadvantages
1) It is very costly system of wiring.
2) Its erection is not so easy and requires time.
3) Experienced and highly skilled labour is required for carrying out the job.
4) Internal condensation of moisture may cause damage to the insulation unless the system
outlets are properly drained and ventilated.
Fields of Application
As this system of wiring provides protection against fire, mechanical damage
and dampness so this is the only approved system of wiring for:
SNIT ADOOR Page 15
Electrical workshop manual
1) Places where considerable dust or puff is present such as in textile mills, saw
mills, flour mills etc.
2) Damp situations.
3) In workshops for lighting and motor wiring.
4) Places, where there is a possibility of fire hazards such as in oil mills, varnish
factories etc.
5) Places, where important documents are kept such as a record room.
6)Residential and public buildings, where the appearance is the prime thing. The
recessed type conduit wiring is preferred for residential and public buildings.
CHOICE OF WIRING
The following factors should be considered before selecting a
particular type of wiring.
1. Safety: The first and foremost consideration is safety to a person using electricity
against leakage or shock. Where there is a possibility of fire hazard,
conduit wiring is used.
2. Mechanical Protection: The wiring must be protected from mechanical
damage during use.
3. Permanency: The wiring must not deteriorate unduly by action of
weather, fumes, dampness etc.
4. Appearance: The wiring should he good looking.
5. Durability: The wiring must be durable.
6.Accessibility: In wiring system there should be facilities for extension,
renewal or alterations.
7. Initial Cost: The wiring selected should suit the pocket of the owner of the
building.
8. Maintenance Cost: The wiring should have, as far as possible, the lowest
maintenance cost.
The other factors, in addition to above, to be kept in view while making the choice of
wiringis load voltage to be employed, type of building etc. Some of the most commonly used
tools are described below:
SNIT ADOOR Page 16
Electrical workshop manual
To
ol Size Uses
SNIT ADOOR Page 17
Electrical workshop manual
STUDY OF WIRING ACCESSORIES
Any device, associated with the wiring and electrical appliance of an installation,
such as a switch, a fuse, a plug, a socket-outlet etc. is called the wiring accessory. The
cables, flexible cords and various wiring accessories in common use are briefly
described below.
Cables:
The cable or wire used in internal wiring is covered with insulation. The
conductor is covered with insulation so that it may prevent leakage of current
from the conductor and thus minimize the risk of fire and shock.
The wire employed for internal wiring of buildings may be divided
into different groups according to
1. Conductor used
2. number of cores used
3. voltage grading and
4. type of insulation used
According to the conductor material used in cables, these may be divided into two classes
known as copper cables and aluminum cables.
According to the number of cores, the cable consists of, the cables maybe divided into the
classes known as single core cables; twin core cables; three core cables; two core with
ECC (earth continuity conductor) cables etc.
According to voltage grading the cables may be divided into two classes:
(1)
250/440 volt cables
(2) 650/1,100 volt cables.
According to type of insulation the cables are of the following types:
1. Vulcanized Indian Rubber (VIR) Cables:
VIR cables are available in 250/440 volt as well as in 650/ 1100 volt grades and
are used for general electrical wiring in cleat, casing-capping and conduit
wirings.
VIR cable consists of either tinned copper conductor or aluminum conductor covered
with a layer of vulcanized Indian rubber insulation. Over the rubber insulation cotton
tape sheathed covering is provided with moisture resistant compound bitumen wax or
some other insulating material for making the cables moisture proof. The thickness of
rubber insulation depends upon the voltage grade for which the cable is required.
The copper conductor is tinned to provide protection against corrosion due to presence of
traces of sulphur, zinc oxide and other mineral ingredients in the VIR.
2. Tough Rubber Sheathed (TRS) or Cab Type Sheathed (CTS) Cables:
These cables are available in 250/440 volt grades and used in CTS'(or TRS) wiring.
TRS cable is nothing but a vulcanized rubber insulated conductor with an outer
protective covering of tough rubber. These cables are water proof, hence can be used in
wet conditions. These cables are available as single core, circular twin core, circular three
core, flat three cores, twin core with an earth continuity conductor etc. In wiring of a
three pin plug separate earth wire may be used, as it will be cheaper in cost and easy
in installation.
These cables are cheaper in cost and lighter in weight than lead alloy sheathed
cables, described later and have the properties similar to those, of lead sheathed
cables.
3. Lead Sheathed Cables:
These cables are also available in 250/440 volt grades and are used for internal
wiring where climatic condition is not dry and has a little bit moisture. The lead
SNIT ADOOR Page 18
Electrical workshop manual
sheathed cable is a vulcanized rubber insulated conductor covered with a continuous
sheath of lead. The lead sheath provides very good protection against the absorption of
moisture and sufficient protection against mechanical injury and so can be used without
casing or conduit system. It is available as a single core, twin core, flat three core and
flat twin core with an earth continuity conductor.
4. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Insulated Cables:
These cables are available in 250/440 and 650/1,100 volt grades and are used in
concealed wiring system. In this type of cable conductor is insulated with PVC
insulation. Since PVC is harder than rubber so PVC cable does not require cotton
tapping and braiding over it for mechanical and moisture protection.
Since the PVC is thermo-plastic insulation, so it is affected at high temperatures and it may
soften and flow down. These cables cannot be used for giving connections to the heating
appliances, pendant lighting etc. Though the insulation resistance of PVC is lower than that
of VIR but its effect is negligible for low and medium voltages below 600 volts,
5. Weather Proof/Cables
These cables are used for outdoor wiring and for power supply or industrial supply.
These cables are either PVC insulated or vulcanized rubber insulated conductors being
suitably taped (only in case of vulcanized rubber insulated cable) braided and then
compounded with weather resisting material. These cables are available in 250/440
volt and 650/1100 volt grades. These cables are not affected by heat or sun or rain.
Although TRS cables can be used for outdoor purposes but due to their higher cost,
weather proof cables are generally used for outdoor services.
6. Flexible Cords
A cable containing one or more cores, each formed of a group of wires, the diameter of
cores and of the wires being very small to afford flexibility, is known as flexible cord.
These are used as connecting wires for such purposes as from ceiling rose to lamp
holder, or from socket-outlet to portable apparatus such as radios, fans, lamps,
heaters etc. The flexibility of such wires facilitate in handling the appliances and
prevent the wires from breakage. The flexible cords used for house hold appliances
are available in various pleasing colours, sizes and of various thickness of insulation.
These wires should never be used for fixed wiring.
Switches
A manually operated device used for closing and opening or for changing the
connections of a circuit is known as a switch. The switches used in internal wiring may be
classified in various ways. According to the type of base material they are classified as
porcelain or bakelite switches. According to colour of base they are either white or black or
brown coloured switches. According to operation required, they are classified as one way,
two-way, centre off, double pole etc.
1. One-way Switch
This type of switch consists of two terminals which can be easily seen from the back side
of the switch as well, without removing the cover. The switch is always connected in series
with the point (lamp, fan or socket-outlet) to be controlled.
2. Two-way Switch
The switch of this type consists of four terminals, two of them being short-circuited
inside the switch. The switch of this type is usually used for the stair-case wiring or
circuits where one point is to be controlled from two different places.
SNIT ADOOR Page 19
Electrical workshop manual
3. Two-way Centre off Switch
The switch of this type is just like a two-way switch but
having three operations. In the centre it becomes off. Such switches are used when two lamps
are to be operated alternately.
4. Double Pole Switch
This is a combination of two one-way switches, which can be
operated simultaneously as ON-OFF terminals of both the switches, are connected together
by a handle made of bakelite. Such switches are used as interlinked switches when the load
current is less than 5A and supply voltage is under250V.Incaseeither of the voltage or current
exceeds the limits mentioned above DPI C switch is used.
5. Push-button Switches
Such switches are used for controlling the electric bells. When the
knob is pressed, the circuit is completed and the bell rings and as soon as the knob is left, the
circuit becomes open.
6.Table Lamp Switch
This is a small on-off switch which is commonly used in table lamps.
7. Bed Switch
Such switches are used to switch off the table lamps or other lamps while
going to sleep or making the lamp on while getting up at night. It is connected in aeries with
one of the two flexible wires. The specialty with this switch is that fluorescent material is
applied to its knob so that it may glow at night and can easily be seen in darkness. This is a
pendant type switch. The switches are of two types known as surface switches (or tumbler
switches) and flush switches (or concealed switches).
i. Tumbler or Surface Switches
Tumbler switches are those which are fixed on the mounting blocks directly
fixed on the surface of the wall. Such switches project out the surface of the wall
and are in common use. Surface switches are available in round and oblong
base. Round base switches are cheap and in common use. Oblong surface
switches are good in appearance, but being costly, are rarely used.
ii. Flush Switches
Flush switches, as obvious from their name, are fixed in flush with the wall
and do not project out. These switches are used where high quality
performance and appearance are required.
SNIT ADOOR Page 20
Electrical workshop manual
Ceiling Rose
The ceiling rose is used to connect the pendant lamps, fans or fluorescent tubes to the
installation through flexible or silk covered wires. These are not used on a circuit, the voltage
of which normally exceeds 250 volts.
Socket-Outlets
The socket-outlets are used to supply electrical connections whenever required for
electrical appliances such as radios, table fans, table lamps, iron, stoves etc. Socketoutlets are
of two types two pin type and three pin type. Two pin socket-outlets have become obsolete
now-a-days. The three pin type socket-outlet has got three hollow terminals in which three
pin plugs can easily be inserted but not loosely. Two holes being of same size, are meant for
making connections to the flexible wire of the appliance and the third hole, which is bigger
comparatively, is meant for earth connections. Thus three holes or sleeves are for live, neutral
and earth connections. The three pin socketoutlets are also of two types:
(1)
5 A for table fans, table lamps, radios etc, and
(2) 15 A for power circuits as heater, stove, iron etc.
Plugs
Plugs are used to take the supply from the socket-outlets for electrical appliances
such as table lamp, table fan, heater etc. Similar to socket-outlets plugs are also of two types
namely two pin and three pin. Two pin type plugs have become obsolete now-a-days. Three
pin type plugs consist of three pins usually made from brass. To the two pins which are thin
and of same size, flexible wires are connected and then covered up. To the third pin, which is
thicker comparatively, earth wire from the electrical appliance is connected. Similar to 3 pinsocket outlets 3 pin plugs are also of two types5 A and 15 A.
SNIT ADOOR Page 21
Electrical workshop manual
Lamp Holders
As the name indicates the function of lamp holder is to support the lamp
and also to connect it electrically. These are designed for quick removal and replacement of
the lamp. Lamp holders are of many types. A few will be described here. Lamp-holders may
be either of brass or bakelite type with porcelain interior. Brass holders are more durable but
may give shock if connections are poor. Though Bakelite holders are not durable, but do not
give shock. The following are the different types of lamp holders
1. Batten Holders
Such lamp holders are used where the lamp is to he fitted to the roof or to the wall i.e.
it is directly fitted either to batten or to wooden boards. Such lamp holders are bayonet type
i.e. in such a lamp holder the lamp is forced in. turned slightly and left in position.
2. Pendant or Cored Grip Holders
Such a lamp holder is used when the lamp is to be
suspended from the flexible cord. Such a lamp holder is hanged vertically downward from
the ceiling with flu flexible cord, one end of which makes electrical connections with the
ceiling rose and other with the lamp holder and thus with the lamp.
3. Angle Holders
Such lamp holders are used when the lamps are to be fixed directly on the walls and to give
light at an angle. Such lamp holders are available in various fancy designs and colors.
4. Slanting Holders
Such lamp holders are used for lamps to be fixed on advertising boards, for flood lights
and for stage lights. Such lamp holders are used along with shades (hand shape shades) so
that light is concentrated on the material displayed and does not trouble the viewer.
5. Bracket Holders
Such lamp holders are used to give direct light in the room or above a particular place.
These cannot be fixed on the roof or made to hang. Usually these are fixed on the wall.
These may also be used in table lamps.
6. Water Tight Bracket Holders
Such lamp holders are provided with tubular glasses fixed with water tight cover.
Such lamp holders are used outside the houses and for street lighting where
there is no cover to save the bulb from falling of water over it.
SNIT ADOOR Page 22
Electrical workshop manual
Junction Box
In joint box system of wiring all joints in conductors are made by means of suitable
connectors or joint cutouts in junction boxes. In looping back system of wiring, which
is widely used now-a-days, junction boxes are not required.
SNIT ADOOR Page 23
Electrical workshop manual
symbols
Positive
Negative
Earth
resistor
Variable resistor
inductor
Variable inductor
capacitor
Variable capacitor
Voltage source
voltmeter
wattmeter
motor
lamp
switch
transformer
generator
AC voltage source
SNIT ADOOR
Page
24
Electrical workshop manual
battery
Delta connection
Terminal
DC
AC
Overhead line
generator
Motor
SNIT ADOOR Page 25
Electrical workshop manual
Exp no:1
Date:
One lamp controlled by one switch
Aim
To wire up a circuit with one lamp controlled by one switch in surface conduit system of
wiring as per given layout. Prepare the list of material preferred as per the layout
Tools required
Screwdriver, linetester, cutting plair, wire stripper, hammer,hacksaw,pocker
Estimation
Sl
no;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Name of material
Specification
quantity
PVC flexible wire
PVCconduit
PVC saddles
Steady battern holder
Bulb
Fuse unit
Neutral link
SPST switch
3 way junction box
Round block
Switch box
Screws
1
Procedure
2
Wiring conduits are fixed on the board as per the given layout
The circuit consists of one SPST switch and one lamp holder
Make the circuit as per the given circuit diagram
Check the circuit before applying the supply
Give the single phase supply through a fuse and neutral through neutral link
Check the conditions
SNIT ADOOR
Page 26
Electrical workshop manual
Lay out
Circuit diagram
SNIT ADOOR Page 27
Electrical workshop manual
Exp no;2
Date;
One lamp controlled by one switch adding plug point
Aim
To wire up a circuit with one lamp controlled by one switch with addition of plug point in
surface conduit system of wiring as per the given layout. prepare the list of material preferred
as per the layout
Tools required
Screw driver, line tester, cutting plier, stripper, hammer, hack saw, pocker
Estimation
Sl no;
Name of the material
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
PVC flexible wire
PVC conduit
Steady battern holder
Switch SPST
Fuse unit
Neutral link
PVC saddles
Bulb
Plug point
3-way junction box
Switch box
1
Procedure
2
Specification
Wiring conduits are fixed on the board as per the given layout
The circuit consists of one SPST switch and one lamp holder with a plug point
Make the circuit as per the given circuit diagram
Check the circuit before applying the supply
Give the single phase supply through a fuse and neutral through neutral link
Quantity
Check the conditions
SNIT ADOOR
Page 28
Electrical workshop manual
Lay out
Circuit diagram
SNIT ADOOR Page 29
Electrical workshop manual
Exp no;3
Date;
Two lamp controlled by two switch parallel
Aim
To wire up circuit with two lamps controlled by two switch in surface conduit system of
wiring as per the given layout
Tools required
Screw driver, line tester, cutting plier, hammer, pocker, wire stripper, hack saw
Estimation
Sl no;
Name of the material
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
PVC flexible wire
PVC conduit
Steady battern holder
Junction box
SPST switch
Fuse unit
Neutral link
PVC round block
PVC saddles
Bulb
Switch box
screw
1
Procedure
2
Specification
Keep the material on the board as per the given layout
Fix the 4-way and 3-way junction boxes at the appropriate position
Fix the saddle clips and the conduit pipes
Lamp switch is also connected
The neutral required for the second lamp is tapped from the first lamp holder
Single phase supply is given and check the conditions
Quantity
SNIT ADOOR
Page 30
Electrical workshop manual
Layout
SNIT ADOOR Page 31
Electrical workshop manual
Circuit diagram
SNIT ADOOR Page 32
Electrical workshop manual
Exp no;4
Date;
One lamp controlled by one switch adding plug point and bell
Aim
To wire up a circuit with one lamp controlled by one switch with addition of one plug point
and one bell in the surface conduit system of wiring as per the given lay out
Tools
Screw driver, line tester, cutting plier, pocker, wire stripper, hack saw, and hammer
Estimation
Sl no;
Name of material
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
PVC flexible wire
PVC conduit
Steady battern holder
SPST switch
Bell push switch
Plug point
Bell
Fuse unit
Neutral link
Saddles
Bulb
4-way junction box
3-way junction box
Cealing rose
Switch box
screws
1
Procedure
2
Specification
Quantity
PVC pipes are cut into required size and fixed on board using PVC saddle clips
The PVC terminal boxes are fixed using PVC in appropriate position
3
4
The switches, plug and bell are fixed on the switch box and the lamp is connected in
the lamp
holder
and in
bell
push
switch
is also connected to the bell
They
are kept
PVC
round
block
The required amount of wire is cut and is put into the conduit pipes
SNIT ADOOR
Page 33
Electrical workshop manual
1
2
The fuse and neutral link are also connected in appropriate places
After the wiring is completed the line is tested using a tester
Layout
SNIT ADOOR Page 34
Electrical workshop manual
circuit diagram
SNIT ADOOR Page 35
Electrical workshop manual
Exp no;4
Date;
One lamp controlled by one switch adding plug point and bell
Aim
To wire up a circuit with one lamp controlled by one switch with addition of one plug point
and one bell in the surface conduit system of wiring as per the given layout
Tools
Screw driver, line tester, cutting plier, pocker, wire stripper, hack saw and hammer
Estimation
Sl no
Name of the material
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
PVC flexible wire
PVC conduit
Steady battern holder
SPST switch
Bell push switch
Plug point
Bell
Fuse unit
Neutral link
Saddles
Bulb
4-way junction box
3-way junction box
Cealing rose
Switch box
screws
Specification
Quantity
Procedure
1
PVC pipes are cut into required size and fixed on the board using PVC in appropriate
position
2
3
The PVC terminal boxes are fixed on the switch box and the lamp is connected in the
lamp holder
andkept
bellinpush
also connected to the bell
They are
PVCswitch
roundisblock
The required amount of wire is cut and is put into the conduit pipes
The fuse and neutral link are also connected in appropriate places
After the wiring is completed the line is tested using a tester
SNIT ADOOR
Page 36
Electrical workshop manual
Lay out
SNIT ADOOR Page 37
Electrical workshop manual
circuit diagram
SNIT ADOOR Page 38
Electrical workshop manual
Exp no;5
Date;
Two lamp controlled by one switch series circuit
Aim
To wire up a circuit with two lamp controlled by one switch as per the given layout diagram
Tools
Screw driver, line tester, pocker, hammer, wire stripper, plier,mini hacksaw,chisel
Estimation
Sl no;
Name of the material
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
PVC conduit
PVC flexible wire
Switch SPST
Saddle clips
Round block
Junction box
Switch box
Neutral link
Fuse unit
Steady battern holder
Bulb
screws
1
Procedure
2
Specification
Keep the material on the board as per the given layout and centralise them
Fix the 3-way junction box and switch box using screws
Connect them using conduit pipes and fix them using saddle clips
Fix the fuse unit and fix the neutral link
Wires are connected through the pipes as per the connection diagram
Quantity
Switch on the supply after inserting the lamps into the holder
SNIT ADOOR
Page 39
Electrical workshop manual
circuit diagram
SNIT ADOOR Page 40
Electrical workshop manual
Exp no;6
Date;
Staircase wiring
Aim
To wire up a circuit with one lamp controlled simultaneously from 2 places as per the given
layout diagram in conduit system satisfy the conditions
S1
S2
L off
S1
S2
L Bright
S1
S2
L Bright
S1
S2
L off
Tools
Screw driver, line tester, pocker ,hammer, wire stripper, plier, mini. Hack saw, and chisel
Estimation
Sl no;
Name of the material
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
PVC conduit
PVC flexible wire
Switch SPST
Saddle clips
Round block
Junction box
Switch box
Neutral link
Fuse unit
Steady battern holder
Bulb
screws
1
Procedure
2
Specification
Keep the material on the board as per the given layout and centralise them
Fix the 3-way junction box and switch box using screws
Connect them using conduit pipes and fix them using saddle clips
Fix the fuse unit and fix the neutral link
Quantity
Wires are connected through the pipes as per the connection diagram
SNIT ADOOR
Page 41
Electrical workshop manual
Switch on the supply after inserting the lamps into the holder
SNIT ADOOR Page 42
Electrical workshop manual
circuit diagram
SNIT ADOOR Page 43
Electrical workshop manual
Exp no;7
Date;
Godown wiring
Aim
To wire up a circuit with three lamps controlled by three switches in godown wiring. Also
prepare the list of material required as per the given layout
S1
S2
S3
L1
L2
L3
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
Tools
Screw driver, line tester, pocker ,hammer, wire stripper, plier, mini. Hack saw, and chisel
Estimation
Sl no;
Name of the material
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
PVC conduit
PVC flexible wire
Switch SPST
Saddle clips
Round block
Junction box
Switch box
Neutral link
Fuse unit
Steady battern holder
Bulb
screws
Specification
Quantity
SNIT ADOOR
Page 44
Electrical workshop manual
1
Procedure
2
Keep the material on the board as per the given layout and centralise them
Fix the 3-way junction box and switch box using screws
Connect them using conduit pipes and fix them using saddle clips
Fix the fuse unit and fix the neutral link
Wires are connected through the pipes as per the connection diagram
Switch on the supply after inserting the lamps into the holder
SNIT ADOOR Page 45
Electrical workshop manual
circuit diagram
SNIT ADOOR Page 46
Electrical workshop manual
Exp no;8
Date;
Hospital wiring
Aim
To wire up a circuit with two lamps controlled by two switches also conditions are satisfied in
the hospital wiring system . Also prepare the estimation
S1
S2
L1
L2
dark
dark
dim
dim
bright
dark
bright
bright
Tools
Screw driver, line tester, pocker ,hammer, wire stripper, plier, mini. Hack saw, and chisel
Estimation
Sl no;
Name of the material
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
PVC conduit
PVC flexible wire
Switch SPST
Saddle clips
Round block
Junction box
Switch box
Neutral link
Fuse unit
Steady battern holder
Bulb
screws
Specification
Quantity
SNIT ADOOR
Page 47
Electrical workshop manual
1
Procedure
2
Keep the material on the board as per the given layout and centralise them
Fix the 3-way junction box and switch box using screws
Connect them using conduit pipes and fix them using saddle clips
Fix the fuse unit and fix the neutral link
Wires are connected through the pipes as per the connection diagram
Switch on the supply after inserting the lamps into the holder
SNIT ADOOR Page 48
Electrical workshop manual
circuit diagram
SNIT ADOOR Page 49
Electrical workshop manual
Exp no;9
Date;
Fluroscent tube
Aim
To design estimate and wire up circuit containing fluroscent controlled by switch in PVC
conduit system of wiring
Tools
Screw driver, wire stripper, line tester, pocker, and knife
Estimation
Sl no;
Name of the material
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
PVC conduit
PVC box
Saddle clip
PVC flexible wire
Tube frame
Tube holder
Kitkat fuse
Neutral link
Chock
SPST switch
Starter
Ceiling rose
1
Procedure
2
Specification
Quantity
Each coil of the end coil is connected by a wire
This wire is connected to chock
Chock output is connected to the connector
Give phase to chock wire and neutral is the other
In this phase wire a one way switch is also connected
Then fluorescent lamp will glows
The
tube
is in
inserted
the end coil socket field in the tube fitting
The fluorescent
one way switch
is put
positiontoON
SNIT ADOOR
Page 50
Electrical workshop manual
Circuit diagram
SNIT ADOOR Page 51
Electrical workshop manual
Exp no;10
Date;
Wiring DB with ELCB and MCB
Aim
To design and wire up the circuit of main board and a consumer load having ELCB and MCB
for a bed room having one light point. Work is to be done in PVC conduit system as per the
given layout and prepare suitable estimation
Tools required
Pocker, hammer, screw driver, wire stripper, plier, hack saw, and line tester
Materials required
Sl no;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Name of the material
PVC flexible wire
PVC conduit
SPST switch
Bulb
Energy meter
Isolator
ELCB
MCB
MCB
Round block
Switch box
Screws
Specification
quantity
Procedure
The components are laid on the board and arrange according to the connection
diagram
The whole arrangement is centralised
Neutral and phase wire are connected and connections are taken to sub-circuit
board Draw wire through the pipes and connection are made in main board and consumer
SNIT ADOOR
Page 52
Electrical workshop manual
Layout
SNIT ADOOR Page 53
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Topic 3 - Current ProtectionDokument20 SeitenTopic 3 - Current ProtectionVictorNoch keine Bewertungen
- GE6162 EPL Lan Manual - ElectricalDokument42 SeitenGE6162 EPL Lan Manual - ElectricalDhamu DharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Plan Layout GuideDokument65 SeitenElectrical Plan Layout Guidehahadu0% (1)
- Government Polytechnic, Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Electrical Workshop LabDokument15 SeitenGovernment Polytechnic, Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Electrical Workshop LabTapobroto Chatterjee100% (1)
- Special Purpose MotorsDokument16 SeitenSpecial Purpose MotorsHari ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Motors and GeneratorsDokument30 SeitenElectric Motors and GeneratorshafizrahimmitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Accessories. EngDokument14 SeitenElectrical Accessories. EngHI-FINoch keine Bewertungen
- Induction Motors Guide for Farm ApplicationsDokument9 SeitenInduction Motors Guide for Farm ApplicationsramfalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Control Devices Report Ni SottoDokument61 SeitenPower Control Devices Report Ni SottoLEONEL SOTTONoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Electrical Wires & JointsDokument8 SeitenTypes of Electrical Wires & JointsShimpy MaheshwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- InternshipDokument14 SeitenInternshipshah BilalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuit Breakers Lecture Notes 3Dokument124 SeitenCircuit Breakers Lecture Notes 3Varun NarisettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Induction Relay Types - Disc, Cup & Their WorkingDokument8 SeitenInduction Relay Types - Disc, Cup & Their WorkinghilalsherNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9032 Experiment 01Dokument13 Seiten9032 Experiment 01Satish KaradeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Cables and Cable JointsDokument14 Seiten5 Cables and Cable JointsCOLLINS KIPRUTONoch keine Bewertungen
- BP - Res U2 Elect Symbols Outlets Note PDFDokument23 SeitenBP - Res U2 Elect Symbols Outlets Note PDFyeng botzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Solenoid GuideDokument20 SeitenLinear Solenoid GuideAndrei ReventNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overhead InsulatorsDokument17 SeitenOverhead InsulatorskpchakralaNoch keine Bewertungen
- InstallationDokument180 SeitenInstallationtilahuntenaye4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Domestic WiringDokument20 SeitenDomestic Wiringparag_git50% (2)
- Design of 33/11 KV LT Substation DemoDokument39 SeitenDesign of 33/11 KV LT Substation DemoH&B MoviesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Services and Distribution in BuildingsDokument2 SeitenElectrical Services and Distribution in BuildingsAnupriyaSaxenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE OF INDUSTRIAL INDUCTION MOTORS AND CONTROL SYSTEMSDokument59 SeitenINSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE OF INDUSTRIAL INDUCTION MOTORS AND CONTROL SYSTEMSMichael HailuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Practices Lab ManualDokument70 SeitenEngineering Practices Lab Manualkunaraj86% (7)
- DCMTDokument37 SeitenDCMTGloria HolcombNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Electrical SystemDokument18 SeitenIndustrial Electrical SystemH2SO4Noch keine Bewertungen
- DC GeneratorDokument38 SeitenDC Generatoraswardi8756Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cluster 2 Study GuideDokument17 SeitenCluster 2 Study GuideShavoy RichardsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measuring InstrumentDokument86 SeitenMeasuring InstrumenteddoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GE8261-Engineering Practices Lab - EEEDokument21 SeitenGE8261-Engineering Practices Lab - EEEAdnan KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ring Circuits - AdvantagesDokument6 SeitenRing Circuits - AdvantagesHassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Electrical Installations and ComponentsDokument58 SeitenTypes of Electrical Installations and Componentsrobpeter2425Noch keine Bewertungen
- Domestic Electrical WiringDokument4 SeitenDomestic Electrical WiringSyed Showkath AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maintenance of Electric EquipmentDokument130 SeitenMaintenance of Electric EquipmentAnil kadam100% (1)
- EEE3003 Power System Engineering Module - III Insulators and CablesDokument71 SeitenEEE3003 Power System Engineering Module - III Insulators and CablesVeera Vamsi Yejju100% (1)
- Electrical Design Estimation CostingDokument113 SeitenElectrical Design Estimation Costingmlsawhney2996Noch keine Bewertungen
- E. WORKSHOP II by SemereDokument93 SeitenE. WORKSHOP II by SemereSami Ye KiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Systems OverviewDokument102 SeitenElectrical Systems OverviewJeff CallantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-3 Wiring SystemDokument97 SeitenUnit-3 Wiring SystemAayushi Goyal100% (1)
- Godown Wiring - MechatroficeDokument2 SeitenGodown Wiring - MechatroficeKush SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACBDokument19 SeitenACBSingam SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Repair Ofand Maintenance of Electrical GadgetsDokument10 SeitenRepair Ofand Maintenance of Electrical GadgetsVignesh Kumar100% (1)
- BEE Assignment Unit 4Dokument13 SeitenBEE Assignment Unit 4Abhishek RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motors and Motor StartersDokument32 SeitenMotors and Motor StartersbmshivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Motor Control GuideDokument17 SeitenBasic Motor Control GuideHeizen BulanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuses and Circuit Breakers Notes For TVDokument25 SeitenFuses and Circuit Breakers Notes For TVapi-255989257Noch keine Bewertungen
- EM-III Lab DEE C20 Front PagesDokument30 SeitenEM-III Lab DEE C20 Front PagesHarimadhavareddy YenireddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internship KsebDokument97 SeitenInternship KsebVishnu VijayaramanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lm3914 Base Soil Humidity TesterDokument3 SeitenLm3914 Base Soil Humidity TesterVagish PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taswar Abbas 1Dokument62 SeitenTaswar Abbas 1Sumaira SaifNoch keine Bewertungen
- VK MEHTA One liner MCQsDokument203 SeitenVK MEHTA One liner MCQsFakherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contactors and Motor StartersDokument5 SeitenContactors and Motor StartersZdan AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wiring of The Distribution Board With RCD (Residual Current Devices) - Single Phase Home SupplyDokument14 SeitenWiring of The Distribution Board With RCD (Residual Current Devices) - Single Phase Home SupplyKadhir BoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission Tower 1Dokument4 SeitenTransmission Tower 1shahid rasheedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Objectives: Working Principle of Alternator OR Synchronous Generator StatorDokument5 SeitenLecture Objectives: Working Principle of Alternator OR Synchronous Generator StatorZ_JahangeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lightning ProtectionDokument15 SeitenLightning ProtectionEnglish words BY Utkarsh johriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of Power Supply & Safety DevicesDokument27 SeitenStudy of Power Supply & Safety DevicesMueen FaisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- House Wiring MCB MAVDokument7 SeitenHouse Wiring MCB MAVP. ChaudhuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Out of Step Relays PDFDokument10 SeitenApplication of Out of Step Relays PDFViraj Viduranga MuthugalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grundfos CR ManualDokument21 SeitenGrundfos CR Manualfayas100% (1)
- 2 Winding Transformer LongDokument58 Seiten2 Winding Transformer Longnaveendevi13Noch keine Bewertungen
- YaskawaDokument375 SeitenYaskawaCristian IozsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- C050203 - 0710 - 1110 - E - RGL - Specter Summit - FULL - 0Dokument34 SeitenC050203 - 0710 - 1110 - E - RGL - Specter Summit - FULL - 0Dennis ArhinNoch keine Bewertungen
- HF-320 Series Inverter Instruction ManualDokument103 SeitenHF-320 Series Inverter Instruction Manualmoshik99100% (8)
- UPS Handbook Rev C Low PDFDokument36 SeitenUPS Handbook Rev C Low PDFDarrenNoch keine Bewertungen
- REF620ANSI Appl 503120 ENaDokument198 SeitenREF620ANSI Appl 503120 ENaSegeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cantactor Starter NEMA Cuttler HammerDokument48 SeitenCantactor Starter NEMA Cuttler HammerAlfiansyah Dharma Setia DjaketraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trafo k13Dokument4 SeitenTrafo k13danielliram993Noch keine Bewertungen
- E20-E03 - 0 Lighting & Receptacle Circuit Wiring RequirementsDokument6 SeitenE20-E03 - 0 Lighting & Receptacle Circuit Wiring RequirementsMuhammad IrfanNoch keine Bewertungen
- S.N. Description of Works Quantity Unit Rate Total Amount RemarksDokument11 SeitenS.N. Description of Works Quantity Unit Rate Total Amount RemarksSagar AcharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Encapsulated Dry-Type Transformer ManualDokument7 SeitenEncapsulated Dry-Type Transformer ManualAjay AbrahamNoch keine Bewertungen
- BuyLog Smart CatalogDokument1.216 SeitenBuyLog Smart CatalogYoucefChaabnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MT831 Installation ManualDokument92 SeitenMT831 Installation ManualmamijatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Testing of Power TransformerDokument55 SeitenTesting of Power Transformeroedis83% (12)
- Moduflex Power Core (36kW) Rev00Dokument2 SeitenModuflex Power Core (36kW) Rev00Denizhan AkınNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wormgears Bonfiglioli PDFDokument270 SeitenWormgears Bonfiglioli PDFAnonymous hxQ7PNOQNoch keine Bewertungen
- Broyce Product Information V2 - 0 PDFDokument164 SeitenBroyce Product Information V2 - 0 PDFcallmenuandagmail.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRZ200 Brochure 15016-G2A-2.10 PDFDokument45 SeitenGRZ200 Brochure 15016-G2A-2.10 PDFTheaBinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbolite Elf 11 06b-02 - NoctrlDokument30 SeitenCarbolite Elf 11 06b-02 - NoctrlJosé FariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer Voltage Withstand and Insulation TestsDokument7 SeitenTransformer Voltage Withstand and Insulation Testskanchan206100% (1)
- Short Circuit Analysis Objective Type QuestionsDokument7 SeitenShort Circuit Analysis Objective Type Questionsjiguparmar1516Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 10 - Characterstics of Synchronous GeneratorDokument22 SeitenLab 10 - Characterstics of Synchronous GeneratorMomal ARNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATI 390 User Manual Completed Version - 20180410Dokument128 SeitenATI 390 User Manual Completed Version - 20180410williamppNoch keine Bewertungen
- E2M28 and E2M30 Rotary Vacuum PumpsDokument44 SeitenE2M28 and E2M30 Rotary Vacuum Pumpscabo.grosso2193Noch keine Bewertungen
- Distribution System Modeling and Analysis Electric 1 284 299Dokument16 SeitenDistribution System Modeling and Analysis Electric 1 284 299Kampret CebongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machine TrainerDokument2 SeitenElectrical Machine TraineradtronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isolated Bipolar Modular Multilevel DC-DC Converter With Self-Balancing Capability For Interconnection of MVDC and LVDC GridsDokument15 SeitenIsolated Bipolar Modular Multilevel DC-DC Converter With Self-Balancing Capability For Interconnection of MVDC and LVDC GridsAshish kumar N HNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Monitoring Devices Brochure enDokument17 SeitenEnergy Monitoring Devices Brochure entirane durresNoch keine Bewertungen