Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
CV3013 - Tutorials 1 To 3 (2015) PDF
Hochgeladen von
levanviet0410Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CV3013 - Tutorials 1 To 3 (2015) PDF
Hochgeladen von
levanviet0410Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CV3013- Foundation Engineering
Nanyang Technological University
School of Civil & Environmental Engineering
Tutorial 1 Shallow Foundations: Week 1
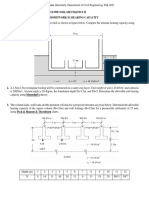
1.1 A site is to be developed for a 10-storey factory building without basement. The building
dimensions are 20 x 40 m. The soil profile consists of 5 m of sand and 10 m of soft
marine clay overlying a highly weathered mudstone as shown in Fig. 1.1. You are
requested to suggest a suitable type of foundation support for this building.
(a) What are the major design considerations?
(b) Can spread footing be used? What are the major geotechnical considerations?
(c) Can raft foundation be used? What are the major geotechnical considerations?
(d) Can compensated foundation be used? What are the major geotechnical
considerations?
(e) Can piles be used? What are the major geotechnical considerations?
Figure 1.1
1.2 If a single-storey warehouse is to be constructed at the same site as in Problem 1.1,
which foundation type would you recommend?
1.3 The mat foundation in Figure 1.3 is 45 m wide and 90 m long. It has a weight of 140 MN.
The sum of the applied structural loads is 1300 MN. Compute the average gross bearing
pressure and average net bearing pressure with the groundwater table at position A.
Then repeat the computation with the groundwater table position B. (modified from
Coduto Q5.4)
Figure 1.3
LEC- 1
CV3013- Foundation Engineering
Nanyang Technological University
School of Civil & Environmental Engineering
Tutorial 2 Shallow Foundations: Week 2
2.1 A strip footing 2 m wide is founded at a depth of 1 m in a stiff clay of saturated unit
weight 21 kN/m3, the water table being at ground level. Determine the bearing capacity
of the foundation when (a) cu = 105 kPa and u = 0, and (b) c = 10 kPa and = 28o.
2.2 A 2-m square, 1.5-m deep spread footing is underlain by a soil with the following
properties: = 16.5 kN/m3, c = 0 kPa, = 36o. Determine the bearing capacity of the
footing.
2.3 A footing 2.5 x 2.5 m carries a pressure of 400 kPa at a depth of 1 m in a sand. The
saturated unit weight of the sand is 20 kN/m3 and the unit weight of the sand above the
water table is 17 kN/m3. The design shear strength parameters are c = 0 kPa and =
40o. Determine the bearing capacity of the footing for the following cases:
(a) The water table is 5 m below ground level;
(b) The water table is 1 m below ground level;
(c) The water table is at ground level and there is seepage vertically upwards under
a hydraulic gradient of 0.2.
LEC- 2
CV3013- Foundation Engineering
Nanyang Technological University
School of Civil & Environmental Engineering
Tutorial 3 Shallow Foundations: Week 3
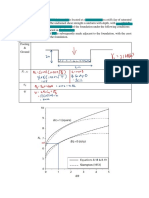
3.1 A footing 3.0 x 3.0 m carries a net foundation pressure of 130 kPa at a depth of 1.2 m in
a deep deposit of sand of unit weight 16 kN/m3; the water table being well below the
surface. The variation of cone resistance (qc) with depth (z) is as follows:
z (m)
qc (MPa)
6.2
6.9
1.2
3.2
6.6
13.2
1.6
2.1
7.0
11.7
2.0
2.8
2.4
2.3
7.4
12.9
2.6
6.1
3.0
5.0
3.4
3.6
3.8
4.5
4.2
3.5
4.6
4.0
5.0
8.1
5.4
6.4
5.8
7.6
8.0
14.8
Determine the settlement of the footing using Schmertmanns method.
3.2 A strip footing is located at a depth of 0.75 m in a sand of unit weight 18 kN/m3; the water
table being well below the foundation level. The characteristic shear strength parameters
are c = 0 and = 38o. The footing supports a design load of 500 kN/m. Determine the
required width of the foundation for the ultimate limit state to be satisfied to EC7 DA1b.
3.3 A foundation 4 x 4 m is located at a depth of 1 m in a layer of saturated clay 13 m thick.
Characteristic parameters for the clay are cu = 100 kPa, u = 0, c = 0 and = 32o, mv =
0.065 m2/MN, A = 0.42, sat = 21. Determine the allowable load to ensure (a) the bearing
resistance limit state is satisfied to EC7 DA1b, and (b) consolidation settlement does not
exceed 30 mm.
3.4 A foundation 3.5 x 3.5 m is to be constructed at a depth of 1.2 m in a deep sand deposit,
the water table being 3.0 m below the surface. The following values of standard
penetration resistance were determined at the location:
Depth (m)
N60
0.70
6
1.35
9
2.20
10
2.95
8
3.65
12
4.40
13
5.15
17
6.00
23
If the settlement is not to exceed 25 mm, determine the allowable load to satisfy the
serviceability limit state.
LEC- 3
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Reinforced Concrete Grade Beams, Piles & Caissons: A Practical Guide for Hillside ConstructionVon EverandReinforced Concrete Grade Beams, Piles & Caissons: A Practical Guide for Hillside ConstructionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Reinforcement and Soil StructuresVon EverandEarth Reinforcement and Soil StructuresBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (4)
- Lecture Notes on Reinforced Concrete DesignVon EverandLecture Notes on Reinforced Concrete DesignNoch keine Bewertungen
- (10 Marks) : Faculty of EngineeringDokument4 Seiten(10 Marks) : Faculty of EngineeringChamin SubhawickramaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procedure of CrossingDokument68 SeitenProcedure of Crossingrizalbaso100% (4)
- 2011 Exam GeotechnicalDokument9 Seiten2011 Exam GeotechnicalAhmed AwadallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WILLIS TOWERpresentation PDFDokument37 SeitenWILLIS TOWERpresentation PDFReshanth VangalapudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE363 Old Homework Solutions Part2Dokument21 SeitenCE363 Old Homework Solutions Part2Irmak ÜnalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Science Cheatsheet For Midterm (NEWEST)Dokument1 SeiteMaterial Science Cheatsheet For Midterm (NEWEST)DillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flash CalcinationDokument4 SeitenFlash CalcinationalulatekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing Capacity of FoundationsDokument4 SeitenBearing Capacity of FoundationsTshepiso NthiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundation Engineering Exam QuestionsDokument3 SeitenFoundation Engineering Exam QuestionsRamiz Keyra0% (1)
- Windposts and Masonry Reinforcement: For The Construction IndustryDokument12 SeitenWindposts and Masonry Reinforcement: For The Construction IndustryKelvin bongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ceu313 CT2Dokument3 SeitenCeu313 CT2Krishna Prasad ENoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Civil Engineering: Indian Institute of Technology Madras, ChennaiDokument2 SeitenDepartment of Civil Engineering: Indian Institute of Technology Madras, ChennaiAnonymous Vx9KTkM8nNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1 - Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationsDokument2 SeitenTutorial 1 - Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationsNametso MoatsheNoch keine Bewertungen
- 52BDokument5 Seiten52BJamie Schultz100% (1)
- Project On GED IIDokument4 SeitenProject On GED IIakhjazrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 ENB371 Tutorial Week 7 Shallow FoundationDokument4 Seiten01 ENB371 Tutorial Week 7 Shallow FoundationMaqsood Xailany0% (1)
- Nse-1491259045342336576-Examples - CH 8 Shallow Foundations-1 - 221020 - 010533 PDFDokument16 SeitenNse-1491259045342336576-Examples - CH 8 Shallow Foundations-1 - 221020 - 010533 PDFTiago PhillipeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE407 - Updated Midsem SolutionsDokument31 SeitenCE407 - Updated Midsem SolutionsManan GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce 441 Foundation Engineering - 2021 Fall Homework 1Dokument2 SeitenCe 441 Foundation Engineering - 2021 Fall Homework 1Yusuf DuranNoch keine Bewertungen
- GT 2 QBDokument6 SeitenGT 2 QBPrajakta ShindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afe QuesDokument8 SeitenAfe Questkumar111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment-7question and SolutionDokument3 SeitenAssignment-7question and SolutionTusharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 1Tu Tu DarNoch keine Bewertungen
- TR 334 Tutorial-1Dokument5 SeitenTR 334 Tutorial-1Adaminovic MrishoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment # 4Dokument2 SeitenAssignment # 4Anonymous Vx9KTkM8nNoch keine Bewertungen
- AssignmentDokument3 SeitenAssignmentsajjadsiyal144Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gte Previous r07 PapersDokument12 SeitenGte Previous r07 PapersyeswanthrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 6149912092880142413Dokument10 Seiten5 6149912092880142413Rushikesh patilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 3 (Due Date 14 Dec 2021)Dokument4 SeitenAssignment 3 (Due Date 14 Dec 2021)Ho JamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important Questions For All UnitDokument4 SeitenImportant Questions For All UnitSheik Althaf Hussain ANoch keine Bewertungen
- M. H. S. S. College of Engineering Department of Civil EngineeringDokument3 SeitenM. H. S. S. College of Engineering Department of Civil Engineeringjay shankar prabhatNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProblemsDokument4 SeitenProblemsbalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems of SoilsDokument3 SeitenProblems of SoilsFaheem Ali AsgharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shallow Foundations 2019 - Assignment - MAKDokument7 SeitenShallow Foundations 2019 - Assignment - MAKOdiit StephenNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE - 321: Foundation Engineering 6 Semester (Spring-2021) : Final Term Paper ExamDokument2 SeitenCE - 321: Foundation Engineering 6 Semester (Spring-2021) : Final Term Paper ExamBilal SaifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Show All The Necessary Steps To Solve The Following ProblemsDokument2 SeitenShow All The Necessary Steps To Solve The Following ProblemsMistireselassieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundation EnggDokument2 SeitenFoundation EnggS M Mozakkir QuadriNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 Geotechnical Engineering - IIDokument2 Seiten04 Geotechnical Engineering - IIMURALI KRISHNANoch keine Bewertungen
- Geotech Engg QuestionsDokument2 SeitenGeotech Engg QuestionsYashasviNoch keine Bewertungen
- FE Imp QuestionsDokument8 SeitenFE Imp QuestionsYeswanth PaluriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 2Dokument4 SeitenHomework 2Ali AratNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Foundation Engineering Rr420101Dokument8 SeitenAdvanced Foundation Engineering Rr420101Andronico BintiNoch keine Bewertungen
- FAD KTU Question Paper - May 2016Dokument3 SeitenFAD KTU Question Paper - May 2016Jimmy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing Capacity of Shalllow FoundationDokument2 SeitenBearing Capacity of Shalllow Foundationrx135boyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment-2 (Foundation Design)Dokument1 SeiteAssignment-2 (Foundation Design)HOD CivilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sem 8 AssignmentsDokument22 SeitenSem 8 AssignmentsChirag MistryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions FinalDokument9 SeitenQuestions FinalRavindra JagadaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- R7410101 Geotechnical Engineering-IIDokument8 SeitenR7410101 Geotechnical Engineering-IIsivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- -4618918اسئلة مدني فحص التخطيط مع الأجوبة من د. طارق الشامي & م. أحمد هنداويDokument35 Seiten-4618918اسئلة مدني فحص التخطيط مع الأجوبة من د. طارق الشامي & م. أحمد هنداويAboalmaail Alamin100% (1)
- r7410101 Geotechnical Engineering IIDokument4 Seitenr7410101 Geotechnical Engineering IISiva SankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 1 (Bearing Capacity Equations) PDFDokument1 SeiteProblem Set 1 (Bearing Capacity Equations) PDFMark Joseph Bandojo VargasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 52CDokument12 Seiten52CDarshit D RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pavement & Foundation Engineering Final ExamDokument2 SeitenPavement & Foundation Engineering Final ExamMuneeb Taseer RajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- BFC+4043 (1) Uthm Reinforced Concrete Design 2Dokument23 SeitenBFC+4043 (1) Uthm Reinforced Concrete Design 2liyana2030Noch keine Bewertungen
- KA35603+Foundation+Design CO2 TutorialDokument87 SeitenKA35603+Foundation+Design CO2 TutorialISMANOORIFAH BINTI ISMAIL -Noch keine Bewertungen
- Home Work - Cem605Dokument5 SeitenHome Work - Cem605neelNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE09 604 Geotechnical Engineering II APR 2015Dokument2 SeitenCE09 604 Geotechnical Engineering II APR 2015Akhil MuralidharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q2 Sa RC2Dokument1 SeiteQ2 Sa RC2Quicksilver 1975Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assnmt 11Dokument2 SeitenAssnmt 11RK MEHTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignments and Project 2014aDokument32 SeitenAssignments and Project 2014aMin Khine KyawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing CapacityDokument14 SeitenBearing CapacityMohamed KadryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turf Wall Architecture and Turf Furniture Assembly GuideVon EverandTurf Wall Architecture and Turf Furniture Assembly GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fila TableDokument3 SeitenFila TableShafiq ShahrulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalouge For Lenton CouplersDokument18 SeitenCatalouge For Lenton Couplerss.skumar1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eutectic Cell and Nodule Count in Cast Irons: International Journal of Cast Metals ResearchDokument8 SeitenEutectic Cell and Nodule Count in Cast Irons: International Journal of Cast Metals ResearchKhairul MuzafarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Grade: Material Data SheetDokument3 SeitenSteel Grade: Material Data SheetHDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Alternative Composite Material For High Speed Precision Machine Tool Structures PDFDokument14 SeitenAnalysis of Alternative Composite Material For High Speed Precision Machine Tool Structures PDFfunkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CITATION Jen15 /L 13321Dokument2 SeitenCITATION Jen15 /L 13321Kent Aldwin MangalinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cement Group 3 Bsce 2204Dokument13 SeitenCement Group 3 Bsce 2204Francis Marc AlcantaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- FS 2004 A - Rev-7Dokument78 SeitenFS 2004 A - Rev-7Maffone NumerounoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feeding Systems eDokument12 SeitenFeeding Systems eadamastortoNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is The Difference Between IPE and HEADokument5 SeitenWhat Is The Difference Between IPE and HEABayar DiyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sum FHT MD-SLDDokument5 SeitenSum FHT MD-SLDNebula RockbandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paraflex Series NewDokument2 SeitenParaflex Series NewJun CrisostomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Timber Joints With Punched Metal Plate FastenersDokument4 SeitenAnalysis of Timber Joints With Punched Metal Plate FastenersBatuhan DerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrolytic Plasma Treatment Processing of Conductive MaterialsDokument5 SeitenElectrolytic Plasma Treatment Processing of Conductive Materialsnicu1212Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 5 - 1D Truss Problem - MergedDokument10 SeitenExp 5 - 1D Truss Problem - MergedVegeta SaiyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plasticity and Structure of SoilDokument28 SeitenPlasticity and Structure of SoilJazmine ValenzonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specifications of Ajmera InfinityDokument4 SeitenSpecifications of Ajmera Infinitysrekha11Noch keine Bewertungen
- MWA Airfoil BrochureDokument2 SeitenMWA Airfoil BrochureDanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EVO 1 Service Manual 115V PDFDokument57 SeitenEVO 1 Service Manual 115V PDFYuhalimih YuhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SLD of MDB-3 Last Update For Print-ModelDokument1 SeiteSLD of MDB-3 Last Update For Print-ModelSharif 087Noch keine Bewertungen
- Avtl 104 Instructions For UseDokument72 SeitenAvtl 104 Instructions For Usechirayus_3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lysaght Trimdek-Optima 2021Dokument12 SeitenLysaght Trimdek-Optima 2021Fahmi YusoffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gruvlok Water-Wastewater ProductsDokument16 SeitenGruvlok Water-Wastewater Productsmax_powerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nippon Company Profile-Unlocked PDFDokument30 SeitenNippon Company Profile-Unlocked PDFAthul T.NNoch keine Bewertungen
- Column Check ListDokument2 SeitenColumn Check ListMalaciucaTGVNoch keine Bewertungen