Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
VAGINAL EXAM TECHNIQUES
Hochgeladen von
Raden Adjeng PalupiOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
VAGINAL EXAM TECHNIQUES
Hochgeladen von
Raden Adjeng PalupiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
TECHNIQUES OF EXAMINATION
EXAMPLES OF ABNORMALITIES
majus. On each side in turn, palpate between your finger and thumb for
swelling or tenderness. Note any discharge exuding from the duct opening
of the gland. If any is present, culture it.
INTERNAL EXAMINATION
Assess the Support of the Vaginal Walls.
With the labia Bulging
separated
from a cystocele or rectoby your middle and index fingers, ask the patient to strain down. Note any
cele. See Table 11-2, Bulges and
bulging of the vaginal walls.
Swelling of Vulva, Vagina, and Ure-
Insert the Speculum.
thra (p. ___).
Select a speculum of appropriate size and shape,
and lubricate it with warm water. (Other lubricants may interfere with cytologic studies and bacterial or viral cultures.) You can enlarge the vaginal introitus by lubricating one finger with water and applying downward pressure
at its lower margin. (You may also wish to check the location of the cervix to
help angle the speculum more accurately.) Enlarging the introitus greatly
eases insertion of the speculum and the patients comfort. With your other
hand (usually the left), introduce the closed speculum past your fingers at a
somewhat downward slope. Be careful not to pull on the pubic hair or pinch
the labia with the speculum. Separating the labia majora with your other hand
can help to avoid this.
SMALL
INTROITUS
392THE
seems
development
delays
for
imperforate
this
unduly
menarche.
possibility
of
late
hymen
aAND
girls
Be
pubic
in
when
relation
sure
occasionally
breasts
hair.
menarche
to TAKING
check
toand
the
Many
nique
spection
examination
the
has
Similar
vagina.
become
so
virginal
possible.
as techniques
to
atrophied
can
use
vaginal
beyour
When
performed
and
orifices
may
index
the
tight.
be
vaginal
finger
indicated
admit
by placing
only.
orifice
a single
inA
one
elderly
is
small
examining
even
finger
Pedersen
women
smaller,
in the
finger.
in
rectum
speculum
a whom
fairly
Modify
rather
good
the
may
introitus
your
bimanual
than
make
techin PHYSICAL
in- An
BATES
GUIDE
TO
EXAMINATION
HISTORY
TECHNIQUES OF EXAMINATION
EXAMPLES OF ABNORMALITIES
Two methods help you to avoid placing pressure on the sensitive urethra.
(1) When inserting the speculum, hold it at an angle (shown below on the
left), and then (2) slide the speculum inward along the posterior wall of
the vagina.
ENTRY ANGLE ANGLE AT FULL INSERTION
After the speculum has entered the vagina, remove your fingers from the introitus. You may wish to switch the speculum to the right hand to enhance
maneuverability of the speculum and subsequent collection of specimens.
Rotate the speculum into a horizontal position, maintaining the pressure
posteriorly, and insert it to its full length. Be careful not to open the blades
of the speculum prematurely.
Inspect
the
Cervix.
speculum
light
the
ing
ent
cotton
cervix
slope.
the
until
swab.
cervix,
If
until
you
points
discharge
withdraw
itFEMALE
more
cups
visualize
the
obscures
anteriorly
the
cervix
Open
the
speculum
your
cervix
the
and
than
speculum
view,
brings
illustrated.
well.
slightly
wipe
itWhen
into
carefully.
and
itIfaway
full
the
reposition
youuterus
view.
have
Rotate
gently
Position
is
difficulty
it with
and
retroverted,
on aadjust
adifferthe
large
findtheretroversion
See
p. ___.
of the uterus,
393
s can
GENITALIA
CHAPTER 11
TECHNIQUES OF EXAMINATION
EXAMPLES OF ABNORMALITIES
Inspect the cervix and its os. Note the color of the cervix, its position, the
See Table 11-3, Variations in the
characteristics of its surface, and any ulcerations, nodules, masses, bleeding,
Cervix (p. ___), and Table 11-4,
or discharge.
Abnormalities of the Cervix
(p. ___).
Maintain the open position of the speculum by tightening the thumb screw.
Obtain Specimens for Cervical Cytology (Papanicolaou Smears). A yellowish discharge on the
Obtain one specimen from the endocervix and another from the ecto- endocervical swab suggests a
mucopurulent
cervicitis, commonly
cervix, or a combination specimen using the cervical brush (broom).
For
best results the patient should not be menstruating. She should avoid inChlamydia
caused
trachomatis,
by
Neisseria gonorrhoeae,
or herpes
tercourse and use of douches or vaginal suppositories for 24 to 48 hours
simplex (p. ___).
before the examination.
OBTAINING THE PAP SMEAR:
OPTIONS FOR SPECIMEN COLLECTION
Cervical Scrape and Endocervical Brush
Cervical Scrape. Place the longer end of
the scraper in the cervical os. Press,
turn, and scrape in a full circle, making
surespecimen
to
include
the
transformation
zone
394endocervical
and
the
slide
Note
reduces
which
the
in
that
sometimes
aobscuring
safe
doing
squamocolumnar
brush.
on
spot
the
a appears
glass
cells
that
cervical
iswith
slide.
easy
with
junction.
scrape
blood,
Set
to
use
reach.
the
of
first
the
Smear
BATES GUIDE TO PHYSICAL EXAMINATION AND HISTORY TAKING
TECHNIQUES OF EXAMINATION
EXAMPLES OF ABNORMALITIES
Endocervical Brush. Now take the endocervical brush and place it in the cervical os.
Roll it between your thumb and index finger, clockwise and counterclockwise. Remove the brush and pick up the slide you
have set aside. Smear the slide with the
brush, using a gentle painting motion to
avoid destroying any cells. Place the slide
into an etheralcohol solution at once, or
spray it promptly with a special fixative.
Note that for pregnant women, a
cotton-tip applicator, moistened with
saline, is advised in place of the endocervical brush.
Cervical Broom
Many clinicians now use a plastic brush
tipped with a broomlike fringe for collection of a single specimen containing both
squamous and columnar epithelial cells.
Rotate the tip of the brush in the cervical
os, in a full clockwise direction, then
stroke each side of the brush on the glass
slide. Promptly place the slide in solution
or spray with a fixative as described
above.
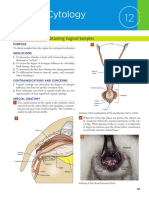
Inspect the Vagina.
Withdraw the speculum slowly while observing
the11-5, Vaginitis (p. ___).
See Table
vagina. As the speculum clears the cervix, release the thumb screw and maintain the open position of the speculum with your thumb. Close the speculum as it emerges from the introitus, avoiding both excessive stretching and
pinching of the mucosa. During withdrawal inspect the vaginal mucosa, noting its color and any in ammation, discharge, ulcers, or masses.
Cancer of the vagina
Perform a Bimanual Examination.
Lubricate the index and
middle
Stool
in the rectum may simulate a
fingers of one of your gloved hands, and from a standing position insert
them mass, but unlike a
rectovaginal
into the vagina, again exerting pressure primarily posteriorly. Your thumb
tumor mass can usually be dented
should be abducted, your ring and little fingers exed into your palm.
by Pressdigital pressure. Rectovaginal exing inward on the perineum with your exed fingers causes little if any
dis- confirms the distinction.
amination
comfort and allows you to position your palpating fingers correctly. Note
any nodularity or tenderness in the vaginal wall, including the region of the
urethra
ity,
pain.
Palpate
tween
and
Feel
the
and
tenderness.
theumbilicus
the
the
cervix,
uterus.
bladder
Normally
noting
Place
and
around
anteriorly.
the
your
itssymphysis
position,
the
the
other
cervix
cervix.
hand
shape,
pubis.
can
onbe
the
consistency,
While
moved
abdomen
you
somewhat
elevate
regularity,
about midway
the
without
cervix
mobiltogether
Painbesuggests
on with
movement
adnexal
pelvic
disease.
of
intenderness,
the
ammatory
cervix,
395
CHAPTER
11
s fornices
FEMALE
GENITALIA
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Bates Thorax Lungs With TermsDokument4 SeitenBates Thorax Lungs With Termscrystalshe100% (1)
- Bates Physical Examination RED NOTESDokument2 SeitenBates Physical Examination RED NOTESAmanda Gomez100% (1)
- Cardiovascular: Common Lab Tests For Cardiovascular DisordersDokument49 SeitenCardiovascular: Common Lab Tests For Cardiovascular Disordersesruneitak100% (1)
- Surgery Tips and ResourcesDokument2 SeitenSurgery Tips and ResourcesAbeebs SalahouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry PDFDokument1.193 SeitenBiochemistry PDFAmna ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Antibiotic Guide for Medical StudentsDokument74 SeitenEssential Antibiotic Guide for Medical StudentskaelenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ectopic PregnancyDokument76 SeitenEctopic PregnancyVivian Jean TapayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GI PathoDokument20 SeitenGI Pathojutah2013Noch keine Bewertungen
- CNS (102 Questions) : Form More Slowly and Insidiously ThanDokument38 SeitenCNS (102 Questions) : Form More Slowly and Insidiously Thanclark146Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bates Outline of Chapter 8Dokument15 SeitenBates Outline of Chapter 8KatherynSotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BATES Cardiovascular SystemDokument3 SeitenBATES Cardiovascular SystemAngelica Mae Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Pre-And Post-Book Study Test For The Shelf Exam: How To Use This ChapterDokument6 SeitenPre-And Post-Book Study Test For The Shelf Exam: How To Use This ChapterMiguel CuevasNoch keine Bewertungen
- S2HY SlideHandoutsDokument506 SeitenS2HY SlideHandoutsFaryal Rios FarooqiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5-Pathology & PathophysiologyDokument2 Seiten5-Pathology & PathophysiologyIbrahimFikryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary Patho PDFDokument623 SeitenPulmonary Patho PDFNabeel Shahzad100% (1)
- Cardio-Physiology Exam QuestionsDokument17 SeitenCardio-Physiology Exam Questionsjimmy100% (1)
- Uworld GI NotesDokument17 SeitenUworld GI NotesAyodeji SotimehinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Bacteria by Site of Infection: Mouth Skin/Soft Tissue Bone and JointDokument72 SeitenCommon Bacteria by Site of Infection: Mouth Skin/Soft Tissue Bone and JointMuthia FadhilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell InjuryDokument23 SeitenCell InjuryFiori MedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Family Medicine PresentationDokument53 SeitenFamily Medicine PresentationNancy BaggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genitourinary 1Dokument9 SeitenGenitourinary 1Leshan PrattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical CasesDokument12 SeitenClinical CasesAndreea HanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Usmle QDokument46 SeitenUsmle QRoh Jiten100% (1)
- Grand Rounds - Pulmonary EmbolismDokument25 SeitenGrand Rounds - Pulmonary EmbolismAdrian CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peds Lecture 3Dokument19 SeitenPeds Lecture 3Suraj Mukatira100% (1)
- CASE 28 Recurrent Abdominal PainDokument5 SeitenCASE 28 Recurrent Abdominal PainRoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bates' Guide To Physical Examination and History Taking, 12th EditionDokument9 SeitenBates' Guide To Physical Examination and History Taking, 12th Editionmanes0% (1)
- EYE PATHOLOGIES REVEALEDDokument11 SeitenEYE PATHOLOGIES REVEALEDDranreb Berylle MasangkayNoch keine Bewertungen
- أدوية الطوارىءDokument162 Seitenأدوية الطوارىءManar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- PE Form - NeonateDokument3 SeitenPE Form - NeonateStef ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- USMLE RX 2012 WorkbookDokument177 SeitenUSMLE RX 2012 WorkbookDina MahmassaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managing Patent Ductus Arteriosus in a Premature InfantDokument93 SeitenManaging Patent Ductus Arteriosus in a Premature InfantDanielle FosterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgery History and PhysicalDokument23 SeitenSurgery History and PhysicalBilal RowaihiNoch keine Bewertungen
- GI Summer Review - Answers - Bosch (2013)Dokument16 SeitenGI Summer Review - Answers - Bosch (2013)Jessica MooreNoch keine Bewertungen
- SB Intern Survival Guide 0Dokument12 SeitenSB Intern Survival Guide 0nevmerkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Usmle QuestionsDokument18 SeitenUsmle QuestionsPat FelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR Kumar Ponnusamy Biochemistry-Genetics USMLE Preparatory Course BIOGEN Reusable On-Line Resources For Large Group Teaching-Learning in Relatively Short TimeDokument1 SeiteDR Kumar Ponnusamy Biochemistry-Genetics USMLE Preparatory Course BIOGEN Reusable On-Line Resources For Large Group Teaching-Learning in Relatively Short TimeDr Kumar Ponnusamy100% (1)
- How Do I Diagnose The Cause of A Cough of Less Than 3 Weeks' Duration?Dokument14 SeitenHow Do I Diagnose The Cause of A Cough of Less Than 3 Weeks' Duration?Sudhir TyagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doctors in Training 2012 Step 1Dokument473 SeitenDoctors in Training 2012 Step 1André LassanceNoch keine Bewertungen
- PedquestDokument120 SeitenPedquests1234321Noch keine Bewertungen
- NBME Form 1 Step 2 ReviewDokument77 SeitenNBME Form 1 Step 2 Reviewalex karevNoch keine Bewertungen
- English TestsDokument43 SeitenEnglish TestsCoral Srinivasa Ramalu0% (2)
- Hepatobiliary ExamDokument10 SeitenHepatobiliary ExamAllison Eunice Servando100% (1)
- Approach To Cyanotic Heart Disease Christopher Cheung Santokh Dhillon PDFDokument13 SeitenApproach To Cyanotic Heart Disease Christopher Cheung Santokh Dhillon PDFsuckeydluffyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09-Emergency Med OSCEDokument16 Seiten09-Emergency Med OSCECodillia CheongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banco Kap. - CK 2Dokument1.099 SeitenBanco Kap. - CK 2Lucas OrtizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obs Cases BlueprintsDokument46 SeitenObs Cases BlueprintsYousra AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- IM 3A PE Cardiology Dr. JumangitDokument12 SeitenIM 3A PE Cardiology Dr. JumangitCzara DyNoch keine Bewertungen
- AntibioticsDokument30 SeitenAntibioticsRoza RahbeniNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhisioDokument15 SeitenPhisiojohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerves ExaminationDokument11 SeitenCranial Nerves ExaminationAlena JosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Physiology and Pharmacology: The EssentialsVon EverandClinical Physiology and Pharmacology: The EssentialsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsVon EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Gastroenterology and Hepatology Board Review ToolkitVon EverandPractical Gastroenterology and Hepatology Board Review ToolkitKenneth R. DeVaultNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaerobic Infections in HumansVon EverandAnaerobic Infections in HumansSydney FinegoldBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Nursing the NeonateVon EverandNursing the NeonateMaggie MeeksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ventricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandVentricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artificial MethodsDokument23 SeitenArtificial MethodsJanna Broqueza RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH Intensive Notes Maternal and Child Nursing 1Dokument42 SeitenPH Intensive Notes Maternal and Child Nursing 1Kris ToffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waxman, Jamye - Getting Off-Seal Press (2011 - 2006)Dokument325 SeitenWaxman, Jamye - Getting Off-Seal Press (2011 - 2006)Ивана ГвозденацNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study About Cervical CancerDokument11 SeitenCase Study About Cervical CancerJisel-Apple Bulan100% (1)
- MenstruationDokument33 SeitenMenstruationmskot100% (3)
- Female Anatomy ExplainedDokument11 SeitenFemale Anatomy ExplainedBARRIENTOS, RITCHELLE C.Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4 The Female and Male External Genitalia DiyaDokument48 Seiten4 The Female and Male External Genitalia DiyaOmotosho DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semi-Detailed LP in Science 5 Fro CODokument6 SeitenSemi-Detailed LP in Science 5 Fro CORonalyn Rugayan BalangatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oogenesis Oogenesis Is The Process Whereby Oogonia Differentiate Into Mature Oocytes. It Starts in TheDokument7 SeitenOogenesis Oogenesis Is The Process Whereby Oogonia Differentiate Into Mature Oocytes. It Starts in ThebarbacumlaudeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dysfunctional uterine bleeding guideDokument8 SeitenDysfunctional uterine bleeding guideCommunity Round3 G1100% (1)
- The Beauty of Female Reproductive SystemDokument9 SeitenThe Beauty of Female Reproductive SystemKlarenz RomNoch keine Bewertungen
- OB - Pelvic Exam ScriptDokument2 SeitenOB - Pelvic Exam ScriptPauline AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 Module 1 The Menstrual CycleDokument20 SeitenUnit 3 Module 1 The Menstrual CycleMARIANNE SORIANO100% (2)
- Histology of Female Reproductive System: Dr. Rajesh Ranjan Assistant Professor Deptt. of Veterinary Anatomy C.V.SC., RewaDokument26 SeitenHistology of Female Reproductive System: Dr. Rajesh Ranjan Assistant Professor Deptt. of Veterinary Anatomy C.V.SC., RewaDiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day6-She Comes FirstDokument18 SeitenDay6-She Comes FirstGabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mini CaseDokument3 SeitenMini CaseCrizle Ellen BalbinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Your Complete Guide to Understanding Your Menstrual CycleDokument54 SeitenYour Complete Guide to Understanding Your Menstrual CycleJanaica JuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ovarian Cycle & Menestrual CycleDokument16 SeitenOvarian Cycle & Menestrual CycleRolando Ian Maranan RNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Englissh Reproduction by MeDokument6 SeitenEnglissh Reproduction by Meayu sekar indah lestariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproductive System QuizDokument6 SeitenReproductive System QuizMarilyn Castro Laquindanum100% (2)
- Biology of Human Reproductive SystemDokument51 SeitenBiology of Human Reproductive Systemlen lehangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vaginal CytologyDokument4 SeitenVaginal Cytologyابراهيم عبدالله100% (1)
- Care of Mother and Child at RiskDokument33 SeitenCare of Mother and Child at RiskjomariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Female Reproductive AnatomyDokument35 SeitenFemale Reproductive AnatomySasikala MohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Female Reproductive System: Related Kidshealth LinksDokument7 SeitenFemale Reproductive System: Related Kidshealth Linksrichy0% (1)
- 04 Kelainan Bawaan Kasus Uroginekologi Dan Pengobatan SaatDokument23 Seiten04 Kelainan Bawaan Kasus Uroginekologi Dan Pengobatan SaatHerdinda Erudite Rizkinya100% (1)
- Menstrual CycleDokument6 SeitenMenstrual CycleAthirah BidinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Repositioning an Inverted UterusDokument5 SeitenRepositioning an Inverted Uterusshraddha vermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan in ScienceDokument4 SeitenLesson Plan in ScienceDearlene NugasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hotpantz: Herbal GynecologyDokument28 SeitenHotpantz: Herbal GynecologyMandy M.100% (20)