Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Please Fill in Your Scantron, INCLUDING Your Version/Test Form (A)
Hochgeladen von
FUSION Academics0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
33 Ansichten4 SeitenMidterm 2 Solutions for ECON 13
S. Skaperdas
Originaltitel
ECON 13 W15: Midterm 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenMidterm 2 Solutions for ECON 13
S. Skaperdas
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
33 Ansichten4 SeitenPlease Fill in Your Scantron, INCLUDING Your Version/Test Form (A)
Hochgeladen von
FUSION AcademicsMidterm 2 Solutions for ECON 13
S. Skaperdas
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
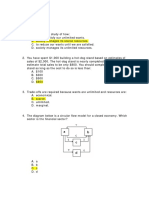
IS and Econ 13 - 2nd Midterm Examination
Answer Key (correct answers with *)
S. Skaperdas February 23, 2015
Version A
Please fill in your scantron, INCLUDING
YOUR VERSION/TEST FORM (A)
There are 35 questions in this exam (for a total
of 45 points). Questions 1-25 are worth 1 point
each. Questions 26-35 are worth 2 points each.
6. Which of the following is an example of
negative externality?
a. Cathy dislikes her new hairstyle
b. Mike ate too much bread and felt
sick
c. Rachel missed an episode of her
favorite TV show
d. John drives recklessly*
e. None of the above
1. When a country has a trade deficit,
a. Exports exceed imports
b. The countrys economy produces
more than it consumes
c. Imports exceed exports*
d. The current account is positive.
e. a and b.
7. Suppose that Brazil has a comparative
advantage in coffee and Peru has a comparative
advantage in tomatoes. Which of the following
groups would be worse off if these countries
specialize and trade?
a. Coffee producers in Peru*
b. Coffee producers in Brazil
c. Tomato producers in Peru
d. Always everybody is better off
when specialization and trade take
place
e. All groups are worse off when
specialization and trade take place
2. The following are factors that help explain
trade protection EXCEPT for
a.
trade policy creating losers as well as
gainers from freer trade.
b.
strategic trade policy.
c.
security concerns.
d.
the infant industry argument.
e.
comparative advantage*
3. Pursuing freer trade is
a. always best for a country.
b. sometimes not in the interest of a
country.*
c. always bad for a country.
d. always benefits the citizens of a
country.
e. a and d.
4. If the social cost of fishing is greater than its
private cost, then we can conclude that
a. a positive externality exists
b. government should encourage
fishing
c. there is no externality
d. a negative externality exists*
e. None of the above
5. In general, the social benefit of an activity
equals
a. Its private benefit
b. Its external benefit
c. Its private benefit plus its external
benefit*
d. Its price
e. All of the above
8. When you talk during class with your friend
a. you create a positive externality because
your friend is lonely.
b. you create a positive externality because
your friend has a positive view of you.
c. you create a positive externality when
your friend was late in class.
d. you create a negative externality
because you bother others around you.*
e. a and b.
9. The ozone depletion in the upper layers of the
atmosphere
a. is an example of a positive externality.
b. has been largely mitigated through the
banning of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).*
c. is a worsening problem.
d. has reduced air pollution is Southern
California.
e. a and d.
10. Methane produced by cattle, an activity that
adversely affects the environment,
a. could be reduced by subsidizing cattle
production.
b. could be increased by taxing cattle
production.
c. could be reduced by taxing cattle
production.*
d. is an example of a positive externality.
e. b and d.
11. A well-maintained yard
a. induces a positive externality because it
increases the homes market value.
b. induces a negative externality because it
increases the property tax liability of the
owner.
c. induces a positive externality because it
increases the value of adjacent properties in
the neighborhood.*
d. cannot provide any type of externality.
e. a and c.
12. The smoking ban on all UC campuses
a. can be expected to yield few known
benefits as a result of the absence of second-hand
smoke.*
b. can be expected to yield large benefits as
a result of the absence of second-hand smoke.
c. is expected to have no costs.
d. a and c.
e. b and c.
13. When an activity has a positive externality,
a. its social costs exceed its private costs.
b. its private costs exceed its social costs.
c. its social benefits exceed its private
benefits.*
d. its private benefits exceed its social
benefits.
e. its external costs exceed its social costs.
14. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) consists of
a. Consumption plus Savings plus net
exports.
b. Consumption plus Investment plus
Government expenditures.
c. Consumption plus Investment plus
Savings plus net exports.
d. Consumption plus Savings plus the
Current Account Surplus.
e. Consumption plus Investment plus
Government expenditures plus net
exports.*
15. An Iowa farmer buys a new truck made in
Connecticut by a Japanese company. As a result
a. US GDP increases, but Japanese
GDP is unaffected*
b. GDP for both US and Japan
increase
c. US GDP increases, but Japanese
GDP decreases
d. Japanese GDP increases, but US
GDP is unaffected
e. None of the above
Suppose in year 1, company XYZ produces 3000
light bulbs and 300 tables, selling at the price of
$2 per light bulb and $50 per table. In year 2,
company XYZ produces 4000 light bulbs and
200 tables, selling at the price of $3 per light
bulb and $60 per table. Assuming that year 1 is
the base year, use this information to answer the
following questions:
16. Nominal income for year 1 is:
a. $20,000
b. $21,000*
c. $24,000
d. $18,000
e. $25,000
17. Nominal income for year 2 is:
a. $20,000
b. $21,000
c. $24,000*
d. $18,000
e. $25,000
18. Real income for year 2 using year 1 as the
base year is:
a. $20,000
b. $21,000
c. $24,000
d. $18,000*
e. $25,000
19. An example of a government transfer is a(n)
a. expenditure on an interstate highway.
b. inheritance from a deceased relative.
c. tax on inheritance.
d. subsidy to corn producers.*
e. salary for members of the armed forces.
20. Which of the following transactions will be
included in Canadian GDP?
a. An American buys a bottle of French
perfume.
b. Mr. Moneybags buys an existing share
of the Bank of Montreal.
c. Coca-Cola builds a new bottling plant in
California.
d. A California winery produces a bottle of
Pinot Noir and sells it to a customer in
Vancouver, Canada.
e. United Airlines buys a new plane from
Canadas Bombardier.*
21. Suppose that the Chinese Renminbi has
appreciated relative to the US dollar. What
happens to Chinese and US imports?
a. Imports for both China and US fall
b. Imports for both China and US rise
c. Chinese imports fall, US imports rise
d. Chinese imports rise, US imports
fall*
e. None of the above
22. Which of the following is not a factor behind
the demand for US dollars?
a. Tourists who want to visit US
b. Those who want to buy US assets
c. Those who want to invest in the US
stock market
d. American tourists abroad*
e. Speculators betting in favor of US
dollars.
23. The Financial (or, Capital) account equals
a. Foreign purchases of US assets
minus US purchases of foreign
assets plus reserves adjustments.*
b. Net income received from
investment abroad
c. Net transfer payments from abroad
d. Exports minus imports
e. Trade balance
24. The exchange rate is the
a. interest rate differential between counties.
b. balance of trade differential between
countries.
c. price of gold.
d. the price of different goods in different
countries.
e. relative price of currencies of different
countries.*
25. Examples of activities that typically have
positive externalities include
a. fishing.
b. smoking.
c. eating junk food.
d. driving.
e. public debate.*
Please note that questions 26-35 are worth 2
points each.
26. Which of the following are benefits of trade?
a. Specialization in production and
Comparative advantage
b. Availability of new goods
c. Learning-by-doing
d. Productivity gains due to
competition
e. All of the above*
27. Government subsidies to U.S. farm products
a. are highly uncommon.
b. tend to lower their international price.
c. can be considered a form of trade
protection
d. b and c.*
e. All of the above.
28. Suppose the U.S. market for a certain
industry, say textiles, opens to international
competition through a complete elimination of
trade barriers. Then, other things being equal,
we can expect
a. no effect on employment or wages since
industries such as textiles are never
affected by international competition.
b. an increase in the number of U.S.
workers employed in that industry and
an increase in their wages.
c. a decrease in the number of U.S.
workers employed in that industry and
an increase in their wages.
d. an increase in the number of U.S.
workers employed in that industry and a
decrease in their wages.
e. a decrease in the number of U.S.
workers employed in that industry and a
decrease in their wages.*
29. When you ask a question in class
a. you create a positive externality because
your friend has a positive view of you
b. you create a negative externality
because you interrupt the train of
thought of others around you.
c. you create a positive externality because
you make a positive impression on the
professor.
d. you create a positive externality because
other students who had the same
question, but did not ask, benefit.*
e. you never induce an external effect on
others.
30. Mitigating the effects of climate change is
complicated because of
a. the uncertainty about future costs and the
effects of possible measures.
b. domestic and international politics.
c. making proper intergenerational
valuations.
d. a and b.
e. all of the above.*
31. Flexible exchange rates
a. have existed continuously throughout
the West for over two centuries.
b. have been adopted by every country,
including China.
c. were an integral part of the industrial
revolution.
d. imply that exchange rates are
determined by the supply and demand
for currencies.*
e. a and d.
32. The Bretton Woods system was
characterized by
a. the universal adoption of the Gold
standard.
b. the absence of recessions.
c. flexible exchange rates.
d. low levels of cross-country capital
movements.*
e. All of the above.
33. For the past decade, the US
a. had a yearly trade deficit (negative trade
balance).
b. had a yearly trade surplus (positive
trade balance).
c. some years it had a trade deficit and
some years a trade surplus.
d. consumed more goods and services than
it produced.
e. a and d.*
34. When a country has a trade surplus,
a. The financial (or, capital) account must
necessarily be negative.
b. The financial account is positive.
c. The financial account is zero.
d. the value of its exports is higher than
the value of its imports.*
e. a and d.
35. Since 1971
a. restrictions on trade gradually increased.
b. only the U.S. dollar has been backed by
gold.
c. no currency has been backed by either
gold or silver.*
d only a new currency, the euro, followed
the practice of the Swiss franc to be backed
by gold.
e. only the Icelandic kroner has been
backed by a precious metal successfully.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- ECON 13 W15: Sample Midterm 2Dokument4 SeitenECON 13 W15: Sample Midterm 2FUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECON 13 W15: FinalDokument8 SeitenECON 13 W15: FinalFUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECON 13 W15: Sample Midterm 1Dokument4 SeitenECON 13 W15: Sample Midterm 1FUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Income Accounting Test BankDokument95 SeitenNational Income Accounting Test BankMariam100% (1)
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Exam 2 Multiple Choice QuestionsDokument18 SeitenAP Macroeconomics Practice Exam 2 Multiple Choice QuestionsKayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macro Economy Today 14th Edition Schiller Test Bank 1Dokument96 SeitenMacro Economy Today 14th Edition Schiller Test Bank 1deborah100% (49)
- Exam Review QuestionsDokument22 SeitenExam Review QuestionsanalyiticNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bài tập MacroDokument8 SeitenBài tập MacroBảo Châu VươngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identifying key economic concepts on a testDokument12 SeitenIdentifying key economic concepts on a testNgọc Ninh NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECON 13 W15: Practice FinalDokument6 SeitenECON 13 W15: Practice FinalFUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 1,2,3 (Ans)Dokument5 SeitenChap 1,2,3 (Ans)Julia Kently MiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 1,2,3Dokument5 SeitenChap 1,2,3Julia Kently MiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Professor Elliott Parker Spring 2006 Name: ECON 102 - Principles of MicroeconomicsDokument8 SeitenProfessor Elliott Parker Spring 2006 Name: ECON 102 - Principles of Microeconomicshyung_jipmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 23 QuizDokument15 SeitenChapter 23 QuizRhobie CuaresmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics exam questionsDokument14 SeitenEconomics exam questionsbopgalebelayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trắc nghiệm môn Kinh tế vĩ môDokument8 SeitenTrắc nghiệm môn Kinh tế vĩ môGia HânNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Macroeconomics (Eco 1102) C. Théoret Practice Exam #1 Answers On Last PageDokument19 SeitenIntroduction To Macroeconomics (Eco 1102) C. Théoret Practice Exam #1 Answers On Last Pagerei makiikoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Problems Ch. 9 International Trade and Comparative AdvantageDokument7 SeitenPractice Problems Ch. 9 International Trade and Comparative AdvantageGabby CustodioNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECN204 Midterm 2014WDokument12 SeitenECN204 Midterm 2014WexamkillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics II Assignment 1: Chapter 15 Measuring GDPDokument9 SeitenEconomics II Assignment 1: Chapter 15 Measuring GDP許雅婷Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Paper MCQ Micro EconomicsDokument8 SeitenSample Paper MCQ Micro EconomicsbineshwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam2 B PDFDokument7 SeitenExam2 B PDFDhoom AldossaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1Dokument11 Seiten1PHƯƠNG ĐẶNG DƯƠNG XUÂNNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECON 1000 Midterm W PracticeDokument7 SeitenECON 1000 Midterm W Practiceexamkiller100% (1)
- Macro Multiple ChoiceDokument41 SeitenMacro Multiple ChoiceNghi Lê Nguyễn PhươngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Microeconomics Midterm ExamDokument6 SeitenBasic Microeconomics Midterm ExamAriel Manalo100% (1)
- Mankiw-Test Chapter 10-22Dokument55 SeitenMankiw-Test Chapter 10-22Nhật Lan PhươngNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH6 EconDokument8 SeitenCH6 EconJason OstlerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 101 Old FinalDokument13 Seiten101 Old Finalntc7035Noch keine Bewertungen
- International Finance Quiz ReviewDokument17 SeitenInternational Finance Quiz ReviewKhail GoodingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mankiw-Test Chapter 10Dokument4 SeitenMankiw-Test Chapter 10Vân Hà100% (1)
- Economics Competition Question Book 2017 - AnswersDokument8 SeitenEconomics Competition Question Book 2017 - AnswersDIVA RTHININoch keine Bewertungen
- ECON 203 Midterm1 2012WDokument13 SeitenECON 203 Midterm1 2012WexamkillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Econ 202 Fall 2009 Ch. 10: National Income: Multiple ChoiceDokument8 SeitenEcon 202 Fall 2009 Ch. 10: National Income: Multiple ChoiceAnkur SaurabhNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECON 1000 - Final - 2012WDokument8 SeitenECON 1000 - Final - 2012WexamkillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eco QuizzDokument6 SeitenEco Quizzthuptahs186417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Neither A Stock Nor A FlowDokument12 SeitenNeither A Stock Nor A FlowShabnam NazirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Economics Mcqs Paper AnswersDokument27 SeitenBasic Economics Mcqs Paper Answerslog manNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Edit HereDokument15 SeitenChapter 1 - Edit HereNguyễn Chí ĐứcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microeconomics Test 3Dokument26 SeitenMicroeconomics Test 3a24dkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macroeconomics Measures of PerformanceDokument6 SeitenMacroeconomics Measures of Performancechen zhekaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bai Tap Mau Chapter 1 3Dokument11 SeitenBai Tap Mau Chapter 1 3Anh NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Questions 1 (GDP)Dokument7 SeitenStudy Questions 1 (GDP)Syed Karim100% (1)
- Test Bank For Macroeconomics 8th Canadian Edition Andrew AbelDokument16 SeitenTest Bank For Macroeconomics 8th Canadian Edition Andrew AbelstebinrothNoch keine Bewertungen
- Econ 101, Sections 4 and 5, S09 Schroeter Exam #3, BlueDokument7 SeitenEcon 101, Sections 4 and 5, S09 Schroeter Exam #3, BlueexamkillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 23: Measuring A Nation'S Income (Ans)Dokument5 SeitenUnit 23: Measuring A Nation'S Income (Ans)Minh Châu Tạ ThịNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maco QuestionsDokument25 SeitenMaco QuestionsKumari VBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 35 Practice QuestionsDokument24 SeitenChapter 35 Practice QuestionsHannah Ma Ya LiNoch keine Bewertungen
- International EconomicsDokument13 SeitenInternational EconomicsUn Copil ZapacitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 1Dokument42 SeitenQuiz 1Tuan NganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final 2016Dokument15 SeitenFinal 2016Ismail Zahid OzaslanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Macroecnomics Practice Exam 1Dokument20 SeitenAP Macroecnomics Practice Exam 1KayNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Macroecnomics Practice Exam 1Dokument20 SeitenAP Macroecnomics Practice Exam 1KayNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPC QuestionsDokument4 SeitenPPC Questionssumedhasajeewani100% (1)
- Measuring a Nation's Income: GDP and the Circular FlowDokument9 SeitenMeasuring a Nation's Income: GDP and the Circular FlowAl Arafat RummanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECON MID Test PreDokument10 SeitenECON MID Test PreSamuel YehNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECON 1050 Midterm 2 2013WDokument20 SeitenECON 1050 Midterm 2 2013WexamkillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- CFP Certification Exam Practice Question Workbook: 1,000 Comprehensive Practice Questions (2018 Edition)Von EverandCFP Certification Exam Practice Question Workbook: 1,000 Comprehensive Practice Questions (2018 Edition)Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Development and Diplomacy: Resetting Caribbean Policy Analysis in the Aftermath of the COVID-19 PandemicVon EverandDevelopment and Diplomacy: Resetting Caribbean Policy Analysis in the Aftermath of the COVID-19 PandemicWinston DookeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSYCH 9A F14: Final PreparationDokument18 SeitenPSYCH 9A F14: Final PreparationFUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSYCH 9A F14: Midterm PrepDokument20 SeitenPSYCH 9A F14: Midterm PrepFUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICS 4 W15: Sample MidtermDokument6 SeitenICS 4 W15: Sample MidtermFUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 3A W15: Quiz 7Dokument1 SeiteMath 3A W15: Quiz 7FUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICS 6D W15: Quiz 3Dokument1 SeiteICS 6D W15: Quiz 3FUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 3A W15: Midterm 1Dokument2 SeitenMath 3A W15: Midterm 1FUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 3A W15: Quiz 6Dokument1 SeiteMath 3A W15: Quiz 6FUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATH 3A W15: Quiz 5Dokument1 SeiteMATH 3A W15: Quiz 5FUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 3A W15: Quiz 2Dokument1 SeiteMath 3A W15: Quiz 2FUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 3A W15: Quiz 3Dokument1 SeiteMath 3A W15: Quiz 3FUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATH 3A W15: Quiz 4Dokument1 SeiteMATH 3A W15: Quiz 4FUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 3A W15: Quiz 1Dokument1 SeiteMath 3A W15: Quiz 1FUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICS 6D W15: Quiz 4Dokument1 SeiteICS 6D W15: Quiz 4FUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICS 6D W15: Quiz 1Dokument1 SeiteICS 6D W15: Quiz 1FUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATH 13 W15: Quiz 2Dokument1 SeiteMATH 13 W15: Quiz 2FUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICS 6D W15: Quiz 2Dokument1 SeiteICS 6D W15: Quiz 2FUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pridtiwo: Roblen1 1 Ulti Ple Choice (20 Points) Rite Your Answer Or1 The First PageDokument4 SeitenPridtiwo: Roblen1 1 Ulti Ple Choice (20 Points) Rite Your Answer Or1 The First PageFUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATH 13 W15: Final Study GuideDokument3 SeitenMATH 13 W15: Final Study GuideFUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECON 13 W15: Final ReviewDokument8 SeitenECON 13 W15: Final ReviewFUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECON 13 W15: Practice FinalDokument6 SeitenECON 13 W15: Practice FinalFUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATH 13 W15: Quiz 1Dokument1 SeiteMATH 13 W15: Quiz 1FUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATH 13 W15: Quiz 4Dokument1 SeiteMATH 13 W15: Quiz 4FUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECON 13 W15: Midterm ReviewDokument1 SeiteECON 13 W15: Midterm ReviewFUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATH 13 W15: Sample FinalDokument9 SeitenMATH 13 W15: Sample FinalFUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATH 13 W15: Quiz 3Dokument1 SeiteMATH 13 W15: Quiz 3FUSION AcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medication - Safety - v4 Last Update 2015Dokument81 SeitenMedication - Safety - v4 Last Update 2015Retno PalupiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASSEMBLING COMPUTER: HOW TO BUILD A PCDokument48 SeitenASSEMBLING COMPUTER: HOW TO BUILD A PCCeejaay PelinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment #1: 1 HgjyygbykvrfDokument1 SeiteAssignment #1: 1 HgjyygbykvrfJuan Sebastian ArangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DUB01CB Eng PDFDokument4 SeitenDUB01CB Eng PDFAnonymous hj273CMNoch keine Bewertungen
- HHG4M - Lifespan Development Textbook Lesson 4Dokument88 SeitenHHG4M - Lifespan Development Textbook Lesson 4Lubomira SucheckiNoch keine Bewertungen
- อัตราภาษีของไทยที่ลดให้เปรูDokument124 Seitenอัตราภาษีของไทยที่ลดให้เปรูDante FilhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- S10 Electric Power PackDokument12 SeitenS10 Electric Power PackrolandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mercedes ManDokument7 SeitenMercedes Manien yeyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Check Valves SlamDokument2 SeitenWhy Check Valves SlamBramJanssen76Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ex Ophtalmo Eng 1Dokument4 SeitenEx Ophtalmo Eng 1Roxana PascalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prom 2Dokument3 SeitenProm 2arvindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lession Plan - MIDokument21 SeitenLession Plan - MINithya SannidhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inkontinensia Urin: Dr. Adhi Permana, SPPDDokument35 SeitenInkontinensia Urin: Dr. Adhi Permana, SPPDTiara KhairinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 The Truth About Air TravelDokument14 Seiten3.1 The Truth About Air TravelСвітлана Свирид0% (1)
- Self-Balancing Two-Wheeler Using GyroscopeDokument33 SeitenSelf-Balancing Two-Wheeler Using Gyroscopemilan mottaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Features General Description: 3A 24V 340Khz Synchronous Buck ConverterDokument18 SeitenFeatures General Description: 3A 24V 340Khz Synchronous Buck ConverterAntonioNobregaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Design Hardware Guide for EVM CE-2Dokument7 SeitenReference Design Hardware Guide for EVM CE-2Angie FoleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NTE56004 Thru NTE56010 TRIAC, 15 Amp: FeaturesDokument2 SeitenNTE56004 Thru NTE56010 TRIAC, 15 Amp: FeaturesFreddy SarabiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.case Study: Effects of Homeopathic Medicines in AdultsDokument2 Seiten5.case Study: Effects of Homeopathic Medicines in AdultsAMEEN ARTSNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.pharm Course Handbook 2017 18Dokument74 SeitenB.pharm Course Handbook 2017 18Md RaquibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outline 1. Background of Revision: JEITA CP-1104BDokument4 SeitenOutline 1. Background of Revision: JEITA CP-1104BkksdnjdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotary Gear Pump Manufacturers in India, Pulp Valve Manufacturers IndiaDokument3 SeitenRotary Gear Pump Manufacturers in India, Pulp Valve Manufacturers IndiaKirit IndustriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Acoustics: André M.N. Spillere, Augusto A. Medeiros, Julio A. CordioliDokument13 SeitenApplied Acoustics: André M.N. Spillere, Augusto A. Medeiros, Julio A. CordioliAbdelali MoumenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deam Edan M8 Monitor - User ManualDokument248 SeitenDeam Edan M8 Monitor - User Manualvelasquez diazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synopsis THESIS 2022: Aiswarya Vs Tqarebc005 S10Dokument5 SeitenSynopsis THESIS 2022: Aiswarya Vs Tqarebc005 S10Asna DTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pump Characteristics ExperimentDokument7 SeitenPump Characteristics ExperimentJam JoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mouse Deer and TigerDokument2 SeitenMouse Deer and Tigeralan.nevgan100% (1)
- CEFIC Guidelines Transport Equipment Packed Cargo (2010)Dokument7 SeitenCEFIC Guidelines Transport Equipment Packed Cargo (2010)sl1828Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dcom QuestionDokument3 SeitenDcom Questionsushant sahooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ebook Scientific InstrumentsDokument9 SeitenEbook Scientific InstrumentsPavans LuckyNoch keine Bewertungen