Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Conjugate Beam METHOD
Hochgeladen von
Adam AhmedCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Conjugate Beam METHOD
Hochgeladen von
Adam AhmedCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Structural Analysis (II)
Method (2)
Chapter 5: Deflection
Conjugate beam Method ....
. Slope() Deflection (y)
Conjugate beam:
Deflection (y) ) (
. Slope( )
( M ) ( -M ) ( Elastic load ) ( Conjugate beam)
EI
:
Rotation or Slope( )or (y')= Shear force of elastic load = Qelastic
Deflection ( )or (y)= Moment of elastic load = Melastic
Real(Original) beam
Conjugate beam:
Elastic load = d(y) =- M
Load = dM(x) = w
EI
dx
Rotation = d(y) = Qelastic
dx
dx
Shear = dM(x) = Q
dx
Deflection = y = Melastic
Moment = M(x)
- M/EI
wt/m'
Rotation)
Deflection)
Structural Analysis (II)
Chapter 5: Deflection
(Conjugate beam) ( Original beam)
Conjugate Support
Real Support
Fixed support
Free end
M 0 , Q0
0 ,0
Free end
Fixed support
M = 0 , Q=0
= 0 , =0
End support (Roller or Hinge)
End support (Roller or Hinge)
M = 0 , Q0
= 0 , 0
Interior support (Roller or Hinge)
Internal hinge
= 0 , 0
M = 0 , Q0
L
Internal hinge
L
0 , L R 0
(QL=QR)
(R = L)
R
Interior support (Roller or Hinge)
M 0 , QL QR
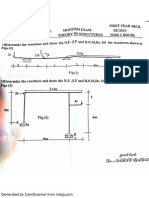
Examples
Real Beam
Conjugate Beam
(???)
Indetreminate Beam
Structural Analysis (II)
Chapter 5: Deflection
Steps of Solution :
.Conjugate beam method ( ) ( y)
FOR Real beam
Reactions
Bending Moment Diagram
Examples
. ( B.M.D)
6t
(1)
12t.m
WL
= 24m.t
3t/m`
12t.m
B.M.D
WL
= 24m.t
(2)
4 t/m`
6t
2 t/m`
C
15 t
21 t
WL/8=32m.t
8 m.t
14 t
WL/8=9m.t
12 m.t
B.M.D
8 m.t
12 m.t
B.M.D
WL/8=32m.t
WL/8=9m.t
)Structural Analysis (II
Chapter 5: Deflection
) ( Inertia )( Inertia
:
8t
8t
2I
8t
12mt
6mt
B.M.D
12mt
12mt
12mt
2I
Modified B.M.D
6mt
Or
3mt
6mt
12mt
6mt
I
12mt
24mt
FOR Conjugate beam
) (Given ) (Conjugate Beam .
) (Conjugate Beam ) (Elastic loads ).(Modified B.M.D
) (Elastic loads ).(Conjugate Beam
= ) (
).( B.M.D
= ) (C.g ).( B.M.D
) ( B.M.D ) ( Elastic loads .
ML
Datum
1
2ML
Datum
Structural Analysis (II)
Chapter 5: Deflection
1
2M1L
M1
Datum
1
2M2L
M2
Datum
2
3ML
M1
1
2M1L
M1
Datum
M2
Datum
M2
1
2M2L
Datum
M1
Datum
M1
M2
1
2M1L
Datum
M2
Datum
M1
M1
1
2M2L
1
2M1L
2
3ML
Datum
1
2M2L
M2
M2
Datum
2
3ML
Structural Analysis (II)
Chapter 5: Deflection
.( Rotation) (Deflection )
Rotation ( )=
Qelastic
Deflection (y) =
Qelastic
Melastic
Moment
Shear force
Negtive )
Positive )
Q
-ve
+ve
+ve
( )= - ve
Negtive )
Positive )
M
( )= + ve
Melastic
( y )= + ve
-ve
( y )= - ve
Solved Examples
Ex(1)
Using the Conjugate beam method, determine the rotation at points (a,b,c and d)
and deflection at points(c,d and e).
a
10t
2t/m'
c
Solution
10t
d
3t
EI = Constant
Reactions and Bending moment diagram (Original beam)
10t
2t/m'
10t
18.8t
a
3t
16.2t
6.0t.m
c
2*3
t.m
8 =2.25
47.4t.m
46.8t.m
2*3
t.m
8 =2.25
Structural Analysis (II)
Chapter 5: Deflection
Elastic loads( Area of bending moment)
6.0
6.0
2.25
12
71.1
t.m
47.4
46.8
71.1 70.2
Modified B.M.D( M )
EI
93.6
4.5
4.5
Conjugate beam
93.6
71.1
4.5
70.2
b
d
138.7
12
4.5
71.1
164.3
( M)
EI
6.0
12
Elastic Reactions
269.4
e
6.0
93.6
4.5
71.1
71.1
4.5
70.2
Elastic loads on Conjugate beam
132.7
Structural Analysis (II)
Chapter 5: Deflection
Required rotation and deflection
Rotation ( )=
Qelastic
Melastic
Deflection (y) =
Left
Right
+ve Sign summary
+ ve
Point (a)
a = 1 [164.3] = + 164.3 (Clockwise)
EI
EI
164.3
Point (c)
c = 1 [164.3-4.5-71.1] = + 88.7 (Clockwise)
EI
EI
yc = 1 [164.3(3)-4.5(1.5)-71.1(1)] = + 415.05 (Down)
EI
EI
93.6
164.3
Point (d)
b
d
12
d = 1 [ -138.7 -12 +93.6] = - 57.1 (Anti-Clockwise)
EI
EI
Point (e)
e = 1 [ -132.7] = - 132.7 (Anti-Clockwise)
EI
EI
ye = 1 [ -268.8] = - 269.4 (Upward)
EI
EI
138.7
b = 1 [-138.7] = - 138.7 (Anti-Clockwise)
EI
EI
138.7
4.5
71.1
Point (b)
269.4
e
132.7
Structural Analysis (II)
Ex(2)
Chapter 5: Deflection
Using the Conjugate beam method, determine the rotation at points (a,b,c and d )
and deflection at points(c and d ).
4t
d
4t/m'
2I
Solution
12t.m
d
Required rotation and deflection
B.M.D
Point (a)
a = 1 [+7.88] = + 7.88 (Clockwise)
EI
EI
18
18
12
3
9t.m
Conj.beam
d = 1 [-10.12] = - 10.12 (Anti-Clockwise)
EI
EI
yd = 1 [+ 12.36] = + 12.36 (Downward)
EI
EI
12.36
10.12
4.5
36
Elastic loads
a
d
18
36
9
18
18
7.88
9
18
Point (d)
18t.m
36
d
18
14.62
c = 1 [18 - 14.62 - 4.5]
EI
= - 1.12 (Anti-Clockwise)
EI
yc = 1 [14.62(3) + 4.5(1.0) -18(1.125)]
EI
= + 28.11 (Downward)
EI
18
4.5
14.62
18
4.5
4.5
18
b = 1 [-14.62] = - 14.62 (Anti-Clockwise)
EI
EI
d
2I
4*6
t.m
8 =18.0
Point (b)
Point (c)
6t.m
Elastic Reactions
Structural Analysis (II)
Ex(3)
2t/m'
Chapter 5: Deflection
Using the Conjugate beam method, determine :
* the rotation at points (a ,b,d and e ),
* the relative (change in) rotation at point( f ),
* the deflection at points(d ,e ,f and j).
j
6t
Solution
f
16t
2t/m'
j
4t
6t
EI = Constant
c
3t
6.75t
16.25t
40
10
10t.m
5t.m
b
9t.m
1t.m
16t.m
1.33
27
85.33
85.33
1.33
27
40
85.33
10
b
29.33
40
16
16
1.33
27
10
24.13
10.2
10
Structural Analysis (II)
Chapter 5: Deflection
Required rotations and deflections
a = 1 [+29.33]
EI
29.33
= +
(Clockwise)
EI
Point (b)
29.33
Point (f)(Internal Hinge )
f/L = 1 [-16+10-1.33] = - 7.33 (Anti-Clockwise)
EI
EI
f/R = 1 [-16+10-1.33+24.13 ] = + 16.8 (Clockwise)
EI
EI
16
f/L ]= + 16.8- -7.33 = + 24.13 = Rf
EI
EI
EI
EI
yf = 1 [-16(2)+10(1.33)-1.33(1)] = - 20 (Upward)
EI
EI
16
24.13
10
f/rel = [f/R
b = 1 [-16] =-16
EI
EI
(Anti-Clockwise)
1.33
Point (a)
10
Point (d)
d = 1 [29.33+10-42.7] = - 3.37 (Anti-Clockwise)
EI
EI
5t.m
d
29.33
yd= 1 [+29.33(4)+10(1.33)-42.7(1.5)]
EI
=+66.6
(Downward)
EI
16t.m
Point (e)
42.7
e = 1 [13.5-10.2 ] = + 3.3 (Clockwise)
EI
EI
ye= 1 [+10.2(3)-13.5(1)] = + 17.1 (Downward)
EI
EI
9t.m
10.2
13.5
Point (j)
Real beam
6t
2t/m'
Conj. beam
16.88
6.75t
29.33
2.25
t.m
11.25t.m
4.5
M = 6.75(3) - 6(1.5) = 11.25t.m
j
y = 1 [+29.33(3)-16.88(1) -4.5(1.5)] = + 64.36
EI
EI
j
(Downward)
11
Structural Analysis (II)
Ex(4)
Chapter 5: Deflection
Using the Conjugate beam method, determine :
* the rotation at points (c and e ),
* the relative (change in) rotation at point( d ),
* the deflection at points(c ,e and d ).
2t/m'
Solution
I d
2I
2I
7t
a
2I
8t.m
4t.m
B.M.D(Original beam)
16t.m
3.5
3.5
24.2
4t.m
4t.m 2t.m
4.0
c
21.33
16t.m
21.33
42.67
a
8.0
4.0
8.0
42.67
Elastic Reactions
4t
I d
7t.m
Conjugate beam
13t
7t
7t.m
2I
4t
16t
2t/m'
Reactions(Original beam)
7.0t.m
[take EI = 6000 t/cm]
8.0
4.0
8.0
16.29
c
4.0
27.25
12.29
12
Structural Analysis (II)
Chapter 5: Deflection
Required rotations and deflections
Point (c)
27.25
12.29
1 [-12.29] = - 0.002rad (Anti-Clockwise)
c = 6000
1 [-27.25] = - 0.454 cm (Upward)
yc = 6000
Point (d)(Internal Hinge )
3.5
24.2
1 [+ 3.5] = 5.833*10 -4 rad (Clockwise)
d/L = 6000
1 [+ 3.5 + 24.2 ] = + 4.6167*10 -3 (Clockwise)
d/R = 6000
d/rel =
d/R
24.2 = 4.033*10-3 rad
- d/L = Rd = 6000
EI
1 [3.5(0.67)] = + 0.039 cm (Downward)
yd = 6000
21.33
Point (e)
e
4.0
8.0
16.29
1 [-16.29-8-4+21.33] = - 0.00116 rad (Anti-Clockwise)
e = 6000
1 [16.29*4 + 8*2.67+ 4*1.33-21.33*1.5] = + 0.997 cm
ye = 6000
(Downward)
13
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Sa-2 Kani's Method ObjDokument7 SeitenSa-2 Kani's Method Objnirmalraj100% (2)
- IL For Indeterminate Structures7-37Dokument37 SeitenIL For Indeterminate Structures7-37Nirjhor KabirNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Asce) 0733-9445 (1984) 110 5 (1021)Dokument14 Seiten(Asce) 0733-9445 (1984) 110 5 (1021)susana_montero_5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions To Exercises PDFDokument6 SeitenSolutions To Exercises PDFJordan DimovNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1957-Dynamic Pressure On Accelerated Fluid ContainersDokument21 Seiten1957-Dynamic Pressure On Accelerated Fluid ContainersbehzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essay Questions FEMDokument21 SeitenEssay Questions FEMharshamech360Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 - Theory of Structure 2 PDFDokument23 SeitenLecture 1 - Theory of Structure 2 PDFChristopher PaladioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing Capacity 2019Dokument26 SeitenBearing Capacity 2019عبدالرحمن محمدNoch keine Bewertungen
- JNTU BTech Civil Engineering Advanced Structural Analysis Exam QuestionsDokument19 SeitenJNTU BTech Civil Engineering Advanced Structural Analysis Exam QuestionsMohammed AbidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frame Analysis: Determine Natural Periods and Design Base Shear ForcesDokument6 SeitenFrame Analysis: Determine Natural Periods and Design Base Shear Forcesnial69100% (1)
- 6 - Engesser's Theorem and Truss Deflections by Virtual Work PrinciplesDokument14 Seiten6 - Engesser's Theorem and Truss Deflections by Virtual Work PrinciplesFrans Alen SarmientoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Dynamics (Elective I) (CE72501) PDFDokument23 SeitenStructural Dynamics (Elective I) (CE72501) PDFAnonymous GaaXAYYNoch keine Bewertungen
- C&ENVENG 3020/7020 - Impulse Loading AnalysisDokument2 SeitenC&ENVENG 3020/7020 - Impulse Loading AnalysisShahidul Islam ShahariarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture-Three Moment TheoremDokument17 SeitenLecture-Three Moment TheoremIMJ JNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simplified Reinforced Concrete Edward G. NawyDokument342 SeitenSimplified Reinforced Concrete Edward G. NawyAref Malkawi100% (1)
- Direct Displacement MethodDokument5 SeitenDirect Displacement MethodTewodros AbateNoch keine Bewertungen
- TR 334 Tutorial-1Dokument5 SeitenTR 334 Tutorial-1Adaminovic MrishoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earthquake Analysis of StructuresDokument42 SeitenEarthquake Analysis of StructuresManmatha KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Soil Mechanics OverviewDokument5 SeitenAdvanced Soil Mechanics OverviewZack FengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duhamel's IntegralDokument5 SeitenDuhamel's IntegralMichael Bautista Baylon0% (1)
- Sheeting Wall Analysis by The Method of Dependent PressuresDokument7 SeitenSheeting Wall Analysis by The Method of Dependent PressuresRosey DalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel-Concrete Composite Columns-Ii PDFDokument38 SeitenSteel-Concrete Composite Columns-Ii PDFJaisree RathinamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stiffness Analysis of FramesDokument37 SeitenStiffness Analysis of FramesCarolina VacaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matrix Analysis of Framed Structures Exam QuestionsDokument2 SeitenMatrix Analysis of Framed Structures Exam QuestionsAmit ThoriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Influence LineDokument7 SeitenInfluence Linemr_sam91Noch keine Bewertungen
- Memo STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS II - SAN2601 Assignments 2020Dokument28 SeitenMemo STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS II - SAN2601 Assignments 2020Rachel Du PreezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Highway Curves NoteDokument47 SeitenHighway Curves NoteHarish joshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geotechnical Engineering-Ii: BSC Civil Engineering - 5 SemesterDokument15 SeitenGeotechnical Engineering-Ii: BSC Civil Engineering - 5 SemesterMuhammad HaroonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural dynamics problems and solutionsDokument8 SeitenStructural dynamics problems and solutionsamadeus135Noch keine Bewertungen
- Earthquake Analysis of Linear SystemsDokument67 SeitenEarthquake Analysis of Linear SystemsPrantik Adhar Samanta67% (3)
- Structural Dynamics UpdatedDokument24 SeitenStructural Dynamics UpdatedatifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Analysis TutorialDokument2 SeitenDynamic Analysis TutorialTharaka VidanageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matrix Analysis of Beams and GridsDokument34 SeitenMatrix Analysis of Beams and GridsGirish ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Direct Stiffness MethodDokument18 SeitenDirect Stiffness MethodJayChristian Quimson100% (1)
- Advanced Mechanics of Solids - Question SetDokument3 SeitenAdvanced Mechanics of Solids - Question SetAshish ZachariahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Retaining Walls (B&W)Dokument29 SeitenDesign of Retaining Walls (B&W)Abdul SalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Mindanao College of Engineering EducationDokument42 SeitenUniversity of Mindanao College of Engineering EducationLi LiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 1 1Dokument21 SeitenProblem 1 1Jingwei ZhongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Derive bending equation: M/I = σ/y = E/RDokument3 SeitenDerive bending equation: M/I = σ/y = E/Ryogesh vNoch keine Bewertungen
- Config Cppudm Model Load Userssoft - DLL Gen Zone Bric Size 2 2 2 Model UserssoftDokument13 SeitenConfig Cppudm Model Load Userssoft - DLL Gen Zone Bric Size 2 2 2 Model Userssoftdce_40Noch keine Bewertungen
- Direct Shear Test ReportDokument5 SeitenDirect Shear Test ReportRiya RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter One in Elastic Moment RedistributionDokument8 SeitenChapter One in Elastic Moment RedistributionHaftom GebreegziabiherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isolated foundation design and reinforcement calculationDokument10 SeitenIsolated foundation design and reinforcement calculationDino AbdelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plane Frame Analysis ModuleDokument8 SeitenPlane Frame Analysis ModuleRashedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bi-Axial Bending Column Design ExampleDokument4 SeitenBi-Axial Bending Column Design ExampleEmerson EdwigeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excess Pore-Water Pressure Using Skemptons B-BarDokument5 SeitenExcess Pore-Water Pressure Using Skemptons B-BarPuspa ChandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deflection of BeamsDokument28 SeitenDeflection of BeamsishwaryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determinacy and IndeterminacyDokument12 SeitenDeterminacy and IndeterminacyMode NaseerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7Dokument18 SeitenChapter 7René A. BarreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newmarks Method Script1Dokument2 SeitenNewmarks Method Script1Kintu MunabangogoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finalized Geo ReportDokument26 SeitenFinalized Geo ReportErik Yiew Tuang NgoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slab Design Sandhi KholaDokument15 SeitenSlab Design Sandhi Kholasakar shresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE4070 Structural Modelling Yield Line Analysis of Slab IETDokument18 SeitenCE4070 Structural Modelling Yield Line Analysis of Slab IETkartheepan100% (1)
- Celebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985Von EverandCelebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985Noch keine Bewertungen
- GATE Mechanical Engineering 2010 question paperDokument8 SeitenGATE Mechanical Engineering 2010 question paperaeroherozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuzzy PID Control For A Cubic Robot Balancing On Its Corner: Xiao-Gang RUAN, Yuan LI and Zhi-Gang CHENDokument8 SeitenFuzzy PID Control For A Cubic Robot Balancing On Its Corner: Xiao-Gang RUAN, Yuan LI and Zhi-Gang CHENantonio spalloneNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Make Colliding Pattern of Device ClearDokument4 Seiten1 Make Colliding Pattern of Device ClearAnonymous 48jYxR1CNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec9 Ex94 Beam Column HAZDokument5 SeitenEc9 Ex94 Beam Column HAZimotalpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hotel (A) Slabs - :: Bearing CapacityDokument50 SeitenHotel (A) Slabs - :: Bearing CapacityAdam AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Doc 3Dokument1 SeiteNew Doc 3Adam AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Doc 24Dokument2 SeitenNew Doc 24Adam AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Doc 4Dokument1 SeiteNew Doc 4Adam AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Introduction ModelDokument12 Seiten1-Introduction ModelAdam AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Doc 3Dokument1 SeiteNew Doc 3Adam AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Doc 4Dokument1 SeiteNew Doc 4Adam AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4-Internal Forces Beams - 1 ModelDokument15 Seiten4-Internal Forces Beams - 1 ModelAdam AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- NewDokument8 SeitenNewAdam AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 - Inclined BEAMSDokument12 Seiten7 - Inclined BEAMSAdam AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Install GmtsarDokument24 SeitenHow To Install GmtsardedetmixNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2:4 Decoder: DECODER: A Slightly More Complex Decoder Would Be The N-To-2n Type Binary Decoders. These TypesDokument6 Seiten2:4 Decoder: DECODER: A Slightly More Complex Decoder Would Be The N-To-2n Type Binary Decoders. These TypesPavithraRamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coco Press KitDokument55 SeitenCoco Press KitPaula RiddenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision of Bs 8002, 8004, AND 8081Dokument34 SeitenRevision of Bs 8002, 8004, AND 8081Rupesh Kaushik100% (1)
- For Steel Cage Lapping by Using U-ClipDokument4 SeitenFor Steel Cage Lapping by Using U-Cliptin aungtunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Please Note That This Form Details Exploration and Production Api Titles Available For OrderDokument8 SeitenPlease Note That This Form Details Exploration and Production Api Titles Available For Orderhaotran68Noch keine Bewertungen
- Schneider LV Switchboard Inspection GuideDokument59 SeitenSchneider LV Switchboard Inspection GuideAlp Arslan Ok100% (1)
- 06-Fc428mar Water-in-Fuel Indicator Sensor Circuit - Voltage Above Normal or Shorted To High SourceDokument3 Seiten06-Fc428mar Water-in-Fuel Indicator Sensor Circuit - Voltage Above Normal or Shorted To High SourceSuryadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Mining Shovel 6040AC: 08. Attachment Functions - FSDokument20 SeitenHydraulic Mining Shovel 6040AC: 08. Attachment Functions - FShector50% (2)
- Catálogo King LaiDokument144 SeitenCatálogo King LaiJason Salas FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oksd Icwh 1993 RoisumDokument40 SeitenOksd Icwh 1993 RoisumKamalam CloudsoftNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gps VulnerabilityDokument28 SeitenGps VulnerabilityaxyyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mixers Towable Concrete Essick EC42S Rev 8 Manual DataId 18822 Version 1Dokument84 SeitenMixers Towable Concrete Essick EC42S Rev 8 Manual DataId 18822 Version 1Masayu MYusoffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Government Engineering College Surveying Lab ManualDokument26 SeitenGovernment Engineering College Surveying Lab ManualNittin BhagatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 - Critical Customers Complains enDokument8 Seiten02 - Critical Customers Complains enKJDNKJZEF100% (1)
- CFS50 motor feedback installation instructionsDokument1 SeiteCFS50 motor feedback installation instructionsJavier AlzateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hino 500S Catalog LR PDFDokument8 SeitenHino 500S Catalog LR PDFZulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duet CE-3301 Geotechnical Engineering - IDokument37 SeitenDuet CE-3301 Geotechnical Engineering - IShekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Lab ReportDokument2 SeitenPhysics Lab ReportFelix SonsunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zener DataDokument2 SeitenZener Dataapi-27149887Noch keine Bewertungen
- LDX2101 Spec SheetDokument2 SeitenLDX2101 Spec SheetGaurav NarulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crompton Greaves LimitedDokument3 SeitenCrompton Greaves LimitedNitish SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- As ISO 128.23-2005 Technical Drawings - General Principles of Presentation Lines On Construction DrawingsDokument9 SeitenAs ISO 128.23-2005 Technical Drawings - General Principles of Presentation Lines On Construction DrawingsSAI Global - APAC0% (3)
- EXPERIMENT 3a and 3b - Aluminum Content Via Redox and ColorimeterDokument13 SeitenEXPERIMENT 3a and 3b - Aluminum Content Via Redox and ColorimeterTrupti soniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determining The Redundancy FactorDokument6 SeitenDetermining The Redundancy FactorEdris Salehi GolsefidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5TH Week EnergyDokument6 Seiten5TH Week EnergyMira VeranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Switching Theory and Logic Design PDFDokument159 SeitenSwitching Theory and Logic Design PDFSai TejaswiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caterpillar 914GDokument28 SeitenCaterpillar 914GForomaquinas100% (3)
- As 4123.4-2008 Mobile Waste Containers Containers With Four Wheels With A Capacity From 750 L To 1700 L WithDokument7 SeitenAs 4123.4-2008 Mobile Waste Containers Containers With Four Wheels With A Capacity From 750 L To 1700 L WithSAI Global - APACNoch keine Bewertungen