Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
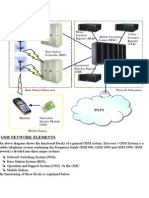
20.cellular System
Hochgeladen von
deepak19m0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
65 Ansichten2 SeitenOriginaltitel
20.Cellular System
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
65 Ansichten2 Seiten20.cellular System
Hochgeladen von
deepak19mCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
Cellular system
In a cellular system, the covering area of an operator is divided into cells. A
cell corresponds to the covering area of one transmitter or a small collection
of transmitters. The size of a cell is determined by the transmitter’s power.
The concept of cellular systems is the use of low power transmitters in order
to enable the efficient reuse of the frequencies. In fact, if the transmitters
used are very powerful, the frequencies cannot be reused for hundred of
kilometers as they are limited to the covering area of the transmitter.
The frequency band allocated to a cellular mobile radio system is distributed
over a group of cells and this distribution is repeated in all the covering area
of an operator. The whole number of radio channels available can then be
used in each group of cells that form the covering area of an operator.
Frequencies used in a cell will be reused several cells away. The distance
between the cells using the same frequency must be sufficient to avoid
interference. The frequency reuse will increase considerably the capacity in
number of users.
In order to work properly, a cellular system must verify the following two
main conditions:
The power level of a transmitter within a single cell must be limited in
order to reduce the interference with the transmitters of neighboring
cells. The interference will not produce any damage to the system if a
distance of about 2.5 to 3 times the diameter of a cell is reserved
between transmitters. The receiver filters must also be very
performant.
Neighboring cells cannot share the same channels. In order to reduce
the interference, the frequencies must be reused only within a certain
pattern.
In order to exchange the information needed to maintain the communication
links within the cellular network, several radio channels are reserved for the
signaling information.
Cluster
The cells are grouped into clusters. The number of cells in a cluster must be
determined so that the cluster can be repeated continuously within the
covering area of an operator. The typical clusters contain 4, 7, 12 or 21 cells.
The number of cells in each cluster is very important. The smaller the
number of cells per cluster is, the bigger the number of channels per cell will
be. The capacity of each cell will be therefore increased. However a balance
must be found in order to avoid the interference that could occur between
neighbouring clusters. This interference is produced by the small size of the
clusters (the size of the cluster is defined by the number of cells per cluster).
The total number of channels per cell depends on the number of available
channels and the type of cluster used.
Types of cells
The density of population in a country is so varied that different
types of cells are used:
Macro cells
Micro cells
Selective cells
Umbrella cells
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- HandoffDokument1 SeiteHandoffdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 30.trafic in Interfacing-MocDokument2 Seiten30.trafic in Interfacing-Mocdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 33.benefits From TrainingDokument1 Seite33.benefits From Trainingdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mon Control ChannelsDokument1 SeiteMon Control Channelsdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 28.traffic ChannelsDokument1 Seite28.traffic Channelsdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24.air Interface ChannelsDokument2 Seiten24.air Interface Channelsdeepak19m100% (1)
- 27.dedicated Control ChannelsDokument1 Seite27.dedicated Control Channelsdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21.radio ChannelDokument2 Seiten21.radio Channeldeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 22.transmission Rate& Channel ConceptDokument1 Seite22.transmission Rate& Channel Conceptdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oadcast ChannelsDokument2 SeitenOadcast Channelsdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 23.bursts and FramesDokument1 Seite23.bursts and Framesdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- DatabaseDokument1 SeiteDatabasedeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work ElementsDokument1 SeiteWork Elementsdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14.functioning of MSCDokument2 Seiten14.functioning of MSCdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17.authentication CenterDokument2 Seiten17.authentication Centerdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18.functions of EirDokument1 Seite18.functions of Eirdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16.functioning of HLRDokument2 Seiten16.functioning of HLRdeepak19m100% (1)
- 13.the Base Station ControllerDokument1 Seite13.the Base Station Controllerdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15.functioning of VLRDokument1 Seite15.functioning of VLRdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12.the SIMDokument1 Seite12.the SIMdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.mobile StationDokument1 Seite11.mobile Stationdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9.introduction To GSM TechnologyDokument2 Seiten9.introduction To GSM Technologydeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.tech. Dept.& Org - StructureDokument2 Seiten8.tech. Dept.& Org - Structuredeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Company ProfileDokument2 SeitenCompany Profiledeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- SIB 15 in eMBMSDokument9 SeitenSIB 15 in eMBMSAshish ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rfid Based Theft Prevention SystemDokument3 SeitenRfid Based Theft Prevention SystemCrispNoch keine Bewertungen
- tronics Unit. This enables connection to any radio from any crew position. 20. B737 Typical Radio tuning Panel Each VHF radio has an Active and Standby frequency. Radio Tuning Switch light indicates which radio is selected on this panel 21. B737 Typical Radio tuning Panel Panel OFF light illuminated White. Not connected to any Radio. 22. B737 Typical Radio tuning Panel HF Sensitivity Knob. Hard wire connected to ON SIDE HF Radio. Captain HF 1 and F/O HF 2 as installed. 23. B737 Typical Radio tuning Panel AM Switch Push – light on sets the AM (amplitude modulation) or light off USB (upper side band) mode for the selected HF radio. 24. B737 Typical Radio tuning Panel VHF TEST Switch Push – • removes automatic squelch feature, permitting reception of background noise and thereby testing receiver operation • improves reception of weak signals. 25. The selected Radio is not available The Panel is not able to communicate with the selected Radio. It does not mean a Radio failure has occurred.Dokument3 Seitentronics Unit. This enables connection to any radio from any crew position. 20. B737 Typical Radio tuning Panel Each VHF radio has an Active and Standby frequency. Radio Tuning Switch light indicates which radio is selected on this panel 21. B737 Typical Radio tuning Panel Panel OFF light illuminated White. Not connected to any Radio. 22. B737 Typical Radio tuning Panel HF Sensitivity Knob. Hard wire connected to ON SIDE HF Radio. Captain HF 1 and F/O HF 2 as installed. 23. B737 Typical Radio tuning Panel AM Switch Push – light on sets the AM (amplitude modulation) or light off USB (upper side band) mode for the selected HF radio. 24. B737 Typical Radio tuning Panel VHF TEST Switch Push – • removes automatic squelch feature, permitting reception of background noise and thereby testing receiver operation • improves reception of weak signals. 25. The selected Radio is not available The Panel is not able to communicate with the selected Radio. It does not mean a Radio failure has occurred.Syed Salman UddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sharing An Antenna Doesn't Mean Giving Up Control: White PaperDokument12 SeitenSharing An Antenna Doesn't Mean Giving Up Control: White PaperWalter MazibukoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular System Design Trade OffsDokument15 SeitenCellular System Design Trade OffsAzeem IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amphenol - 7833600 - LogperiodicDokument2 SeitenAmphenol - 7833600 - Logperiodicfar333Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3G KpisDokument60 Seiten3G KpisdongarsinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lege All ChartsDokument16 SeitenLege All ChartsJaucafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Frequency ModulationDokument88 SeitenChapter 4 Frequency ModulationtestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Continuous Wave RadarDokument6 SeitenContinuous Wave RadarVenkat SaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 800 10292V02Dokument2 Seiten800 10292V02Atef EssidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ruckus RFX Template - 1Dokument42 SeitenRuckus RFX Template - 1HendriJuniantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZTE RAN Sharing Solution-MOCNDokument43 SeitenZTE RAN Sharing Solution-MOCNNeoRa Ndivo Rams100% (3)
- Activity 5 SUPPRESSED CARRIER AMDokument9 SeitenActivity 5 SUPPRESSED CARRIER AMNichole BalagatNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMS2Dokument490 SeitenCOMS2Mora JoramNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTE RadioDokument162 SeitenLTE RadioLatycia ChalistyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monitoring and Fault Detection System For Power Transmission Using GSM TechnologyDokument6 SeitenMonitoring and Fault Detection System For Power Transmission Using GSM Technologynatnael belayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless and Mobile NetworksDokument15 SeitenWireless and Mobile NetworksKumar MuruganNoch keine Bewertungen
- VHLPX3 26 1WH - ADokument5 SeitenVHLPX3 26 1WH - ANijad NasrNoch keine Bewertungen
- UH013 Owners ManualDokument19 SeitenUH013 Owners ManualRoxana Aldea-CiaciruNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPS AssignmentDokument8 SeitenGPS AssignmentChristine M M Mariwo100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Cellular ConceptDokument46 SeitenChapter 3 Cellular ConceptAnand DeshbhratarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Phone Radiation: Analysis of DataDokument2 SeitenMobile Phone Radiation: Analysis of DataŚáńtőśh MőkáśhíNoch keine Bewertungen
- IstructE Question Selection 2015-2020Dokument74 SeitenIstructE Question Selection 2015-2020Vasile BudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TV-5 Downlink ParametersDokument1 SeiteTV-5 Downlink ParametersSrinivas ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- eRAN KPI Reference (V100R013C10 - 01) (PDF) - ENDokument98 SeiteneRAN KPI Reference (V100R013C10 - 01) (PDF) - ENTry Test100% (1)
- An Overview of Transceiver SystemsDokument11 SeitenAn Overview of Transceiver SystemssurvivalofthepolyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scalable Cell-Free Massive MIMO SystemsDokument15 SeitenScalable Cell-Free Massive MIMO SystemsMuteen MunawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- P25 Training GuideDokument104 SeitenP25 Training Guidesimon_mitchell_367% (3)
- Digital Modulation TechniquesDokument34 SeitenDigital Modulation TechniquesSerial SpyNoch keine Bewertungen