Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 3
Hochgeladen von
JUSASBCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 3
Hochgeladen von
JUSASBCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
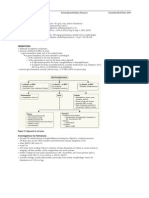
NP3 Nephrology
Basic Anatomy Review
Essential Med Notes 2015
Afferent arteriole
Renal Hemodynamic Parameters
RBF = 20% of CO, ~1 L/min
RPF = RBF*(1-Hct)
GFR = ~120 mL/min in healthy adult
(99% of this volume is reabsorbed)
FF = GFR/RPF (normally 20%)
Prostaglandins = dilation NSAIDs = constriction
Efferent arteriole
ACEI = dilation
Afferent arteriole
Angiotensin II = constriction
Bowmans space
Proximal
tubule
Juxtaglomerular
cells
Podocyte
Capillary
Endothelium
Mesangial cell
Mesangial cell
Podocyte
(visceral epithelium)
Bowmans capsule
(parietal epithelium)
Bowmans space
Endothelial
cell
Tobi Lam 2012
Efferent arteriole
Figure 1. The glomerulus
The Renal Tubules
reabsorption and secretion occur between the renal tubules and vasa recta forming urine for
excretion
each segment of the tubule selectively transports various solutes and water and is targeted by
specific diuretics
Proximal tubule:
Osmotic diuretics
Organic acids
Glucose 90%
Amino acids 90%
Phosphates 90%
H+
+
K+ H
Aldosterone receptor
(late distal tubule
and collecting duct)
ENaC
channels
Na+
K+
Distal tubule:
Cortex
Medulla
NaCl 5% H 0 HCO
2
3
Ca2+
Thiazide diuretics
Na+ 10%- K - 2Cl
Ca - Mg
2+
2+
H20 2%
Descending thin limb
of loop of Henle
Ascending thick
limb of loop
of Henle:
Loop diuretics
Ascending thin
limb of loop
of Henle:
Loop diuretics
Figure 2. Tubular segments of the nephron
ADH receptor
Aquaporin
channel
ADH
H2O
NaCl
Urea
H2O
Collecting duct:
K+ sparing
diuretics
Andrew Q. Tran 2014 (after Jerusha Ellis 2014)
HCO3 90%
Na+ 80%
H20 80%
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Kidney Biopsy Finding of The Glomeruli - SUN 2019Dokument78 SeitenKidney Biopsy Finding of The Glomeruli - SUN 2019Galih AryyagunawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nephrology PDFDokument38 SeitenNephrology PDFOmar AyashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 35Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 35JUSASB50% (2)
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 35Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 35JUSASB50% (2)
- Renal PhysiologyDokument129 SeitenRenal PhysiologynehaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Renal PhysiologyDokument56 Seiten2 Renal PhysiologyNoraine Princess TabangcoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- PD Prescription Present 4-8-52Dokument74 SeitenPD Prescription Present 4-8-52Kong Kong KongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Approach To RPRF PDFDokument6 SeitenClinical Approach To RPRF PDFshankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antipsychotics - FactsheetDokument12 SeitenAntipsychotics - FactsheetColonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 9 - Renal System PhysiologyDokument18 SeitenExercise 9 - Renal System Physiologynhungto740% (1)
- Clinical Nephrology Dialysis and TransplantationDokument1.539 SeitenClinical Nephrology Dialysis and Transplantationalrafeek1050100% (1)
- NephroTube Synopsis - GNDokument41 SeitenNephroTube Synopsis - GNSelena GajićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Continuous Renal Replacement TherapyDokument40 SeitenContinuous Renal Replacement TherapyDiane Angela100% (1)
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 10Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 10JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Physiology For The BoardsDokument37 SeitenRenal Physiology For The BoardsRainy Day100% (1)
- References: NP40 Nephrology Landmark Nephrology Trials/References Essential Med Notes 2015Dokument1 SeiteReferences: NP40 Nephrology Landmark Nephrology Trials/References Essential Med Notes 2015JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 5Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 5JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- NephrologyDokument9 SeitenNephrologyRohit BharadwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Update On Glomerulopathies - Clinical and Treatment AspectsDokument482 SeitenAn Update On Glomerulopathies - Clinical and Treatment AspectsJulio SobremazasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 23Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 23JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revise Nephrology Manipal - CME BrochureDokument2 SeitenRevise Nephrology Manipal - CME BrochureLydia IsaacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specialty Certificate Examination in Nephrology BlueprintDokument2 SeitenSpecialty Certificate Examination in Nephrology BlueprintTariq ZayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intra and Intradialytic Hypotension and Hypertension InrigDokument29 SeitenIntra and Intradialytic Hypotension and Hypertension InrigMonica HerreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Questions by Dr. OkashaDokument78 SeitenRenal Questions by Dr. Okashamohammed okashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical School Renal ReviewDokument32 SeitenMedical School Renal ReviewwmtxbbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 7Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 7JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 21Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 21JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 12Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 12JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 31Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 31JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- AKI in SepsisDokument45 SeitenAKI in SepsisIkeBundaAdellulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 20Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 20JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tubulopathies. Interstitial NephritisDokument34 SeitenTubulopathies. Interstitial NephritisIaros OlgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Acute Glomerulonephritis in Children: Children's Services Medical GuidelinesDokument7 SeitenManagement of Acute Glomerulonephritis in Children: Children's Services Medical GuidelinesdaypranitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Writing The Home Hemodialysis PrescriptionDokument22 SeitenWriting The Home Hemodialysis Prescriptionstudent_physicianNoch keine Bewertungen
- UAB CRRT Academy 2018 FormulasDokument5 SeitenUAB CRRT Academy 2018 FormulasJelena Obrenovic StankovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tubulointerstitial Diseases: Dr. Raid JastaniaDokument48 SeitenTubulointerstitial Diseases: Dr. Raid JastaniaThomas McconnellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal PathologyDokument28 SeitenRenal PathologyApril Deveras JudillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decision Algorithm For Prescribing SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Receptor AgonistsDokument11 SeitenDecision Algorithm For Prescribing SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Receptor AgonistsNati BocciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nephrology CritiquesDokument18 SeitenNephrology CritiquesYelle QuilatanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NQQ AnswersDokument16 SeitenNQQ AnswersNizar ShormanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute On Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokument6 SeitenAcute On Chronic Kidney DiseaseElizabeth LieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lange Nephrology EssentialsDokument9 SeitenLange Nephrology EssentialsAlejandro GarcíaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potassium For Med StudentsDokument28 SeitenPotassium For Med StudentsJoel Topf100% (11)
- CJN 04330418 FullDokument8 SeitenCJN 04330418 FullJúlia Andrade SossaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Pearls in NephrologyDokument5 SeitenClinical Pearls in NephrologyEdmilson R. LimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diabetic Nephropathy: Assisstant Professor Dr. Mihaela-Dora DonciuDokument65 SeitenDiabetic Nephropathy: Assisstant Professor Dr. Mihaela-Dora DonciuFloreaAndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nephrology DR Osama Mahmoud PDFDokument83 SeitenNephrology DR Osama Mahmoud PDFMaria PatituNoch keine Bewertungen
- 28.03.23 Nephrology SeminarDokument5 Seiten28.03.23 Nephrology SeminarJerin XavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tubular Functions of KidneyDokument161 SeitenTubular Functions of KidneyPhysiology by Dr RaghuveerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 39Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 39JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intradialitic HypotensionDokument7 SeitenIntradialitic HypotensionanitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyponatremia in Children 03.19.2010Dokument23 SeitenHyponatremia in Children 03.19.2010Emily EresumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Core Curriculum NefrolitiasisDokument13 SeitenCore Curriculum NefrolitiasisOscar MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Approach To A Patient With An Acid-Base DisturbanceDokument3 SeitenClinical Approach To A Patient With An Acid-Base Disturbancefidelurtecho4881Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sodium and Potassium DisordersDokument7 SeitenSodium and Potassium DisordersShia LevyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Update in Internal Medicine - 2020: AnnualDokument8 SeitenUpdate in Internal Medicine - 2020: AnnualVictor Hugo MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robert W. Schrier - Atlas of Diseases of The Kidney Volume 03 PDFDokument175 SeitenRobert W. Schrier - Atlas of Diseases of The Kidney Volume 03 PDFRobertoBacaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nephrology: Omar K MRCP IrelandDokument54 SeitenNephrology: Omar K MRCP IrelandManmeet SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetic Diseases of the KidneyVon EverandGenetic Diseases of the KidneyRichard P. LiftonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Disease in Cancer PatientsVon EverandRenal Disease in Cancer PatientsKevin W. FinkelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Notes Unit 1Dokument66 SeitenRenal Notes Unit 1Zha-Raa'iaam L SamoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 37Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 37JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antipsychotics Factsheet pg2Dokument1 SeiteAntipsychotics Factsheet pg2JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- FA 2016 Step 1 - Reference ValuesDokument2 SeitenFA 2016 Step 1 - Reference ValuesJUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMLEX Normal Adult Laboratory ValuesDokument5 SeitenCOMLEX Normal Adult Laboratory ValuesJUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 33Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 33JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 34Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 34JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 36Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 36JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 38Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 38JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 27Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 27JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 17Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 17JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 39Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 39JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 28Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 28JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 32Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 32JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 30Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 30JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 29Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 29JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 31Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 31JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 24Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 24JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 23Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 23JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 18Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 18JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 26Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 26JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 25Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 25JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 22Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 22JUSASB0% (1)
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 15Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 15JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 14Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 14JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 20Dokument1 SeiteToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 20JUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen