Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Atm
Hochgeladen von
Ankit Jandial0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
98 Ansichten6 Seiten1. An ATM allows bank customers to access their accounts and conduct financial transactions without a bank teller. Customers can check balances, deposit funds, withdraw cash, and transfer funds using the ATM.
2. Key use cases for the ATM include checking balances, making deposits by inserting cash and checks into an envelope, withdrawing cash which is dispensed from the machine, and transferring funds between accounts.
3. An ATM technician maintains and repairs the ATM by replenishing supplies like cash and paper, performing upgrades, running diagnostics, and fixing problems with components like card readers and cash dispensing systems.
Originalbeschreibung:
none
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument melden1. An ATM allows bank customers to access their accounts and conduct financial transactions without a bank teller. Customers can check balances, deposit funds, withdraw cash, and transfer funds using the ATM.
2. Key use cases for the ATM include checking balances, making deposits by inserting cash and checks into an envelope, withdrawing cash which is dispensed from the machine, and transferring funds between accounts.
3. An ATM technician maintains and repairs the ATM by replenishing supplies like cash and paper, performing upgrades, running diagnostics, and fixing problems with components like card readers and cash dispensing systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
98 Ansichten6 SeitenAtm
Hochgeladen von
Ankit Jandial1. An ATM allows bank customers to access their accounts and conduct financial transactions without a bank teller. Customers can check balances, deposit funds, withdraw cash, and transfer funds using the ATM.
2. Key use cases for the ATM include checking balances, making deposits by inserting cash and checks into an envelope, withdrawing cash which is dispensed from the machine, and transferring funds between accounts.
3. An ATM technician maintains and repairs the ATM by replenishing supplies like cash and paper, performing upgrades, running diagnostics, and fixing problems with components like card readers and cash dispensing systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 6
EXP.
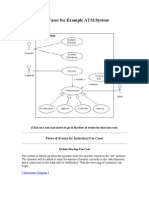
2 :- BANK ATM USE CASE
VIEW
A bank is a financial intermediary that creates credit by
lending money to a borrower, thereby creating a
corresponding deposit on the bank's balance sheet.
Lending activities can be performed either directly or
indirectly through capital markets.
An automated teller machine (ATM) or the automatic
banking machine (ABM) is a banking subsystem (subject)
that provides bank customers with access to financial
transactions in a public space without the need for a
cashier, clerk or bank teller.
Customer (actor) uses bank ATM to check balances of
his/her bank accounts, deposit funds, withdraw cash
and/or transfer funds (use cases). ATM Technician
provides maintenance and repairs. All these use cases
also involve Bank actor whether it is related to customer
transactions or to the ATM servicing.
CHECK BALANCE :
At most ATMs, one of the screen options is whether or not
you want a receipt. Request a receipt when you use the
ATM, and your account balance will usually show up on
the printout. Depending on the ATM machine, you may
have to request the balance to have it show up on your
receipt.
DEPOSIT FUNDS :A deposit transaction asks the customer to choose a type
of account to deposit to (e.g. checking) from a menu of
possible accounts, and to type in a dollar amount on the
keyboard. The transaction is initially sent to the bank to
verify that the ATM can accept a deposit from this
customer to this account. If the transaction is approved,
the machine accepts an envelope from the customer
containing cash and/or checks before it issues a receipt.
Once the envelope has been received, a second message
is sent to the bank, to confirm that the bank can credit
the customer's account - contingent on manual
verification of the deposit envelope contents by an
operator later.
WITHDRAW CASH :A withdrawal transaction asks the customer to choose a
type of account to withdraw from (e.g. checking) from a
menu of possible accounts, and to choose a dollar
amount from a menu of possible amounts. The system
verifies that it has sufficient money on hand to satisfy the
request before sending the transaction to the bank. (If
not, the customer is informed and asked to enter a
different amount.) If the transaction is approved by the
bank, the appropriate amount of cash is dispensed by the
machine before it issues a receipt.
TRANSFER FUNDS :A transaction use case is started within a session when
the customer chooses a transaction type from a menu of
options. The customer will be asked to furnish appropriate
details (e.g. account(s) involved, amount). The
transaction will then be sent to the bank, along with
information from the customer's card and the PIN the
customer entered.
If the bank approves the transaction, any steps needed to
complete the transaction (e.g. dispensing cash or
accepting an envelope) will be performed, and then a
receipt will be printed. Then the customer will be asked
whether he/she wishes to do another transaction.
If the bank reports that the customer's PIN is invalid, the
Invalid PIN extension will be performed and then an
attempt will be made to continue the transaction. If the
customer's card is retained due to too many invalid PINs,
the transaction will be aborted, and the customer will not
be offered the option of doing another.
If a transaction is cancelled by the customer, or fails for
any reason other than repeated entries of an invalid PIN,
a screen will be displayed informing the customer of the
reason for the failure of the transaction, and then the
customer will be offered the opportunity to do another.
The customer may cancel a transaction by pressing the
Cancel key as described for each individual type of
transaction below.
All messages to the bank and responses back are
recorded in the ATM's log.
MAINTENANCE & REPAIR:ATM Technician maintains or repairs Bank ATM.
Maintenance use case includes Replenishing ATM with
cash, ink or printer paper, Upgrades of hardware,
firmware or software, and remote or on-site Diagnostics.
Diagnostics is also included in (shared with) Repair use
case.
Automated teller machine (ATM) technicians, also called
ATM servicers or repairers, diagnose, repair and install
ATM machines. ATM field technicians travel to client
locations to diagnose and fix the problem on site or
remove the machine and take it back to the shop where it
5
will be worked on by ATM bench technicians. Using
equipment that includes multimeters, diagnostic software
and hand tools, ATM technicians fix problems such as
worn card readers and malfunctioning cash dispensing
systems. As the financial industry implements new
technology, more ATM technicians are required to work
on electronic kiosks as well.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Summary of Ahmed Siddiqui & Nicholas Straight's The Anatomy of the SwipeVon EverandSummary of Ahmed Siddiqui & Nicholas Straight's The Anatomy of the SwipeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Payment Collection for Small Business: QuickStudy Laminated Reference Guide to Customer Payment OptionsVon EverandPayment Collection for Small Business: QuickStudy Laminated Reference Guide to Customer Payment OptionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Requirements Statement For Example ATM SystemDokument11 SeitenRequirements Statement For Example ATM SystemBibhu R. TuladharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Requirements For Example ATM SystemDokument14 SeitenRequirements For Example ATM Systemamel2910Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test Cases For Atm SystemDokument26 SeitenTest Cases For Atm Systembrijesh100% (1)
- Requirements Statement For Example ATM SystemDokument2 SeitenRequirements Statement For Example ATM Systemsushil_programmerNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Use Case?Dokument5 SeitenWhat Is A Use Case?Waqas Zafar BhattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use Cases For ATM SystemDokument10 SeitenUse Cases For ATM SystemNitin PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use Case ATMDokument14 SeitenUse Case ATMMohd FirdausNoch keine Bewertungen
- Requirements Statement For ATM SystemDokument2 SeitenRequirements Statement For ATM SystemcnjoyusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 2 - Test Execution From Ad-Hoc Specification: 1.0 Requirements Statement For ATM SystemDokument4 SeitenLab 2 - Test Execution From Ad-Hoc Specification: 1.0 Requirements Statement For ATM Systemillusion90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Use Case - Example ATM SystemDokument5 SeitenUse Case - Example ATM Systemvictorj63Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bank ATM: Subject Actor Use CasesDokument3 SeitenBank ATM: Subject Actor Use CasestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ooad AtmDokument5 SeitenOoad AtmHarikrishna NethaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automated Teller Machine-RevisionDokument10 SeitenAutomated Teller Machine-RevisionwaweruhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automated Teller MachineDokument11 SeitenAutomated Teller MachinewaweruhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use Cases For Example ATM SystemDokument54 SeitenUse Cases For Example ATM SystemGayatri SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banking SystemDokument6 SeitenBanking SystemSapuan HussinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use CasesDokument8 SeitenUse CasesGwen HarrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Simulated ATM For A BankDokument10 SeitenA Simulated ATM For A BankNAUGHTYNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATM Case Study With Class Diagram and State Transition DiaDokument5 SeitenATM Case Study With Class Diagram and State Transition DiaKaustubh KulkarniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atm-Fr Atm Functional RequirementsDokument4 SeitenAtm-Fr Atm Functional RequirementsYO BOY'SNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATM Management SystemDokument2 SeitenATM Management SystemKanu Priya100% (1)
- Atm ProjectDokument17 SeitenAtm ProjectSreyoshi Shoili100% (2)
- ATM UC Model ElaborationDokument2 SeitenATM UC Model ElaborationsachinbiherNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCBL - Prime Cash (ATM)Dokument38 SeitenPCBL - Prime Cash (ATM)Saadat KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Out Sources of ATMDokument55 SeitenOut Sources of ATMRadhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RealizeDokument9 SeitenRealizeNabuteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use Cases For AtmDokument5 SeitenUse Cases For Atmsupernatural123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Software Architecture ATM ExampleDokument3 SeitenSoftware Architecture ATM ExampleOswald_Alving100% (1)
- Atm Sym Ot AssnmtDokument9 SeitenAtm Sym Ot AssnmtKeerthi HmNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATM RequirementsDokument4 SeitenATM RequirementsCristea Maria ClaudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atm Use Case ToolsDokument13 SeitenAtm Use Case Toolssathvik0% (1)
- ATM DescriptionDokument8 SeitenATM DescriptionKomal SrivastavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1: Software Requirement DevelopmentDokument5 SeitenAssignment 1: Software Requirement DevelopmentMahazir ShezanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uml Diagram For Banking SystemDokument63 SeitenUml Diagram For Banking SystemVivek TamrakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hospital Management System Use Case Diagram ExampleDokument10 SeitenHospital Management System Use Case Diagram Examplebooks_sumi33% (3)
- ATM Simulation Example: AG Software Engineering: Processes and MeasurementDokument47 SeitenATM Simulation Example: AG Software Engineering: Processes and MeasurementSafi SamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Payment Gateway TestingDokument15 SeitenPayment Gateway TestingavinashrocksNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is An Automated Teller MachineDokument9 SeitenWhat Is An Automated Teller Machine719d0011Noch keine Bewertungen
- Muffakham Jah College: Department of Information TechnologyDokument11 SeitenMuffakham Jah College: Department of Information TechnologyishaqkhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Banking Transactions: Your CustomerDokument6 SeitenE-Banking Transactions: Your CustomerJasleen KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Software Engineering: Section 3Dokument25 SeitenSoftware Engineering: Section 3Mohamed Abdel-AzizNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATM Requirement DocumentDokument9 SeitenATM Requirement Documentdeverpo leandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATM Problem StatementDokument1 SeiteATM Problem StatementHarshavardhan Reddy67% (12)
- Use Case Template and ATM ExampleDokument13 SeitenUse Case Template and ATM Exampleadil054Noch keine Bewertungen
- Software Requirement Specification For ATM: 1. Cash DepositDokument10 SeitenSoftware Requirement Specification For ATM: 1. Cash DepositRai JiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uml Exp 1 DiscriptionDokument3 SeitenUml Exp 1 Discriptionswathi.nNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment CBMS: Ques 1. Explain Pre-Paid and Post-Paid Payment Systems in DetailDokument8 SeitenAssignment CBMS: Ques 1. Explain Pre-Paid and Post-Paid Payment Systems in Detail19001601062 VAISHALINoch keine Bewertungen
- Pranjal SEDokument39 SeitenPranjal SEHarry potterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fin113 12FDokument2 SeitenFin113 12FMOLINA JEAN BERNARD T.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Software Design & Development Spring 2010 Sheller: Atm Use Cases - Work (s10)Dokument1 SeiteSoftware Design & Development Spring 2010 Sheller: Atm Use Cases - Work (s10)Kumar Anupam100% (1)
- SRS For ATM SystemDokument21 SeitenSRS For ATM SystemUrja DhabardeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atm - ApplicationDokument2 SeitenAtm - ApplicationŽoHřa NīšA ŚỹEð50% (2)
- Program-2: Use Case of Atm MachineDokument3 SeitenProgram-2: Use Case of Atm MachineSumer SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Merchant Accounts Are Bank Accounts That Allow Your Business To Accept Card Payments From CustomersDokument43 SeitenMerchant Accounts Are Bank Accounts That Allow Your Business To Accept Card Payments From CustomersRohit Kumar Baghel100% (1)
- Electronic Fund TransferDokument12 SeitenElectronic Fund TransferShravan Kumar DoosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MishiiDokument3 SeitenMishiiSidra AmjadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bank Management Project ReportDokument28 SeitenBank Management Project ReportRahul ChopadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATM System Problem StatementsDokument2 SeitenATM System Problem StatementsMD BIKASH SK0% (1)
- Standard Support: Figure 1: Pressing F1 Redirects User To A Bing SearchDokument4 SeitenStandard Support: Figure 1: Pressing F1 Redirects User To A Bing SearchDbluepengLumNoch keine Bewertungen
- TI 20220909 SG320HX and SG350HX Short-Circuit Current V1 enDokument5 SeitenTI 20220909 SG320HX and SG350HX Short-Circuit Current V1 en2D EngenhariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vallorbs Guide Cut Vs Rolled ThreadsDokument3 SeitenVallorbs Guide Cut Vs Rolled ThreadsOrlando AriasNoch keine Bewertungen
- HOUSEKEEPING - WEEK 1 UpdatedDokument5 SeitenHOUSEKEEPING - WEEK 1 UpdatedMaria Rizza IlaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stadium Planning and Construction.Dokument60 SeitenStadium Planning and Construction.shrikant96% (68)
- Lesson Outline: Introduction To LeadershipDokument2 SeitenLesson Outline: Introduction To LeadershipAmritpal SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visual Programming NotesDokument0 SeitenVisual Programming NotesSamuel VictorNoch keine Bewertungen
- PMRC Mar Va 115Dokument11 SeitenPMRC Mar Va 115adamsaufimahmud1988Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2001 Daewoo Nubira Service Manual2 PDFDokument685 Seiten2001 Daewoo Nubira Service Manual2 PDFalberto 32100% (1)
- Updated Eva ResumeDokument1 SeiteUpdated Eva Resumeapi-534826411Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cpu 2000 App ListDokument11 SeitenCpu 2000 App ListKaiser IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revo Uninstaller Pro HelpDokument61 SeitenRevo Uninstaller Pro HelpGuy Sinclaire OmbeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parrot: by Alan BrownjohnDokument2 SeitenParrot: by Alan BrownjohnPADUMI SASIKALA50% (2)
- Add Maths F4 Topical Test 3 (E)Dokument3 SeitenAdd Maths F4 Topical Test 3 (E)HANIFAH50% (2)
- LGIT CatalogueDokument11 SeitenLGIT CatalogueArjun SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Speeches and Speech StyleDokument1 SeiteTypes of Speeches and Speech StyleSai RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- AWS Cloud Architect: Nanodegree Program SyllabusDokument14 SeitenAWS Cloud Architect: Nanodegree Program Syllabustausif shaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- RESEARCH FORM and STYLEDokument8 SeitenRESEARCH FORM and STYLEKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychology Concepts and Applications 4Th Edition Nevid Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDokument49 SeitenPsychology Concepts and Applications 4Th Edition Nevid Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFfidelmanhangmhr100% (9)
- Reference Manual: Buildings and Infrastructure Protection SeriesDokument514 SeitenReference Manual: Buildings and Infrastructure Protection SeriesmydearteacherNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study On Pushover Analysis Using Capacity Spectrum Method Based On Eurocode 8Dokument13 SeitenA Study On Pushover Analysis Using Capacity Spectrum Method Based On Eurocode 8ephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allen: Pre Nurture & Career Foundation DivisionDokument7 SeitenAllen: Pre Nurture & Career Foundation DivisionSiddharth Singh100% (1)
- Recap For Inset 03-16-2021Dokument1 SeiteRecap For Inset 03-16-2021Melicia LimboNoch keine Bewertungen
- MHSIR00491976Dokument1 SeiteMHSIR00491976Patan Rafiq KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABB Review 2 2020 en 72 TruOne Zenith ArticleDokument4 SeitenABB Review 2 2020 en 72 TruOne Zenith ArticlePrakash KandasamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optoacoplador Integrado 4N25Dokument7 SeitenOptoacoplador Integrado 4N25aureliocsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV - Pinki Arindra P&GDokument6 SeitenCV - Pinki Arindra P&GPinqi Arindra PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4UIE - AB - Nov 23Dokument2 Seiten4UIE - AB - Nov 23aaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Psychometrician Licensure Examinations (Pmle) : Impact To The Behavioral Science CurriculumDokument21 SeitenThe Psychometrician Licensure Examinations (Pmle) : Impact To The Behavioral Science CurriculumghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Family Tree Template With DetailsDokument8 SeitenFamily Tree Template With DetailsJude WellsNoch keine Bewertungen