Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Mind Map Classroom Management Theories
Hochgeladen von
leahblackOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Mind Map Classroom Management Theories
Hochgeladen von
leahblackCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
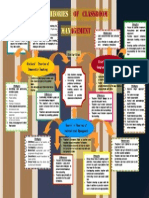
Strengths
Promotes a degree of
autonomy for pupils
Incorporates a preventive
approach to discipline
Helps pupils learn correct
behaviour
Promotes mutual respect
between teachers and pupils
Helps teachers focus on
causes for behavior before
they take action
Theories
Weaknesses
Teachers have trouble determining the
actual motives of the pupils. Pupils may
not admit their real motives
Teachers may find it difficult to respond
to pupils in a non-controlling way
Teacher may have problem dealing
with the complexity of engaging in a
dialogue with pupils
of classroom
MANAGEMENT
Weaknesses
Lack comprehensive and cohesive
model
Less effective in dealing with severe
behaviour infractions
Similarities
Strategies
1. Identifying and addressing
mistaken goals:
Confront mistaken-goal behavior and
help students redirect it in positive
ways.
Help all pupils meet their need for belonging
Attention getting
Power seeking
Revenge
Feelings of inadequacy
2. Using logical consequences
Set classroom rules
Outline a sequence of logical consequences
Pupils must accept responsibility
for their own behavior
Differences
Confronting mistaken goals after misbehaviour happen
The teachers role is helping
pupils to impose limit on themselves.
Teachers can model democratic
behavior by providing guidance
Help teachers manage
classroom discipline
Reducing behavior
problems to minimum
Help teaching and
learning process run
smoothly
Promote a positive
classroom environment
3. Using encouragement rather
than praise
Harmonious communication between
a teacher and pupils.
Pupils learning and behavior are
greatly influenced by the way teachers
communicate with them
Differences
Teacher should always be respectful of pupils needs.
Teacher must model communication that is congruent with pupils; emotions and surroundings
Teacher must include cooperative learning
Kounins Theories of
Instructional Management
Strategies
1. Whititness: aware of all events, ac-
tivities and pupils behavior
2. Overlapping: multitasking
3. Momentum: appropriate pace and
progression through lesson
4. Smoothness: smooth transitions between activity
5. Group Focus: keep the whole class
Ginots Theories of
Congruent Communication
Dreikurs Theories of
Democratic Teaching
Strengths
Focus on positive treatment.
Acceptance and acknowledgement
Positive rapport enhance
classroom learning environment
Develop positive self-esteem
by encouraging pupils to take
responsibility for their behaviour
involved and interested
Teachers behaviors have a positive and
negative impact on learners behaviors.
Good discipline depends on how the teachers presented the lesson and dealt with various groups in class
Differences
Focuses on preventative
discipline: - using techniques and strategies to
prevent misbehaviours
from occurring
Teacher was primarily responsible for the pupils
behaviour.
Strengths
Group focus helps in gaining pupils
attention. It also allows teachers to
present to pupils expectations that
they have for the class.
Overlapping provides teacher with
control over several activities
Interesting lesson can avoid satiation
Teacher develop a pace with the
class to achieve a precise momentum to teach a lesson appropriately
Strategies
1. Express anger appropriately
2. Use sane message
3. Invite cooperation
4. Accept and acknowledge
pupils feeling
5. Avoid labeling/ sarcasm
6. Use direction as a means
of correction
7. Avoid harmful questions
8. Accepts pupils comments
9. Avoid hurried help
10. Be brief when dealing with
minor mishaps
Weaknesses
Teachers eyes cannot be on every
pupil at all times
Teacher can get distracted by pupils
or other outside variables
Teacher can lose track of time when
performing a lesson
Teacher can lose control over a disruptive pupil
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Classroom Management Theories ComparedDokument1 SeiteClassroom Management Theories ComparedKhairunnisa Sharom100% (4)
- EDU 3104 SEM 3 QuestionDokument7 SeitenEDU 3104 SEM 3 QuestionAudrina Mary JamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 9 - Making InferencesDokument17 SeitenChapter - 9 - Making InferencesGaming User100% (1)
- Reading Skills in Malaysian Primary SchoolsDokument11 SeitenReading Skills in Malaysian Primary SchoolsWan Amir Iskandar IsmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strengths and Weaknesses of The Theory of DemocraticDokument12 SeitenStrengths and Weaknesses of The Theory of DemocraticQin KaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESL/EFL instructors' classroom assessment practices and purposesDokument30 SeitenESL/EFL instructors' classroom assessment practices and purposesOriana GSNoch keine Bewertungen
- M-U-F FrameworkDokument12 SeitenM-U-F FrameworkNor NarjihahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surveys StudentDokument6 SeitenSurveys StudentSwÏng Talunay Taborda100% (1)
- TSLB 3063 Tutorial Week 4Dokument16 SeitenTSLB 3063 Tutorial Week 4siti munirah binti sahrirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formative Assessment PresentationDokument34 SeitenFormative Assessment Presentationapi-279184573Noch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophy of Classroom ManagementDokument3 SeitenPhilosophy of Classroom Managementapi-542969247Noch keine Bewertungen
- Interview With TeacherDokument5 SeitenInterview With Teacherapi-457860691Noch keine Bewertungen
- Classroom Management AssignmentDokument5 SeitenClassroom Management Assignmentapi-281336195Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Philosophy StatementDokument6 SeitenAssessment Philosophy Statementapi-336570695Noch keine Bewertungen
- Collaborative LearningDokument6 SeitenCollaborative LearningMANISHA DASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Educating Special Education StudentsDokument6 SeitenEducating Special Education StudentsamandasykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example of A Lesson PlanDokument5 SeitenExample of A Lesson PlanCnc ChrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 10 - The Textbook Method of TeachingDokument6 SeitenLecture 10 - The Textbook Method of TeachingJaverea Rafique100% (1)
- Effective Lesson Observation Form SLT 2010 2011Dokument3 SeitenEffective Lesson Observation Form SLT 2010 2011Charlotte GriersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planning and Resources For Different Teaching ContextDokument20 SeitenPlanning and Resources For Different Teaching ContextPinky Mariel MangayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation Assessment and TestingDokument6 SeitenEvaluation Assessment and TestingBe Creative - كن مبدعاNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Student BehaviourDokument1 SeiteManagement of Student BehaviourDebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Standards - Workbook - Focus Group Standards PreliminaryDokument3 SeitenCurriculum Standards - Workbook - Focus Group Standards Preliminaryapi-250421371Noch keine Bewertungen
- Classroom Management Theorists Kounin and GlasserDokument4 SeitenClassroom Management Theorists Kounin and GlasserMuhammad Mukhlis WanlahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theme Based Teaching PDFDokument28 SeitenTheme Based Teaching PDFFazlı ŞAHİNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muhammad Wasim ShahzadDokument12 SeitenMuhammad Wasim ShahzadZafar Iqbal Yousuf Zai100% (1)
- Teaching Writing Skills Using Pictures, Readings and Language Skills (TSL3107Dokument19 SeitenTeaching Writing Skills Using Pictures, Readings and Language Skills (TSL3107Claire B.L.100% (1)
- Managing Large and Mixed-Ability ClassDokument18 SeitenManaging Large and Mixed-Ability Classsikucingmiaow14100% (1)
- Observationfeedback Ed201Dokument3 SeitenObservationfeedback Ed201api-305785129Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edfd 459 Teaching Philosophy PaperDokument3 SeitenEdfd 459 Teaching Philosophy Paperapi-356289068Noch keine Bewertungen
- WEEK 12 & 13 Simulated TeachingDokument30 SeitenWEEK 12 & 13 Simulated TeachingyshianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines Macro Teaching Evaluation Form Ef5 2009Dokument4 SeitenGuidelines Macro Teaching Evaluation Form Ef5 2009Shahril Affandi Mat YusofNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Animals Adapt to Extreme WeatherDokument7 SeitenHow Animals Adapt to Extreme WeathertombamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fs 6.on Becoming A TeacherDokument7 SeitenFs 6.on Becoming A TeacherGlenn Harold Ballad100% (1)
- Curriculum DevelopmentDokument9 SeitenCurriculum DevelopmentDawson MwendaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 8. Discussion Forum For EDUC 5240Dokument4 SeitenUnit 8. Discussion Forum For EDUC 5240Kiptoo KiruiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Research Paper On ICT IntegrationDokument8 SeitenA Research Paper On ICT IntegrationjenniferNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Practice Kit - English - 2017Dokument95 SeitenTeaching Practice Kit - English - 2017Andreea PopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primary English Curriculum OverviewDokument52 SeitenPrimary English Curriculum OverviewThavapriya SeloamoneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sains - Integrated Curriculum For Primary SchoolDokument17 SeitenSains - Integrated Curriculum For Primary SchoolSekolah Portal100% (6)
- Teaching Methods GuideDokument20 SeitenTeaching Methods GuideMarla Annie Marquez-MagcalayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effective Classroom-Management & Positive TeachingDokument10 SeitenEffective Classroom-Management & Positive TeachingJaderick CroesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classroom ManagementDokument5 SeitenClassroom ManagementSudhiksha SurmughiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intended VsDokument14 SeitenIntended VsRyan Morales67% (3)
- Assessment For Learning PDFDokument25 SeitenAssessment For Learning PDFprakas.rao39695Noch keine Bewertungen
- RPS - Teaching English For TeenagersDokument6 SeitenRPS - Teaching English For Teenagersnormanofianto poltekkes100% (1)
- WEEK 2 LECTURE NOTES Part 1Dokument5 SeitenWEEK 2 LECTURE NOTES Part 1Harold Saldy CasalemNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASSESSMENT - Fromative - SummativeDokument23 SeitenASSESSMENT - Fromative - SummativeEsther PérezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evolution of English Language Teaching in MalaysiaDokument2 SeitenEvolution of English Language Teaching in MalaysiaAishah Baith100% (2)
- Classroom Management Strategies for Disciplinary IssuesDokument6 SeitenClassroom Management Strategies for Disciplinary IssuesSyafiq AddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using Puppets to Teach GrammarDokument8 SeitenUsing Puppets to Teach GrammarCik EmbunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Progressive Education In Nepal: The Community Is the CurriculumVon EverandProgressive Education In Nepal: The Community Is the CurriculumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classroom Observation Task 1Dokument5 SeitenClassroom Observation Task 1api-252713389Noch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Literacies in Diverse ContextsVon EverandTeaching Literacies in Diverse ContextsSinéad HarmeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- School ManagementDokument4 SeitenSchool ManagementFrancis D. MagsipocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles and Methods of Teaching: (Chapter 9)Dokument27 SeitenPrinciples and Methods of Teaching: (Chapter 9)Joniel GetanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 7&8 BuildingDokument11 SeitenWeek 7&8 BuildingMaybe Calunsag - AbucayNoch keine Bewertungen
- ScoreboardDokument9 SeitenScoreboardleahblackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Our Classroom Rules: Listen When Your Teacher Is TalkingDokument1 SeiteOur Classroom Rules: Listen When Your Teacher Is TalkingleahblackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pet Showcase: 10 Animals in Unusual PlacesDokument1 SeitePet Showcase: 10 Animals in Unusual PlacesleahblackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teacher and Current ChallengesDokument48 SeitenTeacher and Current ChallengesleahblackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Our Classroom Rules: Listen When Your Teacher Is TalkingDokument1 SeiteOur Classroom Rules: Listen When Your Teacher Is TalkingleahblackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mind Map Classroom Management TheoriesDokument1 SeiteMind Map Classroom Management Theoriesleahblack100% (1)
- My 5 Senses: Name: - Date: - ClassDokument3 SeitenMy 5 Senses: Name: - Date: - ClassleahblackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Puzzle Rearrange WordsDokument3 SeitenPuzzle Rearrange WordsleahblackNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Rainbow Colour Song: Instruction: Read and ColourDokument2 SeitenThe Rainbow Colour Song: Instruction: Read and ColourleahblackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proverb PosterDokument1 SeiteProverb PosterleahblackNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Teddy BeaDokument3 SeitenThe Teddy BealeahblackNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Teddy BeaDokument3 SeitenThe Teddy BealeahblackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schedule of Implementation ARDokument2 SeitenSchedule of Implementation ARleahblackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Butterfly Song LyricsDokument1 SeiteButterfly Song LyricsNur Afizah SulaimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Superheroes PoemDokument1 SeiteSuperheroes PoemleahblackNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Blackberry Gnome StoryDokument1 SeiteThe Blackberry Gnome StoryleahblackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance:: Symmetrical-Occurs When The Elements of A Composition Are The Same On Either Side of An Axis LineDokument3 SeitenBalance:: Symmetrical-Occurs When The Elements of A Composition Are The Same On Either Side of An Axis LineleahblackNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Teddy BeaDokument3 SeitenThe Teddy BealeahblackNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Ant and The DoveDokument2 SeitenThe Ant and The DoveleahblackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alif Is For AllahDokument1 SeiteAlif Is For AllahFatima HyphaNoch keine Bewertungen
- I'm A Little FishDokument1 SeiteI'm A Little FishleahblackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance:: Symmetrical-Occurs When The Elements of A Composition Are The Same On Either Side of An Axis LineDokument3 SeitenBalance:: Symmetrical-Occurs When The Elements of A Composition Are The Same On Either Side of An Axis LineleahblackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Pengajaran Tahunan KSSR Tahun 4 - Bahasa InggerisDokument16 SeitenRancangan Pengajaran Tahunan KSSR Tahun 4 - Bahasa Inggerismrdan100% (1)
- Alif Is For AllahDokument1 SeiteAlif Is For AllahFatima HyphaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using Picture Books To Support LearningDokument3 SeitenUsing Picture Books To Support LearningleahblackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soalan ENGLISH BI Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 3 Paper 1Dokument13 SeitenSoalan ENGLISH BI Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 3 Paper 1sasauball80% (92)
- ButcherDokument7 SeitenButcherleahblackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Meng Ajar Tahunan 2003Dokument41 SeitenRancangan Meng Ajar Tahunan 2003leahblackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handout 1 EdflctDokument4 SeitenHandout 1 Edflctsageichiro8Noch keine Bewertungen
- What is Philosophy? - An Introduction to its Four Major BranchesDokument4 SeitenWhat is Philosophy? - An Introduction to its Four Major BranchesLetlie Zoilo SemblanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discernibility and Rough SetsDokument239 SeitenDiscernibility and Rough SetsHasim IswantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standards Based Lesson Plan Elements: General Plan Academic Content Standard/s: Academic StandardsDokument5 SeitenStandards Based Lesson Plan Elements: General Plan Academic Content Standard/s: Academic Standardsapi-610136255Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan FeedBACK MechanismDokument8 SeitenLesson Plan FeedBACK MechanismQueencess Ara TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Individual Development FactorsDokument9 SeitenIndividual Development Factorshanani_leeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep Work NotesDokument9 SeitenDeep Work NotesKimberly SimbranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employee motivation impact on organisation performanceDokument27 SeitenEmployee motivation impact on organisation performanceShwetha Siddaramu100% (1)
- Present Simple Vs Present Continuous Interactive ReviewDokument2 SeitenPresent Simple Vs Present Continuous Interactive ReviewSteven GuaninNoch keine Bewertungen
- Readingandwriting11 q4 Mod3 Purposefulwritinginthedisciplinesandforprofessions v5Dokument108 SeitenReadingandwriting11 q4 Mod3 Purposefulwritinginthedisciplinesandforprofessions v5Tolo , Precious Kim, V.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Language and Linguist Compass - 2007 - Romaine - Preserving Endangered LanguagesDokument18 SeitenLanguage and Linguist Compass - 2007 - Romaine - Preserving Endangered LanguagesConstanza MuñozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject - Verb AgreementDokument25 SeitenSubject - Verb AgreementIndah SariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biophilic Architecture in HospitalDokument4 SeitenBiophilic Architecture in HospitalJacques OwokelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mastering Your Hidden Self-A Guide To The Huna WayDokument15 SeitenMastering Your Hidden Self-A Guide To The Huna Wayjorgeblotta3489100% (2)
- Managing High PotentialsDokument5 SeitenManaging High PotentialsDũng LưuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peter Had $1800. After He Gave $400 To John, He Had Twice As Much Money As John. How Much Money Did John Have at First?Dokument4 SeitenPeter Had $1800. After He Gave $400 To John, He Had Twice As Much Money As John. How Much Money Did John Have at First?Kamarul Khamis100% (1)
- The Sanskrit Sentence - Verbs, Adjectives, and IndeclinablesDokument6 SeitenThe Sanskrit Sentence - Verbs, Adjectives, and IndeclinablesKalaisan KalaichelvanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Of StudiesDokument16 SeitenOf StudiesHajra usmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 Teaching English To Gifted ChildrenDokument15 Seiten2015 Teaching English To Gifted Childrenapi-413748610Noch keine Bewertungen
- Self - Check - PatalitaDokument3 SeitenSelf - Check - PatalitaJourdyllene Prince PatalitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Yourself Through Holistic DevelopmentDokument3 SeitenUnderstanding Yourself Through Holistic DevelopmentElaineVidalRodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- T-Tess GoalsDokument2 SeitenT-Tess Goalsapi-414999095Noch keine Bewertungen
- Child and Adolescent Development PrinciplesDokument5 SeitenChild and Adolescent Development PrinciplesCiara Janine Meregildo100% (3)
- Report Card Comments for Academic Achievement and ImprovementDokument12 SeitenReport Card Comments for Academic Achievement and ImprovementVivi Vivon100% (1)
- Research paper phrases guide for results & discussionDokument7 SeitenResearch paper phrases guide for results & discussionAlejandro BenavidesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psycho Cybernetics Summary PDF by THBDokument30 SeitenPsycho Cybernetics Summary PDF by THBpritish satpathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annika Park - Poetry Explication EssayDokument6 SeitenAnnika Park - Poetry Explication Essayapi-659162115Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Role of Data Analytics in Modern Day SportsDokument6 SeitenThe Role of Data Analytics in Modern Day SportsSarthak BatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Letter To EditorDokument2 SeitenLetter To EditorKlaudyna Strzępka-BrożekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self-Concept Understanding The SelfDokument3 SeitenSelf-Concept Understanding The SelfSHAILA JEAN TAYABANNoch keine Bewertungen