Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Note 1
Hochgeladen von
Ahmed SobhOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Note 1
Hochgeladen von
Ahmed SobhCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
KFU DAMMAM
COLLEGE OF MEDCINE
PHARMACOLOGY SUMMARY & REVIEW
Dr. Abdulaziz Al-Khawaja
Dr. Mohammed Akram
Dr. N. B. Biswas
Done by: Ahmed Ali Al-Ghareeb
207
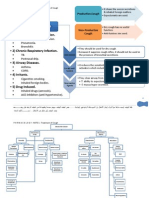
P H R M A C O L O G Y - NOTE 1 - Treatment of Asthma
Drugs for Asthma
Anti-inflammatory
(glucorticosteroids)
Bronchodilators
2-adrenergic
agonist
Methylxanthines
Salbutamole
Theophylline
Terbutaline
Aminophylline
Anti-muscarinic
Beclomethasone
Ipratropium
Hydrocortisone
Anti-leukotrienes
LT synthesis
inhibitor
Clinical features of bronchial
asthma.
leading to bronchodema
LT receptor
antagonist
Zileuton
Mucosal
inflammation
Bronchoconstriction
Sodium
Cromoglycate
Montelukast
Prednisolone
Salmaterol
Contraction of airway smooth muscle.
leading to acute dyspnea & airway
obstruction.
Mucus hypersecretion.
leading to mucus pulgging.
Airway inflamation.
Mast cell stabilizers
Mucosal
edema
Role of
Leukotrines
in asthma
Mucus
secretion
Uses of bronchodilator
for acute
bronchospasm
during acute
phase of
asthma attack
for quick
reduce airway
constriction
P H R M A C O L O G Y - NOTE 1 - Treatment of Asthma
Bronchodilaters
PHARMACOKINETIC
2 adrenergi
c agonist
DRUG
Salbutamole
Terbutaline
Salmaterol
Methylxanthines
Theophylline
Antimusc
rinic
Aminophylline
Ipratropium
Fast onest.
Short duration.
Given inhaler or Nebulizer.
Less side effect.
Given orally, S.C, IV or IM.
Slow onest.
Large dose.
Long duration.
More side effect.
Has narrow theraputic index.
Given orally.
Cause GI irritant.
Water mixture of Theophylline + Ethylenediamine.
Given orally, rectally (suppositories) or injection.
It is poorly absobed from the GIT.
So,it given by inhalation.
Slower onest & longer duration than salbutamol.
USES
Used for long term therapy.
Inhibit PDEI.
Leading to cAMP.
++
Ca influx
Bronchodilatation
1) CNS stimulation.
2) Cardiac muscle stimulation.
3) Diuresis.
4) S.M. relaxtion of bronchial & uterus.
5) Periphral & cornory vasodilatation.
6) Cerebral vasoconstriction.
Blocking M receptor in bronchial
smooth muscle.
Bronchodilatation
Given by inhalation, orally or IV.
GIT: nausea, vomiting .
CNS: stimulation insomnia,
irritabillity & headach.
CVS: BP, arrhythmia.
Kidney: diuresis.
Anti-Leukotrienes
PHARMACOKINETIC
Zileuton
Montelukast
USES
1) Reduce mucosal edema.
2) Sensitize 2-agonist.
3) Reduce inflammatory cell activation
Hydrocortisone
Prednisolone
DRUG
SIDE EFFECT
Tremor.
Vascular headache.
Used for acute attack.
Anti-inflammatory(Glucorticosteroid)
PHARMACOKINETIC
ACTION
DRUG
Beclomethasone
ACTION
Bind to -receptor & stimulate
adenylcyclase.
Leading to cAMP.
Bronchodilatation.
Mast Cell Stabilizers
PHARMACOKINETIC
SIDE EFFECT
If taken by inhalation,
Dysphonia (hoarseness).
Oral candidiasis (fungal
infection).
ACTION
1) Inhibit lipoxygenase enzyme.
2) Reduce conversion of AA to LT.
So, it is
Broncodilater.
Anti-inflammatory.
1) Blocking LT receptors.
2) Inhibit bronchoconstriction caused by LT
Dry mouth.
USES
SIDE EFFECT
To prevent asthma caused by
Aspirin.
NASID.
To prevent asthma caused by
NASID & Exercise.
Prophylaxis aginst asthma
attack.
DRUG
Na Cromoglycate
Given by inhalation.
Ketotifen
Given orally.
ACTION
Reduce the mediators that release
from mast cell in response to allergen
that cause bronchoconstriction.
USES
SIDE EFFECT
Cough.
Wheeze.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Pharmacology of Respiratory SystemDokument67 SeitenPharmacology of Respiratory Systemmanish086100% (2)
- Lecture 4, 5 - Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDDokument57 SeitenLecture 4, 5 - Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDBalakrishnan Thangaraj100% (1)
- Relieve Angina & Congestive Heart FailureDokument6 SeitenRelieve Angina & Congestive Heart FailureBij Hilario100% (1)
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDokument33 SeitenChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseasealexpharmNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2&3-Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDDokument58 Seiten2&3-Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDKishan SethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fast Facts: Asthma: Improve patient self-management and drug use, achieve asthma controlVon EverandFast Facts: Asthma: Improve patient self-management and drug use, achieve asthma controlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology Made Insanely Easy PowerPointDokument42 SeitenPharmacology Made Insanely Easy PowerPointBetsy Brown Byersmith82% (22)
- Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDDokument84 SeitenPharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDdfngjlnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asthma MedicationDokument6 SeitenAsthma Medicationmomina arshidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sialogogues & Anti SailogoguesDokument43 SeitenSialogogues & Anti SailogoguesTavleen KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory PharmacologyDokument89 SeitenRespiratory PharmacologyEka PuspitasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Pediatric Emergencies - A2Dokument46 SeitenCommon Pediatric Emergencies - A2Ahmad JustNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 14 - Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma L0 COPD - EditedDokument42 SeitenLecture 14 - Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma L0 COPD - EditedAbdallah AlasalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antiasthmatic DrugsDokument36 SeitenAntiasthmatic DrugsJannah ZahraaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory Tract PharmacologyDokument68 SeitenRespiratory Tract PharmacologyRohaan SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory EmergenciesDokument34 SeitenRespiratory EmergenciesRoshana MallawaarachchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology of drugs for bronchial asthma and COPDDokument71 SeitenPharmacology of drugs for bronchial asthma and COPDBriana NdayisabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antiasthma and Cough MedicineDokument47 SeitenAntiasthma and Cough MedicineYordanos EshetuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Effecting Respiratory System (MSCN)Dokument63 SeitenDrugs Effecting Respiratory System (MSCN)Irshad SahilNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH-V Cough, ASthmaDokument40 SeitenCH-V Cough, ASthmaC velmuruganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti Asthmatic DrugsDokument8 SeitenAnti Asthmatic DrugsNavjot BrarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3.2 - Respiratory DrugsDokument3 SeitenModule 3.2 - Respiratory DrugsCatherine Sinen ObinqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cology 3 Unit 1Dokument28 SeitenCology 3 Unit 1imrujlaskar111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDDokument71 SeitenDrugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDShabnam Binte AlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Acting On Respiratory System of AnimalsDokument8 SeitenDrugs Acting On Respiratory System of AnimalsSunil100% (4)
- Respiratory DrugsDokument20 SeitenRespiratory DrugsMelanesiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- At Least 5 Days of Fever PLUS 4 or 5Dokument11 SeitenAt Least 5 Days of Fever PLUS 4 or 5Atiqah ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sas1 ClinpharDokument7 SeitenSas1 ClinpharAlyssa Marie Petonio BialaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory Pharmacolo... Asthma1Dokument55 SeitenRespiratory Pharmacolo... Asthma1ahmed mahamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autacoids, Respiratory Diseases Drug Treatment 2023Dokument38 SeitenAutacoids, Respiratory Diseases Drug Treatment 2023adetola adetayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Rishi Pal: Asstt. ProfessorDokument40 SeitenDr. Rishi Pal: Asstt. ProfessortamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bronchial Asthma 2.0Dokument15 SeitenBronchial Asthma 2.0Bisweswar OjhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- All DrugsDokument482 SeitenAll DrugsJessica IbañezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory Stimulant and Nesal DecongestantDokument22 SeitenRespiratory Stimulant and Nesal DecongestantAyesha AlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saba Hanif Presentation...Dokument19 SeitenSaba Hanif Presentation...Saba KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-Seven (Vii) : Drugs Affecting The Respiratory SystemDokument55 SeitenUnit-Seven (Vii) : Drugs Affecting The Respiratory Systemdinberu tadesseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory DrugsDokument6 SeitenRespiratory DrugsCurtney PedriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Asthma and Copd HandoutDokument10 Seiten6 Asthma and Copd HandoutMd Sakil AminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs For Treatment of Bronchial Asthma: DR Sanjay Junior Resident Department of Pharmacology Ims-BhuDokument19 SeitenDrugs For Treatment of Bronchial Asthma: DR Sanjay Junior Resident Department of Pharmacology Ims-BhuBisweswar OjhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Status Asthmaticus DR Divya JainDokument45 SeitenStatus Asthmaticus DR Divya JainParvathy R NairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs in Treatment of Bronchial AsthmaDokument46 SeitenDrugs in Treatment of Bronchial AsthmaNikita JangraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 - Drugs For AsthmaDokument75 Seiten5 - Drugs For Asthmanica velano100% (1)
- Pharmacotherapy of Bronchial AsthmaDokument7 SeitenPharmacotherapy of Bronchial AsthmaAhmedshaker21100% (2)
- Respiratory SystemDokument27 SeitenRespiratory SystemSowndariyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asthma + COPDDokument60 SeitenAsthma + COPDNur HasanahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Management of Asthma 2Dokument43 SeitenCurrent Management of Asthma 2dan ekelemeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology RCR1 RespiratoryDokument10 SeitenPharmacology RCR1 RespiratoryeamcrawleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary Diseases: Medically Compromised PatientDokument50 SeitenPulmonary Diseases: Medically Compromised Patientمحمد عبدالهادي إسماعيلNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti-Asthmatics: Dr. Sadia Shahid PGT-Pharmacology IimcDokument30 SeitenAnti-Asthmatics: Dr. Sadia Shahid PGT-Pharmacology IimcWafaa AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs for Cough, Bronchial Asthma and InflammationDokument47 SeitenDrugs for Cough, Bronchial Asthma and InflammationNavlika DuttaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BP602T Unit 1-3Dokument207 SeitenBP602T Unit 1-3Gyampoh SolomonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asthma Harrisons ClubDokument84 SeitenAsthma Harrisons ClubLady AngodNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTHMA TreatmentDokument27 SeitenASTHMA TreatmentRho Vince Caño Malagueño0% (1)
- Antiasthamatic DrugsDokument72 SeitenAntiasthamatic DrugsDeepak kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperaldosteronism Is Treated With: Adverse ReactionsDokument7 SeitenHyperaldosteronism Is Treated With: Adverse ReactionsGizelle CorpuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Asthma Exacerbations: Treatment GuideDokument36 SeitenAcute Asthma Exacerbations: Treatment GuideYousef Al-AmeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Affecting The Respiratory Systems: Kuntarti, SKP, MbiomedDokument32 SeitenDrugs Affecting The Respiratory Systems: Kuntarti, SKP, MbiomedRichard BungaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SalbutamolDokument2 SeitenSalbutamolMarck Vincent Garcia OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Note 4 & 5Dokument7 SeitenNote 4 & 5HossamJamaykaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treatment of Peptic Ulcer & Eradication of H. PyloriDokument3 SeitenTreatment of Peptic Ulcer & Eradication of H. PyloriHossamJamaykaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cough DrugsDokument4 SeitenCough DrugsAhmed SobhNoch keine Bewertungen