Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Answer Scheme2007
Hochgeladen von
Shu85Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Answer Scheme2007
Hochgeladen von
Shu85Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
JABATAN PELAJARAN PERAK
___________________________________
PEPERIKSAAN PERCUBAAN
SIJIL PELAJARAN MALAYSIA 2007
FIZIK (4531)
SKEMA PEMARKAHAN
Kertas soalan ini mengandungi 14 halaman bercetak
PHYSICS PAPER 1 (4531/1)
SULIT
4531
PHYSICS PAPER 1 (4531/1)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
4531
D
A
C
C
C
D
B
B
C
C
D
C
C
C
B
A
B
A
A
C
D
D
C
A
C
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
D
C
C
A
B
B
B
C
A
C
A
D
B
B
A
C
D
A
C
A
C
D
B
B
A
2
SULIT
SULIT
4531
PHYSICS PAPER 2 (4531/2)
SECTION A
1.
(a)
(i)
Ammeter
1 mark
(b)
(ii)
(i)
To measure the potential difference across the wire/conductor
Error due to the instrument which has a reading when it is not in
used
1 A
1 mark
1 mark
(ii)
2.
(a)
(i)
(ii)
(b)
(i)
(ii)
More responsive to heat
The fine and uniform tube allows a movement of the liquid to be
observed Easily / higher sensitivity
15 mm/1.5 cm
= 150 - 15 x 100
190 - 15
1 mark
(4 marks)
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
= 77.20
(5 marks)
3.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
electromagnetic waves / transverse waves
Constructive interference takes place and bright fringes are observed.
Destructive interference takes place and dark fringes are observed.
Lights with one colour or one wavelength
ax
D
o.5 x 10 -3 x 6 x 10 -3
5
-7
6 x 10 meter
1 mark
2 marks
1 mark
2 marks
(6 marks)
4.
(a)
(b)
Total internal reflection
Light ray as follow
(i)
1 mark
3 marks
4531
3
SULIT
1 mark
SULIT
(c)
(d)
Inverted / virtual
1
n
sin C
1
1.76
sin C
C 34.6 o
4531
1 mark
2 marks
(7 marks)
5.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
6.
(a)
(b)
(c)
7.
1
2
(ii)
(iii)
(i)
(ii)
(i)
(ii)
(i)
(d)
(i)
(ii)
(a)
(i)
(ii)
(b)
(c)
(i)
(ii)
Distance/time
Before: water levels are the same and the roof stay intact
After : water levels are not the same and the roof rise up
Pressure above the roof is lower compare to pressure below
Speed increases pressure decreases or vice versa
Bernoulli
Speed : Q is slower and R is faster
Pressure : Q is higher and R is lower
1 mark
1mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
(8 marks)
Farthest in Diagram 6.2 compare to Diagram 6.1
Decreases
streamline
W = 10 x 70
= 700 J
Kinetic energy to potential energy to kinetic energy
Sound/ heat
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
2 marks
1 mark
(8 marks)
It has a high resistance and so little or no current flows
through R2. Hence the potential at B is close to 0V
When it is dark, very little light falls on the LDR and so its
resistance is high. The potential at A is close to 0V.
1 mark
When it is bright, a lot of light falls on the LDR. The
potential difference across the LDR drops to 0V and so the
potential at A is close to +6V.
Input A
Input B
Output Q
All correct- 2m
At least 1
0
0
1
wrong 1m
0
1
0
All wrong- 0m
1
0
0
1
1
0
Input A: 0
Input B: 0
Output Q: 1
Light level : dark
Soil condition: dry
1 mark
1 mark
2 marks
3 marks
2 marks
(10 marks)
4531
4
SULIT
SULIT
8.
4531
(a)
(i)
(b)
(ii)
(i)
A resultant force is a single force which is a vector sum of
all the forces that act on the object.
The resultant force is equal to zero
Cos =
20
25
0
(ii)
(c)
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
1 mark
1 mark
2 marks
= 36 52
T Sin + T sin = 20
2 T Sin = 20
T = 16.67 N
Tension of the string in diagram 8.3 is the maximum
because the angle is the smallest
Tension of the string in diagram 8.2 is the minimum
because the angle is the largest
Diagram 8.2
3 marks
2 marks
2 marks
1 mark
(12 marks)
SECTION B
9.
(a)
(i)
(Speed of light in vacuum or air) / (speed of light in the
medium)
(ii)
4531
1 mark
2 marks
(b)
(i)
Draw a diagram to show the rays of light
Total internal reflection.
180 0 fish eye view
Obstacle
(c)
(i)
Draw a correct ray diagram with at least 2 rays
Box
Using two right-angled prisms
Arrangement of prism
Total internal reflection
5
SULIT
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
2 mark
1 mark
1 mark
SULIT
4531
(ii)
Draw a diagram to show arrangement
Right angle prism which cause the the rays to bent through 180 0
4 prism
2 eye piece
2 objective lens
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
(20 marks)
10.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
4531
It is a coil carrying a current field
number of turns in solenoid in Diagram 10.1 is more
the magnitude of current flowing in Diagram 10.1 is bigger
the number of paper clips attracted to solenoid in Diagram 10.1 is
more
(i) the strength of the magnetic field increases when the magnitude
of current increases
(ii) the strength of the magnetic field increases when the number of
turns in solenoid increases
When the switch is on, the soft iron core becomes electromagnet.
End A becomes north pole.
End B becomes south pole
Magnet P repels from end A
Magnet Q attracts to end B
(i) when the switch is on, current flows in the solenoid, soft iron
core becomes electromagnet
electromagnet attracts the iron armature, the hammer hits the
gong and bell rings
when the hammer moves towards the gong, the contacts open,
current stops flowing
The iron core loses its magnetic
(ii) increase the number of turns of wire
the magnetic field produced by each turn overlap to produce a
resultant field which is much stronger.
Increase the magnitude of the current / dry cells
To increase the strength of the resultant magnetic field
Replace the straight iron core with a U-shaped iron core
6
SULIT
1
3
1
1
4
SULIT
4531
Produce stronger magnetic field strength
(20 marks)
SECTION C
11.
(a)
(i)
(ii)
(b)
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(c)
Force per unit area
High altitude low density of air
Less collision of molecules with surface
Low altitude high density of air
More collision of molecules with surface
hg = 0.76 x 13 600 x 10
=103360 Pa
hg = 0.1 x 13 600 x 10
= 13600 Pa
0 Pa
Large tyre better stability
Liquid in hydraulic system liquid cannot be compressed
Large mass big inertia
Large base area better stability
Low centre of gravity better stability
Choose M
Large tyre, liquid in hydraulic system, large mass, large base
area or low centre of gravity/better stability, liquid cannot be
compressed and big inertia
4531
7
SULIT
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
2 marks
2 marks
2 marks
2 marks
2 marks
(maximum
8 marks)
1 mark
1 mark
SULIT
4531
(20 marks)
12
(a)
(i)
(ii)
(b)
(i)
Half-life is the time required for the activity of a sample of
the radioisotope to become halved.
emits particles,
can penetrate the soil and emerge from the ground
sufficiently long half-life
after a period of 2 days the activity of the source will be
weak enough to not pose any danger
A Geiger- muller
Very sensitive detector/ it can be carried about from
place to place
A ratemeter
It gives the count rate directly
R is suitable
Emits particles, have sufficiently long half-life
Arrangement of apparatus:
Observed the reading on the scaler without an absorber
Put a piece of paper, aluminium and lead between the
source and the detector in turns.
For each kind of absorber, record the reading on the
ratemeter.
Carry out the same procedure for the three substances.
radiation will be stopped by all three kinds of absorber
radiation will be stopped by aluminium and lead
will be stopped by lead only
1 mark
2 marks
2 marks
2 marks
2 marks
2 marks
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
1 mark
4531
8
SULIT
SULIT
4531
(c)
wear a photographic badge to measure the intensity of radiation
in the surroundings
store radioactive substances in a lead container
use a pair of forceps or tweezers to hold a radioactive substance.
2 marks
(any two)
(20 marks)
PHYSICS PAPER 3 (4531/3)
SECTION A
NO
1 (a)(i)
MARKING SCHEME
- Base current / IB
MARK
SUB TOTAL
1
1
(ii)
- Collector current / IC
(iii)
-Length of the connection wire
-C
(b)(i)
(ii)
4531
IB and IC
Correct column of manipulated variable and
9
SULIT
1
1
SULIT
4531
(c )
(d)
(e)
responding variable
State the units of IB and IC correctly
All the values of IC are correct
[4 or 3 values of IC are correct..1 mark]
The values of IC are consistently to one
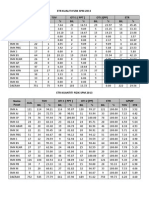
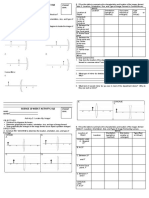
decimal point
IB / A
IC / mA
10.0
0.5
20.0
1.0
30.0
1.5
40.0
2.0
50.0
2.5
Draw a complete graph of IC against IB
Tick based on the following aspects :
A. Show IB on X-axis and IC on Y-axis
B. State the units of the variables correctly
C. Both axes are marked with uniform scale
D. All five points are plotted correctly
E. Best straight line is drawn
F. Show the minimum size of graph at least
5 x 4 ( 2 cm x 2 cm ) square
( counted from the origin until the furthest
point )
Score
Number of ticks
Score
7
5
5-6
4
3-4
3
2
2
1
1
- IC is directly proportional to IB
-Ensure all connections in the circuit are tight
-No short circuit
( any relevant response )
NO
2(a)
(b)
4531
MARKING SCHEME
-Show the method to determine the value of P by
showing the corresponding horizontal line with T
= 60 o C
-State the value of P correctly : 120.0 kPa 0.1
-Show the method to determine the value of the
temperature by showing the extrapolated line
-State the value within acceptable range:
10
SULIT
1
2
1
MARK
SUB TOTAL
1
1
1
1
SULIT
4531
-312 OC 1
( c)
-P increases linearly with T
(d)
-Draw a sufficiently large triangle( 6 cm x 3 cm )
-Correct substitution
100
= 138
160 0
1
1
2.5
State the value / answer with correct unit
=0.238 kPa oC-1
IC / mA
(e)
-State the value of P with correct unit
kPa
-the mixture of water is stirred continuously until the
temperature of the water is steady
(f)
T = ( 227 + 273 )
-Correction substitution
P = 0.238( 227 + 273 )
2.0
1.5
Graph of IC against IB
0.5
4531
1.0
11
SULIT
0
10
20
30
40
50
IB / A
SULIT
4531
4531
12
SULIT
SULIT
4531
Graf P melawan T
P / kPa
120 kPa
120
100
80
60
40
20
-312 o C
T/oC
-320
4531
-280
-240
-200
-160
-120
-80
13
-40
SULIT
40
80
120
SULIT
4531
Section B
Question number 3
(a)
1
If the mass increased so the acceleration decreased.
(b)
1
The acceleration of an object decreases when its mass increases.
(c)
1.
To investigate the relationship between mass and acceleration.
2.
Manipulated variable : Mass of trolley
Responding variable : Acceleration
3.
Constant variable
: Force
4.
Ticker tape, cellophane tape, ticker timer, power supply, trolley, friction
compensated runway and rubber band.
5.
Diagram and label.
6.
A trolley is pulled by rubber band which provides a constant unit of force.
7.
Cut into 5- tick strips and a tape chart for the motion of the trolley is made.
The acceleration of the trolley, a is calculated and recorded in table.
8.
Repeated with two and then three identical trolleys stacked up.
9.
The result is recorded in the table.
Mass, m/Number of
1/m
trolleys
1
2
3
10.
4531
Acceleration, a/cms-2
A graph of a against 1/m is plotted.
14
SULIT
SULIT
4531
Question 4.
(a)
(b)
(c)
1.
1.
1.
2.
5.
The brightness of the bulb increased when the length of the wire decreased.
The length of wire increase, the resistance of a conducting wire also increases
To investigate the relationship between length of wire and resistance.
Manipulated variable : Length of wire
Responding variable : Resistance, R
Constant Variable
: Thickness of wire, type of wire, temperature of wire.
Ammeter, Voltmeter, battery, rheostat, switch, 100 cm constantant (s.w.q 24),
connecting wires.
Figure.
6.
7.
Measure the initial length, l = 20 cm.
Fix the ammeter, I = 0.5 A. The reading of the voltmeter, V is recorded in
3.
4.
table. The value for resistance R =
8.
4531
V
, is calculated.
I
9.
Repeated for l = 40 cm, 60 cm, 80 cm and 100 cm. Calculated the resistance
for each of the length of wire.
Tabulation of the data.
10.
l/cm
I/A
V/V
20.0
40.0
60.0
80.0
100.0
Plot a graph of R against l.
R=V/I
15
SULIT
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Etr Kualiti Fizik SPM 2013Dokument3 SeitenEtr Kualiti Fizik SPM 2013Shu85Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Physics Teacher GuideDokument20 SeitenChapter 1 Introduction To Physics Teacher GuideShu85Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Fric FricDokument1 SeiteFric FricShu85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Integrated Curriculum For Secondary Schools: Ministry of Education MalaysiaDokument3 SeitenIntegrated Curriculum For Secondary Schools: Ministry of Education MalaysiaShu85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Exercise MATTERDokument8 SeitenExercise MATTERShu85Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- For Form 3Dokument1 SeiteFor Form 3Shu85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Exercise Introduction To ScienceDokument17 SeitenExercise Introduction To ScienceShu85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise Cell As The Basic Unit of Living ThingsDokument16 SeitenExercise Cell As The Basic Unit of Living ThingsShu85100% (1)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- ADokument20 SeitenAShu85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- SMK ALOR PONGSU 34300 BAGAN SERAI, PERAK SCHEME OF WORK FOR FORM 4 PHYSICS YEARLY TEACHING PLAN 2013 SMK ALOR PONGSU 34300 BAGAN SERAI, PERAK SCHEME OF WORK FOR FORM 4 PHYSICS YEARLY TEACHING PLAN 2012 LEARNING AREA: 1. INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICS Week / Date Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Suggested Activities Notes Minimum Requirement & Sources 2/1-4/1 1.1 Understanding Physics A student is able to: • explain what physics is • recognize the physics in everyday objects and natural phenomena Observe everyday objects such as table, a pencil, a mirror etc and discuss hoe they are related to physics concepts. View a video on natural phenomena and discuss how they related to physics concepts. Discuss fields of study in physics such as forces, motion, heta, light etc. JPNP Module Ex: Vernier Callipers And Micrometer Screw Gauge 7/1-11/1 1.2 Understanding base quantities and derived quantities A student is able to: • explain what base quanDokument48 SeitenSMK ALOR PONGSU 34300 BAGAN SERAI, PERAK SCHEME OF WORK FOR FORM 4 PHYSICS YEARLY TEACHING PLAN 2013 SMK ALOR PONGSU 34300 BAGAN SERAI, PERAK SCHEME OF WORK FOR FORM 4 PHYSICS YEARLY TEACHING PLAN 2012 LEARNING AREA: 1. INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICS Week / Date Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Suggested Activities Notes Minimum Requirement & Sources 2/1-4/1 1.1 Understanding Physics A student is able to: • explain what physics is • recognize the physics in everyday objects and natural phenomena Observe everyday objects such as table, a pencil, a mirror etc and discuss hoe they are related to physics concepts. View a video on natural phenomena and discuss how they related to physics concepts. Discuss fields of study in physics such as forces, motion, heta, light etc. JPNP Module Ex: Vernier Callipers And Micrometer Screw Gauge 7/1-11/1 1.2 Understanding base quantities and derived quantities A student is able to: • explain what base quanShu85Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hapter: Cell As A Unit of LifeDokument29 SeitenHapter: Cell As A Unit of LifeShu85Noch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Portable CCD SpectroradiometerDokument5 SeitenPortable CCD SpectroradiometerLISUN GROUPNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- General Physics 2Dokument75 SeitenGeneral Physics 2tinay ciprixxNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Calicut: Read:-1. U.O.No - GAI/J2/3601/08 Vol II Dated 19.06.2009Dokument54 SeitenUniversity of Calicut: Read:-1. U.O.No - GAI/J2/3601/08 Vol II Dated 19.06.2009LakshmiVishwanathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Galileo GalileiDokument6 SeitenGalileo Galileiapi-316506870Noch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Fiber Optics CommunicationsDokument136 SeitenFiber Optics Communicationsedugenet100% (4)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Fundamental Physics Experiments 2-FixDokument15 SeitenFundamental Physics Experiments 2-FixDavid HadidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Lecture Note Prepared by Dr. Supriyo SahaDokument4 SeitenLecture Note Prepared by Dr. Supriyo SahasupriyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Center of Mass and The Motion of A SystemDokument13 SeitenCenter of Mass and The Motion of A SystemNitin SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yavorsky Detlaf A Modern Handbook of Physics Mir 1982Dokument719 SeitenYavorsky Detlaf A Modern Handbook of Physics Mir 1982Luka Cristian Mitaš0% (1)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Xii Neet Physics McqsDokument49 SeitenXii Neet Physics Mcqshhhhhhhh50% (2)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Science 10 Week 6 Q2 PrintoutDokument3 SeitenScience 10 Week 6 Q2 PrintoutPaula Luz Panlaqui Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Physics 2 4.1 The Law of ReflectionDokument5 SeitenGeneral Physics 2 4.1 The Law of ReflectionNanzkie Andrei SamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- OutputDokument5 SeitenOutputCarlos FazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of Novel Microstrip Graphene Nano Patch Antenna GNPA For Terahertz RadiationDokument9 SeitenStudy of Novel Microstrip Graphene Nano Patch Antenna GNPA For Terahertz RadiationMirela CimpanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Fiber CommunicationDokument48 SeitenOptical Fiber CommunicationRockShayar Irfan Ali Khan100% (3)
- Quest Test 6 Wave Phenomena KEYDokument7 SeitenQuest Test 6 Wave Phenomena KEYHa ViNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gravitation: Chapter - 01Dokument96 SeitenGravitation: Chapter - 01RICKNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- II Puc Physics Hand BookDokument58 SeitenII Puc Physics Hand BookBeeresha R SNoch keine Bewertungen
- C WavesDokument18 SeitenC WavesTravis TeohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic InductionDokument15 SeitenElectromagnetic InductionLaili Fauziah100% (1)
- The Basics of Confocal MicrosDokument22 SeitenThe Basics of Confocal MicrosViswanathan SundaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDokument9 SeitenNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentGaurav JaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Board Questions CriminalisticsDokument14 SeitenBoard Questions CriminalisticsAries Gallandez100% (1)
- AP Physics Santa Problem2017 Practice While I Am at DentistDokument1 SeiteAP Physics Santa Problem2017 Practice While I Am at DentistQuinn LynchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bromide Printing and EnlargingDokument46 SeitenBromide Printing and EnlargingGutenberg.orgNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2404 Paper AiimsDokument36 Seiten2404 Paper Aiimsvishal giriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture17 PDFDokument9 SeitenLecture17 PDFHuseyin OztoprakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astronomy For BeginnersDokument163 SeitenAstronomy For BeginnersΦΩΤΙΟΣ ΓΟΥΣΙΟΣ100% (2)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- U1 ExercisesDokument6 SeitenU1 ExercisesArturo MarmolejoNoch keine Bewertungen