Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
2.3.3.5 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management Address Newport
Hochgeladen von
gerardo1028Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
2.3.3.5 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management Address Newport
Hochgeladen von
gerardo1028Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Name ______________ Period ___ Rack ___ Partner ____________
2.3.3.5 Lab - Configuring a Switch Management Address
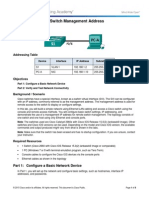
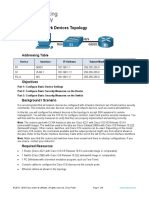
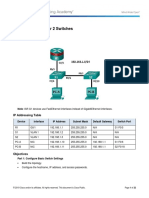
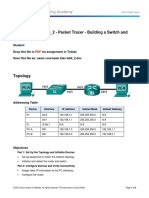
Topology
Instructor Signoff ______________
Addressing Table
Device
Interface
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
S1
VLAN 1
192.168.1.2
255.255.255.0
N/A
PC-A
NIC
192.168.1.10
255.255.255.0
N/A
Objectives
Part 1: Configure a Basic Network Device
Cable the network as shown in the topology.
Configure basic switch settings including hostname, management address, and Telnet access.
Configure an IP address on the PC.
Part 2: Verify and Test Network Connectivity
Display device configuration.
Test end-to-end connectivity with ping.
Test remote management capability with Telnet.
Save the switch running configuration file.
Background / Scenario
Cisco switches have a special interface, known as a switch virtual interface (SVI). The SVI can be configured
with an IP address, commonly referred to as the management address that is used for remote access to the
switch to display or configure settings.
In this lab, you will build a simple network using Ethernet LAN cabling and access a Cisco switch using the
console and remote access methods. You will configure basic switch settings and IP addressing, and
demonstrate the use of a management IP address for remote switch management. The topology consists of
one switch and one host using only Ethernet and console ports.
Note: The switches used are Cisco Catalyst 2960s with Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2) (lanbasek9 image). Other
switches and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the available
commands and output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs.
Note: Make sure that the switch has been erased and has no startup configuration. If you are unsure, contact
your instructor.
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 1 of 4
Lab - Configuring a Switch Management Address
Required Resources
1 Switch (Cisco 2960 with Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2) lanbasek9 image or comparable)
1 PC (Windows 7, Vista, or XP with terminal emulation program, such as Putty)
Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
Ethernet cables as shown in the topology
Part 1: Configure a Basic Network Device
In Part 1, you will set up the network and configure basic settings, such as hostnames, interface IP
addresses, and passwords.
Step 1: Cable the network.
a. Cable the network as shown in the topology.
b. Establish a console connection to the switch from PC-A.
Step 2: Configure basic switch settings.
In this step, you will configure basic switch settings, such as hostname and configuring an IP address for the
SVI. Assigning an IP address on the switch is only the first step. As the network administrator, you must
specify how the switch will be managed. Telnet and Secure Shell (SSH) are two of the most common
management methods; however, Telnet is a very insecure protocol. All information flowing between the two
devices is sent in plain text. Passwords and other sensitive information can be easily looked at if captured by
a packet sniffer.
a. Assuming the switch had no configuration file stored in nonvolatile random-access memory (NVRAM),
you will be at the user EXEC mode prompt on the switch with a prompt of Switch>. Enter privileged
EXEC mode.
Switch> enable
Switch#
b. Verify a clean configuration file with the show running-config privileged EXEC command. If a
configuration file was previously saved, it will have to be removed. Depending on the switch model and
IOS version, your configuration may look slightly different. However, there should be no configured
passwords or IP address set. If your switch does not have a default configuration, ask your instructor for
help.
c.
Enter global configuration mode and assign the switch hostname.
d. Configure the switch password access.
e. Prevent unwanted Domain Name System (DNS) lookups.
f.
Configure a login message-of-the-day (MOTD) banner.
g. Verify your access setting by moving between modes.
What shortcut keys are used to go directly from global configuration mode to privileged EXEC mode?
____________________________________________________________________________________
h. Return to privileged EXEC mode from user EXEC mode.
Note: Password will not show up on screen when entering.
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 2 of 4
Lab - Configuring a Switch Management Address
i.
Enter global configuration mode to set the SVI IP address to allow remote switch management.
j.
Restrict console port access. The default configuration is to allow all console connections with no
password needed.
k.
Configure the virtual terminal (VTY) line for the switch to allow Telnet access. If you do not configure a
VTY password, you will not be able to Telnet to the switch.
Step 3: Configure an IP address on PC-A.
a. Assign the IP address and subnet mask to the PC, as shown in the Addressing Table on page 1. The
procedure for assigning an IP address on a PC running Windows 7 is described below:
1) Click the Windows Start icon > Control Panel.
2) Click View By: > Category.
3) Choose View network status and tasks > Change adapter settings.
4) Right-click Local Area Network Connection and select Properties.
5) Choose Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4), click Properties > OK.
6) Click the Use the following IP address radio button and enter the IP address and subnet mask.
Part 2: Verify and Test Network Connectivity
You will now verify and document the switch configuration, test end-to-end connectivity between PC-A and
S1, and test the remote management capability of the switch.
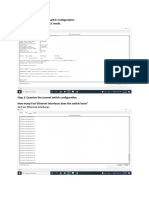
Step 1: Display the S1 device configuration.
a. Return to your console connection using Putty on PC-A to display and verify your switch configuration by
issuing the show run command.
S1# show run
b. Verify the status of your SVI management interface. Your VLAN 1 interface should be up/up and have an
IP address assigned. Notice that switch port F0/6 is also up because PC-A is connected to it. Because all
switch ports are initially in VLAN 1, by default, you can communicate with the switch using the IP address
you configured for VLAN 1.
S1# show ip interface brief
Step 2: Test end-to-end connectivity.
Open a command prompt window (cmd.exe) on PC-A by clicking the Windows Start icon and enter cmd into
the Search for programs and files field. Verify the IP address of PC-A by using the ipconfig /all command.
This command displays the PC hostname and the IPv4 address information. Ping PC-As own address and
the management address of S1.
a. Ping your own PC-A address first.
C:\Users\NetAcad> ping 192.168.1.10
b. Ping the SVI management address of S1.
C:\Users\NetAcad> ping 192.168.1.2
If ping results are not successful, troubleshoot the basic device configurations. You should check both the
physical cabling and IP addressing, if necessary.
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 3 of 4
Lab - Configuring a Switch Management Address
Step 3: Test and verify remote management of S1.
You will now use Telnet to remotely access the switch S1 using the SVI management address. In this lab, PCA and S1 reside side by side. In a production network, the switch could be in a wiring closet on the top floor
while your management PC is located on the ground floor. Telnet is not a secure protocol. However, you will
use it in this lab to test remote access. All information sent by Telnet, including passwords and commands, is
sent across the session in plain text. In subsequent labs, you will use Secure Shell (SSH) to remotely access
network devices.
Note: Windows 7 does not natively support Telnet. The administrator must enable this protocol. To install the
Telnet client, open a command prompt window and type pkgmgr /iu:TelnetClient.
C:\Users\NetAcad> pkgmgr /iu:TelnetClient
a. With the command prompt window still open on PC-A, issue a Telnet command to connect to S1 via the
SVI management address. The password is cisco.
C:\Users\NetAcad> telnet 192.168.1.2
b. After entering the cisco password, you will be at the user EXEC mode prompt. Type enable at the
prompt. Enter the class password to enter privileged EXEC mode and issue a show run command.
Step 4: Save the configuration file. DO NOT DO THIS ON THE LAB EQUIPMENT
a. From your Telnet session, issue the copy run start command at the prompt.
S1# copy run start
Destination filename [startup-config]? [Enter]
Building configuration ..
S1#
b. Exit the Telnet session by typing quit. You will be returned to the Windows 7 command prompt.
Reflection
Why must you use a console connection to initially configure the switch? Why not connect to the switch via
Telnet or SSH?
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 4 of 4
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 2.3.3.4 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management AddressDokument8 Seiten2.3.3.4 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management AddressDaisy Galvan0% (1)
- Sem1 Batch1 PDFDokument73 SeitenSem1 Batch1 PDFMustapha OulcaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.3.3.3 Lab - Building A Simple Network - ILMDokument18 Seiten2.3.3.3 Lab - Building A Simple Network - ILMshm2hotmail.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.3.3.4 Lab - Building A Simple NetworkDokument14 Seiten2.3.3.4 Lab - Building A Simple NetworkMaria Tudosa50% (2)
- 2.3.3.3 Lab - Building A Simple NetworkDokument11 Seiten2.3.3.3 Lab - Building A Simple Networkrafid80% (5)
- 2.3.3.3 Lab - Building A Simple NetworkDokument13 Seiten2.3.3.3 Lab - Building A Simple NetworkDaisy Galvan33% (3)
- 2.3.3.3 Lab - Building A Simple Network PDFDokument13 Seiten2.3.3.3 Lab - Building A Simple Network PDFPetra Miyag-aw100% (1)
- 11.3.4.6 Lab - Using The CLI To Gather Network Device InformationDokument8 Seiten11.3.4.6 Lab - Using The CLI To Gather Network Device InformationSuen Clarke0% (1)
- 2.3.3.4 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management Address - ILMDokument10 Seiten2.3.3.4 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management Address - ILMKevin KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Task 1: Verify The Default Switch Configuration Step 1: Enter Privileged EXEC ModeDokument20 SeitenTask 1: Verify The Default Switch Configuration Step 1: Enter Privileged EXEC ModeAdnan YousafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Lab :building A Simple Network With AnswersDokument14 SeitenCisco Lab :building A Simple Network With AnswersEmzy Soriano50% (2)
- 2.3.3.4 Lab - Building A Simple NetworkDokument14 Seiten2.3.3.4 Lab - Building A Simple Networkroberto002Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2.3.3.5 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management AddressDokument8 Seiten2.3.3.5 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management AddressNicolas Bonina33% (3)
- Lab 2 - Building A Simple Network: TopologyDokument12 SeitenLab 2 - Building A Simple Network: Topologyjramisch44Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab2 - Configuring A Switch Management Address: TopologyDokument8 SeitenLab2 - Configuring A Switch Management Address: Topologymabrouka gmidenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Act 1 Building A Simple NetworkDokument11 SeitenAct 1 Building A Simple Networkchristine booduanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCN LAB ASSIGNMENT 1 - (VLANS AND TRUNKING LAB) - 26feb2020Dokument4 SeitenCCN LAB ASSIGNMENT 1 - (VLANS AND TRUNKING LAB) - 26feb2020luhoni jonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1.4.6 CiscoDokument11 Seiten1.1.4.6 CiscoZeratul322100% (2)
- Laboratory Exercise No 3 - Rev01Dokument11 SeitenLaboratory Exercise No 3 - Rev01John Rhey IbeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.2.4.11 Lab - Configuring Switch Security Features - ScribdDokument9 Seiten2.2.4.11 Lab - Configuring Switch Security Features - ScribdstevehrccNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16.5.2 Lab - Secure Network DevicesDokument5 Seiten16.5.2 Lab - Secure Network DevicesFernando AlburquerqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.9.2 Packet Tracer Basic Switch and End Device Configuration Physical Mode Es XLDokument3 Seiten2.9.2 Packet Tracer Basic Switch and End Device Configuration Physical Mode Es XLFer Nando NakamuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.5.1.3 Packet Tracer - Implementing Basic Connectivity - ILMDokument5 Seiten8.5.1.3 Packet Tracer - Implementing Basic Connectivity - ILMHernan KowalskyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.9.2 Packet Tracer - Basic Switch and End Device Configuration - Physical Mode - Es XLDokument3 Seiten2.9.2 Packet Tracer - Basic Switch and End Device Configuration - Physical Mode - Es XLjjjjjNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.3.4.6 Lab - Using The CLI To Gather Network DeviDokument11 Seiten11.3.4.6 Lab - Using The CLI To Gather Network DeviRichardWhitley20% (5)
- ITNB02 11.2.4.6 Securing Network DevicesDokument8 SeitenITNB02 11.2.4.6 Securing Network DevicesShayneNakagawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab - Configuring and Verifying VTY RestrictionsDokument6 SeitenLab - Configuring and Verifying VTY Restrictionsdaniel ramirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter One Lab-5.2 - Basic Switch and End Device Configuration - Physical ModeDokument3 SeitenChapter One Lab-5.2 - Basic Switch and End Device Configuration - Physical ModeFedasa BoteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment-4: Aim: Connect The Computers in Local Area Network. Procedure: On The Host ComputerDokument19 SeitenExperiment-4: Aim: Connect The Computers in Local Area Network. Procedure: On The Host ComputerAfraz &HallaajNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.5.1.2 Lab - Building A Switch and Router NetworkDokument8 Seiten6.5.1.2 Lab - Building A Switch and Router NetworkParthPatel100% (8)
- 6.3.1.1 Lab - Securing Layer 2 SwitchesDokument22 Seiten6.3.1.1 Lab - Securing Layer 2 SwitchesJson CañedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp4 To Exp11Dokument24 SeitenExp4 To Exp11Viney ChhillarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.3.4.6 Lab - Using The CLI To Gather Network Device InformationDokument8 Seiten11.3.4.6 Lab - Using The CLI To Gather Network Device InformationSachinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.2.4.11 Lab - Configuring Switch Security Features - ILMDokument15 Seiten2.2.4.11 Lab - Configuring Switch Security Features - ILMJose Maria Rendon Rodriguez100% (1)
- 11.2.4.6 Lab - Securing Network DevicesDokument8 Seiten11.2.4.6 Lab - Securing Network DevicesRichardWhitleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 2.3Dokument3 SeitenLab 2.3Zulaikha ZakariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.7.6 Packet Tracer - Implement Basic ConnectivityDokument3 Seiten2.7.6 Packet Tracer - Implement Basic Connectivityanthonyykh01Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2.3.3.4 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management AddressDokument9 Seiten2.3.3.4 Lab - Configuring A Switch Management AddressIchwan Habibie20% (5)
- 11.3.4.6 Lab - Using The CLI To Gather Network Device InformationDokument11 Seiten11.3.4.6 Lab - Using The CLI To Gather Network Device InformationRazvan Buicliu0% (4)
- 2.7.6 Packet Tracer Implement Basic ConnectivityDokument10 Seiten2.7.6 Packet Tracer Implement Basic Connectivityانور الحاجNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.7.6 Packet Tracer - Implement Basic ConnectivityDokument3 Seiten2.7.6 Packet Tracer - Implement Basic ConnectivityPol PlomekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab - Configure Network Devices With SSH: TopologyDokument10 SeitenLab - Configure Network Devices With SSH: TopologyBárbaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 9 - RSS100 - Securing Layer 2 SwitchesDokument38 SeitenLab 9 - RSS100 - Securing Layer 2 SwitchessecuopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab6 - 2 CiscoDokument8 SeitenLab6 - 2 CiscoMoussa MarNoch keine Bewertungen
- L.Carrazco.8.5.1.3 Packet Tracer - Implementing Basic ConnectivityDokument5 SeitenL.Carrazco.8.5.1.3 Packet Tracer - Implementing Basic ConnectivityFernando CarrazcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.3.3.4 Lab - Building A Simple Network - ILMDokument18 Seiten2.3.3.4 Lab - Building A Simple Network - ILMcisocsyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Exploration 1: Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA - Network Fundamentals v4.0 Answers 2013-2014 Answer FullDokument10 SeitenCCNA Exploration 1: Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA - Network Fundamentals v4.0 Answers 2013-2014 Answer FullMimmoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Actividad 2.9.2-Packet-Tracerl202207003Dokument4 SeitenActividad 2.9.2-Packet-Tracerl202207003Jesús MunguiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- En Security Chp9 PTActA Secure-Network StudentDokument7 SeitenEn Security Chp9 PTActA Secure-Network StudentmyropieNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.3.1.1 Lab - Securing Layer 2 Switches PDFDokument23 Seiten6.3.1.1 Lab - Securing Layer 2 Switches PDFnganga0% (2)
- 4.1.4.6 Lab - Configuring Basic Router Settings With IOS CLIDokument10 Seiten4.1.4.6 Lab - Configuring Basic Router Settings With IOS CLIAhmadHijaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.7.6 Packet Tracer - Implement Basic Connectivity - 1207050038 Faza Mohamad FarsyafatDokument3 Seiten2.7.6 Packet Tracer - Implement Basic Connectivity - 1207050038 Faza Mohamad Farsyafatfaza farsyafatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Packet Tracer - Implement Basic Connectivity: Addressing TableDokument4 SeitenPacket Tracer - Implement Basic Connectivity: Addressing TableBenj MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationVon EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNoch keine Bewertungen
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkVon EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3Von EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3Noch keine Bewertungen
- PLC Programming from Novice to Professional: Learn PLC Programming with Training VideosVon EverandPLC Programming from Novice to Professional: Learn PLC Programming with Training VideosBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Von EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksVon EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 OkDokument37 SeitenChapter 8 OkMa. Alexandra Teddy Buen0% (1)
- PR-Unit1-ERP EvolutionDokument13 SeitenPR-Unit1-ERP EvolutionSiddhant AggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Global Business 2nd Edition Gaspar Test BankDokument26 SeitenIntroduction To Global Business 2nd Edition Gaspar Test BankJerryGarrettmwsi100% (56)
- Logiq 180 UsuarioDokument414 SeitenLogiq 180 UsuariolaboratorioelectroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency Incidents AssignmentDokument4 SeitenEmergency Incidents Assignmentnickoh28Noch keine Bewertungen
- Real Estate Merger Motives PDFDokument13 SeitenReal Estate Merger Motives PDFadonisghlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cobas B 123 POC System: Instructions For Use, Version 13.0 Software Version 4.17Dokument354 SeitenCobas B 123 POC System: Instructions For Use, Version 13.0 Software Version 4.17zelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentasi AkmenDokument18 SeitenPresentasi AkmenAnonymous uNgaASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Display PDF PDFDokument7 SeitenDisplay PDF PDFSandeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2 Empowerment MidtermDokument5 SeitenLesson 2 Empowerment Midtermaronfranco223Noch keine Bewertungen
- Neeraj Kumar: Nokia Siemens Networks (Global SDC Chennai)Dokument4 SeitenNeeraj Kumar: Nokia Siemens Networks (Global SDC Chennai)Kuldeep SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planning For Good AcousticsDokument1 SeitePlanning For Good Acousticsa_j_sanyal259Noch keine Bewertungen
- IBPS PO Preliminary Practice Set 5Dokument41 SeitenIBPS PO Preliminary Practice Set 5Nive AdmiresNoch keine Bewertungen
- TeramisoDokument1 SeiteTeramisoNasriyah SolaimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Probe Filter 5.1 SNMP Support Reference GuideDokument8 SeitenProbe Filter 5.1 SNMP Support Reference GuideOrlando MondlaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Create Config Files Python ConfigParserDokument8 SeitenCreate Config Files Python ConfigParserJames NgugiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate of IncorporationDokument1 SeiteCertificate of IncorporationVaseem ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final ThoughtDokument6 SeitenFinal ThoughtHaroon HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021-2022 Reopening Plan 2.0Dokument22 Seiten2021-2022 Reopening Plan 2.0Dan LehrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12V Laptop ChargerDokument12 Seiten12V Laptop ChargerSharon Babu0% (1)
- PW Trail Beaver Valley Oct 25Dokument63 SeitenPW Trail Beaver Valley Oct 25Pennywise PublishingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Long Vowel SoundsDokument15 SeitenLong Vowel SoundsRoselle Jane PasquinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concepts in Enterprise Resource Planning: Chapter Six Human Resources Processes With ERPDokument39 SeitenConcepts in Enterprise Resource Planning: Chapter Six Human Resources Processes With ERPasadnawazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Francisco v. Boiser PDFDokument12 SeitenFrancisco v. Boiser PDFPia Christine BungubungNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE5 Writing Revision Unit1-5Dokument8 SeitenEE5 Writing Revision Unit1-5Chuc VuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schedule of BPSC Teacher - S 6 Day - SDokument1 SeiteSchedule of BPSC Teacher - S 6 Day - SNarendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acetanilide C H Nhcoch: Aniline Acetic Acid Reactor Filter Crystallizer Centrifuge DryerDokument4 SeitenAcetanilide C H Nhcoch: Aniline Acetic Acid Reactor Filter Crystallizer Centrifuge DryerAnonymous 4hx84J3Noch keine Bewertungen
- 09 e 4150 C 0305 CB 1 A 37000000Dokument217 Seiten09 e 4150 C 0305 CB 1 A 37000000Dani GarnidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is International Business?: Educator Resource PPT To AccompanyDokument41 SeitenWhat Is International Business?: Educator Resource PPT To AccompanyArif Raza100% (1)
- Solaris 10 Service - (Management Facility (SMF: Oz Melamed E&M Computing Nov 2007Dokument18 SeitenSolaris 10 Service - (Management Facility (SMF: Oz Melamed E&M Computing Nov 2007Anonymous 4eoWsk3100% (3)