Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Questions Election Physics
Hochgeladen von
Katerina SchinochoritiOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Questions Election Physics
Hochgeladen von
Katerina SchinochoritiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Arden School
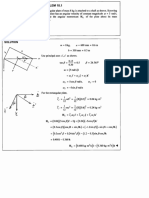
Q5.
The diagram shows a narrow beam of electrons directed at right angles into a uniform
electric field between two oppositely-charged parallel metal plates at a fixed potential
difference.
(a)
The electrons enter the field at O and leave it at P. Sketch the path of the beam from
O to P and beyond P.
(2)
(b)
A uniform magnetic field is applied to the beam perpendicular to the electric field and
to the direction of the beam. The magnetic field reduces the deflection of the beam
from its initial direction.
(i)
Explain why the magnetic field has this effect on the beam.
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
(ii)
The magnetic flux density is adjusted until the beam passes through the two
fields without deflection. Show that the speed v of the electrons when this
occurs is given by
v =
where E is the electric field strength and B is the magnetic flux density.
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
Page 1
Arden School
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
(5)
(c)
In an experiment to measure the specific charge of the electron, electrons were accelerated
from rest through a potential difference of 2900 V to a speed of
3.2 10 m s . Use this information to calculate the specific charge of the electron.
7
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 10 marks)
Q21.
The mass of the nucleus of an isolated copper atom is 63 u and it carries a charge
of +29 e. The diameter of the atom is 2.3 10 m.
10
P is a point at the outer edge of the atom.
(a)
Calculate
(i)
the electric field strength at P due to the nucleus,
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
(ii)
the gravitational potential at P due to the nucleus.
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
Page 2
Arden School
.............................................................................................................
(5)
(b)
Draw an arrow on the above diagram to show the direction of the electric field at the
point P.
(1)
(Total 6 marks)
Q23.
A simple pendulum consists of a 25 g mass tied to the end of a light string 800 mm
long. The mass is drawn to one side until it is 20 mm above its rest position, as shown in
the diagram. When released it swings with simple harmonic motion.
(a)
Calculate the period of the pendulum.
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
(2)
(b)
Show that the initial amplitude of the oscillations is approximately 0.18 m, and that
the maximum speed of the mass during the first oscillation is about 0.63 m s .
1
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
(4)
Page 3
Arden School
(c)
Calculate the magnitude of the tension in the string when the mass passes through
the lowest point of the first swing.
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 8 marks
Q24.
An particle and a particle both enter the same uniform magnetic field, which is
perpendicular to their direction of motion. If the particle has a speed 15 times that of the
particle, what is the value of the ratio
Q25.
3.7
7.5
60
112.
The diagram shows a vertical square coil whose plane is at right angles to a
horizontal uniform magnetic field B. A current, I, flows in the coil, which can rotate about a
vertical axis OO.
Which one of the following statements is correct?
A
The forces on the two vertical sides of the coil are equal and opposite.
A couple acts on the coil.
Page 4
Arden School
No forces act on the horizontal sides of the coil.
If the coil is turned through a small angle about OO, it will remain in position.
(Total 1 mar
Q26.
Two horizontal parallel plate conductors are separated by a distance of 5.0 mm in air.
The lower plate is earthed and the potential of the upper plate is + 50 V.
Which line, A to D, gives correctly the electric field strength, E, and the potential, V, at a
point midway between the plates?
electric field strength E/V m
potential V/V
1 10 upwards
25
1 10 downwards
25
1 10 upwards
50
1 10 downwards
50
(Total 1 mark
Q27.
Q28.
Which one of the following has different units to the other three?
A
gravitational potential
gravitational field strength
force per unit mass
gravitational potential gradient
A small mass is situated at a point on a line joining two large masses ml and m2 such
that it experiences no resultant gravitational force. If its distance from the mass m1 is r1 and
its distance from the mass m2 is r2, what is the value of the ratio
Page 5
Arden School
D
(Total 1 mark)
Q29.
A model car moves in a circular path of radius 0.8 m at an angular speed of
rad s .
1
What is its displacement from point P, 6 s after passing P?
Q30.
Q31.
zero
1.6 m
0.4 m
1.6 m
A particle oscillates with undamped simple harmonic motion. Which one of the
following statements about the acceleration of the oscillating particle is true?
A
It is least when the speed is greatest.
It is always in the opposite direction to its velocity.
It is proportional to the frequency.
It decreases as the potential energy increases.
Which one of the following gives the phase difference between the particle velocity
and the particle displacement in simple harmonic motion?
rad
rad
C
D
rad
2 rad
(Total 1 mark)
Page 6
Arden School
Q42.
A girl kicks a ball along the ground at a wall 2.0 m away. The ball strikes the wall
normally at a velocity of 8.0 m s and rebounds in the opposite direction with an initial
velocity of 6.0 m s . The girl, who has not moved, stops the ball a short time later.
1
(a)
Explain why the final displacement of the ball is not 4.0 m.
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
(1)
(b)
Explain why the average velocity of the ball is different from its average speed.
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
(2)
(c)
The ball has a mass of 0.45 kg and is in contact with the wall for 0.10 s. For the
period of time the ball is in contact with the wall,
(i)
calculate the average acceleration of the ball.
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
(ii)
calculate the average force acting on the ball.
.............................................................................................................
(iii)
state the direction of the average force acting on the ball.
.............................................................................................................
(5)
(Total 8 marks
Page 7
Arden School
Q43.
The diagram represents part of an experiment that is being used to estimate the
speed of an air gun pellet.
The pellet which is moving parallel to the track, strikes the block, embedding itself. The
trolley and the block then move along the track, rising a vertical height_, h.
(a)
Using energy considerations explain how the speed of the trolley and block
immediately after it has been struck by the pellet, may be determined from
measurements of h. Assume frictional forces are negligible.
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
(3
(b)
The following data is collected from the experiment
mass of trolley and block
mass of pellet
speed of trolley and block immediately after impact
0.50 kg
0.0020 kg
0.40 m s
Calculate
(i)
the momentum of the trolley and block immediately after impact,
.............................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................
(ii)
the speed of the pellet just before impact.
.............................................................................................................
Page 8
Arden School
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
(4)
(c)
(i)
State what is meant by an inelastic collision.
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................
(ii)
Use the data from part (b) to show that the collision between the pellet and
block is inelastic.
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
Q52.
A small charged sphere of mass 2.1 10 kg, suspended from a thread of insulating
material, was placed between two vertical parallel plates 60 mm apart. When a potential
difference of 4200 V was applied to the plates, the sphere moved until the thread made an
angle of 6.0 to the vertical, as shown in the diagram below.
4
(a)
Show that the electrostatic force F on the sphere is given by
F = mg tan 6.0
where m is the mass of the sphere.
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
(3)
Page 9
Arden School
(b)
Calculate
(i)
the electric field strength between the plates,
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
(ii)
the charge on the sphere.
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 6 marks)
Q56.
An electric motor in a machine drives a rotating drum by means of a rubber belt
attached to pulleys, one on the motor shaft and one on the drum shaft, as shown in the
diagram below.
(a)
The pulley on the motor shaft has a diameter of 24 mm. When the motor is turning
at 50 revolutions per second, calculate
(i)
the speed of the belt,
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
Page 10
Arden School
(ii)
the centripetal acceleration of the belt as it passes round the motor pulley.
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
(5)
(b)
When the motor rotates at a particular speed, it causes a flexible metal panel in the
machine to vibrate loudly. Explain why this happens.
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 7 ma
Q57.
A narrow beam of electrons at a speed of 3.2 10 m s travels along a circular path
in a uniform magnetic field of flux density, B, as shown in the diagram.
7
Page 11
Arden School
(a)
Explain why the path of the beam in the field is circular.
You may be awarded marks for the quality of written communication in your answer.
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
(3)
(b)
(i)
Show that the speed, v, of the electrons in the field is given by
where r is the radius of the circular path of the beam in the field.
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
(ii)
When the flux density was 7.3 mT, the radius of the circular path of the beam
in the field was 25 mm. Use the data to calculate the specific charge of the
electron.
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
Page 12
Arden School
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
(5)
(Total 8 marks)
Q60.
In an experiment to measure the charge of an oil droplet, a positively charged oil
droplet was held stationary by means of a uniform electric field of strength 4.9 10 V m .
5
(a)
(i)
What was the direction of the electric field?
............................................................................................................
(ii)
Show that the specific charge of the oil droplet was 2.0 10 C kg .
5
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................
(b)
When the electric field was switched off the oil droplet fell and quickly reached
constant speed.
Explain why the oil droplet reached constant speed.
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................
Page 13
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chapter 18Dokument260 SeitenChapter 18Gabriela Sequeira100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in KinematicsDokument5 SeitenLesson Plan in KinematicsEmman RevillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A-Level Exam (2001) Papers and AnswersDokument46 SeitenA-Level Exam (2001) Papers and AnswersAston Hamilton100% (3)
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsVon EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Electricity and Induction IB Physics Practice ProblemsDokument12 SeitenElectricity and Induction IB Physics Practice ProblemsLiozNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 TestrDokument5 Seiten14 TestrΧρίστος ΠαπαναστασίουNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 TopicwiseDokument19 SeitenUnit 1 TopicwiseSimran singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.7.5.1 Magnetic Flux DensityDokument24 Seiten3.7.5.1 Magnetic Flux Densitymata4cholNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 7 ExercisesDokument6 SeitenUnit 7 ExercisesBao Hoang LeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preboard Physics 2023-24Dokument5 SeitenPreboard Physics 2023-24rishitasarkar875Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fields - QP IBDP PhysicsDokument9 SeitenFields - QP IBDP PhysicsArham ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre BoardDokument15 SeitenPre Boardfakesmilelover07Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test Paper 7Dokument10 SeitenTest Paper 7ashishgambhir1986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 24 - Electric PotentialDokument12 SeitenChapter 24 - Electric PotentialVV CepheiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics XII Practice PaperDokument10 SeitenPhysics XII Practice PaperAvinashNoch keine Bewertungen
- QP - Physics - Xii - SPDokument7 SeitenQP - Physics - Xii - SPriteshsamrath440Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1990 Multiple Choice Past PaperDokument11 Seiten1990 Multiple Choice Past PaperNalini Rooplal100% (1)
- 12 2005 Physics 1Dokument6 Seiten12 2005 Physics 1Shudhanshu VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- G12 Phy Pa2 Q.PDokument8 SeitenG12 Phy Pa2 Q.PnjragavendaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Total 1 Mark) : IB Questionbank Physics 1Dokument41 Seiten(Total 1 Mark) : IB Questionbank Physics 1Romeo SiriguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Magnetic EffectsDokument3 SeitenAssignment Magnetic EffectsabcdefgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics SQPDokument10 SeitenPhysics SQPPankaj SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Paper 8Dokument8 SeitenTest Paper 8rajeshsharma4121Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2024Dokument9 SeitenPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2024dhitiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.7.5.2 Moving Charges in A Magnetic FieldDokument67 Seiten3.7.5.2 Moving Charges in A Magnetic Fieldtheolamey1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Pre BoardDokument10 SeitenPhysics Pre Boardizumigamer69Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity 1 - ElectrostaticsDokument7 SeitenElectricity 1 - ElectrostaticsPaola MedranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Charges and Field 01 April 2TESTDokument2 SeitenElectric Charges and Field 01 April 2TESTcrawlskullNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spty, Yr6ti7iuhliphysics2013allindia PDFDokument14 SeitenSpty, Yr6ti7iuhliphysics2013allindia PDFyeateshwarriorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy Set-2 QPDokument5 SeitenPhy Set-2 QPSiddhartha HadimaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Test Term 1 QP Xii 2020 SeptDokument9 SeitenSample Test Term 1 QP Xii 2020 SeptEdwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topics 1,2,6 Summative SLDokument14 SeitenTopics 1,2,6 Summative SLAhmad OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 .2013 El Force and El Field Hw-PracticeDokument12 Seiten1 .2013 El Force and El Field Hw-PracticerbgrossNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap.-1 (Electric Charges and Filds)Dokument5 SeitenChap.-1 (Electric Charges and Filds)lanfury45Noch keine Bewertungen
- Joshi Classes Test (+2) : One Marks QuestionsDokument15 SeitenJoshi Classes Test (+2) : One Marks QuestionsPaavni SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2024Dokument7 SeitenPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2024fizajangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Field and CapacitorsDokument18 SeitenElectric Field and CapacitorsTharushiNethmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summer Holiday Homework - 22Dokument19 SeitenSummer Holiday Homework - 22Ananya DashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phys 1402 Final ReviewDokument8 SeitenPhys 1402 Final ReviewAline MurilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xam Idea Previous Years Question Papers 2008-2012Dokument419 SeitenXam Idea Previous Years Question Papers 2008-2012Mohammed Farhad77% (13)
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023Dokument7 SeitenPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023shagun sinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test I 2021Dokument5 SeitenTest I 2021shagunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ques PaperDokument10 SeitenQues Papergupta.sg003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 2018Dokument29 SeitenPhysics 2018milapdhruvcomputerworkNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 4-MCM-WSDokument8 SeitenCH 4-MCM-WSmmkishore067Noch keine Bewertungen
- HSC Physics Sample ExamsDokument346 SeitenHSC Physics Sample Examsn100% (1)
- 12 Physics Pre BordDokument7 Seiten12 Physics Pre Bordasthaajmera29Noch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Apr14 Sample Paper 2023 24Dokument10 SeitenCBSE Class 12 Physics Apr14 Sample Paper 2023 24aisha.lambeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Set B: Test Code: JS-P-07-22Dokument5 SeitenSet B: Test Code: JS-P-07-2231th batchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank 2022-2023Dokument18 SeitenQuestion Bank 2022-2023Jamil Ahmed XI- ANoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.physics Qp-XiiDokument6 Seiten2.physics Qp-XiiEMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12TH PHYSICS FTDokument10 Seiten12TH PHYSICS FTABHISHEK PANDANoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Paper 8 (Answers)Dokument17 SeitenTest Paper 8 (Answers)ashishgambhir1986Noch keine Bewertungen
- +2 Physics QPDokument7 Seiten+2 Physics QPvkushagra06Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Year 9 Mid-TermDokument9 SeitenPhysics Year 9 Mid-TermPeter TaremwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EP Assignment Spring 2015 PDFDokument6 SeitenEP Assignment Spring 2015 PDFanon_429934438Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 04 (Magnetic Effects of Currents)Dokument3 SeitenChapter - 04 (Magnetic Effects of Currents)ghuNoch keine Bewertungen
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Von EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1Von EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1Bewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (4)
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyVon EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNoch keine Bewertungen
- A New Approach to the Quantum Theory: Think Physics, #7Von EverandA New Approach to the Quantum Theory: Think Physics, #7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Neutron SourcesDokument64 SeitenNeutron SourcesJenodi100% (1)
- RabagoDokument22 SeitenRabagoJoshua O. RabagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quarter 2 Week 1 Activity 3: Moment of InertiaDokument2 SeitenQuarter 2 Week 1 Activity 3: Moment of InertiaJ-heart Basabas MalpalNoch keine Bewertungen
- W5 Kinetics of Particle Impulse Momentum (Ch15)Dokument74 SeitenW5 Kinetics of Particle Impulse Momentum (Ch15)Shah KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 1 - Mechanics: Useful WeblinksDokument2 SeitenPart 1 - Mechanics: Useful WeblinksSandeep KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Fields 2Dokument6 SeitenElectric Fields 2Lim Hui YanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHY IIT ADV Test 4 Paper1Dokument5 SeitenPHY IIT ADV Test 4 Paper1Jitendra PaliwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Precession and Nutation of A Gyroscope Ue1040500 Ue1040500: Spinning Mo T IonDokument1 SeitePrecession and Nutation of A Gyroscope Ue1040500 Ue1040500: Spinning Mo T IonZiad Al-ZeinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moving Charge in A Magnetic FieldDokument3 SeitenMoving Charge in A Magnetic FieldEntertainmentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 10 - MechanicsDokument8 SeitenWeek 10 - MechanicsRafael Jotojot Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test 07-04-2022Dokument5 SeitenTest 07-04-2022AIRUNINoch keine Bewertungen
- PhysicsDokument10 SeitenPhysicsNaqvi play'sNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 6 Review - Newtons Third Law PDFDokument4 SeitenCH 6 Review - Newtons Third Law PDFapi-305977811Noch keine Bewertungen
- BMMM s1-1 Group 5 Rotational InertiaDokument13 SeitenBMMM s1-1 Group 5 Rotational InertiaZul HairiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time Speed and Distance QuestionsDokument10 SeitenTime Speed and Distance QuestionsNishant Kumar Sittu dpsruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edit Source Edit: Inductive ReactanceDokument1 SeiteEdit Source Edit: Inductive ReactancesenthilanviewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teacher: Ms. Susana Alulod: Physic 11 Lab ReportDokument8 SeitenTeacher: Ms. Susana Alulod: Physic 11 Lab Reportapi-343197055Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1ST Summative Test Science 8Dokument3 Seiten1ST Summative Test Science 8Sid QuijanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MasteringPhysics - Assignment 4 - Forces Part OneDokument7 SeitenMasteringPhysics - Assignment 4 - Forces Part OneStrange Sht100% (2)
- Bab 13 Mekanika Lagrange1Dokument27 SeitenBab 13 Mekanika Lagrange1Front Line 7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 15 NotesDokument20 SeitenChapter 15 NotesMian EjazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 6: ENERGY Conservation and Projectile Motion: Group 4Dokument10 SeitenExperiment 6: ENERGY Conservation and Projectile Motion: Group 4ParZiValNoch keine Bewertungen
- MPP 2 K1 2022Dokument20 SeitenMPP 2 K1 2022najwa08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes For Section 17-5Dokument20 SeitenLecture Notes For Section 17-5Joshua D'CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circular MotionDokument51 SeitenCircular MotionPankaj KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- File 68244Dokument25 SeitenFile 68244Atul SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Power Test Paper-IDokument3 SeitenElectrical Power Test Paper-IhksaifeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 101 Chapter 2Dokument39 SeitenPhysics 101 Chapter 2Andrew GoolsbyNoch keine Bewertungen