Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
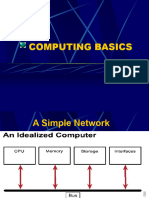
Provides Interface To End-Users Processes Provides Standardized Services To Applications Function
Hochgeladen von
Sushil SharmaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Provides Interface To End-Users Processes Provides Standardized Services To Applications Function
Hochgeladen von
Sushil SharmaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
7
LAYER 7 APPLICATION LAYER
User Interface
Provides interface to end-users processes
Provides standardized services to applications
FUNCTION
used for applications specifically written to run over the network
allows access to network services that support applications;
directly represents the services that directly support user applications
handles network access, flow control and error recovery
PROTOCOLS
DNS; FTP; TFTP; BOOTP; SNMP;RLOGIN; SMTP; MIME; NFS; FINGER;
TELNET; NCP; APPC; AFP; SMB
NETWORK COMPONENTS
Gateway
LAYER 6 PRESENTATION LAYER
Translation
Specifies architecture independent data transfer format
Encodes and decodes data, encrypt and decrypts data,
compresses data
FUNCTION
Translates from application to network format and vice-versa
all different formats from all sources are made into a common uniform
format that the rest of the OSI model can understand
responsible for protocol conversion, character conversion, data
encryption / decryption, expanding graphics commands, data
compression
sets standards for different systems to provide seamless
communication from multiple protocol stacks
not always implemented in a network protocol
PROTOCOLS
None
NETWORK COMPONENTS
Gateway
Translation
LAYER 5 SESSION LAYER
Sync & Session
FUNCTION
establishes, maintains and ends sessions across the network
responsible for name recognition (identification) so only the
designated parties can participate in the session
provides synchronization services by planning check points in the
data stream => if session fails, only data after the most recent
checkpoint need be transmitted
manages who can transmit data at a certain time and for how long
Examples are interactive login and file transfer connections, the
session would connect and re-connect if
there was an interruption; recognize names in sessions and
register names in history
PROTOCOLS
NetBIOS , Names Pipes, Mail Slots, RPC
NETWORK COMPONENTS
Gateway
LAYER 4 TRANSPORT LAYER
Packets; Flow control & error-handling
Manages network layer connections
Provide reliable packet delivery mechanism
FUNCTION
additional connection below the session layer
manages the flow control of data between parties across the network
divides streams of data into chunks or packets; the transport layer of
the receiving computer reassembles the message from packets
"train" is a good analogy => the data is divided into identical units
provides error-checking to guarantee error-free data delivery, with on
losses or duplications
provides acknowledgment of successful transmissions; requests
retransmission if some packets dont arrive error-free
provides flow control and error-handling
PROTOCOLS
TCP, ARP, RARP; SPX, NWLink, NetBIOS / NetBEUI, ATP
NETWORK COMPONENTS
Gateway, Advanced Cable Tester
LAYER 3 NETWORK
Addressing; Routing
Addresses and router packets
FUNCTION
translates logical network address and names to their physical address
(e.g. compute name ==> MAC address)
responsible for
(a) addressing
(b) determining routes for sending
(c) managing network problems such as packet switching, data
congestion and routing
if router cant send data frame as large as the source computer
sends, the network layer compensates by breaking the data into
smaller units. At the receiving end, the network layer
reassembles the data
think of this layer stamping the addresses on each train car
PROTOCOLS
IP; ARP; RARP, ICMP; RIP; OSFP; IGMP; IPX, NWLink , NetBEUI, OSI, DDP,
DECnet
NETWORK COMPONENTS
Router, Frame Relay Device, Switches,
LAYER 2 DATA-LINK LAYER
Data Frames to Bits
Frames packets
Control physical layer data flow
FUNCTION
rns packets into raw bits 100101 and at the receiving end turns bits into packets.
handles data frames between the Network and Physical layers
the receiving end packages raw data from the Physical layer into data frames for
delivery to the Network layer
responsible for error-free transfer of frames to other computer via the Physical
Layer
this layer defines the methods used to transmit and receive data on the network. It
consists of the wiring, the devices use to connect the NIC to the wiring, the
signaling involved to transmit / receive data and the ability to detect signaling errors
on the network media
PROTOCOLS
Logical Link Control
error correction and flow control
manages link control and defines SAPs
802.1 OSI Model , 802.2 Logical Link Control
Media Access Control
communicates with the adapter card
controls the type of media being used:
802.3 CSMA/CD (Ethernet), 802.4 Token Bus (ARCnet), 802.5 Token Ring, 802.12 Demand
Priorit
NETWORK COMPONENTS
BRIDGES, SWITCHES
LAYER 1 PHYSICAL LAYER
Hardware; Raw Bit
Stream
Interface between network medium and network devices
Defines electrical and mechanical characteristics
PROTOCOLS
transmits raw bit stream over physical cable
defines cables, cards, and physical aspects
defines NIC attachments to hardware, how cable is attached to NIC
defines techniques to transfer bit stream to cable
PROTOCOLS
None
NETWORK COMPONENTS
7
Bridge, Hub, NIC, Advanced Cable Tester
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Network+ Exam Cram Study SheetDokument3 SeitenNetwork+ Exam Cram Study SheetDan Sheets86% (21)
- Psalm151 160Dokument3 SeitenPsalm151 160Gina KristenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Serial Port Complete: COM Ports, USB Virtual COM Ports, and Ports for Embedded SystemsVon EverandSerial Port Complete: COM Ports, USB Virtual COM Ports, and Ports for Embedded SystemsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (9)
- Motorcycle Troubleshooting ManualDokument15 SeitenMotorcycle Troubleshooting ManualJan Warmerdam100% (1)
- OSI Model Layers: Layer Function Protocols Network Components ApplicationDokument3 SeitenOSI Model Layers: Layer Function Protocols Network Components ApplicationJohn SextonNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSI Model Reference TableDokument4 SeitenOSI Model Reference Tablem_karthikeyan1118264Noch keine Bewertungen
- OSI Model Reference TableDokument4 SeitenOSI Model Reference Tablem_karthikeyan1118264Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Device Configuration PDFDokument24 SeitenChapter 1 Device Configuration PDFShambel WorkuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The OSI Model: Layer 1 - PhysicalDokument7 SeitenThe OSI Model: Layer 1 - PhysicalJon FordNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter TwoDokument71 SeitenChapter TwoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Protocols: Lecturer SlidesDokument33 SeitenNetwork Protocols: Lecturer SlidesevhyajahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7-Layer OSI MODELDokument11 Seiten7-Layer OSI MODELBabu CamNoch keine Bewertungen
- T OSI: He Seven Layers of The ModelDokument4 SeitenT OSI: He Seven Layers of The Modellolimazn1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Internetworking ModelsDokument4 SeitenInternetworking ModelsDip KunduNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSI Model:: Application CiscoDokument16 SeitenOSI Model:: Application CiscoHAINHDT2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networks Set 2Dokument19 SeitenComputer Networks Set 2madhavibandari609Noch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA 640-802 Study Guide: A P S T N D PDokument8 SeitenCCNA 640-802 Study Guide: A P S T N D PPietersen VinothNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA 640-802 Study Guide: Tutorial Quick LinksDokument14 SeitenCCNA 640-802 Study Guide: Tutorial Quick Linksahmad_naser12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Network Models: Ambo University Woliso Campus Technology and Informatics School Department of Computer ScienceDokument73 SeitenNetwork Models: Ambo University Woliso Campus Technology and Informatics School Department of Computer ScienceNoel GirmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Study SheetDokument20 SeitenCisco Study Sheetjavier garcia santosNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSI Model Data Unit Layer Function: ApplicationDokument6 SeitenOSI Model Data Unit Layer Function: ApplicationSanyam JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSI LayersDokument19 SeitenOSI LayersJayanthikrishnan SNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSI ModelDokument6 SeitenOSI ModelmushahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSI ModelDokument10 SeitenOSI ModelRajkumar TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jason Zandri : TCP/IP Protocol Within Windows XP ProfessionalDokument29 SeitenJason Zandri : TCP/IP Protocol Within Windows XP ProfessionalruvinduNoch keine Bewertungen
- FAQ'sDokument24 SeitenFAQ'sduvvuruvitNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Interface: Protocols: FTPDokument4 SeitenUser Interface: Protocols: FTPAngates1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Communications Layers SummaryDokument7 SeitenCommunications Layers SummaryKarthickmanikandan GNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Layers of OSIDokument4 Seiten7 Layers of OSIMayank JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capture All HTTP Packets by Using Wireshark and Try To Fetch All HTTP Usernames & PasswordsDokument38 SeitenCapture All HTTP Packets by Using Wireshark and Try To Fetch All HTTP Usernames & PasswordsCandy AngelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semester One - Day1Dokument67 SeitenSemester One - Day1jigschuwa74Noch keine Bewertungen
- Used To Manage and Monitor The NetworkDokument35 SeitenUsed To Manage and Monitor The NetworkFikru TesefayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 4Dokument10 SeitenAssignment 4anil rajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explanations and Answers For The Cisco ObjectivesDokument23 SeitenExplanations and Answers For The Cisco ObjectivesIuliaNiculaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- IS 103 Chapter 4Dokument20 SeitenIS 103 Chapter 4Batang PasawaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2Dokument8 SeitenLecture 2jasmhmyd205Noch keine Bewertungen
- The OSI ModelDokument5 SeitenThe OSI ModelNidhi ChoudhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSI ModelDokument32 SeitenOSI ModelBhanu Singh0% (1)
- Tutorial Week 1Dokument4 SeitenTutorial Week 1Lasse IngdahlNoch keine Bewertungen
- NetworkingDokument55 SeitenNetworkingRey Allen TenosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networking Chapter 2: OSI LAYER Chapter 2 OSI LAYERDokument4 SeitenNetworking Chapter 2: OSI LAYER Chapter 2 OSI LAYERRaymart BuendiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Layers of TCPDokument2 SeitenThe Layers of TCPNaveen RecizNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSI and TCP - IP Lecture SlideDokument28 SeitenOSI and TCP - IP Lecture SlideBobby IgbeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Net 102 Prelim ModulesDokument36 SeitenNet 102 Prelim ModulesNovy Airhris MianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osi and Tci-Ip ModelDokument17 SeitenOsi and Tci-Ip ModelSohaibDanishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccna Basic FinalDokument273 SeitenCcna Basic FinalTanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osi 1Dokument36 SeitenOsi 1api-216820839Noch keine Bewertungen
- VSATDokument11 SeitenVSATShashwat TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Network ProtocolsDokument32 SeitenFinal Network ProtocolsArth Vince Uy Malaca50% (4)
- Networking OverviewDokument87 SeitenNetworking Overviewhaiprodt3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networks:: OSI Reference ModelDokument11 SeitenComputer Networks:: OSI Reference ModelMasterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Systems Interconnection Model (OSI) PDFDokument20 SeitenOpen Systems Interconnection Model (OSI) PDFLink NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osi Model LanDokument8 SeitenOsi Model LanRenegade DiverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Three Layer Vs OSI LayersDokument8 SeitenCisco Three Layer Vs OSI LayersDinesh LoitongbamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osi and ProtocolsDokument7 SeitenOsi and ProtocolsGilgamesh berserkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interview QuestionsDokument9 SeitenInterview Questionshatfied862Noch keine Bewertungen
- The OSI Model: How Network Protocols WorkDokument5 SeitenThe OSI Model: How Network Protocols WorkRafena MustaphaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are Network Protocols - IT Glossary - SolarWindsDokument3 SeitenWhat Are Network Protocols - IT Glossary - SolarWindsTefeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asics F Nternet: UNIT-4Dokument26 SeitenAsics F Nternet: UNIT-4Gaurav TharejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer CommunicationDokument7 SeitenComputer Communicationsaravanamuthaly1397Noch keine Bewertungen
- OSItables PDFDokument3 SeitenOSItables PDF900913n008Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisVon EverandHacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synopsis Ethical HckingDokument7 SeitenSynopsis Ethical HckingSushil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethical Hacking QuizDokument3 SeitenEthical Hacking QuizSushil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 Tips On How To Use Curl' Command in LinuxDokument5 Seiten15 Tips On How To Use Curl' Command in LinuxSushil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethical Hacking Quiz 2Dokument1 SeiteEthical Hacking Quiz 2Sushil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- List All Open Files With Lsof CommandDokument4 SeitenList All Open Files With Lsof CommandSushil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Static Ip KaliDokument1 SeiteStatic Ip KaliSushil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clipgrab and Extract But Before Running Install Some DependenciesDokument1 SeiteClipgrab and Extract But Before Running Install Some DependenciesSushil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ie Install PlayonlinuxDokument1 SeiteIe Install PlayonlinuxSushil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virtual Private NetworkDokument77 SeitenVirtual Private NetworkSushil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Squid Proxy ServerDokument3 SeitenSquid Proxy ServerSushil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 3Dokument37 SeitenTopic 3Sushil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Points For The Exam: Vices & SupportDokument3 SeitenStudy Points For The Exam: Vices & SupportSushil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Configuring HSRP (Hot Standby Routing Protocol)Dokument3 SeitenConfiguring HSRP (Hot Standby Routing Protocol)Sushil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing & Virtualization: Prepared By: Er - Priyanka Aggarwal M.Tech CSEDokument29 SeitenCloud Computing & Virtualization: Prepared By: Er - Priyanka Aggarwal M.Tech CSESushil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- XEN and KVM In: INFN Production Systems and A Comparison Between ThemDokument28 SeitenXEN and KVM In: INFN Production Systems and A Comparison Between ThemSushil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virtualization Technologies: IBM Haifa Research LabDokument28 SeitenVirtualization Technologies: IBM Haifa Research LabSushil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS431 Virtualization 12 BWDokument38 SeitenCS431 Virtualization 12 BWSushil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-1 Infancy: S.Dharaneeshwari. 1MSC - Home Science-Food &nutritionDokument16 SeitenUnit-1 Infancy: S.Dharaneeshwari. 1MSC - Home Science-Food &nutritionDharaneeshwari Siva-F&NNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabi: The Institution of Engineers, Sri LankaDokument107 SeitenSyllabi: The Institution of Engineers, Sri LankaAmal Priyashantha Perera100% (2)
- Plaquette - PRECASEM - CIMEC 2019 English VersionDokument18 SeitenPlaquette - PRECASEM - CIMEC 2019 English VersionFranck BertrandNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADC ManualDokument47 SeitenADC ManualRavi ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSR Codes - 1Dokument108 SeitenDSR Codes - 1lakkireddy seshireddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Vino Gano Ginger and Herbal Liquor On The Heamatological Parameters of The Wistar RatsDokument5 SeitenEffect of Vino Gano Ginger and Herbal Liquor On The Heamatological Parameters of The Wistar RatsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermobaric Effects Formed by Aluminum Foils Enveloping Cylindrical ChargesDokument10 SeitenThermobaric Effects Formed by Aluminum Foils Enveloping Cylindrical ChargesAnonymous QFUEsUAnNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZW250-7 BROCHURE LowresDokument12 SeitenZW250-7 BROCHURE Lowresbjrock123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topik 3 - Hazard Di Air Selangor, Penilaian Risiko Langkah Kawalan Rev1 2020 090320Dokument59 SeitenTopik 3 - Hazard Di Air Selangor, Penilaian Risiko Langkah Kawalan Rev1 2020 090320Nuratiqah SmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 01Dokument16 SeitenChapter 01deepak_baidNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hollow Boy Excerpt PDFDokument52 SeitenThe Hollow Boy Excerpt PDFCathy Mars100% (1)
- MetDokument41 SeitenMetadityaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Specifications: MB3F-PSA4-19DEDokument2 SeitenProduct Specifications: MB3F-PSA4-19DEВадим ЧеховскийNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical 3.1 Determining The Specific Heat CapacityDokument3 SeitenPractical 3.1 Determining The Specific Heat CapacityiAlex11Noch keine Bewertungen
- HACH LANGE Amino Acid F Reagent Powder (2353255)Dokument6 SeitenHACH LANGE Amino Acid F Reagent Powder (2353255)kerem__22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Dewa Inspection CommentsDokument2 SeitenSample Dewa Inspection Commentsrmtaqui100% (1)
- Classical Feedback Control With MATLAB - Boris J. Lurie and Paul J. EnrightDokument477 SeitenClassical Feedback Control With MATLAB - Boris J. Lurie and Paul J. Enrightffranquiz100% (2)
- A Collection of Ideas For The Chemistry Classroom by Jeff HepburnDokument14 SeitenA Collection of Ideas For The Chemistry Classroom by Jeff HepburnPaul SchumannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Penetration Test & Softening PointDokument7 SeitenPenetration Test & Softening PointAli M. Chehadeh100% (4)
- Neuropsychological Performance in Neurofibromatosis Type 1: Original ArticleDokument5 SeitenNeuropsychological Performance in Neurofibromatosis Type 1: Original ArticleRaquel DuarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inspirational Quotes General and ExamsDokument6 SeitenInspirational Quotes General and Examsasha jalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical - 2: Preparation of The FixativeDokument14 SeitenPractical - 2: Preparation of The FixativeIseth ISethNoch keine Bewertungen
- No Client Too Far: Flexible Antenna Options TDMA GPS Sync ClientDokument2 SeitenNo Client Too Far: Flexible Antenna Options TDMA GPS Sync ClientFelix MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- PositioningDokument2 SeitenPositioningKishan AndureNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smith KJ Student Mathematics Handbook and Integral Table ForDokument328 SeitenSmith KJ Student Mathematics Handbook and Integral Table ForStrahinja DonicNoch keine Bewertungen
- (ARTICLE) Misguided in Understanding The Term Open MindedDokument8 Seiten(ARTICLE) Misguided in Understanding The Term Open MindedMuhammad Rafeli FakhlipiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Latent Phase of LaborDokument8 SeitenThe Latent Phase of LaborLoisana Meztli Figueroa PreciadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Field-Effect Transistor - August 1972 Popular ElectronicsDokument5 SeitenThe Field-Effect Transistor - August 1972 Popular Electronicsmac9papNoch keine Bewertungen