Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
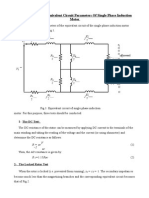
Equivalent Circuit of A Single Phase Induction Motor AIM:-Apparatus
Hochgeladen von
UdayKiranOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Equivalent Circuit of A Single Phase Induction Motor AIM:-Apparatus
Hochgeladen von
UdayKiranCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT OF A SINGLE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR
AIM :-To Determine Parameters Of Single Phase Induction Motor And Draw The
Equivalent Circuit
APPARATUS :
S.no
1
2
3
4
Name of the equipment
Ammeter
Voltmeter
Wattmeter
Wattmeter
Range
0-10A
0-300V
300V,10A
300V,10A
Type
MI
MI
LPF
UPF
Quantity
1No
1No
1N0
1N0
THEORY
When the rotor is stationary, the pulsating stator field induces voltages in the
rotor by the transformer action. The e.m.f induced in the stator winding by the alternating
field is referred to as ( E s )in the equivalent circuit of the motor shown in the fig(1) r 1 and x1
are the resistance and reactance of the stator winding.r2 and x2 are the resistance and
reactance of rotor referred to the stator side. Using the concept of the rotating field, the e.m.f
induced,( Es ) can be shown as composed of equal components induced by the two oppositely
rotating fields of the same strength, namely ( Ef )and (Eb).Then the Es = Ef + Eb
The magnetizing and rotor impedances are divided into two equal halves
connected in series. The motor behaves like a two series connected motors, one
corresponding to each rotating field. The circuit elements of the two component
motors are identical with the condition of stationary rotor since the rotor has
same slip with respect to each rotating field.
However, when the rotor is running at a speed N in the direction of the
forward field with a slip s, the corresponding slip with backward running field will be ( 2s)and the equivalent circuit components of the two rotors are then modified shown in
fig(2).It can be seen from these parameters that the impedance ( z f/2)of the rotor to forward
field is much higher than the impedance ( zb/2 )offered to the backward field, and therefore Ef
will be much greater than Eb. This implies that the resultant torque is generally by the
forward field which is dominant one.
r1
V1
x21
x1
Es
xm
Fig (1)
Equivalent circuit when the rotor is stationary (Transformer action)
r21
r1 / 2
x21 / 2
x1 / 2
Vf Z f / 2
I2f1
xm / 2
r21 / 2s
x21 / 2
V1
I2b1
Vb Zb / 2
Fig (2) xm / 2
r1 / 2
r21 /
2(2-s)
x1 / 2
Equilent circuit of single phase induction motor based on the rotating field
rotor is stationary.
when the
PROCEDURE :NO-LOAD TEST :(1) Connections are done as per the circuit diagram.
(2) By using 1- auto transformer apply rated voltage to the motor.
(3) After getting rated speed of motor tabulate all the meter readings and speed.
BLOCKED ROTOR TEST :(1) Replace the meters as per the blocked rotor test.
(2) Block the rotor of the 1- induction motor by brake.
(3) By using the 1- auto transformer apply reduced voltage to the motor till the motor
draws the rated current of the motor
(4) After getting rated current tabulate all the meter readings
From the above two tests we can find the parameters of 1- induction motor
OBSERVATIONS
NO-LOAD TEST
S.NO
V0 in volts
I0 in amps
W0 in watts
Speed in r.p.m
BLOCKED ROTOR TEST
S.NO
RESULT
Vs in volts
Is in amps
Ws in watts
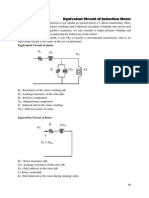
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM: EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT OF A SINGLE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR
10 A
Ph
||
||
||
||
|| D
230V,
|| P
1|| S
,50Hz
AC Supply || T
||
||
||
||
230/0-270V
1- variac
0-10AMI
No-Load300V,10A,LPF
Centrifugal
switch
Blocked300V,10A,UPF
M1
NAME PLATE DETAILS:
S1
(0-300V)MI
M2
10 A
S2
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsVon EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Electrical Machines Technology II-EMT226C-Three Phase Induction Motors-New NotesDokument63 SeitenElectrical Machines Technology II-EMT226C-Three Phase Induction Motors-New NotesTinyiko ChaukeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsVon EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Induction Motors PDFDokument108 SeitenInduction Motors PDFKshitij ShrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Induction MotorDokument21 SeitenChapter 3 Induction Motorahmed aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speed Control of 3 Phase Induction Motor 1 Aim: Experiment No: 3Dokument10 SeitenSpeed Control of 3 Phase Induction Motor 1 Aim: Experiment No: 3rohitkjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Black Box" Model For DC-fed Trains Equipped With VSI Traction Drives and Three-Phase Induction MotorsDokument19 SeitenBlack Box" Model For DC-fed Trains Equipped With VSI Traction Drives and Three-Phase Induction MotorsCPiresNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Induction Motor - A Short Circuited Rotating Transformer - A Comparative Analysis C1503021014Dokument5 SeitenThe Induction Motor - A Short Circuited Rotating Transformer - A Comparative Analysis C1503021014mkdir911Noch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of Equivalent Circuit Parameters of Single Phase Induction MotorDokument6 SeitenDetermination of Equivalent Circuit Parameters of Single Phase Induction MotorReeta DuttaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Induction MotorDokument39 SeitenInduction MotorAhmed MagdyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Session 8 Squirrel Cage Induction Motor CharacteristicsDokument15 SeitenLaboratory Session 8 Squirrel Cage Induction Motor CharacteristicshinsermuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsVon EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5Dokument86 SeitenChapter 5Selva SamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Passive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2Von EverandPassive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- U6 L42 - Blondel'sTwo Reaction TheoryDokument7 SeitenU6 L42 - Blondel'sTwo Reaction Theorykjel reida jøssanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Voltage Regulation of Three-Phase Alternator: No Load Full Load Full Load o T T o TDokument8 SeitenVoltage Regulation of Three-Phase Alternator: No Load Full Load Full Load o T T o TethanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC MachinesDokument102 SeitenDC MachinesmohamedashrafkotpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 1 DC Shunt GeneratorDokument13 SeitenExp 1 DC Shunt GeneratorKlydeJoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT-II Transformers & Alternator-2marksDokument5 SeitenUNIT-II Transformers & Alternator-2marksashwen30Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 6 Alternator (Synchronous Generator) : StructureDokument29 SeitenUnit 6 Alternator (Synchronous Generator) : StructureMahir Asif Shadman100% (1)
- User Manual The ResolverDokument8 SeitenUser Manual The ResolverRaminNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC MotorsDokument8 SeitenDC MotorsgireeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE 320 Energy Conversion and Power Electronics: Chapter ObjectivesDokument7 SeitenECE 320 Energy Conversion and Power Electronics: Chapter ObjectivesHüseyin Murat PolaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 5472401978556416138 PDFDokument97 Seiten2 5472401978556416138 PDFZayn AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Brake Test On DC Shunt MotorDokument12 Seiten2 Brake Test On DC Shunt MotorMahesh Patil100% (1)
- Exp2 - DC Generators (2 Parts) (1) XXDokument16 SeitenExp2 - DC Generators (2 Parts) (1) XXLheidyy36Noch keine Bewertungen
- 02 DC Machines LabDokument8 Seiten02 DC Machines LabAndubekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Three-Phase Induction MachinesDokument46 SeitenThree-Phase Induction MachinesWakgari TadesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- D 01Dokument209 SeitenD 01Raj Boda0% (1)
- Experiment 04Dokument7 SeitenExperiment 04Zeynal Abidin ŞabaşNoch keine Bewertungen
- E M 1 Lab ManualDokument63 SeitenE M 1 Lab ManualdsparanthamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument15 SeitenChapter 3Moin AshrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel Institute of Technology, Vasad: Equivalent Circuit of Induction Motor & Phasor DiagramDokument23 SeitenSardar Vallabhbhai Patel Institute of Technology, Vasad: Equivalent Circuit of Induction Motor & Phasor DiagramSANJAYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working Principle of A DC Motor: Unit-IiDokument12 SeitenWorking Principle of A DC Motor: Unit-IiMaheedhar ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4Dokument24 SeitenChapter 4javeria zafeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Material Module IIDokument15 SeitenControl Material Module IIAbiodun MustaphaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Injection of EMF in Rotor Circuit PDFDokument5 SeitenInjection of EMF in Rotor Circuit PDFkhidirtay50% (2)
- Lecture Notes Elec A6: Induction MachinesDokument39 SeitenLecture Notes Elec A6: Induction MachinesRam PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- TransformerDokument54 SeitenTransformerdubuli123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Voltage RegulatorDokument46 SeitenVoltage RegulatorYunus SiregarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 - SynchronousDokument12 SeitenChapter 8 - SynchronousLin ChongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Simulation of Field Oriented Control of VSI Fed Induction Motor DriveDokument10 SeitenDesign and Simulation of Field Oriented Control of VSI Fed Induction Motor Drivesuhail ahmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC-Motor Time ConstantDokument32 SeitenAC-Motor Time ConstantMorten BroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anser Key EM - I 2019Dokument15 SeitenAnser Key EM - I 2019Manoharan ManuNoch keine Bewertungen
- InductionMotors Gate Material PartBDokument38 SeitenInductionMotors Gate Material PartBpraveen6494Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ee 316 - Electrical Machines 1 Week 8: ISUE-EIE-Syl-014 Revision: 02 Effectivity: August 1, 2020Dokument5 SeitenEe 316 - Electrical Machines 1 Week 8: ISUE-EIE-Syl-014 Revision: 02 Effectivity: August 1, 2020Laurence Abrogena AlmazanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synchronous Machine Characteristics and OperationDokument20 SeitenSynchronous Machine Characteristics and Operationhozipek5599Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kramer DriveDokument42 SeitenKramer DriveSenthil Kumar100% (1)
- Chapter 7: D.C MACHINES: INTRODUCTION: DC Generators and Motors Are Collectively Known AsDokument13 SeitenChapter 7: D.C MACHINES: INTRODUCTION: DC Generators and Motors Are Collectively Known AsJayakumar JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- EM Mattaria Ch1Dokument25 SeitenEM Mattaria Ch1Osama AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.0 Transformers: 3.1 The Ideal TransformerDokument16 Seiten3.0 Transformers: 3.1 The Ideal Transformerhafiz_jaaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lectures Synchronous MachinesDokument47 SeitenLectures Synchronous MachinesSaddy CoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal UTS 2017Dokument6 SeitenSoal UTS 2017Kukuh WidarsonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Solid State Power ElectronicsDokument111 SeitenIntroduction To Solid State Power ElectronicsMj Tichy H100% (2)
- Thyristor Commutation Techniques: Prof. T.K. Anantha Kumar, E&E Dept., MSRITDokument137 SeitenThyristor Commutation Techniques: Prof. T.K. Anantha Kumar, E&E Dept., MSRITUdayKiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIT OpenCourseWare Http://Ocw - Mit.eduDokument7 SeitenMIT OpenCourseWare Http://Ocw - Mit.edusnehithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brake Test On 3-Ph Slip Ring Im, OkDokument3 SeitenBrake Test On 3-Ph Slip Ring Im, OkUdayKiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS Lab Manual PDFDokument118 SeitenCS Lab Manual PDFrakheep123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Key of Advanced CareDokument1 SeiteKey of Advanced CareUdayKiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer VirusDokument18 SeitenComputer VirusUdayKiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nuclear BatteriesDokument3 SeitenNuclear BatteriesUdayKiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNS ProbeDokument1 SeiteDNS ProbeUdayKiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compact Fluorescent Lamps: Presented by K.K.Chaithanya (13761A0227)Dokument29 SeitenCompact Fluorescent Lamps: Presented by K.K.Chaithanya (13761A0227)UdayKiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Text DocumentDokument1 SeiteNew Text DocumentUdayKiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- SP13Dokument17 SeitenSP13Rajesh SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS Lab Manual PDFDokument118 SeitenCS Lab Manual PDFrakheep123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Robotic Monitoring of Power Systems: Bing Jiang, Student Member, IEEE, and Alexander Mamishev, Member, IEEEDokument7 SeitenRobotic Monitoring of Power Systems: Bing Jiang, Student Member, IEEE, and Alexander Mamishev, Member, IEEEBeena Ravi0% (1)
- Generator Are Used To Describe A Device Which Uses Energy From TheDokument5 SeitenGenerator Are Used To Describe A Device Which Uses Energy From TheUdayKiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devon GrecoDokument7 SeitenDevon GrecoShruthi HarshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SpeedDokument1 SeiteSpeedUdayKiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nuclear Battery Seminar ReportDokument22 SeitenNuclear Battery Seminar ReportPratik Patil100% (1)
- Research Report Wit Ri CityDokument8 SeitenResearch Report Wit Ri Citypretty15Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Gas Power CycleDokument14 Seiten1 Gas Power CyclejehadyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 470 - Mce 204 Lecture Note 2Dokument61 Seiten470 - Mce 204 Lecture Note 2Wahyu WijanarkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nuclear Battery Seminar ReportDokument22 SeitenNuclear Battery Seminar ReportPratik Patil100% (1)
- 5 5Dokument18 Seiten5 5prabhuar8Noch keine Bewertungen
- PDC NotesDokument149 SeitenPDC NotesvamsikiranreddyeruvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lakkikludy 13alikludy Lulltut Ui Tnuintt - KinuDokument2 SeitenLakkikludy 13alikludy Lulltut Ui Tnuintt - KinuUdayKiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Devices and CircuitsDokument23 SeitenElectronic Devices and CircuitsUdayKiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDC NotesDokument149 SeitenPDC NotesvamsikiranreddyeruvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IEEE Xplore - New Empirical Unified Dispersion Model For Shielded-, Suspended-, and Composite-Substrate Micro Strip Line For MicDokument3 SeitenIEEE Xplore - New Empirical Unified Dispersion Model For Shielded-, Suspended-, and Composite-Substrate Micro Strip Line For MicektudrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 Energy and PowerDokument5 SeitenChapter 7 Energy and Powerelizabeth ellsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Induction Motors Faults and ProtectionDokument2 SeitenInduction Motors Faults and ProtectionMuhammad Ali Khan AwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Utilities 1 Module 1Dokument13 SeitenEngineering Utilities 1 Module 1Fra KENoch keine Bewertungen
- The Speed of GravityDokument8 SeitenThe Speed of GravitymasharecoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sigma Institute of EngineeringDokument13 SeitenSigma Institute of EngineeringbhavikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Assignment Sheet Topic: (Collision & Centre of Mass) SECTION BDokument6 SeitenPhysics Assignment Sheet Topic: (Collision & Centre of Mass) SECTION Brebel rocksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q1 Week 2 - Module 3 Uniform Circular MotionDokument21 SeitenQ1 Week 2 - Module 3 Uniform Circular MotionLullaby GomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spectral Characterisation of Infrared Optical Materials and FiltersDokument180 SeitenSpectral Characterisation of Infrared Optical Materials and FiltersmarcoedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid Mechanics - Torsion Part 2Dokument11 SeitenSolid Mechanics - Torsion Part 2azlan haziqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuit Theory 2-MarksDokument16 SeitenCircuit Theory 2-MarksJagadish Babu KondraguntaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP BC TNS 60-100 v01 en DBDokument1 SeiteIP BC TNS 60-100 v01 en DBMaria Da Graça RomãoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mu Iso 04 GBDokument8 SeitenMu Iso 04 GBjoepdekker1100% (1)
- Grid-Connected Wind Photo Voltaic Cogeneration Using Back To Back Voltage Source ConvertersDokument84 SeitenGrid-Connected Wind Photo Voltaic Cogeneration Using Back To Back Voltage Source ConvertersThulasi Prasad0% (1)
- Motorcycle Dynamics Library in ModelicaDokument10 SeitenMotorcycle Dynamics Library in ModelicaSaufiy SarminNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEE MCQ CH 2 Part 1Dokument6 SeitenBEE MCQ CH 2 Part 1Ashmit RaghavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Christoph Schiller MOTION MOUNTAIN The Adventure of PhysicsDokument372 SeitenChristoph Schiller MOTION MOUNTAIN The Adventure of PhysicsHariom SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14.2 - Boundary Details PDFDokument10 Seiten14.2 - Boundary Details PDFChristian MavarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- NICE3000 - Technical Manual-060710Dokument109 SeitenNICE3000 - Technical Manual-060710Ken Lee100% (8)
- Projectile Motion ProblemsDokument7 SeitenProjectile Motion Problemsomar_oj_4Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Light of Allah in The Heavens and The Earth The Creation of The Atom 24 35 and The Physics of SpiritualityDokument162 SeitenThe Light of Allah in The Heavens and The Earth The Creation of The Atom 24 35 and The Physics of SpiritualityLaura Gomez100% (2)
- Uttar Banga Krishi Viswavidyalaya: Faculty of Technology Mid Term Examination-2022Dokument1 SeiteUttar Banga Krishi Viswavidyalaya: Faculty of Technology Mid Term Examination-2022Arijit PramanikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factors Affecting Speed of Wave On A StringDokument2 SeitenFactors Affecting Speed of Wave On A StringAref DahabrahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Yaw Angle Misalignment On BrakeDokument20 SeitenEffect of Yaw Angle Misalignment On BrakeakkkkNoch keine Bewertungen
- HF Transformer Design-IEEEDokument5 SeitenHF Transformer Design-IEEECataNoch keine Bewertungen
- g484 Module 2 4 2 3 Simple Harmonic Oscillations ADokument10 Seiteng484 Module 2 4 2 3 Simple Harmonic Oscillations Aapi-236179294Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jun 03Dokument13 SeitenJun 03Saddam RiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 3 Phase SeqDokument5 SeitenExperiment 3 Phase Seqp00debshitbasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodical Exam Science 8Dokument5 SeitenPeriodical Exam Science 8Mike Guerzon100% (1)
- Applied Sciences: The Power System and Microgrid Protection-A ReviewDokument30 SeitenApplied Sciences: The Power System and Microgrid Protection-A ReviewEngidNoch keine Bewertungen