Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
LS4 - Forced Convection
Hochgeladen von
Mohd Khairudin Abdul RadzakCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
LS4 - Forced Convection
Hochgeladen von
Mohd Khairudin Abdul RadzakCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Thermalfluids Lab-MEC 554/ LS 4/ THOMAS Rev.
01-2007
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
FACULTY OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
________________________________________________________________________
Program
:
Bachelor Of Engineering ( Hons ) Mechanical
Course
:
Thermalfluids Lab
Code
:
MEC 554
________________________________________________________________________
LAB SHEET NO:
HEAT TRANSFER LABORATORY SHEET
TITLE : FORCED CONVECTION
1.
OBJECTIVE
Demonstrate the use of a fin (extended surface) to improve the heat transfer in forced convection.
2.
THEORY
Heat transfer from an object can be improved by
increasing the surface area in contact with the air by
adding fins or pins normal to the surface. This can be
seen in Newtons Law of Cooling, which defines the
convection heat transfer rate:
Q h As Ts T
The effect of the surfaces can be demonstrated by
comparing finned and unfinned surfaces with a flat
plate under the same conditions of power and flow.
Thermalfluids Lab-MEC 554/ LS 4/ THOMAS Rev. 01-2007
3.
EQUIPMENT
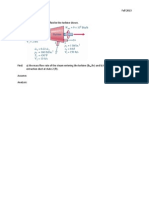
The surfaces are shown in the figure below. The finned surface consists of 9 fins that are each 0.1
m high and 0.068 m wide. The pinned surface consists of 17 pins that each have a diameter of
0.013 m and are 0.068 m long.
Thermalfluids Lab-MEC 554/ LS 4/ THOMAS Rev. 01-2007
4.
PROCEDURES
a. Place the heat exchanger into the test duct and record the ambient temperature (T).
b. Set the heater power control to 75 W. Allow the temperature to rise to 80C then adjust the
heater power control to 20 W.
c. Start stopwatch wait 5 minute and record the heated plate surface temperature (Ts).
d. Repeat step (b). Then set the fan speed control to give a reading of 1.0 m/s on the thermal
anemometer. Allow 5 min for the reading to stabilize and then again record Ts.
e. Then adjust the fan speed to 2.0 m/s and then 2.5 m/s, recording the Ts for each speed.
[Same Procedure at step (d) ].
5.
RESULTS
1.
Start with the unfinned flat plate. Using the data tables shown below, record the
ambient temperature (T) and the power input ( Q )
Ambient air temperature (T) = __________ C
Power input ( Q )
Table A
Air
Velocity
[m/s]
= __________ W
Flat Base Plate (Unfinned)
Heater
Temperature (Ts)
[C]
Ts-T
[C]
[W/(mC)]
0
1.0
2.0
2.5
2.
Calculate the temperature difference (TsT) and record on the data table.
3.
Calculate the surface area of the base plate (Abase).
Thermalfluids Lab-MEC 554/ LS 4/ THOMAS Rev. 01-2007
4.
Calculate the convection heat transfer coefficient (h) from the equation:
5.
Q
As Ts T
Replace the flat plate with the finned surface plate and repeat the experiment. Then
replace the finned surface with the pinned surface plate and repeat the experiment. An
equation for the surface areas (As) of the finned and pinned plates are shown below:
A finned 9 L w Abase
plate
Apinned 17
DL
plate
Table B
Air
Velocity
[m/s]
Abase
Finned Plate
Heater
Temperature (Ts)
[C]
Ts-T
[C]
[W/(mC)]
0
1.0
2.0
2.5
Table C
Air
Velocity
[m/s]
Pinned Plate
Heater
Temperature (Ts)
[C]
Ts-T
[C]
[W/(mC)]
0
1.0
2.0
2.5
6.
Plot graphs of air velocity versus surface temperature (T s-T) of each plate. Compare the
ability of each plate surface to disseminate heat by convection.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Busy BusDokument4 SeitenBusy BusMohd Khairudin Abdul RadzakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Results & Analysis - Centrifugal Pump #F4Dokument8 SeitenResults & Analysis - Centrifugal Pump #F4Mohd Khairudin Abdul RadzakNoch keine Bewertungen
- LI Report AbstractDokument1 SeiteLI Report AbstractMohd Khairudin Abdul RadzakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 1 March-June 2012 Completed SchemeDokument6 SeitenTest 1 March-June 2012 Completed SchemeMohd Khairudin Abdul RadzakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pedal Setup Dual Master GuideDokument7 SeitenPedal Setup Dual Master GuideMustafa TajkhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Log Sheet: Mec532 Mechanical Engineering Design IiDokument1 SeiteLog Sheet: Mec532 Mechanical Engineering Design IiAhmad Syazni Bin MoktarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Isbn-13: 978-0078028182 Isbn-10: 0078028183Dokument24 SeitenIsbn-13: 978-0078028182 Isbn-10: 0078028183pham minhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystallization MechanismsDokument20 SeitenCrystallization MechanismsZayra OrtizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook of Residual Stress and Deformation of Steel PDFDokument478 SeitenHandbook of Residual Stress and Deformation of Steel PDFKevinElemJordyVílchezLópez100% (3)
- Bi BCTZDokument10 SeitenBi BCTZSamah SamahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tổng hợp tải trọng Summation phần mềm MIDASDokument8 SeitenTổng hợp tải trọng Summation phần mềm MIDASAnonymous DNb6yWERfBNoch keine Bewertungen
- CFD Analysis in A Heat Sink For Cooling Of-LibreDokument11 SeitenCFD Analysis in A Heat Sink For Cooling Of-LibreVedant DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- TGGuideline 114 Viscosity of LiquidsDokument7 SeitenTGGuideline 114 Viscosity of LiquidsDonig FermanianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renman 2019Dokument10 SeitenRenman 2019Shohan GaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Properties of Low-Alloy-Steels With Bainitic Microstructures and Varying Carbon ContentDokument10 SeitenMechanical Properties of Low-Alloy-Steels With Bainitic Microstructures and Varying Carbon ContentPuteri NurhayaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- IEC 61000-4-5-2017 Surge GeneratorDokument342 SeitenIEC 61000-4-5-2017 Surge GeneratorSOUMEN PARUINoch keine Bewertungen
- Che 133-202 Lab Report (WQ 2013)Dokument8 SeitenChe 133-202 Lab Report (WQ 2013)api-281000515Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jrs Tutorials: Physics Practice Sheet Electromagnetic InductionDokument18 SeitenJrs Tutorials: Physics Practice Sheet Electromagnetic InductionSumSetNoch keine Bewertungen
- 140MXC Nano Composite WireDokument5 Seiten140MXC Nano Composite WireAnonymous QsXfPXxDMNoch keine Bewertungen
- A New Approach To Design For StabilityDokument39 SeitenA New Approach To Design For StabilitytamerragaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogue Vitzro AtsDokument2 SeitenCatalogue Vitzro Atsvhoa309Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S1044580322004053 MainDokument16 Seiten1 s2.0 S1044580322004053 MainSree SabariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete Columns PDFDokument9 SeitenConcrete Columns PDFAnne Karollynne CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Sensors For Multi-Axis Angle andDokument33 SeitenOptical Sensors For Multi-Axis Angle andAnant PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geotech - Rockmass ClassDokument65 SeitenGeotech - Rockmass ClassNoviandryNoch keine Bewertungen
- StructurePoint Software Impact of Changes From ACI 318-14 To ACI-318-19Dokument10 SeitenStructurePoint Software Impact of Changes From ACI 318-14 To ACI-318-19zaidg9876553Noch keine Bewertungen
- ECD en HGH Temp WellsDokument162 SeitenECD en HGH Temp WellsWalter MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aluminum-Alloy Sand Castings: Standard Specification ForDokument14 SeitenAluminum-Alloy Sand Castings: Standard Specification Foranurag yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch10 Solid StateDokument30 SeitenCh10 Solid StateKrish VeniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework BDokument28 SeitenHomework BPravallika Kollipara0% (2)
- 18 Mineral PigmentsDokument22 Seiten18 Mineral PigmentsDharmendra B MistryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assnmt 11Dokument2 SeitenAssnmt 11RK MEHTANoch keine Bewertungen
- AER 309 Course Outline PDFDokument4 SeitenAER 309 Course Outline PDFUrshia Likes CookiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter2 DesignofShallowFoundationsDokument15 SeitenChapter2 DesignofShallowFoundationsErgin Acar50% (2)
- Vishwajeet Yadav Pharmacy PracticeDokument21 SeitenVishwajeet Yadav Pharmacy PracticeAkash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caesar II TrainingDokument22 SeitenCaesar II TrainingPetar Jankovic50% (2)