Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Experiment 7a
Hochgeladen von
Alvin TusiOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Experiment 7a
Hochgeladen von
Alvin TusiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
DISCUSSION
Theory
Permeability is a property of soil which permits flow of water through its
interconnecting voids; it is an important engineering property which governs the
rate of settlement of saturated compressible soil layers and the rate of flow of
aquifer.
The rate of flow under laminar flow conditions through a unit cross sectional are of
porous medium under unit hydraulic gradient is defined as coefficient of
permeability. Constant Head Permeameters are used for coarse grained
cohesionless soils.
The coefficient of permeability, k, is a product of Darcys Law. Darcy
established an empirical relationship for the flow of water through porous
media. This relationship has evolved into Darcys Law, which states: Q = A . k . I
Constant Head Permeability Test is performed on sands as the pore openings are
large and hence high permeability (k >10 -4 cm/s)
Observation
The soil sample has a cylindrical form with its diameter being large enough in order
to be representative of the tested soil. The testing apparatus is equipped with an
adjustable constant head reservoir and an outlet reservoir which allows maintaining
a constant head during the test. Water used for testing is de-aired water at constant
temperature. The permeability cell is also equipped with a loading piston that can
be used to apply constant axial stress to the sample during the test.
Before starting the flow measurements, however, the soil sample is saturated.
During the test, the amount of water flowing through the soil column is measured
for given time intervals. Knowing the height of the soil sample column L, the sample
cross section A, and the constant pressure difference h, the volume of passing
water Q, and the time interval T
Application
The knowledge of this property is much useful in solving problems involving yield
of water bearing strata, seepage through earthen dams, stability of earthen dams,
and embankments of canal bank affected by seepage, settlement etc.
Calculation of seepage through earth dams, embankments of canals, under sheet
pile walls.
Estimate settlements in foundations and slope stability analysis.
CONCLUSION
This test method covers the determination of the coefficient of permeability by a
constant-head method for the laminar flow of water through granular soils. The
procedure is to establish representative values of the coefficient of permeability of
granular soils that may occur in natural deposits as placed in embankments, or
when used as base courses under pavements.
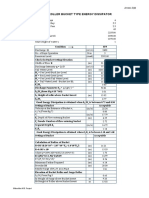
The result we obtained for the average value of the coefficient of permeability is
0.270 cm/sec. The value for the permeability coefficient for sands should be greater
than 10-4 cm/sec, and with the result of the experimentation our value is within the
range of the expected results. Thus, the result is valid and the procedure of the
experiment was correctly done and accurately efficient.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Determination of The Permeability of Granular SoilDokument19 SeitenDetermination of The Permeability of Granular SoilKaluki Judy Rosebell100% (1)
- DiscussionDokument4 SeitenDiscussionOchini ChandrasenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Falling Head MethodDokument4 SeitenFalling Head MethodYash PersÌeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Permeability Test Discussion of TheoryDokument3 SeitenPermeability Test Discussion of TheoryBryanHarold BrooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constant HeadDokument17 SeitenConstant Headahmadusmaan67% (3)
- Theory Costant Head MethodDokument4 SeitenTheory Costant Head MethodsyathirohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Permeability of SoilDokument19 SeitenPermeability of SoilDipakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 8Dokument16 SeitenLesson 8Joash SalamancaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Permeability - 4 MtechDokument70 SeitenPermeability - 4 MtechViky ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 One Dimensional Flow of Water Through SoilsDokument28 Seiten5 One Dimensional Flow of Water Through SoilsJenina LogmaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Zia-ur-RehmanDokument41 SeitenDr. Zia-ur-RehmanMohsin AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6Dokument13 SeitenChapter 6Ma. Niña Michelle ElicNoch keine Bewertungen
- G Acceleration Due To Gravity V Velocity U Pressure Where H Total HeadDokument23 SeitenG Acceleration Due To Gravity V Velocity U Pressure Where H Total HeadMinhaz Khan100% (1)
- Permeability of SoilDokument58 SeitenPermeability of SoilAntony GodwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- The State of The Practice of Foundation EngineeringDokument21 SeitenThe State of The Practice of Foundation EngineeringPradip AdhikariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Permeability TestDokument2 SeitenPermeability Testmilfer aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 7bDokument2 SeitenExperiment 7bAlvin TusiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment - 8 - BSETC-021R19-4 - Muhammad Zohaib Khan PDFDokument24 SeitenAssignment - 8 - BSETC-021R19-4 - Muhammad Zohaib Khan PDFEngr MahwishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Permeability and Seepage 034355Dokument74 SeitenPermeability and Seepage 034355Joeven Dinawanao100% (1)
- Lecture 08Dokument18 SeitenLecture 08muzamil ismailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture # 7Dokument27 SeitenLecture # 7naveedsidhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Permeability Group 01 (Section-B) : Submitted To DR - Tayyab AkramDokument55 SeitenSoil Permeability Group 01 (Section-B) : Submitted To DR - Tayyab AkramCh Hammad GujjarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Permeability: G Acceleration Due To Gravity V Velocity U Pressure Where H Total HeadDokument22 SeitenPermeability: G Acceleration Due To Gravity V Velocity U Pressure Where H Total HeadSabiha sultanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 PermeabilityDokument76 Seiten7 PermeabilityB4-63-Harshit RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment in Hydraulics: Limuel Villapando Bsce-Iv TTH / 8:00-9:00Dokument3 SeitenAssignment in Hydraulics: Limuel Villapando Bsce-Iv TTH / 8:00-9:00Limuel VillapandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Packer TestingDokument76 SeitenPacker TestingnattymenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bernoulli's Equation: From Fluid Mechanics, We Know That, According To Bernoulli'sDokument40 SeitenBernoulli's Equation: From Fluid Mechanics, We Know That, According To Bernoulli'sJami Ahmed100% (1)
- Ce-305 Seepage TheoryDokument31 SeitenCe-305 Seepage Theorylance carterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constant HeadDokument14 SeitenConstant HeadmlakkissNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE240 Lect W043 Permeability 1Dokument41 SeitenCE240 Lect W043 Permeability 1ridminjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination o F SeepageDokument2 SeitenDetermination o F SeepageFely Cuales SucgangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constant Head Permeability TestDokument12 SeitenConstant Head Permeability Testanis098Noch keine Bewertungen
- Job#7 PDFDokument5 SeitenJob#7 PDFMazharYasinNoch keine Bewertungen
- PermeabilityDokument15 SeitenPermeabilityTejeshwini SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Darcy's LawDokument5 SeitenDarcy's LawEKWUE ChukwudaluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 PermeabilityDokument27 SeitenChapter 3 PermeabilityLivingstone LGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Permeability in SoilsDokument47 SeitenPermeability in SoilsRusmar LaverosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1Dokument2 SeitenUnit 1Arun KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Permeability and Seepage - Unit IDokument26 SeitenPermeability and Seepage - Unit Icebongubane104Noch keine Bewertungen
- CE 411 AssignmentDokument2 SeitenCE 411 Assignmentibrahimaabdullahi0508Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 - PERMEABILITY PDFDokument39 SeitenChapter 7 - PERMEABILITY PDFVivekka Olivia JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6: Stability Analysis in Presence of WaterDokument27 SeitenChapter 6: Stability Analysis in Presence of WaterMagali SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mini Project On Hydraulic Characterestics of SoilsDokument32 SeitenMini Project On Hydraulic Characterestics of SoilsVidhun RavindranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lissu Soil 1Dokument16 SeitenLissu Soil 1Joshua StevenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Name:ahmed Moayad Jameel Course:2 Instructor:Sayran Ahmed Ibrahim Date:6/7/2020Dokument19 SeitenStudent Name:ahmed Moayad Jameel Course:2 Instructor:Sayran Ahmed Ibrahim Date:6/7/2020Ahmed AmediNoch keine Bewertungen
- PermeabilityDokument26 SeitenPermeabilityvijjikewlguy7116100% (3)
- Gte Unit 3Dokument9 SeitenGte Unit 3amol bardeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subsurface HydrologyDokument3 SeitenSubsurface HydrologyGerald Ordoñez Delos ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow Through SoilsDokument13 SeitenFlow Through SoilsChidanand JadarNoch keine Bewertungen
- AECC29 Lecture-12: Presented by Ksh. Monika Devi Guest Faculty, Assam University, SilcharDokument78 SeitenAECC29 Lecture-12: Presented by Ksh. Monika Devi Guest Faculty, Assam University, SilcharTanusha ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Permeability of SoilDokument14 SeitenPermeability of SoilHelen Grace LaverintoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DrainageDokument45 SeitenDrainageRaku IchijouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constant HeadDokument14 SeitenConstant HeadfujiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ground Water Hydrology: 30% of Fresh Water Exist in The Form of Ground WaterDokument41 SeitenGround Water Hydrology: 30% of Fresh Water Exist in The Form of Ground WateralifNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0449 PDFDokument7 Seiten0449 PDFMuhammad Iqbal SeptiandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Conductivity and SeepageDokument6 SeitenHydraulic Conductivity and SeepageSheenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constant Head Permeability TestDokument14 SeitenConstant Head Permeability Testfuji0% (1)
- 07 Simulation of WaterDokument16 Seiten07 Simulation of WaterWIDYA PUSPA DWI HARNUMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4: Hydraulic Fundamentals - Pilot Operated Hydraulic SystemDokument28 SeitenUnit 4: Hydraulic Fundamentals - Pilot Operated Hydraulic Systemoscar el carevergaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PS 3Dokument9 SeitenPS 3naverfallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure: Unit 2Dokument14 SeitenPressure: Unit 2Sumit ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Hydraulics-2022Dokument118 SeitenEngineering Hydraulics-2022olingxjcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valves and Fittings Losses in Equivalent Feet of Pipe: Y-StrainerDokument3 SeitenValves and Fittings Losses in Equivalent Feet of Pipe: Y-Strainerthilina lakhithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valve Sizing: Cepde AssignmentDokument15 SeitenValve Sizing: Cepde AssignmentVRUSHABHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam Jet RefrigerationDokument3 SeitenSteam Jet RefrigerationParag ParekhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water PotentialDokument16 SeitenWater PotentialJeffrey Yoonwhan KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSMTGuide PDFDokument77 SeitenSSMTGuide PDFChawanakorn NontapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 04Dokument16 SeitenAssignment 04Pritam SahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Oil Types and Applications: 3 YearDokument5 SeitenReport On Oil Types and Applications: 3 YearMahmoud KassabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part A - Part A Question No.1 Bookmark: (Chosen Option)Dokument1 SeitePart A - Part A Question No.1 Bookmark: (Chosen Option)Adlin JoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report 3Dokument14 SeitenLab Report 3Siti Syuhadah0% (1)
- AgitationDokument3 SeitenAgitationKuo SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fulton, George P Diatomaceous Earth Filtration For Safe Drinking WaterDokument225 SeitenFulton, George P Diatomaceous Earth Filtration For Safe Drinking WaterHarry Yucra100% (1)
- Flow Correlation SelectionDokument14 SeitenFlow Correlation SelectionHamza Ali100% (3)
- A T A 2 9 PDFDokument36 SeitenA T A 2 9 PDFozaozaozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pump Head CalculationDokument15 SeitenPump Head CalculationYashapuja100% (1)
- Agrifarm Mot 15W-40Dokument3 SeitenAgrifarm Mot 15W-40Ahmed KabbajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pump Primer 2 AssDokument33 SeitenPump Primer 2 AssGkou DojkuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minimac GCC - CredentialsDokument2 SeitenMinimac GCC - CredentialsigordirennaNoch keine Bewertungen
- VHM Lu01 Pi SP 001 - Piping Material SpecificationDokument7 SeitenVHM Lu01 Pi SP 001 - Piping Material SpecificationchintanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GAS FLOW MEASUREMENT - PPSXDokument47 SeitenGAS FLOW MEASUREMENT - PPSXMasood Alam Farooqui100% (2)
- TCV 205 BFV DatasheetDokument1 SeiteTCV 205 BFV DatasheetSardar PerdawoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annex 3 (B) - Solid Roller BucketDokument1 SeiteAnnex 3 (B) - Solid Roller Bucketblisscutest beagleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dacnis SEDokument1 SeiteDacnis SEironite100% (1)
- Piping Vibration Design ConsiderationsDokument1 SeitePiping Vibration Design ConsiderationsKroya HunNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Micfil) Produkt ModularDokument9 Seiten(Micfil) Produkt ModularAbdulrahman Al HuribyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Archemids PrincipleDokument10 SeitenArchemids PrincipleMUHAMMAD AKRAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 4 (Re No.)Dokument21 SeitenExperiment 4 (Re No.)Mervin PerezNoch keine Bewertungen