Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
GroupB Round1
Hochgeladen von
uthso royOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
GroupB Round1
Hochgeladen von
uthso royCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1ST OXFORD-THE DAILY STAR NATIONAL PHYSICS OLYMPIAD DHAKA, BANGLADESH, (APRIL 29,2011)
THE 1STOXFORD-THE DAILY STAR NATIONAL PHYSICS OLYMPIAD
DHAKA
FRIDAY, APRIL 29, 2011
PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS:
1.
Please write your student code and school name on the box provided in the answer script.
2.
The examination consists of two rounds and the stipulate time for each round is one hour.
3.
In the First Round there are 30 MCQ & 25 one word questions.
4.
Each MCQ carries [1] mark and one word question carries [2] marks.
5.
Use the Answer Sheets provided is to fill in your answers. Numerical results should be given
in 2 decimal places. Do not forget to state the units.
6.
No rough sheet will be provided. All the working should be done in the space provided on the
question paper.
7.
You may use the calculator to solve the problems.
8.
Turn over the page only when you are instructed to do so.
9.
This question Paper consists of 9 printed pages and I blank page.
1ST OXFORD-THE DAILY STAR NATIONAL PHYSICS OLYMPIAD DHAKA, BANGLADESH, (APRIL 29,2011)
1.
A glass tank contains some water. The length QR and the width RS of the tank are known.
What other distance needs to be measured in order to be able to calculate the volume of the
water?
A. ST
B. SV
C. TU
D. TV
2.
As a rocket is accelerating vertically upward at 9.8 m/s2 near Earths surface, it releases a
projectile. Immediately after release the acceleration (in m/s2) of the projectile is:
A. 9.8 down
B. 0
C. 9.8 up
D. 9.6 up
3.
A person holds a glass beaker in one hand and fills it quickly with hot water. It takes several
seconds before his hand starts to feel the heat. Why is there this delay?
A. Glass is a poor conductor of heat.
B. Glass is a good conductor of heat.
C. Water is a poor conductor of heat.
D. Water is a good conductor of heat.
4.
A student connects two lamps in the circuit shown.
Which switches must he close to light both lamps?
A. 1 and 2
B. 1, 2 and 3
C. 1 and 3
D. 2 and 3
5.
A sphere with a radius of 1.7 cm has a volume of:
A. 2.1 105 m3
B. 9.1 104 m3
C. 3.6 103 m3
D. 0.11 m3
6.
The average speed of a moving object during a given interval of time is always:
A. the magnitude of its average velocity over the interval
B. the distance covered during the time interval divided by the time interval
C. one-half its speed at the end of the interval
D. its acceleration multiplied by the time interval
1ST OXFORD-THE DAILY STAR NATIONAL PHYSICS OLYMPIAD DHAKA, BANGLADESH, (APRIL 29,2011)
7.
What is the source of the energy converted by a hydro-electric power station?
A. hot rocks
B. falling water
C. oil
D. waves
8.
A block is first placed on its long side and then on its short side on the same inclined plane, as
shown. The block slides down the plane on its short side but remains at rest on its long side. A
possible explanation is:
A.
B.
C.
D.
the short side is smoother
the frictional force is less because the contact area is less
the center of gravity is higher in the second case
the normal force is less in the second case
9.
An ice skater is in a fast spin with her arms held tightly to her body. When she extends her
arms, which of the following statements is not true?
A. She increases her moment of inertia.
B. She decreases her angular speed.
C. Her moment of inertia remains constant.
D. Her total angular momentum remains constant.
10.
The center of mass of the system consisting of Earth, the Sun, and the planet Mars is:
A. closer to Earth than to either of the other bodies
B. closer to the Sun than to either of the other bodies
C. closer to Mars than to either of the other bodies
D. at the geometric center of the triangle formed by the three bodies
11.
The higher the frequency of a wave
A. the smaller its speed.
B. the shorter its wavelength.
C. the greater its amplitude.
D. the longer its period.
12.
At a height of 10 km (33000 ft) above sea level, atmospheric pressure is about 210 mm of
2
mercury. What is the resultant normal force on a 600 cm window of an airplane flying at this
height? Assume the pressure inside the plane is 760 mm of mercury. The density of mercury is
3
13 600 kg/m .
A. 6.1 kN
3
B. 4.4 x 10 kN
3
C. 1.2 x 10 kN
D. 4.4 kN
1ST OXFORD-THE DAILY STAR NATIONAL PHYSICS OLYMPIAD DHAKA, BANGLADESH, (APRIL 29,2011)
13.
The speed of sound is 340m/s. A plane flies horizontally at an altitude of 10, 000m and a speed
of 400m/s. When an observer on the ground hears the sonic boom the horizontal distance from
the point on its path directly above the observer to the plane is:
A. 5800m
B. 6200m
C. 8400m
D. 12, 000m
14.
An atom of lithium contains three protons and three electrons. The nucleon number (mass
number) of the atom is 7. How many neutrons are there in the atom?
A. 3
B. 4
C. 7
D. 10
15.
The speed of waves in a stretched string depends upon which one of the following?
A. The tension in the string
B. The amplitude of the waves
C. The wavelength of the waves
D. The gravitational field strength
16.
An electron is traveling horizontally east in Earth's magnetic field. What is the direction of the
magnetic force on the particle?
A. Up
B. Down
C. West
D. Zero
17.
A rock is swung on the end of a rope in a horizontal circle at constant
speed.
The
rope
breaks.
Immediately after the rope breaks, the ball will
A. fall straight down to the ground.
B. move inward toward the center of the circle.
C. move outward normal to the circle from the point the rope broke.
D. move outward tangent to the circle from the point the rope broke.
18.
Which of the following effects could not be observed for sound waves in air?
A. interference
B. refraction
C. polarization
D. diffraction
19.
An object 7.0 cm high is placed 15 cm from a convex spherical mirror of radius 45 cm.
Describe its image.
A. virtual, erect, 9.0 cm behind mirror, 4.2 cm high
B. virtual, erect, 45.0 cm behind mirror, 4.2 cm high
C. virtual, erect, 9.0 cm behind mirror, 0.6 cm high
D. virtual, inverted, 9.0 cm behind mirror, 4.2 cm high
20.
The speed of light in a certain glass is 1.91 x 10 m/s. What is the refractive index of the glass?
A. 1.57
B. 0.64
C. 1.09
D. 4.9
1ST OXFORD-THE DAILY STAR NATIONAL PHYSICS OLYMPIAD DHAKA, BANGLADESH, (APRIL 29,2011)
21.
Two isotopes of an element have
A. the same number of nucleons in their nuclei.
B. the same number of protons as well as neutrons.
C. the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
D. a different number of protons but the same number of neutrons.
22.
The wave-particle duality theory is the first to give an adequate explanation of which of the
following facts about the hydrogen atom?
A. Why more than one possible orbit exists for the electron.
B. Why only certain energies are possible for the orbiting electron.
C. Why more than one momentum is possible for the orbiting electron.
D. None of these are correct.
23.
A bimetallic strip made from brass and iron is used as a thermostat. When the strip is heated,
the brass expands more than the iron.
Which shape will the strip become?
24.
A hospital needs to sterilize medical equipment. Which electromagnetic waves could be used?
A. infra-red
B. microwaves
C. radio waves
D. ultraviolet
25.
Which properties make materials suitable for use as a core in an electromagnet?
A. difficult to magnetize and easy to demagnetize
B. difficult to magnetize and retains magnetic strength
C. easy to magnetize and retains magnetic strength
D. easy to magnetize and easy to demagnetize
26.
We desire to measure the current through and the voltage across a resistor connected in a
circuit. How should an ammeter and a voltmeter be connected to the resistor?
A. Both are connected in parallel with the resistor.
B. Both are connected in series with the resistor.
C. The ammeter is connected in series and the voltmeter is connected in parallel with the
resistor.
D. The ammeter is connected in parallel and the voltmeter is connected in series with the
resistor.
1ST OXFORD-THE DAILY STAR NATIONAL PHYSICS OLYMPIAD DHAKA, BANGLADESH, (APRIL 29,2011)
27.
A student tests the circuit of a press-button telephone with a lamp and a battery. Which single
switch can be pressed to make the lamp light?
A.
B.
C.
D.
0
1
5
6
28.
A magnet is pushed slowly into a coil and there is a current in the coil in the direction shown.
The magnet is then pulled out quickly from the same end of the coil.
What happens to the direction and the size of the current?
A
B
C
D
Direction
reversed
reversed
unchanged
unchanged
Size
decreased
increased
decreased
increased
29.
The diagram shows a d.c. motor. Why is a split-ring commutator used?
A.
B.
C.
D.
30.
to change the current direction in the coil as the coil passes the horizontal position
to change the current direction in the coil as the coil passes the vertical position
to change the current direction in the d.c. supply as the coil passes the horizontal position
to change the current direction in the d.c. supply as the coil passes the vertical position
Which row is correct for fission and for fusion?
A
B
C
D
fission of a nucleus
produces larger nuclei
produces larger nuclei
produces smaller nuclei
produces smaller nuclei
fusion
is the energy source of a star
is used to release energy in a power station
is the energy source of a star
is used to release energy in a power station
1ST OXFORD-THE DAILY STAR NATIONAL PHYSICS OLYMPIAD DHAKA, BANGLADESH, (APRIL 29,2011)
ONE WORD QUESTIONS
1.
An auto travels at the rate of 25 km/h for 4.0 minutes, then at 50 km/h for 8.0 minutes and
finally at 20 km/h for 2.0 minutes. Find (a) the total distance covered in km and (b) the average
speed for the complete trip in m/s.
2.
A bottle dropped from a balloon reaches the ground in 20 s. Determine the height of the balloon
if (a) it was at rest in the air and (b) it was ascending with a speed of 50 m/s when the bottle
was dropped.
3.
When a nucleus of Uranium-235 absorbs a neutron, nuclear fission occurs. In a typical reaction
the total mass decreases by 3 x 1028 kg. Given that the speed of light c is 3 x 108 m / s,
approximately how much energy is released?
4.
A measuring cylinder containing some water stands on a scale pan. A solid ball is lowered into
the water. The water level rises from the 30 cm3 mark to the 40 cm3 mark. The scale reading
increases from 100 g to 180 g. What is the density of the material of the ball?
5.
The half-life of a radioactive substance is 5 hours. A sample is tested and found to contain
0.48g of the substance. How much of the substance was present in the sample 20 hours before
the sample was tested?
6.
A tunnel has a length of 50 km. A car takes 20 min to travel between the two ends of the
tunnel. What is the average speed of the car?
7.
Compute the power output of a machine that lifts a 500-kg crate through a height of 20.0 m in a
time of 60.0 s.
8.
A large open tank of non-viscous liquid springs a leak 4.5 m below the top of the liquid. What
2
is the theoretical velocity of outflow from the hole? If the area of the hole is 0.25cm , how
much liquid would escape in exactly 1 minute?
1ST OXFORD-THE DAILY STAR NATIONAL PHYSICS OLYMPIAD DHAKA, BANGLADESH, (APRIL 29,2011)
9.
A pendulum is timed as it swings back and forth. The clock is started when the bob is at the left
end of its swing. When the bob returns to the left end for the 90th return, the clock reads 60.0s.
(a) What is the period of vibration? (b) What is the frequency of vibration?
10.
A proton (q = e, m = 1.67 x 10 kg) is accelerated from rest through a potential difference of
-27
1.0 MV. What is the final speed?
11.
Three resistors, of 8.0 , 12 , and 24 , are in parallel, and a current of 20 A is drawn by the
combination. Determine (a) the potential difference across the combination and (b) the current
through each resistance.
12.
A capacitor with air between its plates has capacitance of 3.0F. What is its capacitance when
wax of dielectric constant 2.8 is placed between the plates?
13.
The half-life of carbon-14 is 5.7 x 10 years. What fraction of a sample of C will remain
unchanged after a period of five half-lives?
14.
The mass of Mars is approximately 0.1 times the mass of Earth and its diameter is
approximately 0.5 times that of Earth. What is the approximate gravitational field strength on
the surface of Mars?
15.
In a given time interval 1200 J of energy is extracted from a refrigerator cabinet and 1800 J of
energy ejected to the outside. The coefficient of performance of the refrigerator is
16.
A ball of mass 2 kg travelling at 8ms1 strikes a ball of mass 4 kg travelling at 2ms1. Both
balls are moving along the same straight line as shown. After collision, both balls move at the
same velocity v. What is the magnitude of the velocity v?
14
17.
A motorist travelling at 10ms1 can bring his car to rest in a distance of 10 m. If he had been
travelling at 30ms1, in what distance could he bring the car to rest using the same braking
force?
18.
The current in a component is reduced uniformly from 100 mA to 20 mA over a period of 8.0 s.
What is the charge that flows during this time?
1ST OXFORD-THE DAILY STAR NATIONAL PHYSICS OLYMPIAD DHAKA, BANGLADESH, (APRIL 29,2011)
19.
The diagram shows an arrangement of four resistors.
What is the resistance between X and Y?
20.
Two forces, each of 10 N, act at a point P as shown in the diagram. The angle between the
directions of the forces is 120.What is the magnitude of the resultant force?
21.
An Olympic athlete of mass 80 kg competes in a 100 m race. What is the best estimate of his
mean kinetic energy during the race?
22.
A semi-circular block is made from a plastic. A ray of light passes through it at the angles
shown. To two decimal places, what is the refractive index of the plastic?
23.
A concrete cube of side 0.50 m and uniform density 2.0 x 103 kg m3 is
lifted 3.0 m vertically
by a crane. What is the change in potential energy of the cube?
24.
A rigid uniform bar of length 2.4 m is pivoted horizontally at its mid-point. Weights are hung
from two points of the bar as shown in the diagram. To maintain horizontal equilibrium, a
couple is applied to the bar. What is the torque and direction of this couple?
25.
The average person can hear sound waves ranging in frequency from about 20 Hz to 20 kHz.
Determine the wavelengths at these limits, taking the speed of sound to be 340 m/s.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Pipe Support Attachment WRC AnalysisDokument17 SeitenPipe Support Attachment WRC AnalysiskalpeshbndNoch keine Bewertungen
- Failure Analysis of Runner Blades in A Francis Hydraulic Turbine Case Study PDFDokument12 SeitenFailure Analysis of Runner Blades in A Francis Hydraulic Turbine Case Study PDFRanjeetTwaynaNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- MR4 SymmediansDokument11 SeitenMR4 SymmediansALIANZA_2013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Properties of Fluids PDFDokument14 SeitenProperties of Fluids PDFmaestro100% (3)
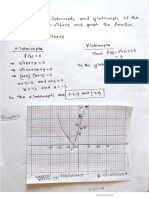
- Equations and GraphsDokument15 SeitenEquations and Graphsyusi rizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MR 2 2016 ProblemsDokument4 SeitenMR 2 2016 Problemsuthso royNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 02 PDFDokument41 SeitenUnit 02 PDFuthso royNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Many Major Races Are There in The WorldDokument4 SeitenHow Many Major Races Are There in The WorldArie PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chittagong University of Engineering & Technology (CUET)Dokument21 SeitenChittagong University of Engineering & Technology (CUET)uthso royNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modality and SyllabusDokument3 SeitenModality and Syllabusuthso royNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nazi Economic System Under HitlerDokument3 SeitenNazi Economic System Under Hitleruthso royNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apmo2016 PRBDokument1 SeiteApmo2016 PRBHoàng LongNoch keine Bewertungen
- D 01 20336014 PDFDokument9 SeitenD 01 20336014 PDFuthso royNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Yr. Sc. Marks Final-2018 (Checked) Notre Dame CollegeDokument13 Seiten2nd Yr. Sc. Marks Final-2018 (Checked) Notre Dame CollegePushan PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- A General Method of Proving Classical Inequalities Using AM-GMDokument10 SeitenA General Method of Proving Classical Inequalities Using AM-GMuthso royNoch keine Bewertungen
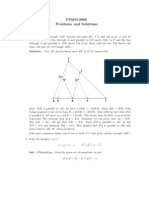
- Inmo Sol 2000Dokument5 SeitenInmo Sol 2000ashu_dwy8605Noch keine Bewertungen
- RGS Mock Test 2018: 1 ProblemsDokument1 SeiteRGS Mock Test 2018: 1 Problemsuthso royNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gva WGK I D"Pgva WGK WK V Evw©, WM Ju - : Òqvoc Îi Abygwzi RB Av E'B DigóDokument1 SeiteGva WGK I D"Pgva WGK WK V Evw©, WM Ju - : Òqvoc Îi Abygwzi RB Av E'B Digóuthso royNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scribd 1Dokument1 SeiteScribd 1uthso royNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scribd 10Dokument1 SeiteScribd 10uthso royNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scribd 2Dokument1 SeiteScribd 2uthso royNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scribd 4Dokument1 SeiteScribd 4uthso royNoch keine Bewertungen
- Junior Problem SetDokument17 SeitenJunior Problem Setuthso royNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scribd 1Dokument1 SeiteScribd 1uthso royNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scribd 2Dokument9 SeitenScribd 2uthso royNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scribd 10Dokument1 SeiteScribd 10uthso royNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soumik Roy.Dokument1 SeiteSoumik Roy.uthso royNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circles TeorumsDokument21 SeitenCircles TeorumsVibhu JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scribd 2Dokument9 SeitenScribd 2uthso royNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scribd 1Dokument1 SeiteScribd 1uthso royNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scribd 5Dokument1 SeiteScribd 5uthso royNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ceva and Menelaus TheoremDokument21 SeitenCeva and Menelaus TheoremJust BarryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1. The Medial TriangleDokument17 SeitenChapter 1. The Medial Triangleanimesh7392Noch keine Bewertungen
- PHYSICS-SCIENTIFIC-PAPER-free Fall (Repaired)Dokument8 SeitenPHYSICS-SCIENTIFIC-PAPER-free Fall (Repaired)France Penalba100% (1)
- FEA PROJECT 5th SemDokument14 SeitenFEA PROJECT 5th SemYuvraj ShindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conservation of Mechanical EnergyDokument5 SeitenConservation of Mechanical EnergyJovelo Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beam Design With Deflection CheckDokument7 SeitenBeam Design With Deflection CheckAnil kumar RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of General Relativity in Astrophysics and CosmologyDokument65 SeitenApplications of General Relativity in Astrophysics and CosmologyNasim SalimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Point Load On Cantilever Beam Using Ansys WorkbenchDokument11 SeitenPoint Load On Cantilever Beam Using Ansys WorkbenchCh Sameer AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moment of Inertia of Flywheel (Theory) - Mechanics Virtual Lab (Pilot) - Physical Sciences - Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham Virtual LabDokument4 SeitenMoment of Inertia of Flywheel (Theory) - Mechanics Virtual Lab (Pilot) - Physical Sciences - Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham Virtual LabkulvindermimitNoch keine Bewertungen
- EN380 Naval Materials Science and Engineering Course Notes, U.S. Naval AcademyDokument16 SeitenEN380 Naval Materials Science and Engineering Course Notes, U.S. Naval AcademyGuillaume Hervé POH'SIÉNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suppress tall building vibrations with hybrid liquid dampersDokument10 SeitenSuppress tall building vibrations with hybrid liquid damperssanh137Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12 ElectrostaticDokument4 SeitenChapter 12 ElectrostaticUmmiSuNoch keine Bewertungen
- SYSTEMS FOR GENERATING SCALAR WAVESDokument55 SeitenSYSTEMS FOR GENERATING SCALAR WAVESAnonymous GIIncAfLRNoch keine Bewertungen
- K.P.Engineering College, Agra Department of Mechanical EngineeringDokument2 SeitenK.P.Engineering College, Agra Department of Mechanical EngineeringPUNEET170488Noch keine Bewertungen
- A New Fracture Model For The Prediction of Longwall Caving Characteristics - 2014 - International Journal of Mining Science and TechnologyDokument4 SeitenA New Fracture Model For The Prediction of Longwall Caving Characteristics - 2014 - International Journal of Mining Science and Technologypradhith kattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LV Jindong 3C The Lagrangian Method and The Hamiltonian Method Physics Portfolio Work 5Dokument14 SeitenLV Jindong 3C The Lagrangian Method and The Hamiltonian Method Physics Portfolio Work 5LVFirestormNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free Electron Theory 2015-16 (VTU) PDFDokument14 SeitenFree Electron Theory 2015-16 (VTU) PDFU and me SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Venturi MeterDokument4 SeitenVenturi Meter01parthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wave Propagation in Solids and FluidsDokument10 SeitenWave Propagation in Solids and FluidsjohnsgdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compression Spring Calculator (Load Based Design)Dokument5 SeitenCompression Spring Calculator (Load Based Design)Amith sathyanarayan k rNoch keine Bewertungen
- Melaku Mohammed PDFDokument62 SeitenMelaku Mohammed PDFfeyselNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETABS 18.1.1 Column Design SummaryDokument2 SeitenETABS 18.1.1 Column Design SummarySandeep ShakyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subsonic Wind Tunnel TestingDokument20 SeitenSubsonic Wind Tunnel TestingGovardhan ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical Mechanics EnsemblesDokument17 SeitenStatistical Mechanics Ensemblesvicente aranguizNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Springer Series in Reliability Engineering) Halil Karadeniz (Auth.) - Stochastic Analysis of Offshore Steel Structures - An Analytical PDFDokument419 Seiten(Springer Series in Reliability Engineering) Halil Karadeniz (Auth.) - Stochastic Analysis of Offshore Steel Structures - An Analytical PDFboboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of DynamicsDokument61 SeitenPrinciples of DynamicsLeah Rivera100% (2)
- 1984, A Molecular Dynamics Method For Simulations in The Canonical Ensemblet by SHUICHI NOSEDokument14 Seiten1984, A Molecular Dynamics Method For Simulations in The Canonical Ensemblet by SHUICHI NOSEAnatoli KrasilnikovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz BowlDokument10 SeitenQuiz BowlponcatoeraNoch keine Bewertungen