Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
GEK1510PC1323AY1415S2 (Online Assessment Question N Answer)
Hochgeladen von
WizardWannabeOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
GEK1510PC1323AY1415S2 (Online Assessment Question N Answer)
Hochgeladen von
WizardWannabeCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
GEK1510/PC1323 Online Assessment (Questions and Answers)
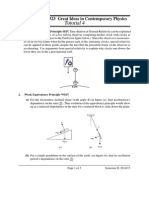
1) In a Feynman diagram, it is known that when the arm of a vertex is rotated, the direction of the
arrows in the line retain their direction with respect to the interaction point. For a particle entering a
vertex, the arrow will be directed towards the interaction point. If the arm of the vertex representing
this particle is now rotated so that it represents a particle leaving the vertex, the arrow will still point
towards the interaction point but it will be pointing in a backwards direction. What can we
understand from this statement?
[Answer]: This tells us that the particle leaving the reaction must be an antiparticle.
[CL]: Particle moving backward in time is equivalent to positive energy anti-particle (moving forward
in time).
2) What is a Feynman diagram/vertices? How should we usually read the diagram?
[Answer]: It is a symbolic diagram that allows us to calculate the amplitude of the probability of the
interaction occurred. Usually we read it from left to right (or vertically up if the time axis is flowing
upward) align with the time flow.
[CL]: There is no deterministic path in quantum theory. Feynman diagrams capture the probability of
the possible events.
3) In the spirit of particle physics, what are the fundamental interactions in nature and their
exchanged force mediator?
[Answer]: Electromagnetic (photons); Weak (W and Z boson), Strong (gluon), Gravity (graviton).
[CL]: From particle physics point of view, there are in total 4 fundamental forces with gravity
(graviton as the mediator boson) included. However, in standard model gravity usually is not treated
as part of the model.
4) Hadrons are grouping of quark/anti-quark pairs. ______________ consists of three quarks or three
anti-quarks, whereas ______________ contains a pair of quark/anti-quarks pair. All of them can be
classified into a geometrical structure called?
[Answer]: Baryon, Meson, Eight-Fold ways.
[CL]: Hadron consists of Baryon (3 quarks or 3 anti-quarks) and Meson (1 quark and 1 anti-quark).
All of them are colourless configuration so far we observed in nature.
5) In Standard Model, what are the main basic components of the particle zoo? How many families of
matter particles are there?
[Answer]: Leptons, Quarks and Interaction Boson. There are in total 2 families of matter particles.
[CL]: Particle Zoo includes both the matter and mediator of the force. There are 2 families of matter
particle, Hadron and Leptons.
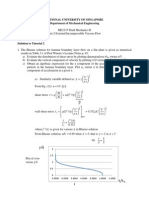
6) The pprobability density
d
for an
n electron thaat has passed
d through an experimentaal apparatus is
i shown
in the figgure. If 41000 electrons paass through tthe apparatuss, what is thee expected nuumber that will
w land
in a 0.100 mm-wide strip
s
centered
d at x = 0.00 mm?
[Answerr]: 140
[CL]: W
With probabiliity density |
(x)|2, the proobability is given
g
by areaa under the ggraph from
x= - 0.055mm to x=0.05mm. For x>0,
x
the funcction of P(x)) is P(x)= -(0
0.333/3) x+ 00.333. At x=0.05mm,
we havee the height of
o the graph is
i P (0.05)=00.32745. Sim
milarly for x<0, the functiion P(x) = (0
0.333/3)x
+ 0.333 and also P(--0.05)= 0.327
745. The areea is thus 2 * (0.5) * (0.33
33+ 0.327455) (0.05) = 0..0330225.
The num
mber of particcle pass through the appaaratus is 4100* (0.033022
25) = 136 140.
7) How fast must a hydrogen
h
ato
om be travelinng for its kin
netic energy to be just eno
nough to exciite the
-19
( eV = 1.60 10 J, m h mproton = 1.67
ground-sstate atom too its first exciited state in a collision? (1
-27
10 kg)
[Answerr]: 44.2 km/ss
[CL]: E
E= -13.6eV [1/(2^2)
[
- 1]=
= mh v^2/2
v= 44.2 km//s
umbers of an electron in an
a atom, n, l, ml , and ms . The energy
y of an
8) Consiider the four quantum nu
electron in an isolateed atom depeends on
[Answerr]: n only; n and l only
[CL]: Thhe principle (general) eneergy of isolat
ated atom dep
pends on prin
nciple quantuum number n only.
Howeveer, due to relaativistic motiion of the eleectron and allso the spin-o
orbit couplinng of the elecctron
spin to th
the nuclear sppin, there aree correctionss to the principle energy. The correctiions are angu
ular
momenttum l dependdent. In this question,
q
I acccepted both solutions ab
bove.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- GEK1510AY1415S2 (Tut4 Suggested Solution)Dokument12 SeitenGEK1510AY1415S2 (Tut4 Suggested Solution)WizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEK1510AY1415S2 (Tut2 Suggested Solution)Dokument14 SeitenGEK1510AY1415S2 (Tut2 Suggested Solution)WizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEK1510 2015 Tutorial 05Dokument1 SeiteGEK1510 2015 Tutorial 05WizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEK1510AY1415S2 (Tut3 Suggested Solution)Dokument11 SeitenGEK1510AY1415S2 (Tut3 Suggested Solution)WizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEK1510AY1415S2 (Tut1 Suggested Solution)Dokument13 SeitenGEK1510AY1415S2 (Tut1 Suggested Solution)WizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEK1510AY1415S2 (Tut5 Suggested Solution)Dokument13 SeitenGEK1510AY1415S2 (Tut5 Suggested Solution)WizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEK1510 2015 Tutorial 04Dokument3 SeitenGEK1510 2015 Tutorial 04WizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEK1510 2015 Tutorial 02Dokument1 SeiteGEK1510 2015 Tutorial 02WizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- EG2401 Final Report v6Dokument23 SeitenEG2401 Final Report v6WizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 3: GEK1510/PC1323 Great Ideas in Contemporary PhysicsDokument1 SeiteTutorial 3: GEK1510/PC1323 Great Ideas in Contemporary PhysicsWizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEK1510 2015 Tutorial 01Dokument2 SeitenGEK1510 2015 Tutorial 01WizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viscous Flow Tutorial 3Dokument1 SeiteViscous Flow Tutorial 3WizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viscous Flow Tutorial 2Dokument1 SeiteViscous Flow Tutorial 2WizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aircraft Structures Notes 1Dokument200 SeitenAircraft Structures Notes 1WizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viscous Flow Tutorial 4Dokument1 SeiteViscous Flow Tutorial 4WizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viscous Flow Tutorial 1Dokument5 SeitenViscous Flow Tutorial 1WizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution To Tutorial 2Dokument5 SeitenSolution To Tutorial 2WizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- AEIS Chap 2 MST RevisionDokument9 SeitenAEIS Chap 2 MST RevisionWizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Solution 1Dokument5 SeitenTutorial Solution 1WizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revised Solution To Tutorial 3Dokument4 SeitenRevised Solution To Tutorial 3WizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- AEIS Chap 3 MST RevisionDokument3 SeitenAEIS Chap 3 MST RevisionWizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aeroma AssignmentDokument35 SeitenAeroma AssignmentWizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- AEIS Chap 3 MST Revision (Answers)Dokument14 SeitenAEIS Chap 3 MST Revision (Answers)WizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- AEIS Chap 1 MST RevisionDokument5 SeitenAEIS Chap 1 MST RevisionWizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- AEIS Chap 1 MST Revision (Answers)Dokument8 SeitenAEIS Chap 1 MST Revision (Answers)WizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- AEIS Chap 2 MST Revision (Answers)Dokument15 SeitenAEIS Chap 2 MST Revision (Answers)WizardWannabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- List of Exercises List of Projects Preface How To Use This BookDokument6 SeitenList of Exercises List of Projects Preface How To Use This BookEdwardklausNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions: Homework Set 2: Due August 21Dokument4 SeitenSolutions: Homework Set 2: Due August 21Michel Rodrigues Andrade100% (2)
- The Problem of Conscious Observation in Quantum Mechanical DescriptionDokument13 SeitenThe Problem of Conscious Observation in Quantum Mechanical DescriptionjohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Electronic PDFDokument23 Seiten2 Electronic PDFHandugan Quinlog NoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discovery of The Subatomic Particles: The Electrons in The Plum Pudding ModelDokument4 SeitenDiscovery of The Subatomic Particles: The Electrons in The Plum Pudding ModelAira Dagus Maraña IINoch keine Bewertungen
- Interestingengineering Com 7 of Albert Einsteins Inventions That Changed The WorldDokument12 SeitenInterestingengineering Com 7 of Albert Einsteins Inventions That Changed The WorldDorinaBurceaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orca Share MediaDokument13 SeitenOrca Share Mediache masanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of Atoms: NEET/JEE: 2020-21Dokument3 SeitenStructure of Atoms: NEET/JEE: 2020-21shantinath123gmailco100% (2)
- Modern Physics SolutionDokument28 SeitenModern Physics Solutionskadogg2250% (2)
- Chemistry Notes For Class 11 STRUCTURE of ATOM Download in PDFDokument10 SeitenChemistry Notes For Class 11 STRUCTURE of ATOM Download in PDFRishabh Garg33% (3)
- Qftnotes 3Dokument15 SeitenQftnotes 3Arnab BhowmikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On The Theory of RelativityDokument26 SeitenPresentation On The Theory of RelativityMonjur Bin Shams 161-15-6812Noch keine Bewertungen
- Phy1701 Engineering-Physics Eth 1.0 46 Phy1701 PDFDokument3 SeitenPhy1701 Engineering-Physics Eth 1.0 46 Phy1701 PDFYegevrvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 6: 2m 00 E E Ikx IkxDokument3 SeitenProblem Set 6: 2m 00 E E Ikx IkxDaljot Singh KangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feynman Path Integrals in Curved Spaces: Bruce DriverDokument33 SeitenFeynman Path Integrals in Curved Spaces: Bruce DriverAhmed BougheraraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 550 Problem Set 6: Kinematics and Dynamics: NameDokument7 SeitenPhysics 550 Problem Set 6: Kinematics and Dynamics: NameVionna BeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Spectrum of HydrogenDokument3 SeitenAtomic Spectrum of HydrogenlovemynaturecountryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feynman's Lecture Utilizing The Aharonov-Bohm Effect: CommentarypaperDokument8 SeitenFeynman's Lecture Utilizing The Aharonov-Bohm Effect: CommentarypaperJoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Set 5 QM III 98 99 1 PDFDokument2 SeitenSet 5 QM III 98 99 1 PDFsajjadNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Scrodinger Wave EquationDokument19 SeitenThe Scrodinger Wave EquationAshwin S PurohitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise4 801Dokument3 SeitenExercise4 801Tehreem FatimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- KF 3 PDFDokument27 SeitenKF 3 PDFmifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Many Body Physics NotesDokument239 SeitenMany Body Physics NotesAnonymous oK0EuQNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transurfing - The New Reality MethodDokument1 SeiteTransurfing - The New Reality MethodabrkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of Lanthanide PhotophysicsDokument45 SeitenBasics of Lanthanide PhotophysicsAngela StefanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Local Density Functionals Meet Many-Body Dispersion: A Hybrid Approach For Van Der Waals CorrelationDokument1 SeiteNon-Local Density Functionals Meet Many-Body Dispersion: A Hybrid Approach For Van Der Waals CorrelationJan HermannNoch keine Bewertungen
- WKB Approx and Problem 1Dokument12 SeitenWKB Approx and Problem 1Anna ShabalinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Deuteron Problem - MISTDokument59 SeitenThe Deuteron Problem - MISTAriful Islam Pranto100% (3)
- 1905 Miraculous YearDokument12 Seiten1905 Miraculous YeardrnnmurtyNoch keine Bewertungen
- HatomDokument3 SeitenHatomstosicdusanNoch keine Bewertungen