Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
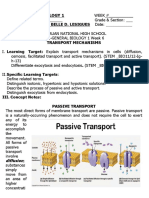
Passive Transport
Hochgeladen von
irnumambreen150 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
11 Ansichten3 Seiten1. Diffusion is the movement of solutes from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration. A concentration gradient exists between two points where the concentration differs, and diffusion works to reduce this gradient.
2. Diffusion is important for transporting nutrients into and waste out of cells, and for transmitting chemical signals across cell membranes. For example, oxygen must diffuse into cells for normal function.
3. Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane, moving from lower to higher solute concentration areas. Osmotic pressure is the force needed to prevent osmosis, and can be measured using a semipermeable membrane in a solution.
Originalbeschreibung:
Informative
Originaltitel
Passive transport
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument melden1. Diffusion is the movement of solutes from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration. A concentration gradient exists between two points where the concentration differs, and diffusion works to reduce this gradient.
2. Diffusion is important for transporting nutrients into and waste out of cells, and for transmitting chemical signals across cell membranes. For example, oxygen must diffuse into cells for normal function.
3. Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane, moving from lower to higher solute concentration areas. Osmotic pressure is the force needed to prevent osmosis, and can be measured using a semipermeable membrane in a solution.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
11 Ansichten3 SeitenPassive Transport
Hochgeladen von
irnumambreen151. Diffusion is the movement of solutes from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration. A concentration gradient exists between two points where the concentration differs, and diffusion works to reduce this gradient.
2. Diffusion is important for transporting nutrients into and waste out of cells, and for transmitting chemical signals across cell membranes. For example, oxygen must diffuse into cells for normal function.
3. Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane, moving from lower to higher solute concentration areas. Osmotic pressure is the force needed to prevent osmosis, and can be measured using a semipermeable membrane in a solution.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
1|Page
Diffusion:
A solution consists of one or more substances called solutes dissolved in the predominant
liquid or gas, which is called the solvent.
Diffusion is the movement of solutes from an area of higher solute concentration to an
area of lower solute concentration.
A concentration difference occurs when the concentration of a
solute is greater at one point than at another point in a solvent. The
concentration difference between two points, divided by the distance between the two
points, is called the concentration, or density gradient.
Diffusion of molecules is an important means by which substances move between the
extracellular and intracellular fluids
in the body.
Some nutrients enter and some waste
products leave the cell by diffusion, and maintenance of the appropriate intracellular
concentration of these substances depends to a
large degree on diffusion. For example, if the extracellular concentration of oxygen is
reduced, inadequate oxygen diffuses into the
cell, and normal cell function cannot occur. Some lipid-soluble chemical signals can
diffuse through the plasma membrane and
attach to receptors inside the cell.
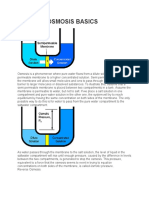
Osmosis
Osmosis is the diffusion of water (solvent) across a selectively permeable membrane.
In osmosis, water moves through a selectively permeable
membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area
of higher solute concentration.
Movement across Plasma membrane
Page 1
2|Page
Osmosis occurs only when a membrane is permeable to water
but is not permeable to certain solutes.
Osmotic pressure is the force required to prevent the movement of water by osmosis
across a selectively permeable membrane.
The osmotic pressure of a solution can be determined by placing
the solution into a tube that is closed at one end by a selectively
permeable membrane
The tube is then immersed in distilled water.
Water molecules move by osmosis through the
membrane into the tube, forcing the solution to move up the tube.
As the solution rises into the tube, its weight produces hydrostatic pressure, which moves
water out of the tube back into the distilled water surrounding the tube.
At equilibrium, net movement of water stops, which means the movement of water into
the tube by osmosis is equal to the movement of water out of the tube caused by
hydrostatic pressure.
The osmotic pressure of the solution in the
tube is equal to the hydrostatic pressure that prevents net movement of water into the
tube.
Movement across Plasma membrane
Page 2
3|Page
Terms describing osmotic pressure:
Three terms describe the osmotic pressure of solutions.
Isosmotic:
Solutions with the same concentration of solute particles have the same osmotic pressure
and are referred to as isosmotic.
Hyperosmotic:
If one solution has a greater concentration of solute particles, and therefore a greater
osmotic pressure than another solution, the first solution is said to be hyperosmotic.
Hyposmotic:
The more dilute
solution, with the lower osmotic pressure, is hyposmotic.
Tendency of cells to swell or shrink when placed in a solution
Three terms:
Isotonic: If a cell is placed into a
solution in which it neither
shrinks nor swells, the solution is
said to be isotonic.
HypertonicIf a cell is placed into
a solution and water moves out
of the cell by osmosis, causing
the
cell to shrink, the solution is
Hypotonic:If a cell is placed into a
solution and water moves into
the cell by
osmosis, causing the cell to swell,
the solution is called hypotonic.
Movement across Plasma membrane
Page 3
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Osmosis and Semipermeable MembranesDokument4 SeitenOsmosis and Semipermeable MembranesAarhan KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem Laboratory Activity 2Dokument4 SeitenBiochem Laboratory Activity 2Kristine PangahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diffusion and OsmosisDokument6 SeitenDiffusion and OsmosisCharlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- OsmosisDokument3 SeitenOsmosisgrace.a.sun18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Osmosis: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument6 SeitenOsmosis: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaallanlopez_2009Noch keine Bewertungen
- Diffusion Vs OsmosisDokument3 SeitenDiffusion Vs OsmosisK TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diffusion and OsmosisDokument2 SeitenDiffusion and OsmosisMera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laporan Physio ExDokument13 SeitenLaporan Physio ExsolideoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmosis: Osmosis Is The Spontaneous Net Movement of SolventDokument3 SeitenOsmosis: Osmosis Is The Spontaneous Net Movement of SolventCHIEF VISHAAL 45Noch keine Bewertungen
- Osmosis: Basic ExplanationsDokument21 SeitenOsmosis: Basic ExplanationsRazana Rastam0% (1)
- Diffusion 222Dokument3 SeitenDiffusion 222jinky_julianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lap 2Dokument11 SeitenLap 2Layan MohammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- BioCLab Mod3Dokument11 SeitenBioCLab Mod3Samantha BolanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intorductory of Crop Physiology Water Arrangement of Water MoleculesDokument17 SeitenIntorductory of Crop Physiology Water Arrangement of Water MoleculesSHADOW GAMINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diffusion and OsmosisDokument3 SeitenDiffusion and Osmosisshaniah100% (1)
- Tonicity: Isotonic SolutionDokument5 SeitenTonicity: Isotonic SolutionGembelle MayorgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Topic Osmotic Pressure and Its ApplicationDokument8 SeitenAssignment Topic Osmotic Pressure and Its ApplicationSohail JihadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell TransportDokument12 SeitenCell TransportAirinne GuardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology-Cell MemraneDokument3 SeitenBiology-Cell Memranekrbedes.pboxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmosis: Diffusion Is The Process Where Molecules of Two or More Substances Move AboutDokument3 SeitenOsmosis: Diffusion Is The Process Where Molecules of Two or More Substances Move AboutizzahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes Movement in & Out of CellsDokument6 SeitenNotes Movement in & Out of CellsddddddffdfdfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transport in PlantsDokument22 SeitenTransport in PlantsShantanu GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research PaperDokument9 SeitenResearch PaperNifemi OlutayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Movement in and Out of CellsDokument25 SeitenMovement in and Out of Cellsmajanga johnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanism: Osmosis Is The Spontaneous Net Movement ofDokument4 SeitenMechanism: Osmosis Is The Spontaneous Net Movement ofm bilalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 13 MedsurdgeDokument14 SeitenChapter 13 MedsurdgeLaurence Angel H OrdonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diffusion LabDokument8 SeitenDiffusion LabGioVanna GVNoch keine Bewertungen
- OsmosisDokument2 SeitenOsmosisUmasalam OdawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Transport NotesDokument10 SeitenCell Transport NotesReyad BarbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmosis and Diffusion Lab VocabularyDokument3 SeitenOsmosis and Diffusion Lab Vocabularydannyf09Noch keine Bewertungen
- CELLSDokument5 SeitenCELLSJermaine CorpuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gene103Lab DiffusionandOsmosisDokument5 SeitenGene103Lab DiffusionandOsmosisbodurr571Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Diffusion & OsmosisDokument27 Seiten3 Diffusion & OsmosisnasserkhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS 1Dokument12 SeitenBS 1JAHANZEB NAZIRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmosis - WikipediaDokument37 SeitenOsmosis - WikipediaBashiir NuurNoch keine Bewertungen
- OsmosisDokument19 SeitenOsmosisdamyangdcsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diffusion and OsmosisDokument1 SeiteDiffusion and OsmosisAhmad NisarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDokument68 SeitenFluid and ElectrolytesMara Jon Ocden CasibenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Las-Q3-Wk6.1 2Dokument12 SeitenLas-Q3-Wk6.1 2Jhude JosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Doc 4Dokument4 SeitenChapter 1 Doc 4Enju ChipepeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5-Mechanisms of Active and Pasive Transport Through TheDokument61 Seiten5-Mechanisms of Active and Pasive Transport Through Thec3rberussNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transport in Plants PDFDokument10 SeitenTransport in Plants PDFAlhiza JoaquinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 General Classification of Cellular Transport SystemDokument5 Seiten2 General Classification of Cellular Transport Systemangela mamauagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmosis Membrane Lab ReportDokument7 SeitenOsmosis Membrane Lab ReportSandra JabrooNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 NotesDokument6 Seiten04 NotesAirus SamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5: Homeostasis and Transport Lesson 5.2: Cell Transport-Passive and ActiveDokument10 SeitenChapter 5: Homeostasis and Transport Lesson 5.2: Cell Transport-Passive and ActiveVanshika VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiologyDokument2 SeitenBiologyChaca LurpheChachos XiaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory: 1 Plant Water RelationsDokument11 SeitenTheory: 1 Plant Water RelationsalekhyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Movement in and Out of CellsDokument40 SeitenMovement in and Out of CellslubaajamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisDokument6 SeitenActivity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisThea Calyn WalicanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Transport: by Felipe Hoffmann, Juan Felipe Canal, Juan Sebastian Lopez, Nicolas Castrillon and Simon KnudsenDokument6 SeitenCell Transport: by Felipe Hoffmann, Juan Felipe Canal, Juan Sebastian Lopez, Nicolas Castrillon and Simon KnudsenSimon KnudsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Movement in and Out of CellsDokument18 SeitenMovement in and Out of CellsEmy AnkrahNoch keine Bewertungen
- GenBio2 - GlossaryDokument1 SeiteGenBio2 - GlossaryVander MorissonNoch keine Bewertungen
- SiglerDokument2 SeitenSigleri kmnwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reverse Osmosis BasicsDokument3 SeitenReverse Osmosis BasicsJohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmosis NotesDokument3 SeitenOsmosis NotessmexiiloriNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.3 Cell Pgy-Transport - 035038Dokument23 Seiten1.3 Cell Pgy-Transport - 035038FAITH KANGWANoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmosis: For Other Uses, SeeDokument4 SeitenOsmosis: For Other Uses, SeeMisrai FaraukNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 Diffusion: Diffusion in Living OrganismsDokument12 Seiten3.1 Diffusion: Diffusion in Living OrganismsX GamerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids and Electrolytes: An Easy and Intuitive Way to Understand and Memorize Fluids, Electrolytes, and Acidic-Base BalanceVon EverandFluids and Electrolytes: An Easy and Intuitive Way to Understand and Memorize Fluids, Electrolytes, and Acidic-Base BalanceBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Grade 5 Averages Mean Median Mode CDokument2 SeitenGrade 5 Averages Mean Median Mode Cirnumambreen15Noch keine Bewertungen
- Prometric MCQs (Blank)Dokument55 SeitenPrometric MCQs (Blank)irnumambreen15Noch keine Bewertungen
- Visionaire BinderDokument15 SeitenVisionaire Binderirnumambreen15Noch keine Bewertungen
- Prometric Pharmacy MCQs (Solved)Dokument45 SeitenPrometric Pharmacy MCQs (Solved)cuami84% (45)
- Kaps GuideDokument3 SeitenKaps Guideirnumambreen1550% (2)
- Laws of LifeDokument168 SeitenLaws of Lifeirnumambreen1550% (2)
- Chapter 5 Final A5 EditDokument8 SeitenChapter 5 Final A5 EditkINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5 - Redox Reactions, Latimer and Frost DiagramsDokument50 SeitenLecture 5 - Redox Reactions, Latimer and Frost DiagramsDaksh GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Formula's Pocket BookDokument113 SeitenMaths Formula's Pocket BookPOLUNATI SAHITHI POLUNATI SAHITHI100% (1)
- 6.user Guide To CAN-bus Tester SoftwareDokument12 Seiten6.user Guide To CAN-bus Tester SoftwareFranco FaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conduction Convection RadiationDokument23 SeitenConduction Convection Radiationsuhaila bakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modbus Communication Card cm1241 rs232 PDFDokument4 SeitenModbus Communication Card cm1241 rs232 PDFOmkar DeshpandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differential Diagnosis of Finger DropDokument4 SeitenDifferential Diagnosis of Finger DropR HariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study 1Dokument2 SeitenCase Study 1Tushar NepaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mivec FaultDokument1 SeiteMivec Faultbjr6627Noch keine Bewertungen
- Report Esomeprazole IV Inj (Guide Batch 03)Dokument60 SeitenReport Esomeprazole IV Inj (Guide Batch 03)Sari Widya Astuti SelianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sampling, Sampling Techniques and Sampling DistributionsDokument70 SeitenSampling, Sampling Techniques and Sampling Distributionssinte beyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No. 8 Casting Defects: Aim: TheoryDokument5 SeitenExperiment No. 8 Casting Defects: Aim: TheoryDhananjay ShimpiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mud Logging Technical Document PDFDokument153 SeitenMud Logging Technical Document PDFasjad raja100% (5)
- TB072A Evaluation of A.C. in Liquid Phase Appl. (Preparation of Isotherms)Dokument7 SeitenTB072A Evaluation of A.C. in Liquid Phase Appl. (Preparation of Isotherms)mhuurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arria 10 FPGA Development Kit User Guide: Subscribe Send FeedbackDokument135 SeitenArria 10 FPGA Development Kit User Guide: Subscribe Send FeedbacklolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Owner's ManualDokument208 SeitenOwner's ManualChantal LilouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cognitive Development of Primary SchoolersDokument9 SeitenCognitive Development of Primary SchoolersKVNDRW100% (2)
- Electromagnetic FlowmeterDokument10 SeitenElectromagnetic FlowmeterAjjay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- TPS51117 Single Synchronous Step-Down Controller: 1 Features 3 DescriptionDokument33 SeitenTPS51117 Single Synchronous Step-Down Controller: 1 Features 3 Descriptionjhon agredoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project 4Dokument11 SeitenProject 4Kara WarnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supplement To Chapter 6: Linear Programming: Answers To Discussion and Review QuestionsDokument37 SeitenSupplement To Chapter 6: Linear Programming: Answers To Discussion and Review Questionsma_sadam100% (1)
- Torque - Slip Characteristic of A Three - Phase Induction MachineDokument28 SeitenTorque - Slip Characteristic of A Three - Phase Induction MachineAli AltahirNoch keine Bewertungen
- C2DP-40CP OptexDokument12 SeitenC2DP-40CP OptexFernando EspinosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10.1109 Jproc.2022.3174030Dokument30 Seiten10.1109 Jproc.2022.3174030Sree Krishna DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.4.7 Factors Affecting Distillation Column Operation 1. Vapor Flow ConditionsDokument13 Seiten6.4.7 Factors Affecting Distillation Column Operation 1. Vapor Flow ConditionsAnita PanthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edexcel Chemistry AS NotesDokument101 SeitenEdexcel Chemistry AS NotesMary Mannu100% (8)
- EKF FinanceDokument5 SeitenEKF Financebogdan.oancea3651Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2.power DiodesDokument15 Seiten2.power DiodesMuhammad Irfan100% (2)
- Abdi CCA2018Dokument16 SeitenAbdi CCA2018jozsefNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSP Product Info 092711Dokument19 SeitenGSP Product Info 092711Joao SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen